BIOS 1300 Ohio University Exam 3 Nielson
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Joint
point where two bones meet
**do not have to be movable (skull sutures)
3 functions of joints
1. link bone to skeletal system
2. permit movement
3. protect soft organs
2 joint classifications
function and structure
Joint classification by function:
the amount of movement possible
Joint classification by structure:
how the bones are held together...material...joint cavity
Three functional groups of joints and their amount of movement?
Synarthrosis- immobile
Amphiarthrosis- slight movement
Diarthrosis- freely mobile
What are the 4 functional joint groups?
bony, fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial
What is it called when sutures ossify completely?
synostosis
Synovial Joint
joint cavity filled with synovial fluid
Which synovial joint is mobile and which is freely mobile: elbow and shoulder
Shoulder- freely mobile
Elbow- mobile
Which class do most joints in the body fall into?
Synovial joints
Complications of damage to synovial joints?
pain, impaired mobility and quality of life
Periosteum of bone is continuous with ____________?
fibrous capsule
What is the fibrous capsule of bone made out of?
connective tissue
The fibrous capsule of bone is continuous with _____?
Peristeum
What two substances make up the synovial membrane?
fibroblasts and macrophages
What is in the joint cavity of bone?
synovial fluid
What makes the articular cartilage of bone?
hyaline
What is the purpose of bone ligament?
Give the joint reinforcement and strength
3 functions of the synovial fluid:
nourishes articular cartilage
removes waste from cartilage
permits friction free movement
Why is it important to "warm up" before exercising?
It protects your cartilage
Compression vs decompression of cartilage during exercise
compression: squeezes fluid and waste out of cartilage
