Chapter 2- The Systems of the Body
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Health psychology McGraw Hills
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Categories of NS
CNS- brain, spine
PNS- SNS, ANS - SyNS, PaNS
Only muscle that doesnt contract during stress
Eyes, take in more light
What are catecholamines
Prepares body for acute stress by ^ o2 and energy delivery to imp organs
Types of catecholamines and job
Epinephrine Norepinephrine - triggers f or f
Effects of cate.
UP: heart rate, bp, energy mobilisation, bronchi width, metabolism
Effects of Allergic reaction
DOWN: BP, bronchi width, heart rate.
Parts of brain
Fore, Hind, Mid
Lobes of Brain
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital
Parts of Hind and fn
Medulla- Regulate- heart rate, bp, respiration
Pons- Controls respiration
Cerebellum- Coord voluntary movements
- maintains balance + equilibrium,
- maintains muscle tone and posture
Fn of midbrain
relay info betn fore and hind
responsible for auditory and visual reflexes
Evolutionarily strong mid => big fore
Parts and Fn of the Fore
Thalamus: recognition of sensory info
Hypothalamus: Regulates- cardiac fns, respiration, hunger, appetite
Cerebral Cortex: HOTS, intelligence, memory, personality, process other lobe info
Fn of frontal
Has the motor cortex- controls voluntary movement
also linked to restraining impulses, control and personality
Fn of Parietal
somatosensory cortex- sensations are interpreted (touch, pressure, temp)
Fn of occipital
Visual cortex- receives visual impulses
also linked to daydreaming, dreaming and sleeping
Fn of temporal
cortical area- auditory and olfactory impulses
Fn of the Limbic system
stress and emotional response
Parts of limbic system
Amygdala: Threat detection
Hippocampus: Emo charged memories detection
(close to the nose- emo response to certain smells)
What causes CTE (Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy)
repeated strikes to the head or srs head injury
What happens due to CTE
Abnormal protein accumulates = destruction of brain (frontal and temporal lobes) - DOWN: critical thinking, impulse control, judgement, positive emotions
DOWN in grey matter
High risk for impulsive suicide.
Describe Epilispy
affects the CNS
Idiopathic (no actual cause)
Risk of inheritance
Seizures can range from irregular and loss of conc to violent convulsions.
NO cure but can be controlled with meds and bhvr interventions (to control stress)
Somatic Epilepsy cause
severe brain injury
harm during birth
infections disease
metabolic / nutritional disorder
Cause of parkinson
damage to the basal ganglia in the cerebellum
damage to the nuclei in the brain= not smooth motor coord
reason for degeneration is unknow maybe low amts of dopamine
Trearment of parkinson
high dose med but they could have bad side effects
Demography of parkinson
50 and older and more in men
Results of Park
tremors, rigidity, slow movement
Cause of cerebral palsy
brain injury due to lack of o2 in childbirth
older teens- severe brain trauma, physical abuse
Results of Cerebral p
May or may not seziures
lack of muscle control
muscle spasms
mental retardation
difficulties with perception and senses (sight, hear, speech)
cause of multiple s
autoimmune disorder that attacks the mylein sheat, reducing conduction of nerve impulse
Results on multiple s
blind deaf mental deteriorate
early symps of sultiple s
numb, double vision, drag feet, no poo piss control, speech hard, extreme fatigue
symps come and go, but deterioration goes on
Cause huntingtons
genetic abnormal, tests shows yes/no and when it effects
Results of huntings
muscle spasm, low motor, mental degrade, personality change