decompression: absorbs warmed synovial fluid. Takes oxygen and nutrients to chondrocytes.
What happens to your cartilage if you do not exercise?
It deteriorates more rapidly
Purpose of fibrocartilage pads in some synovial joints?
absorb shock/pressure
guide bones across each other and increase fit
stabalize joint-- decrease chance of dislocation
Ligaments
join bone to bone
What type of tissue are ligaments made of?
dense regular connective tissue
tendons
join muscle to bone
Bursae
fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid
Where are bursae located?
between bones and tendons or muscles
Purpose of bursae?
decrease friction
Tendon sheath
elongated cylindrical bursae wrapped around tendons
Where are tendon sheaths located?
hands and feet
What is range of motion?
The degree to which a joint can move
what is range of motion determined by?
-structure of articular surface ("fit")
-strength/tautness of ligaments and joint capsules (ligaments can stretch)
-action of muscles and tendons ("muscle tone")
What does range of motion affect?
functional independence
quality of life
training regime
clinical diagnosis and monitoring during rehab
Axes of rotation
passes through the bone in a direction perpendicular to the plane of movement
3 axes of rotation
multiaxial= shoulder (3)
biaxial= wrist
monoaxial= elbow
6 types of synovial joints
Ball & socket multiaxial
Condylar biaxial
Saddle biaxial
Plane (gliding) biaxial
Hinge monoaxial
Pivot monoaxial
*from greatest mobility to least
What is the most mobile synovial joint?
ball and socket (glenohumeral)
Example of a condylar joint:
radiocarpal joint
metacarpophalangeal joint
Example of a saddle joint:
opposable thumb
SC joint
Example of plane joint:
AC joint
between carpal and tarsal bones
What are the main movements of hinge joints?
flexion and extension
Examples of hinge joints:
knee joint and elbow joint
What is the main movement of pivot joints?
rotation
Example of pivot joint:
radioulnar joint
C1 and C2 joint to turn your head
Flexion
movement that decreases joint angle. common in hinge joints

extension
movement that straightens a joint and returns to zero position
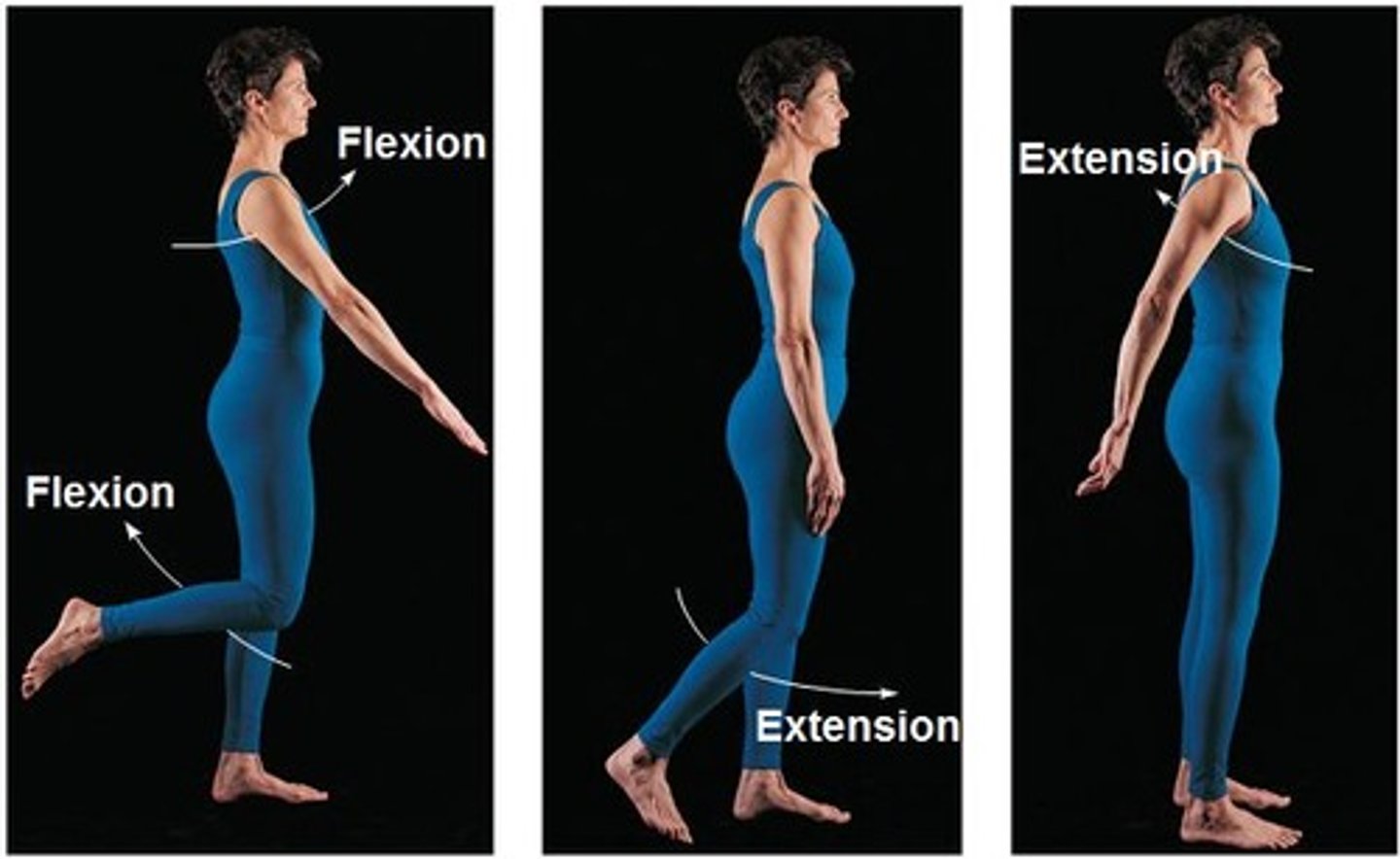
abduction
movement away from midline of body
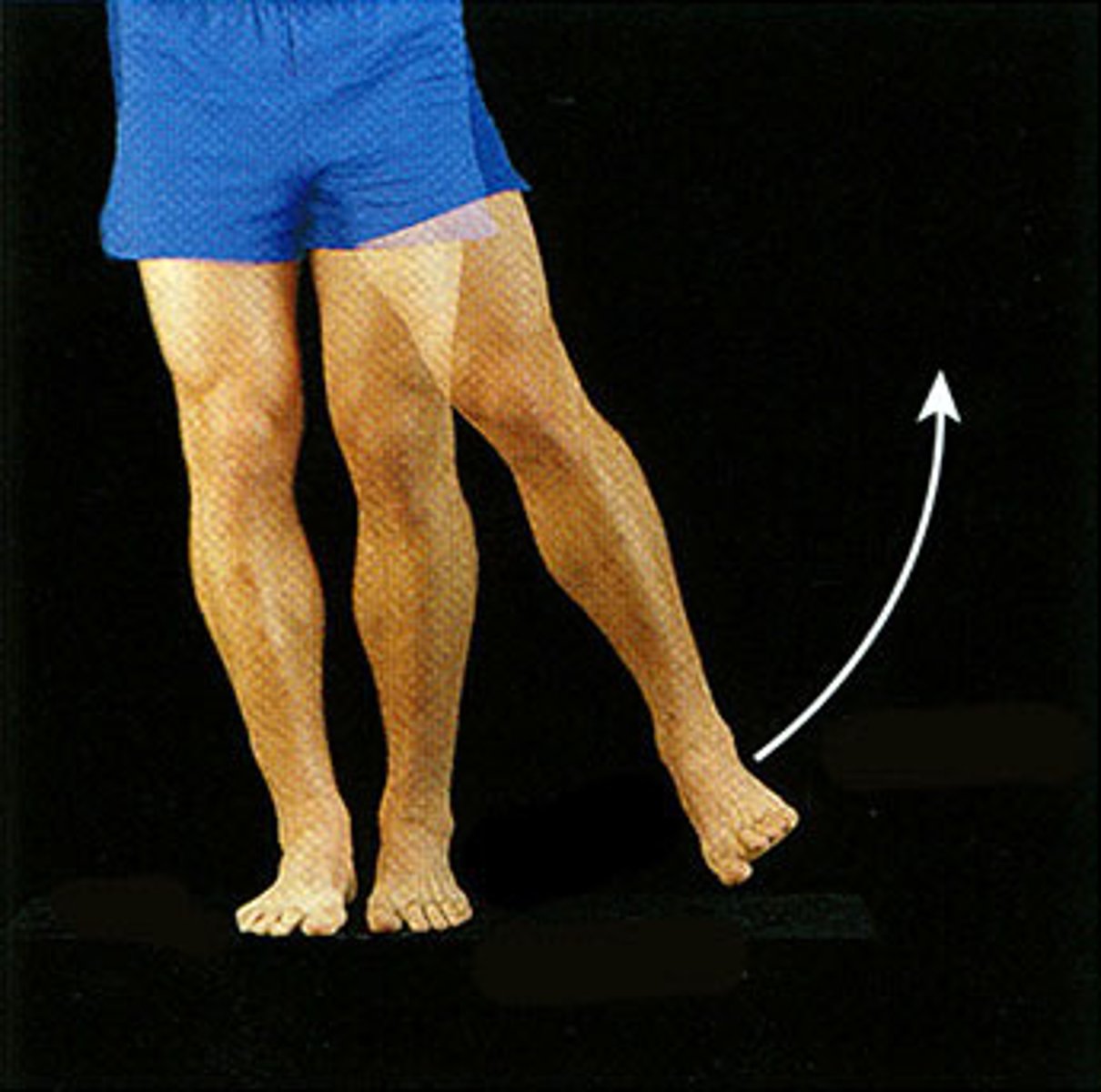
adduction
movement towards midline of body
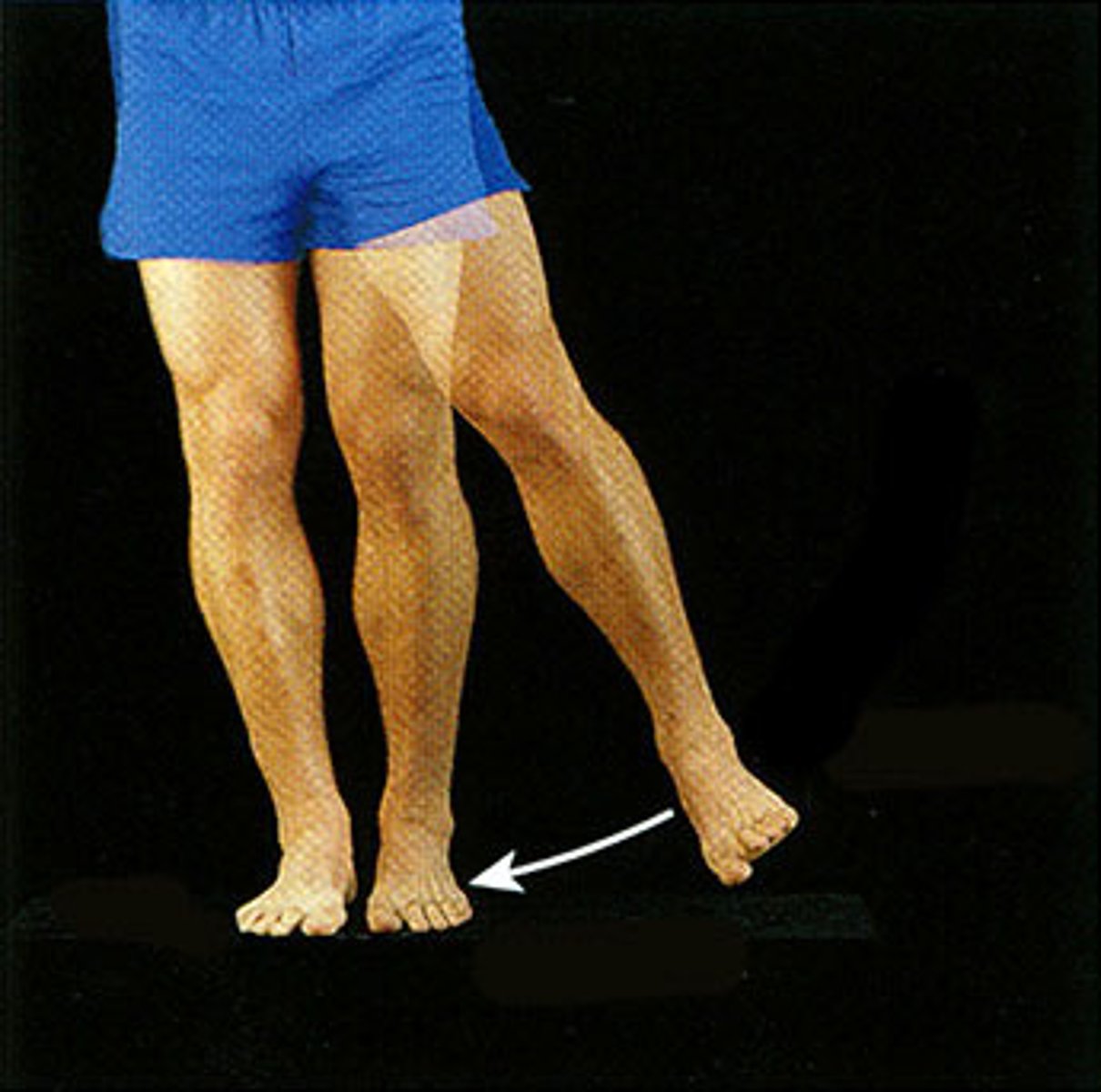
elevation
raises a body part vertically in the frontal plane
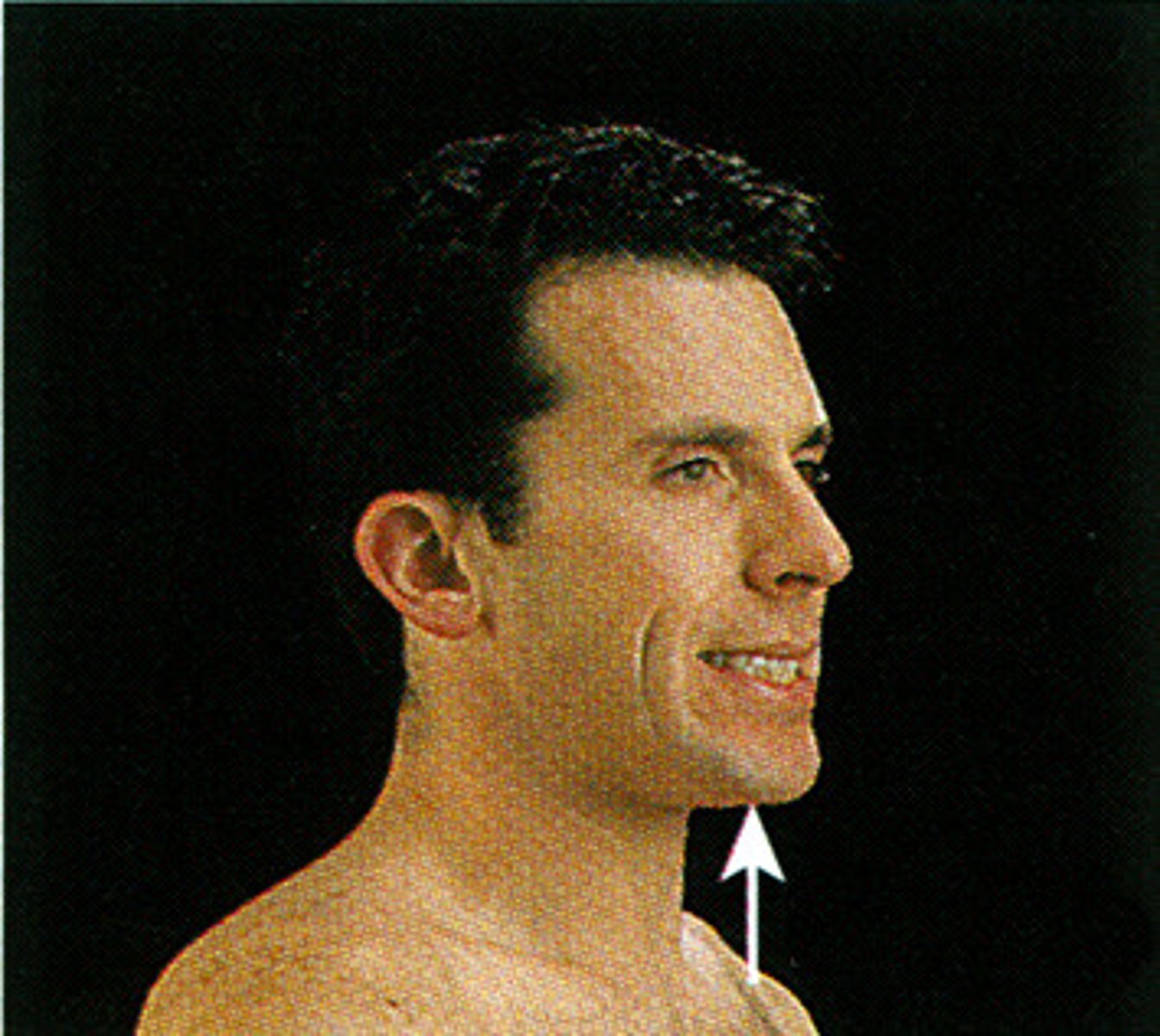
depression
lowers a body part in the same plane
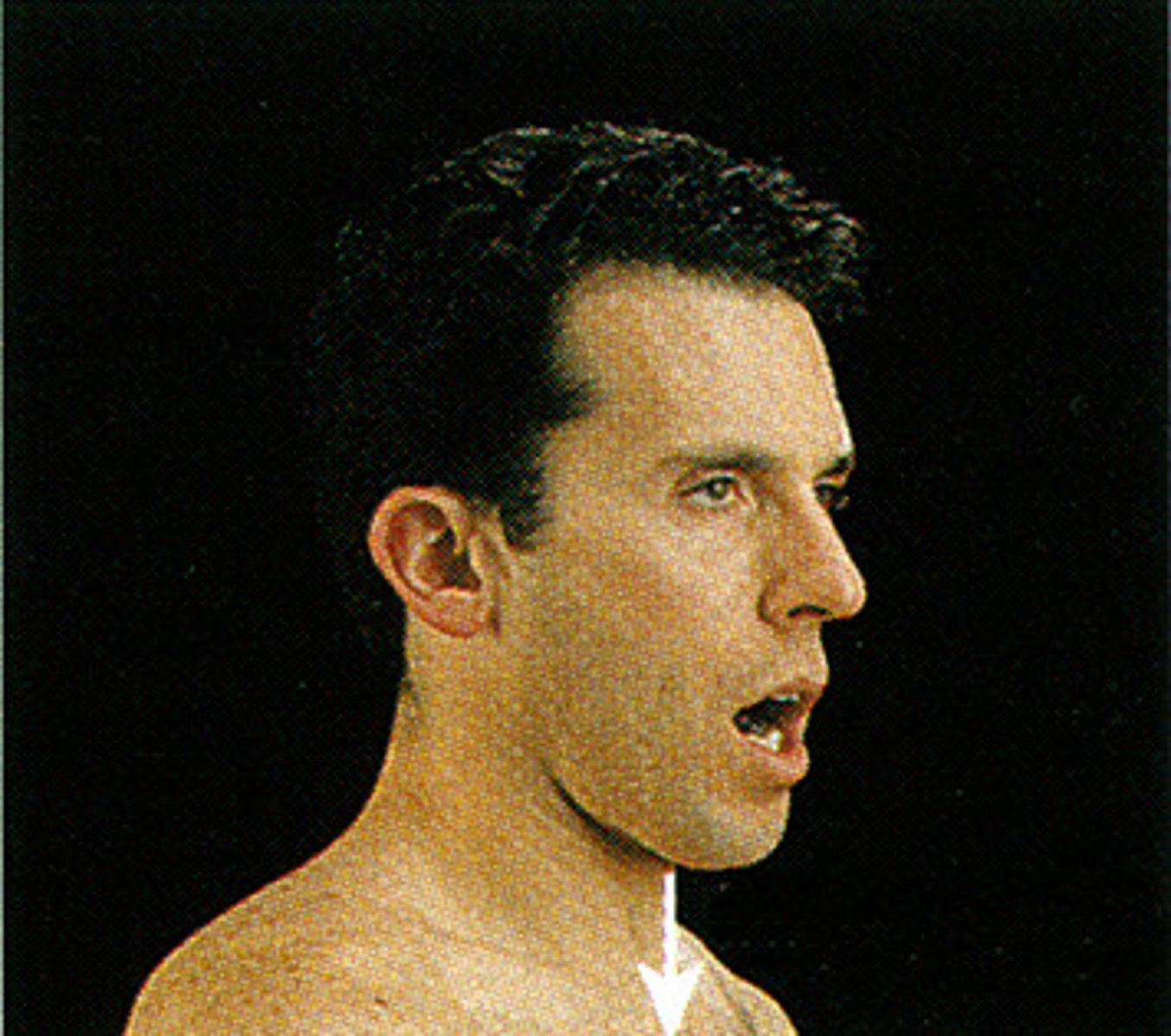
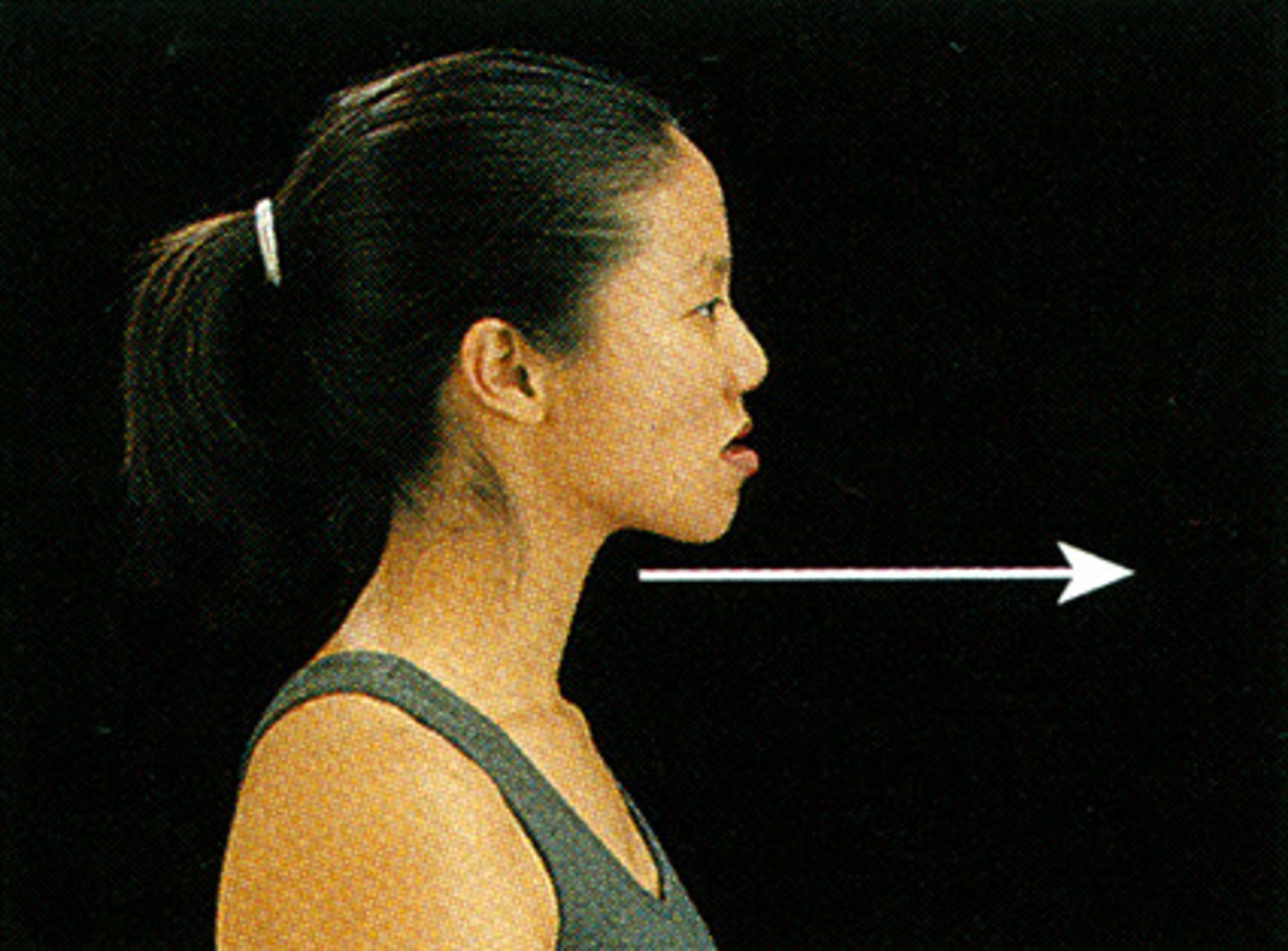
protraction
anterior movement (pushing a door)
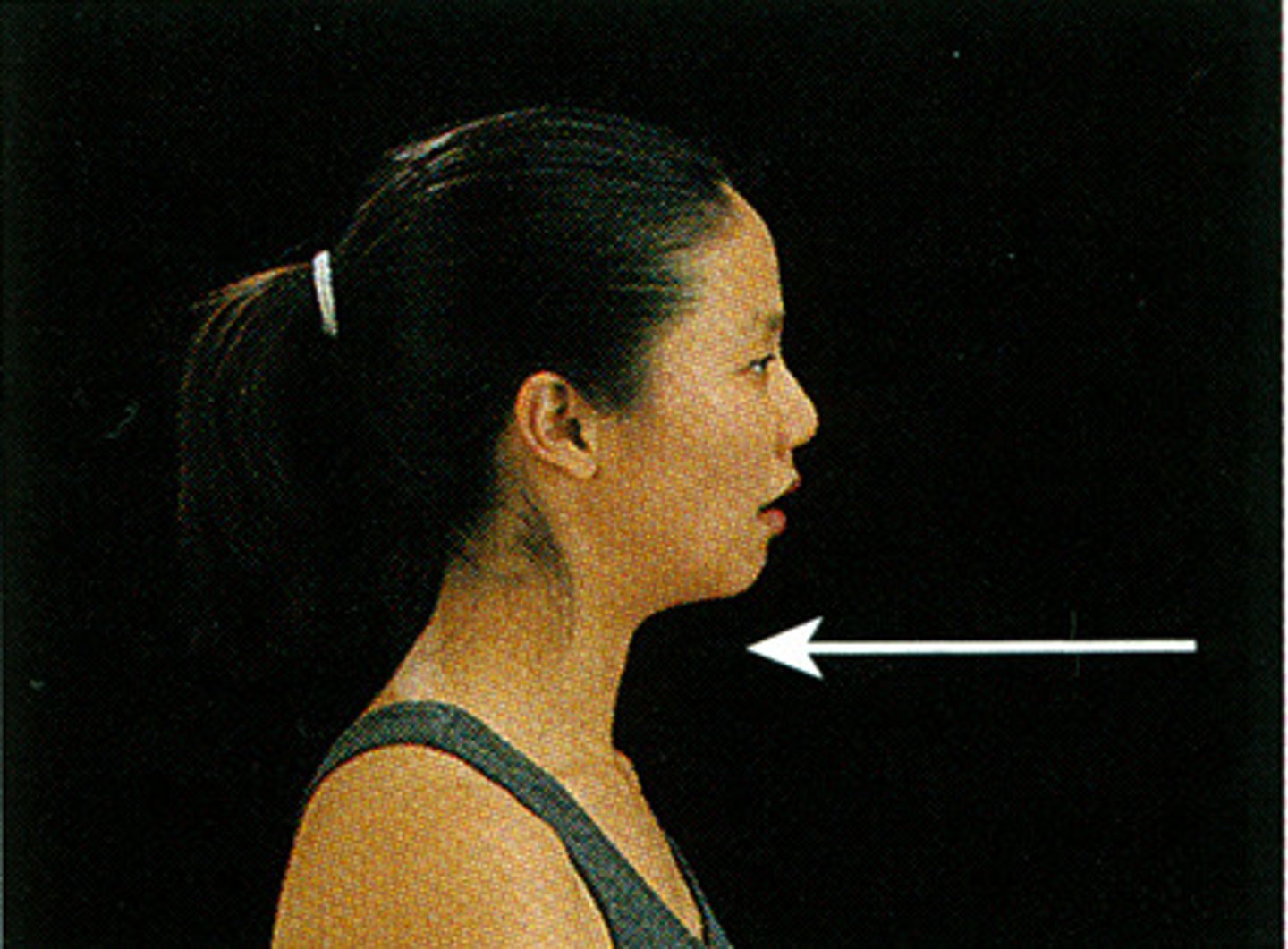
retraction
posterior movement (stand at attention)
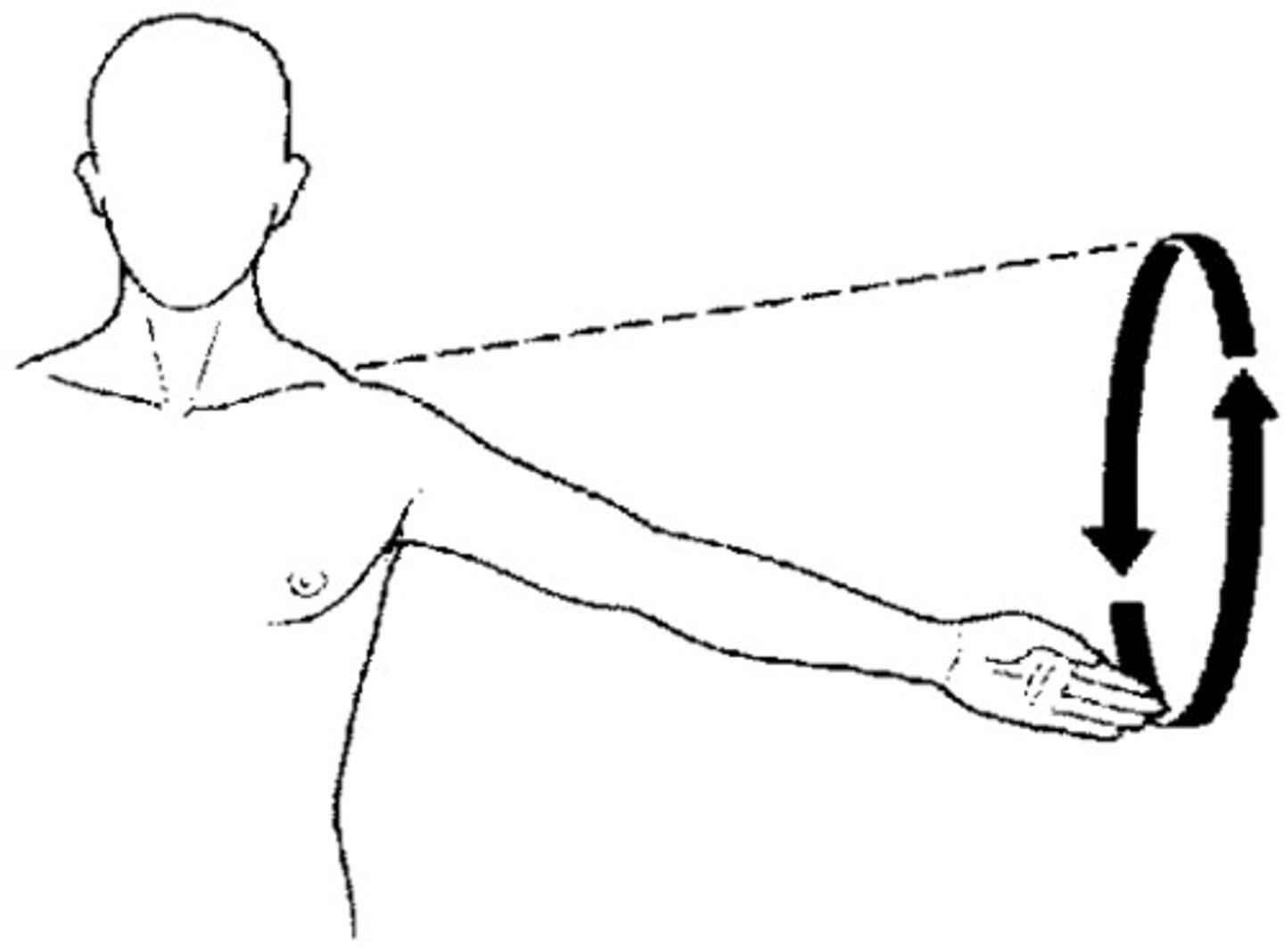