Cause- polio
Viral disease (polio virus) and mostly affects children. Mostly eradicated cept in pakistan and afghan
How does polio affect the body
Attack and destroys the spinal nerves and the cell bodies of motor neurons (thus motor impulses cant be carried)
Results of polio
They vary - difficulties walking and moving
- Shrunken and ineffective limbs
- Full paralysis
cause of para/ quadr peligia
p- damage to lower spinal cord
q- severance of the upper spinal cord
Results- para/quadrapeligia
Both- loss of bowel and bladder control
- loss of muscle tone due to not using them
p- loss of movement in only the lower extremities
q- loss of all 4 extremities and the trunk of body
Cause -dementia
Dementia is the loss of cognitive abilities beyond natural aging
biopsychosocial causes
history of brain damage (psycho)
genetic susceptibility (bio)
chronically stressful life which culd be due to socioeconomic position leading to the atrophy of the hippocampus (socio)
Early symps of dementia
bad memory
attention
language skills
problem solving skills
Demographic - dementia
older adults but is also seen earlier in ppl with highly stressful jobs (stock market brokers etc)
Most common type of dementia
Alzheimer- 60-70% of cases- progressive and irreversible
Demographic of alzheimer
ppl in mid 60s C
Cause alzheimer
less physical activity + less intellectual activity + genetic
What and whats in it - endocrine system
it is a system of ductless glands that secrete hormones and cause changes in other organs
hypothalamus + pituitary
Parts of the pituitary gland
anterior and posterior
hormones secreted by Anterior
Growth h- GH (growth of body tissues)
Prolactin- PRL (milk production from the mammary glands)
Thyroid stimulating h- TSH (stimulates thyroid release)
Adrenocorticotrophic h- ACTH (stimulate hormone released by adrenal cortex)
hormones secreted by posterior
Antidiuretic h (water reabsorption in kidneys)
Oxytocin (utrine contraction during child birth)
What does stress do in the body
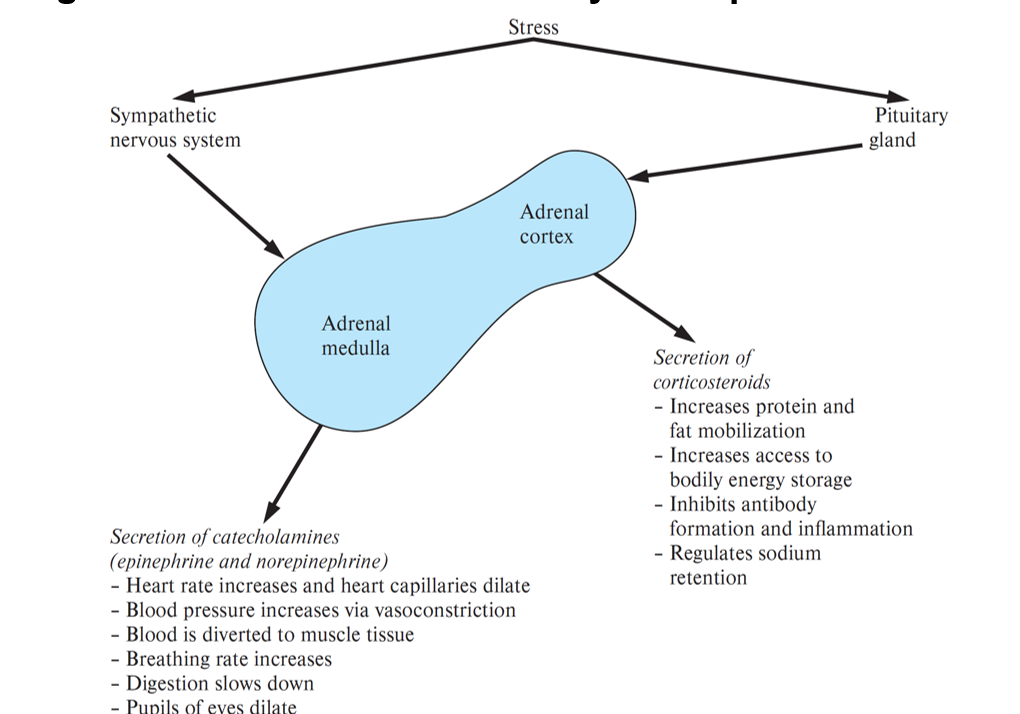
What is diabetes and 2 types
when the body is incapable of producing insulin or is resistant to the effects of insulin
Type 1- autoimmune- used to be called juvenile- body destroys cells needed to produce insulin
Type 2- cant produce or is resistant to insulin- leading cause or blindness in adults- accounts for 40% of ppl who need dialysis-
*Resistance- occurs when you eat more fat then you can burn
*Glucophage- medicine that mimics insulin and is used to treat
*Ozempic- last resort- can cause thyroid enlargement or cancer
Parts of the heart
Left atrium+ ventricle - o2 from lungs to body
right atrium+ ventricle - co2 from body to lungs
cardiac cycle (rhythmic contractions and relaxations)
What is in blood
plasma- fluid protein. contains plasma proteins electrolytes and substances transported by blood
Cells- rbc wbc platelets lymphocytes
Platelets- blocks small holes in blood vessels. necessary for clotting
What is blood pressure?
force excerted on the walls of the blood vessels by blood flow. high during systole. low during diastole
What infuences bp
cardiac output
peripheral resistance (eg- in smaller arteries)
damage, less elasticity deposits in arterial walls
Atherosclerosis
arteries narrowed by plaque+cholesterol+other waste
Angina pectoris
low o2 and build up of co2 and other waste
causes chest pain
Myocardial infraction (heart attack)
clot in coronary vessels => no blood flow to the heart
Ischemia
lack of blood flow to the heart
Congestive heart Failure
hearts delivery of o2 rich blood is inadequate
Arrhythmia
irregular beating of heart => loss of concciousness and possibly death