circumduction
circular motion of one end of an appendage, while the other remains stationary
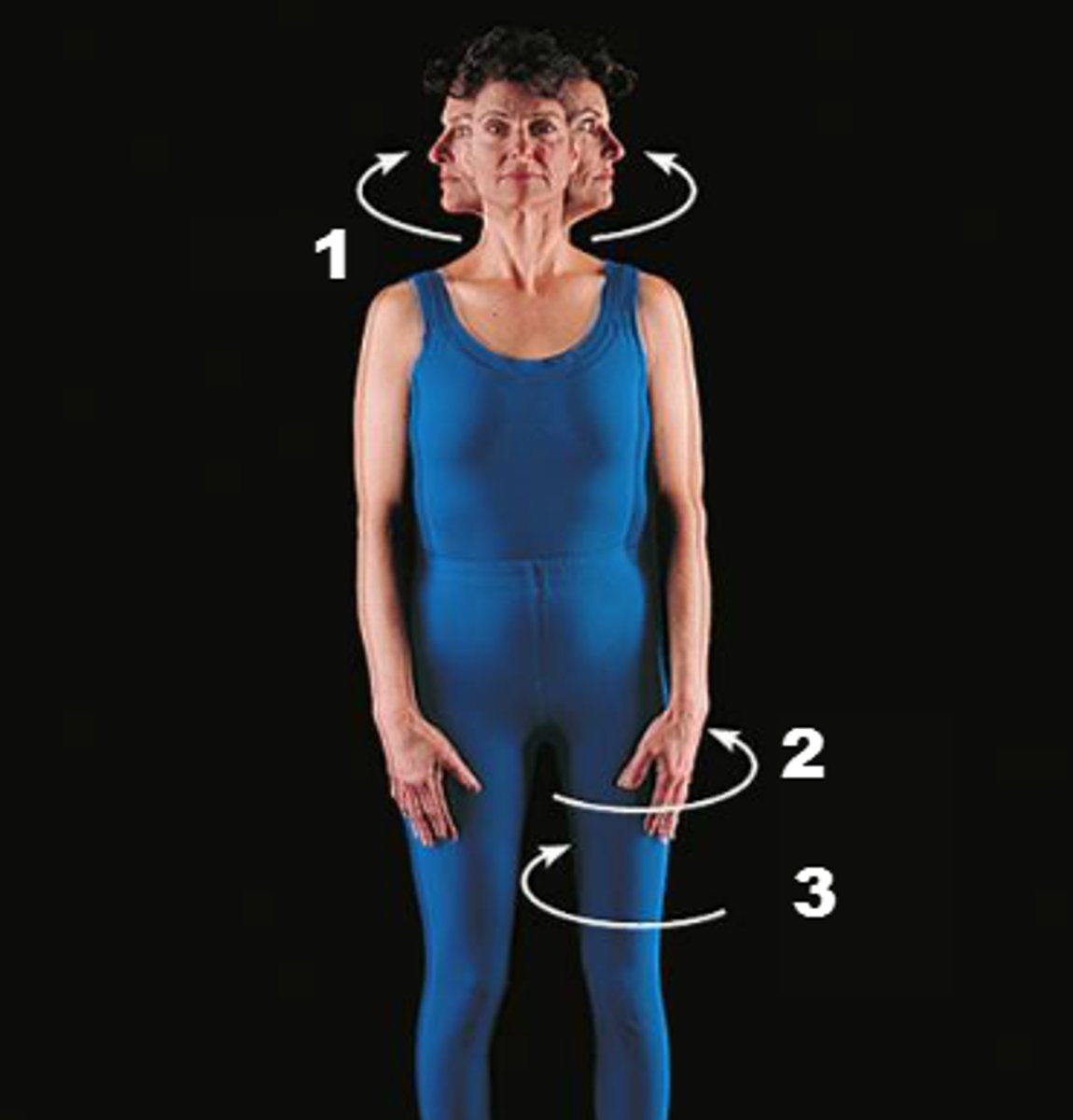
rotation
bone spins on its longitudinal axis
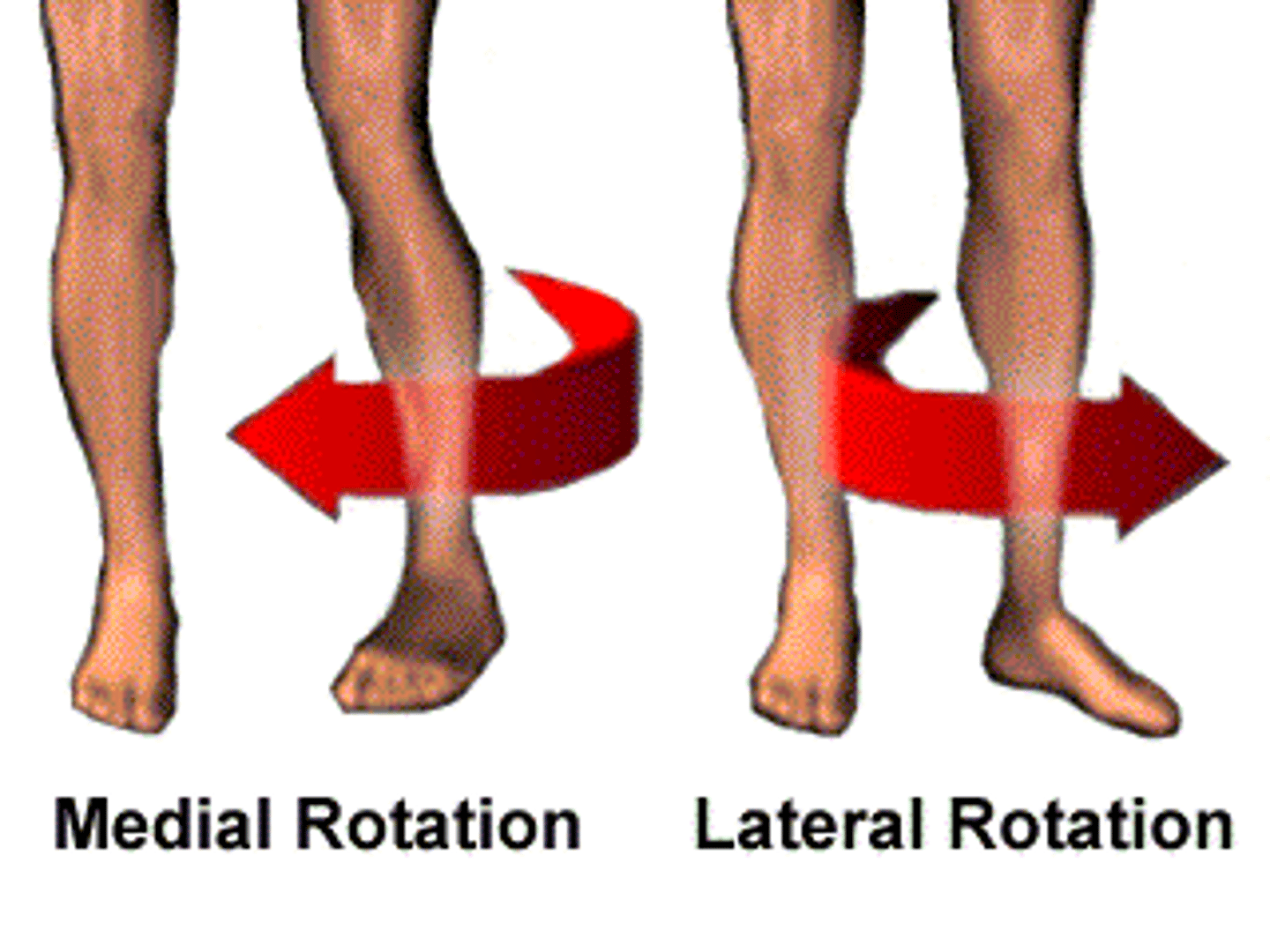
medial (internal)
turns bone inward
lateral (external)
turns bone outward
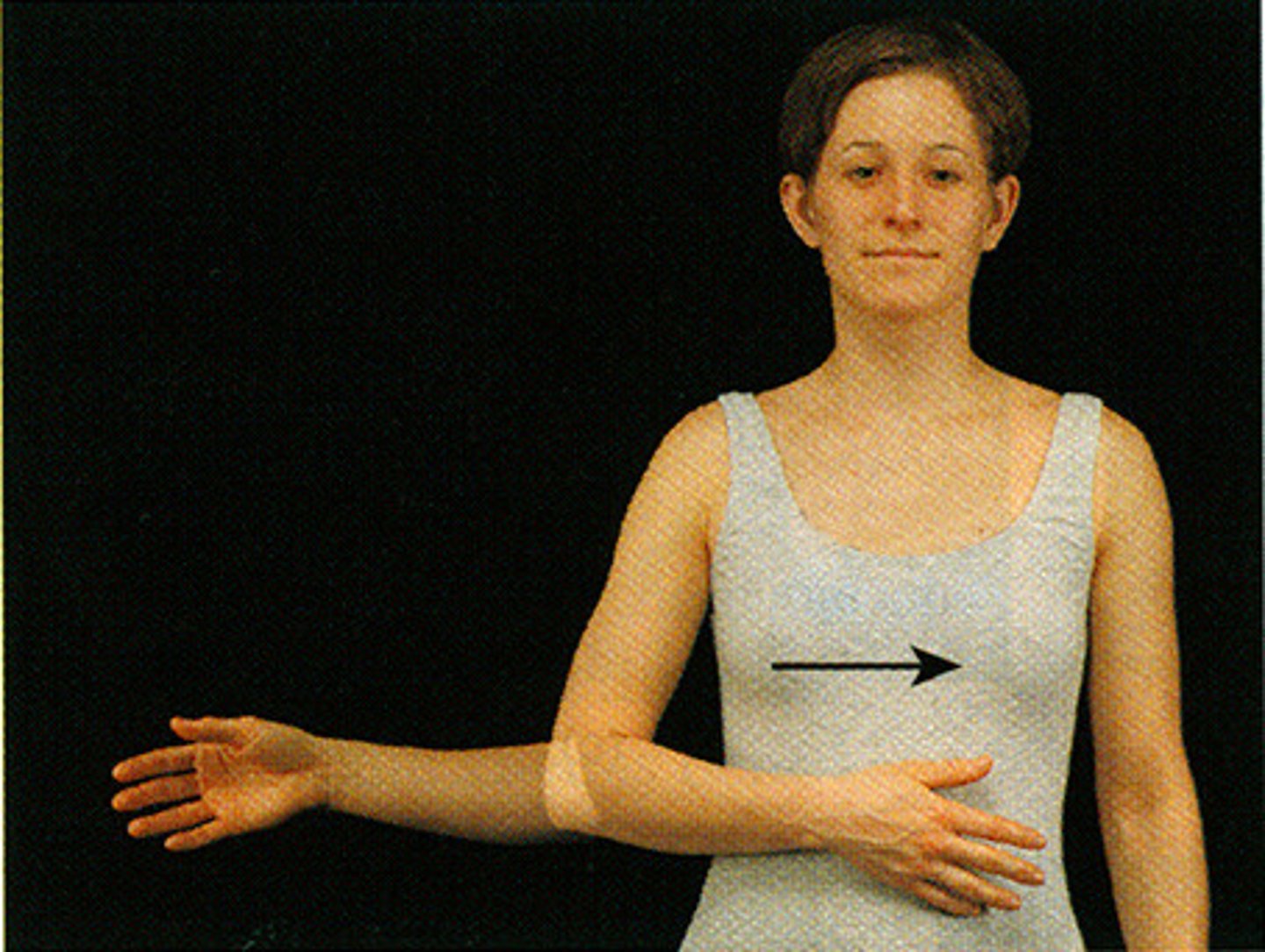
supination
forearm movement turns arm anteriorly or upward
pronation
forearm movement turns palm posteriorly or downward
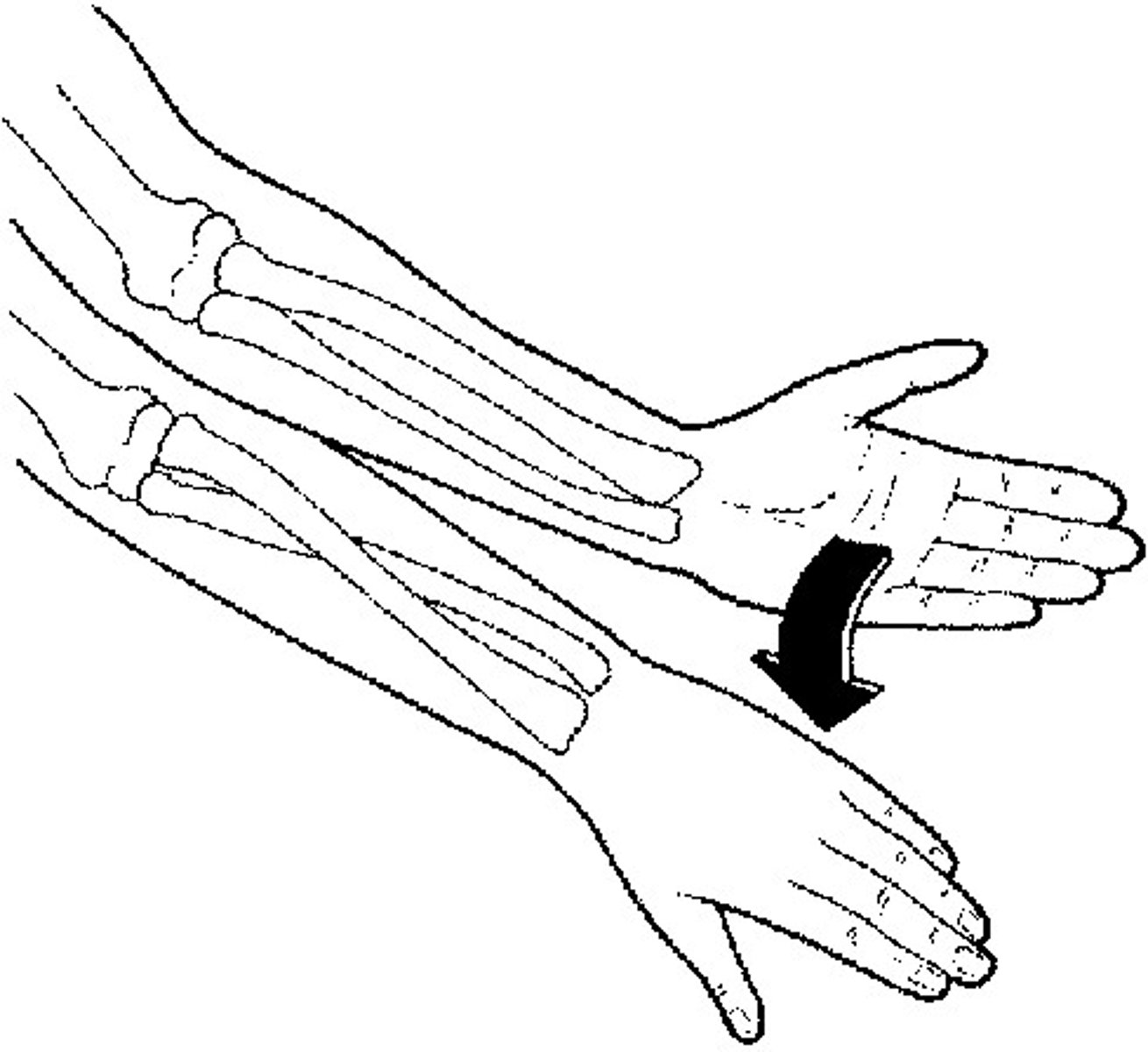
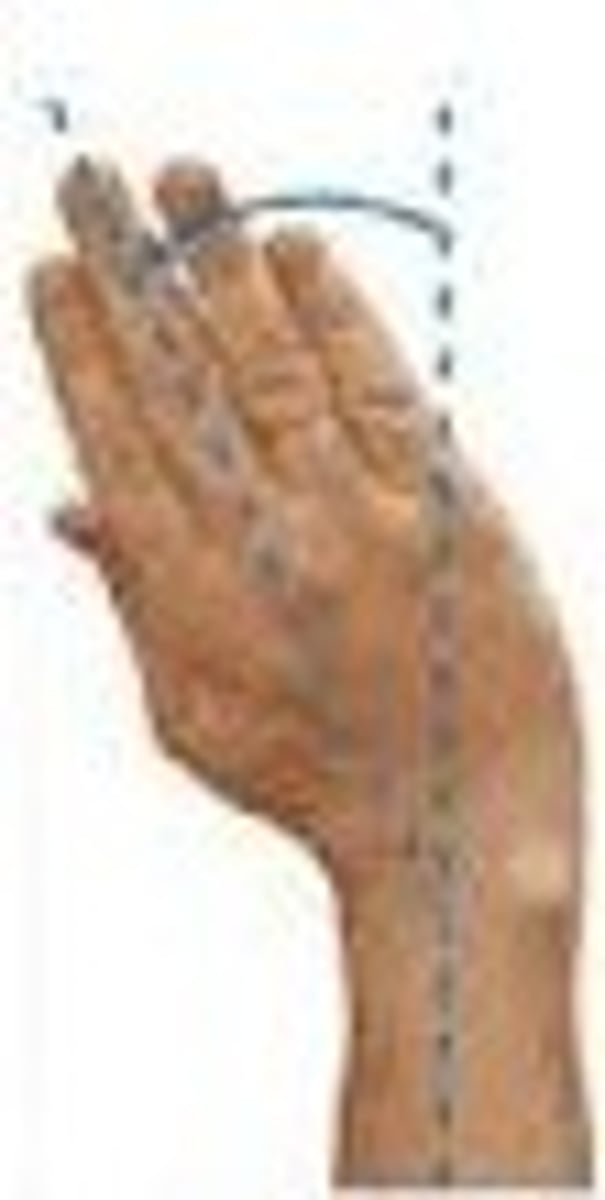
radial flexion
tilting hand towards thumb

ulnar flexion
tilting hand toward little finger
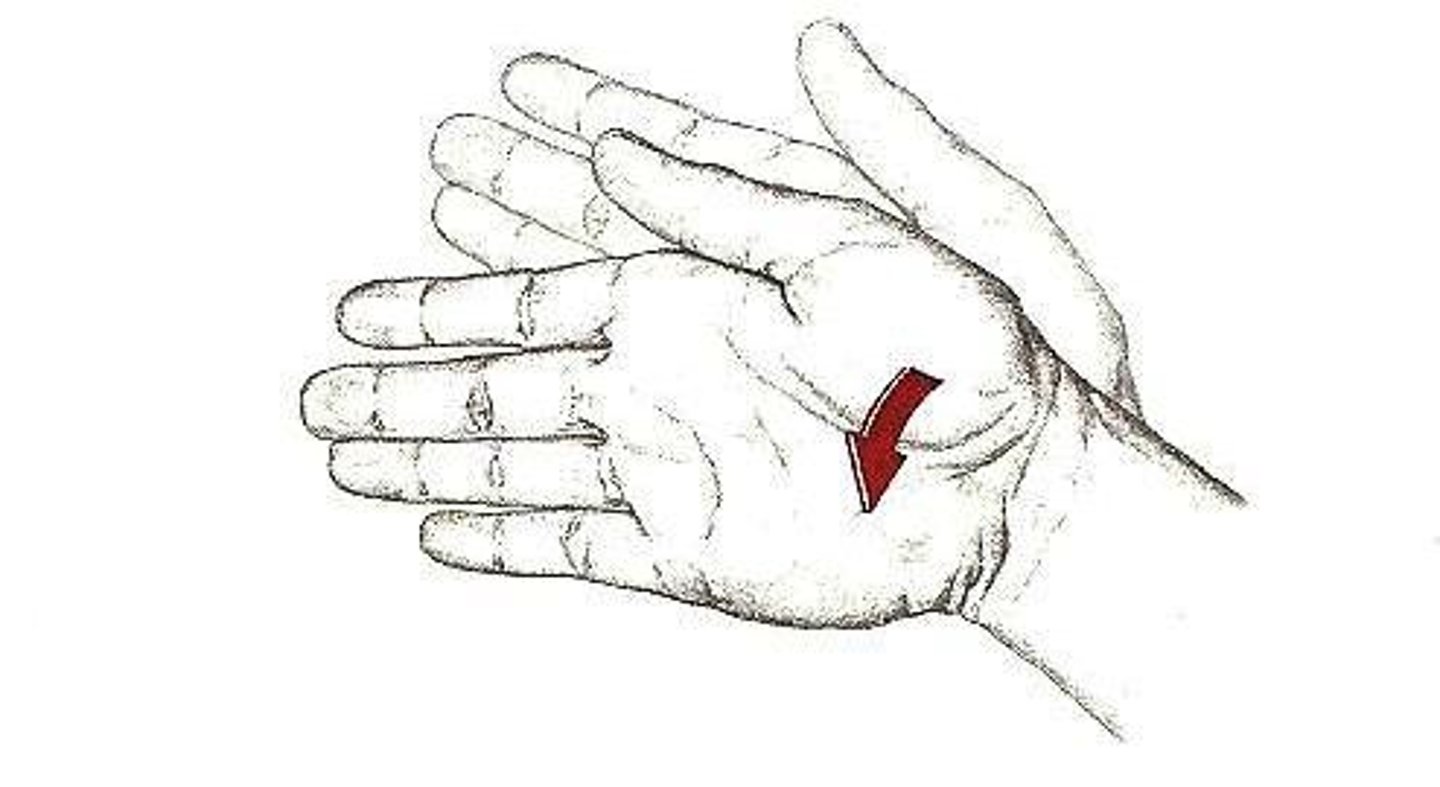
palmar abduction
moving thumb away from hand and pointing it anteriorly
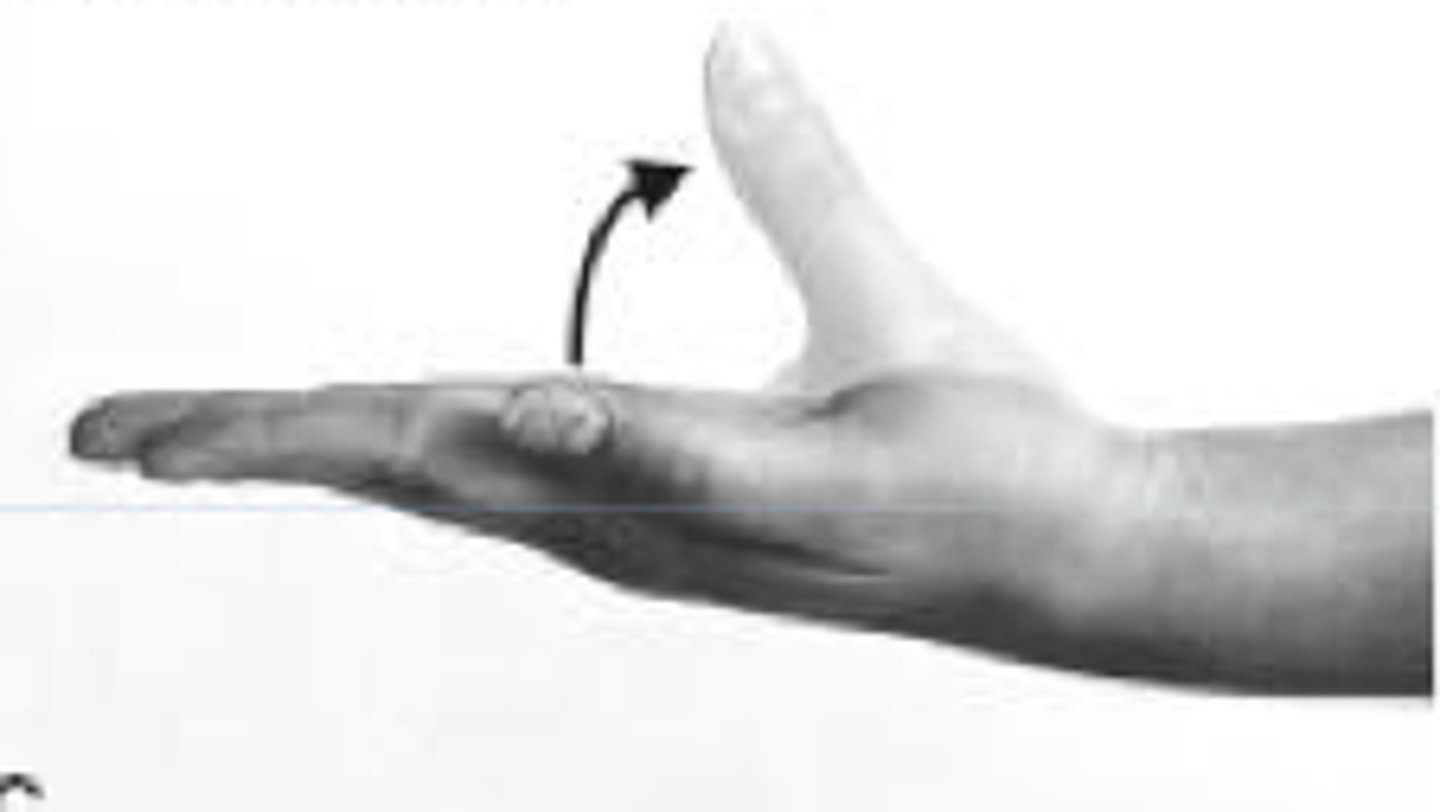

radial abduction
moving thumb away from index finger (90 degrees)
flexion of thumb
tip of thumb directed towards palm
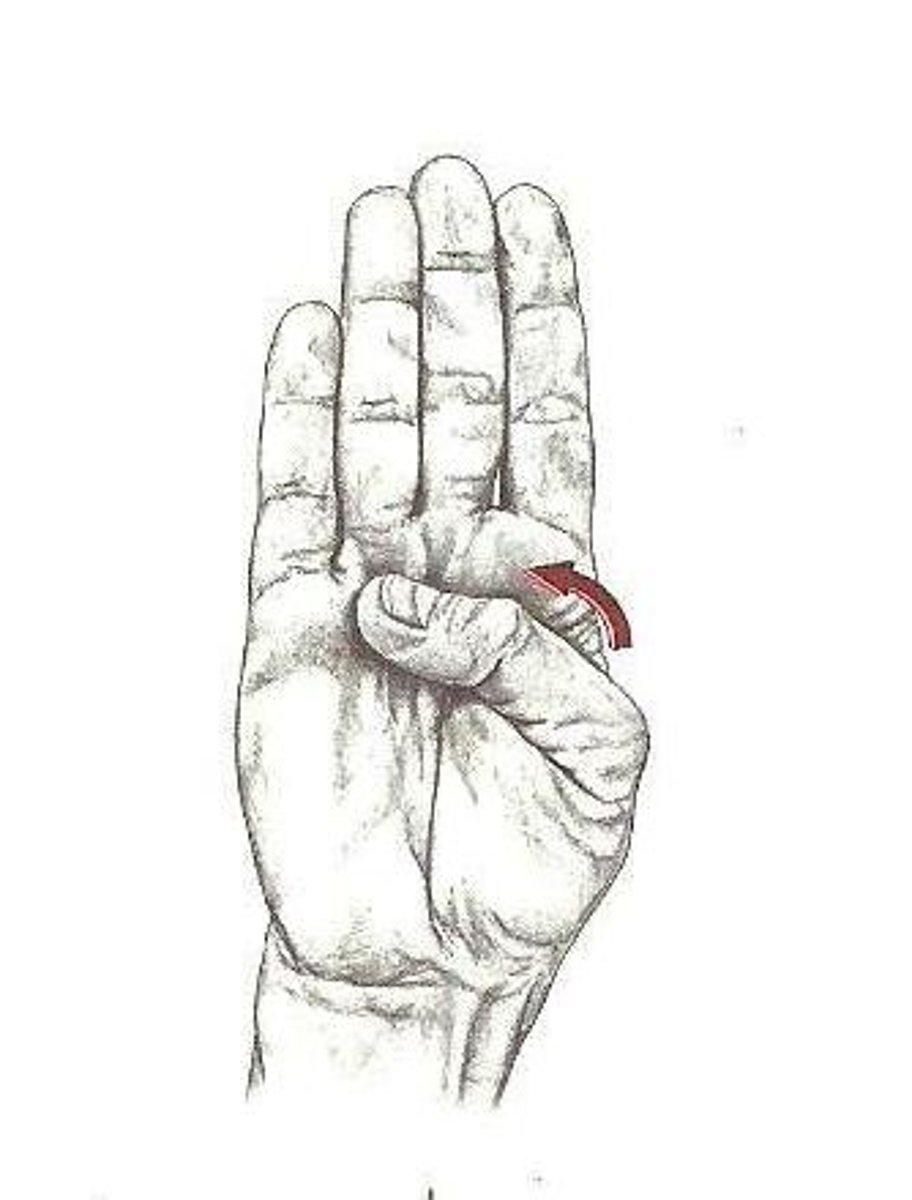
extension of thumb
straightening of the thumb
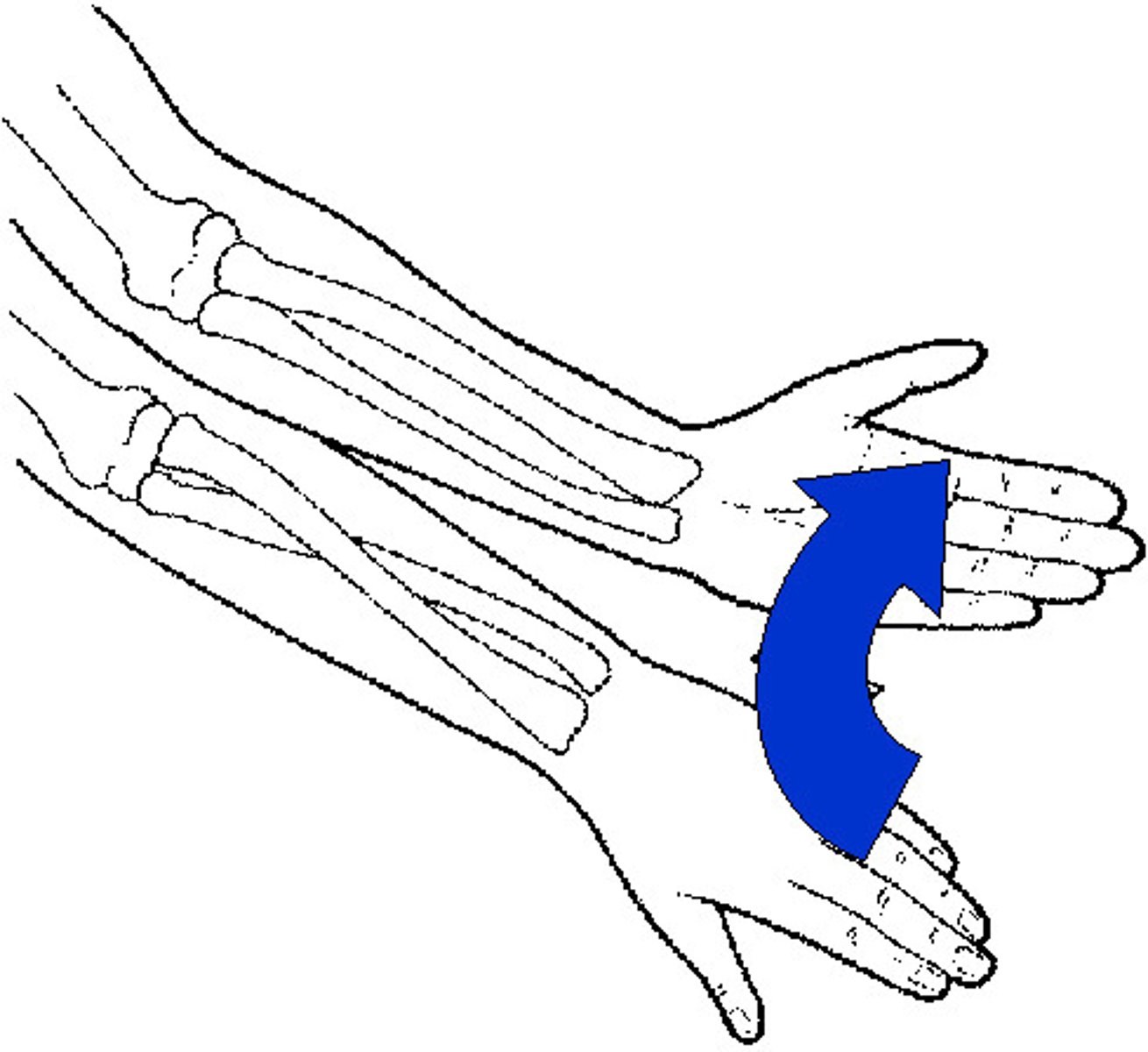
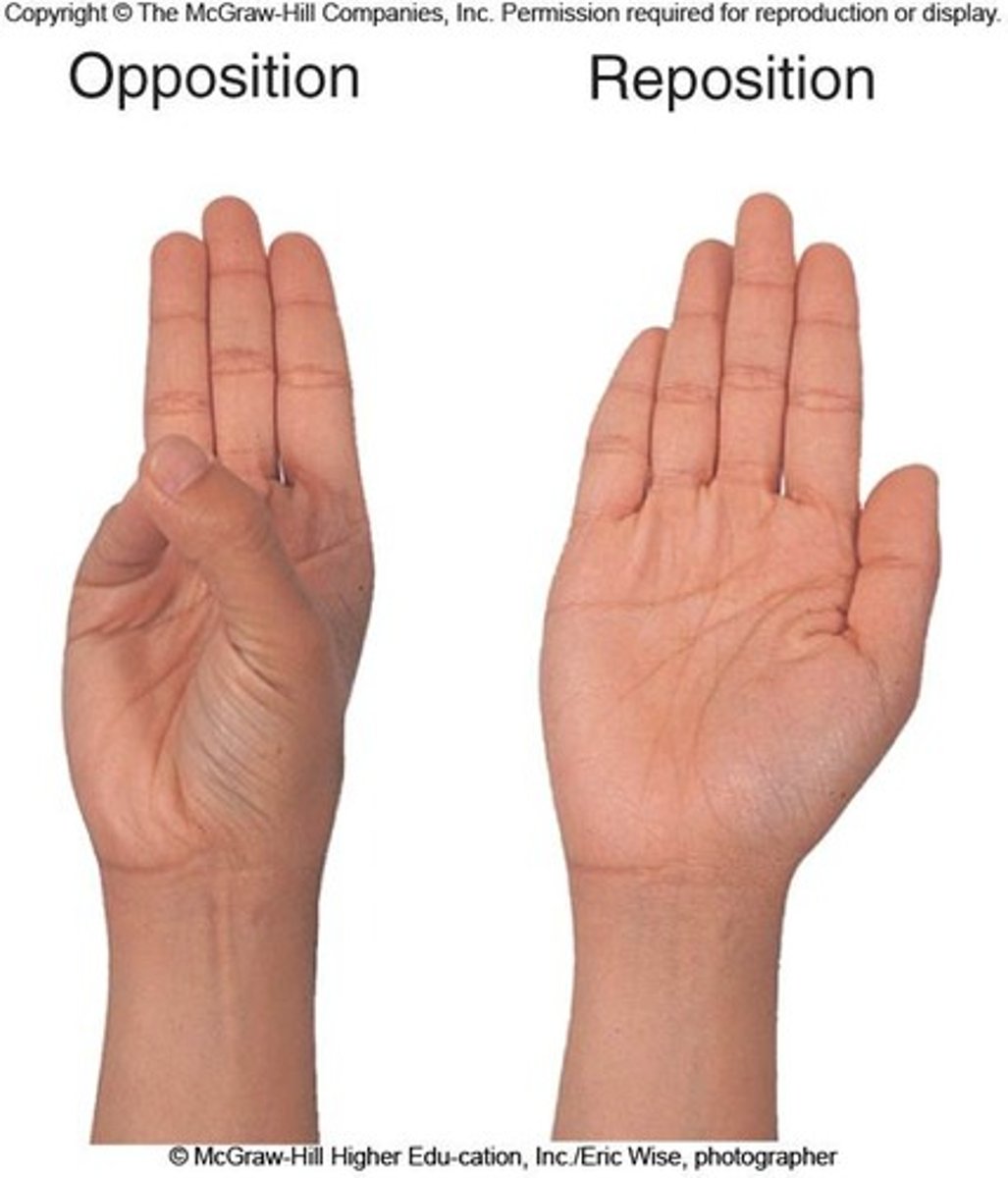
opposition
moving thumb to touch the tip of a finger
reposition
returning thumb to zero position
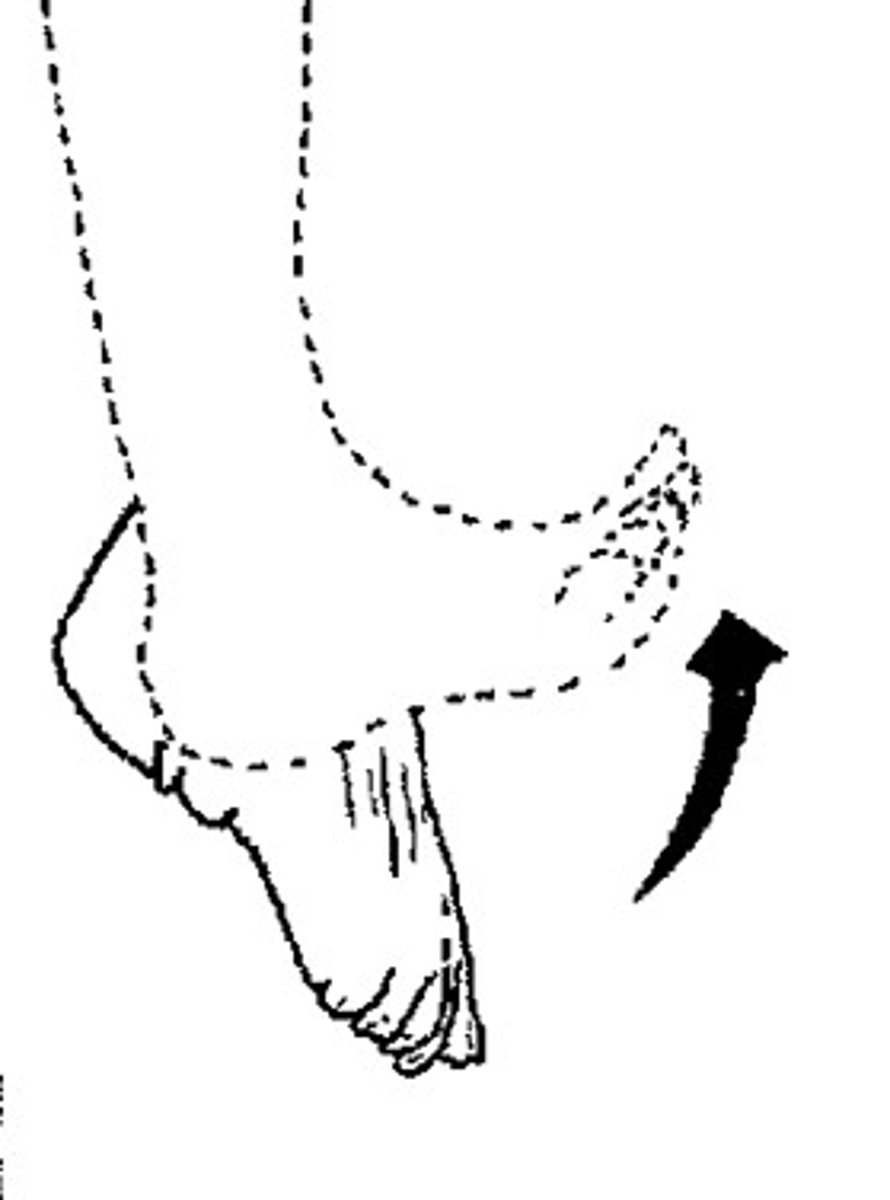
dorsiflexion
elevating toes
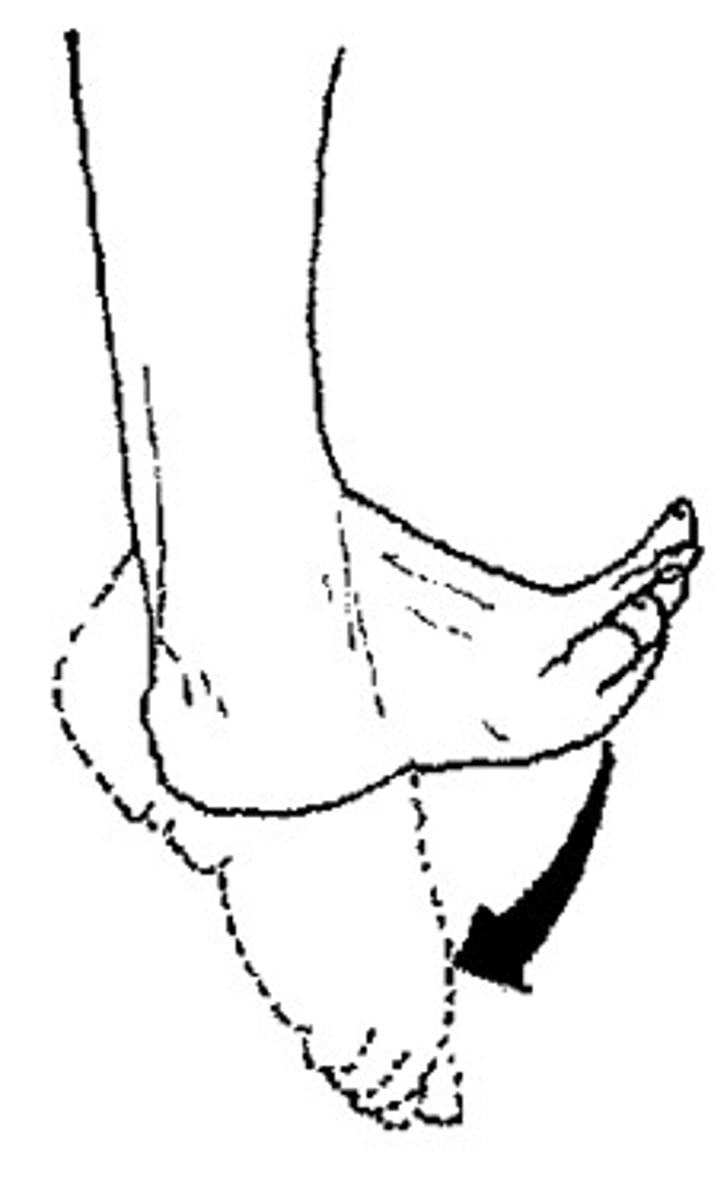
plantar flexion
extending foot so toes point downward as in standing on tip toe
inversion
movement in which the soles are turned medially
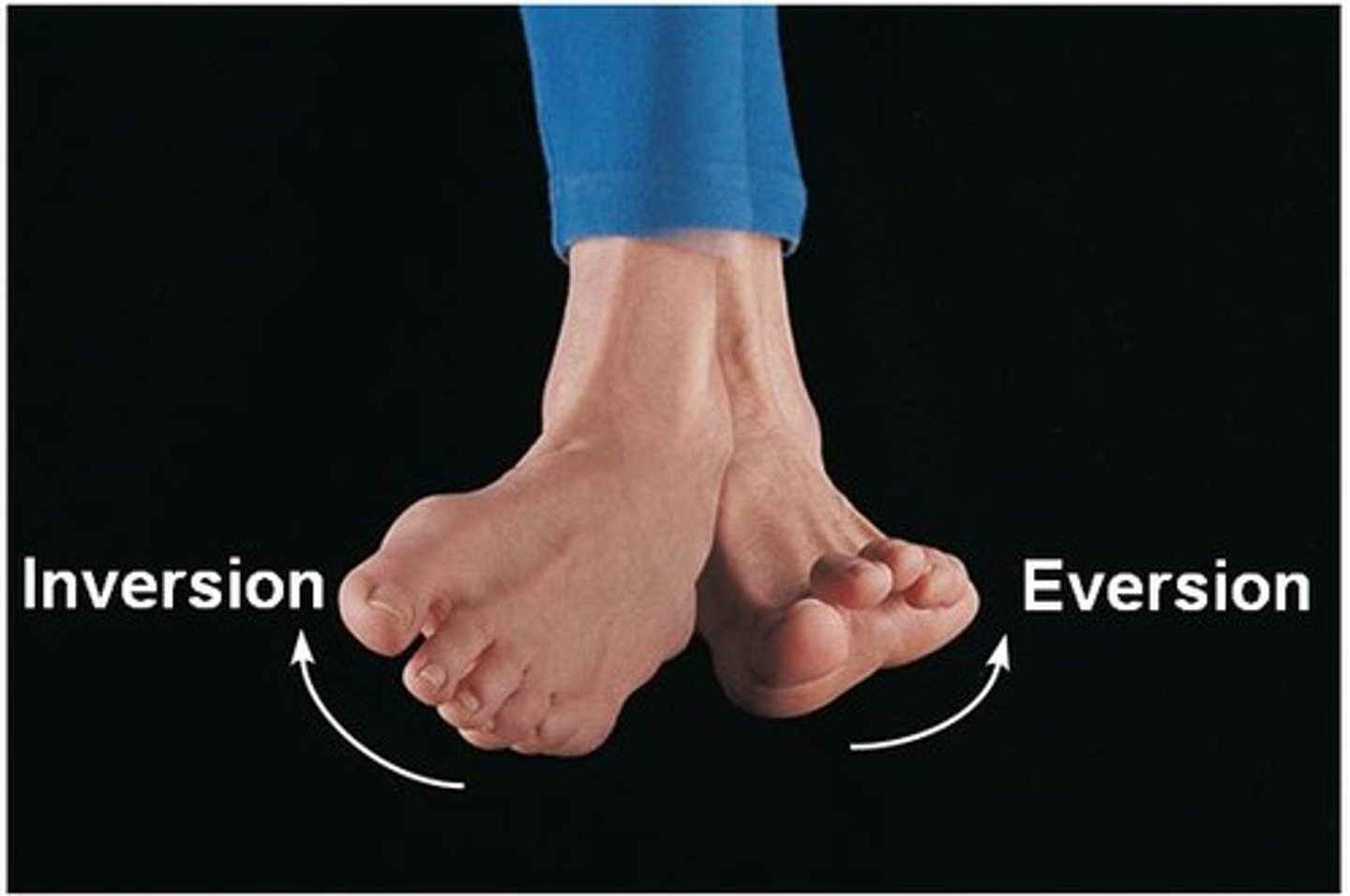
eversion
movement in which the soles are turned laterally
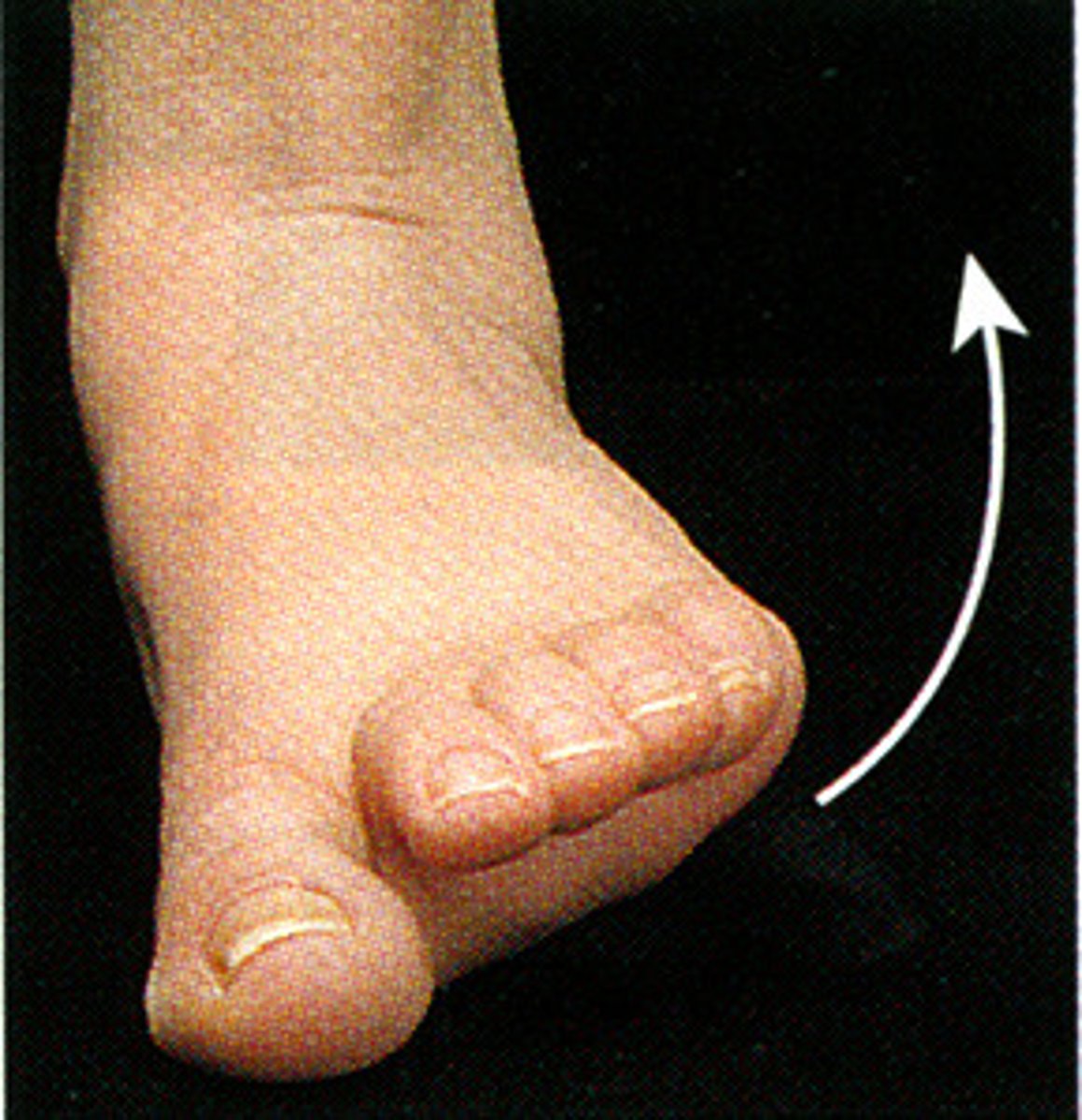
supination of foot
plantar flexion, inversion and adduction
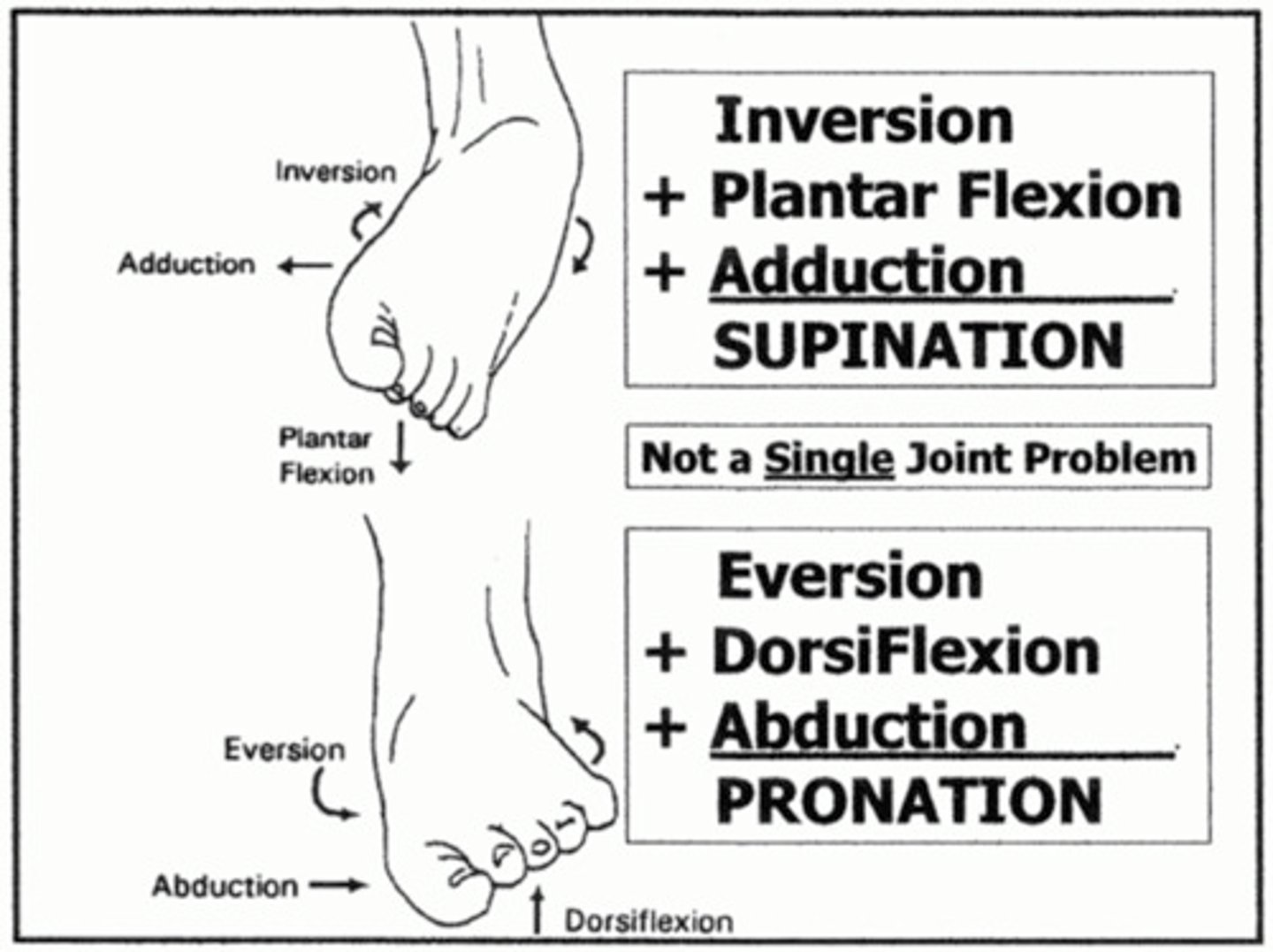
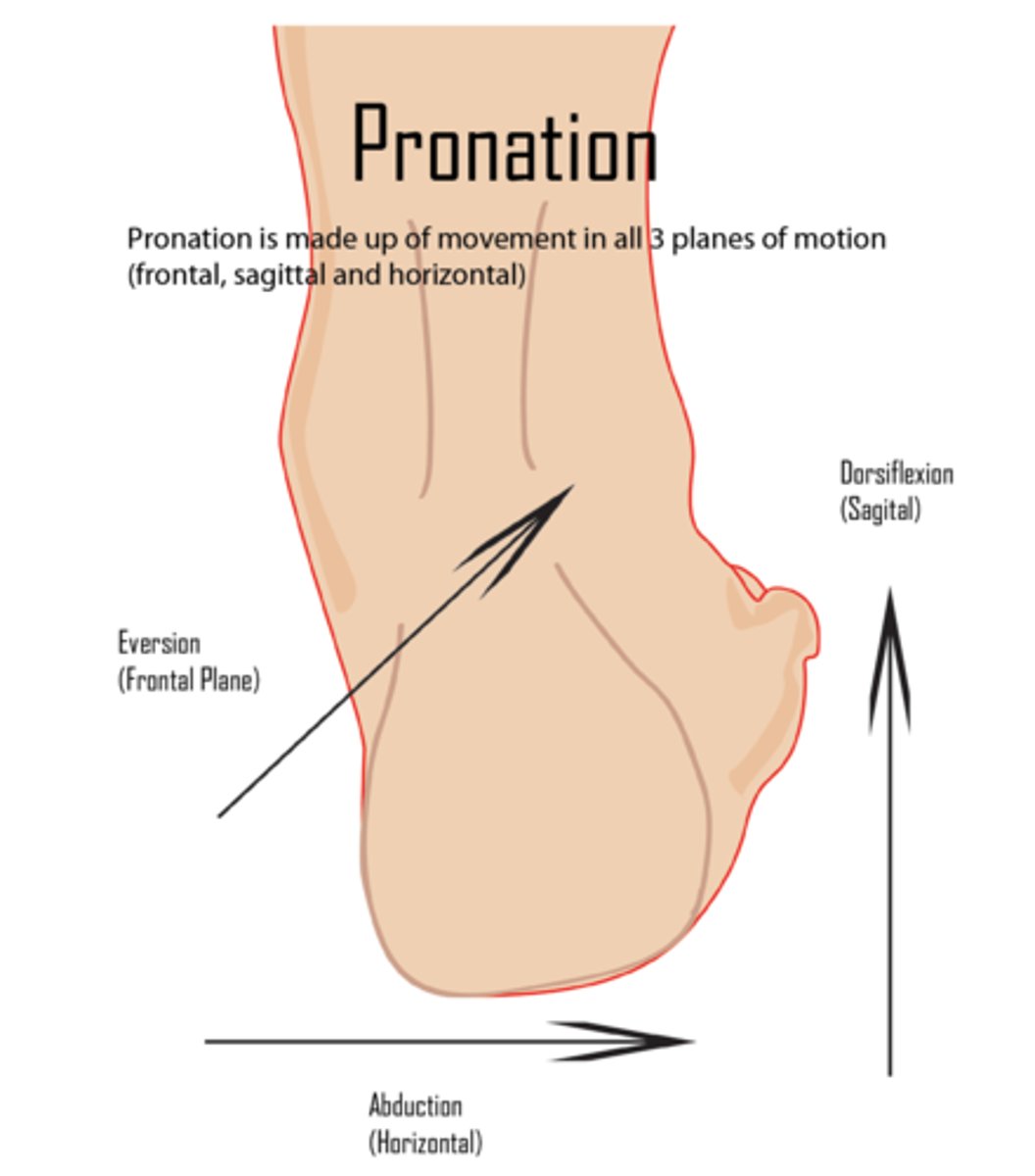
pronation of foot
dorsiflexion, eversion and abduction
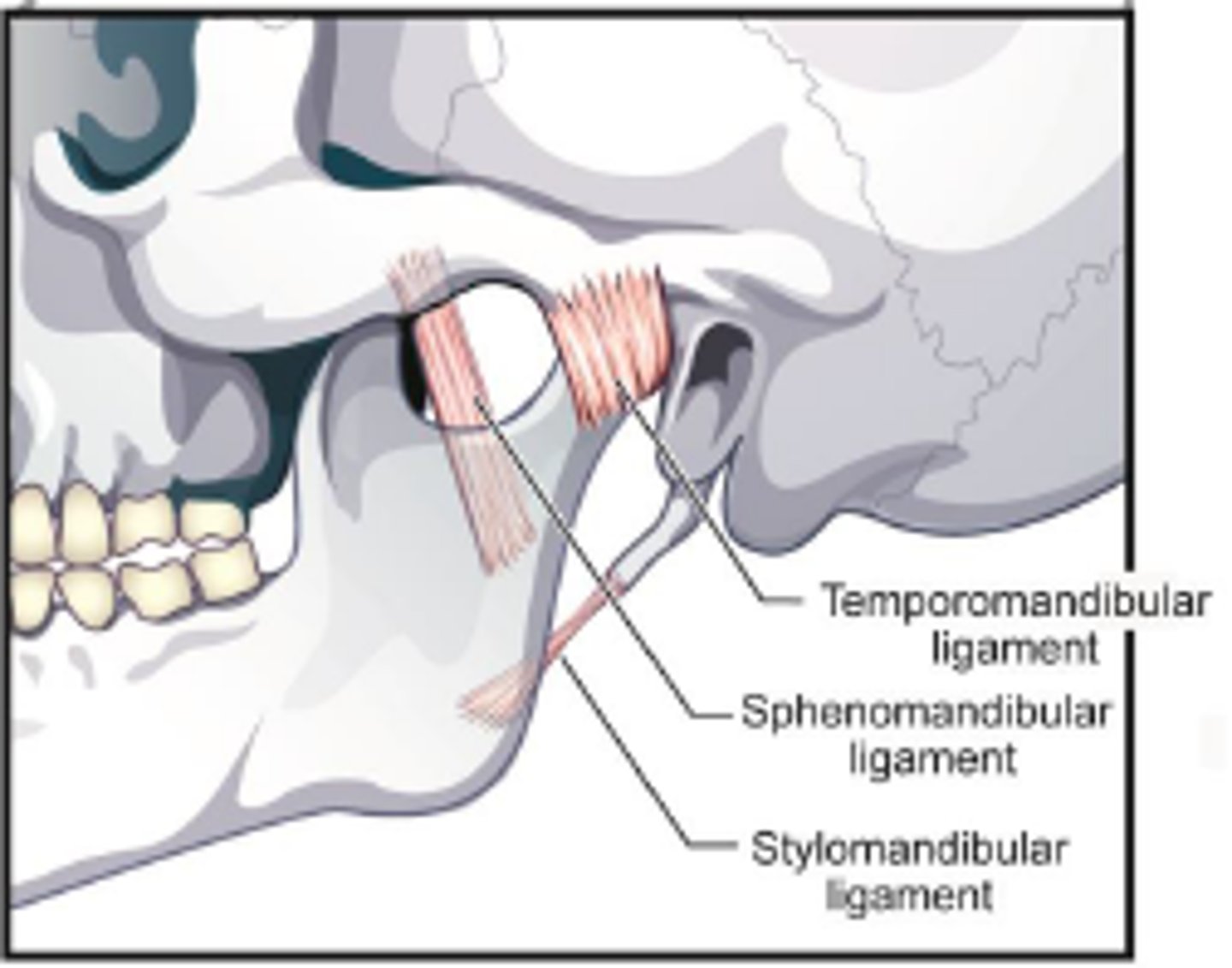
where is the temperomandibular joint located?
on both sides of the face
What does the temperomandibular joint connect?
mandible (jaw) to temperal bones of skull
Function of temperomandibular joint?
open, close, forward and backward, and side to side movement of lower jaw
EX.) talk, chew, yawn
What makes the TMJ an atypical joint disk?
It's made of fibrocartilage not hyaline
Temperomandibular joint ligaments
The sphenomandibular is the primary passive support
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD) causes and treatments:
Causes:
injury, grinding/clenching, arthritis
Treatment:
Nothing (can resolve itself)
night guard
surgery
What makes a vertebral joint an atypical joint?
synovial joint between two processes
symphysis between vertebral bodies
Movements of vertebral joints?
Flexion and extension
Lateral flexion and rotation
Circumduction
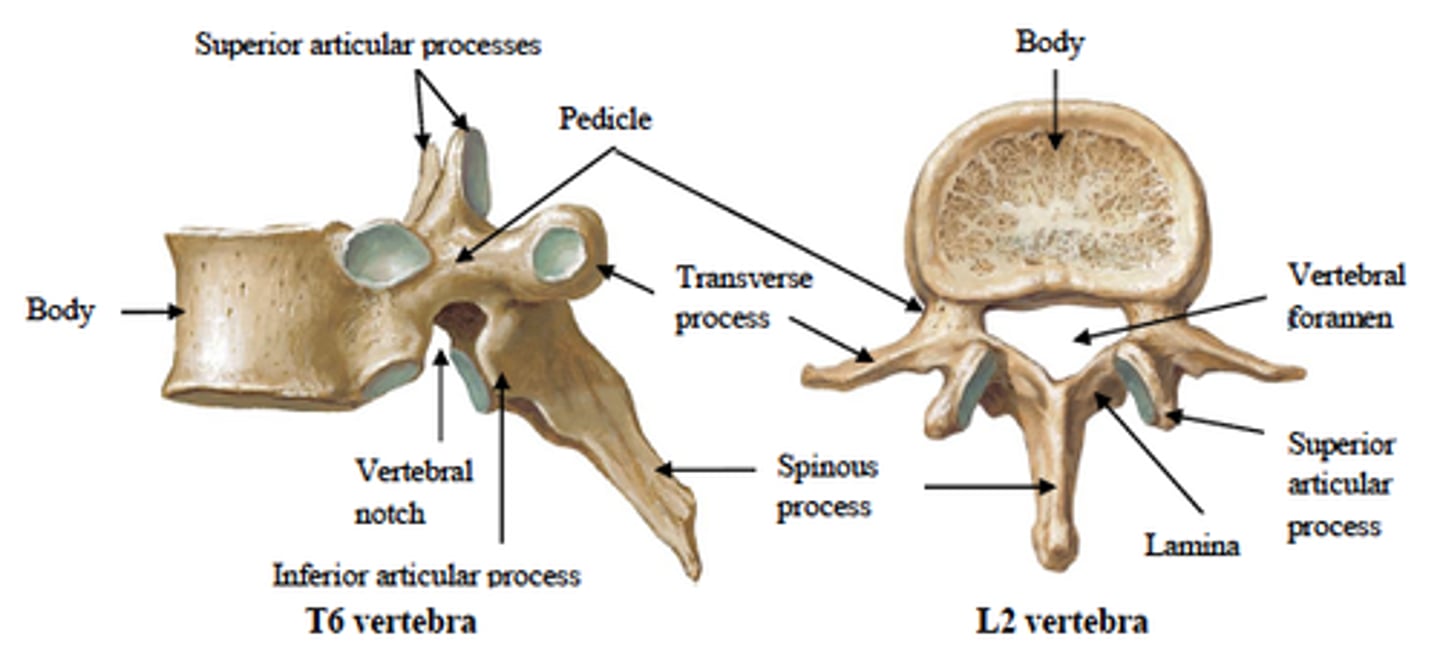
Vertebral joint ANATOMY
superior articular process
inferior articular process
zygapophysial joint
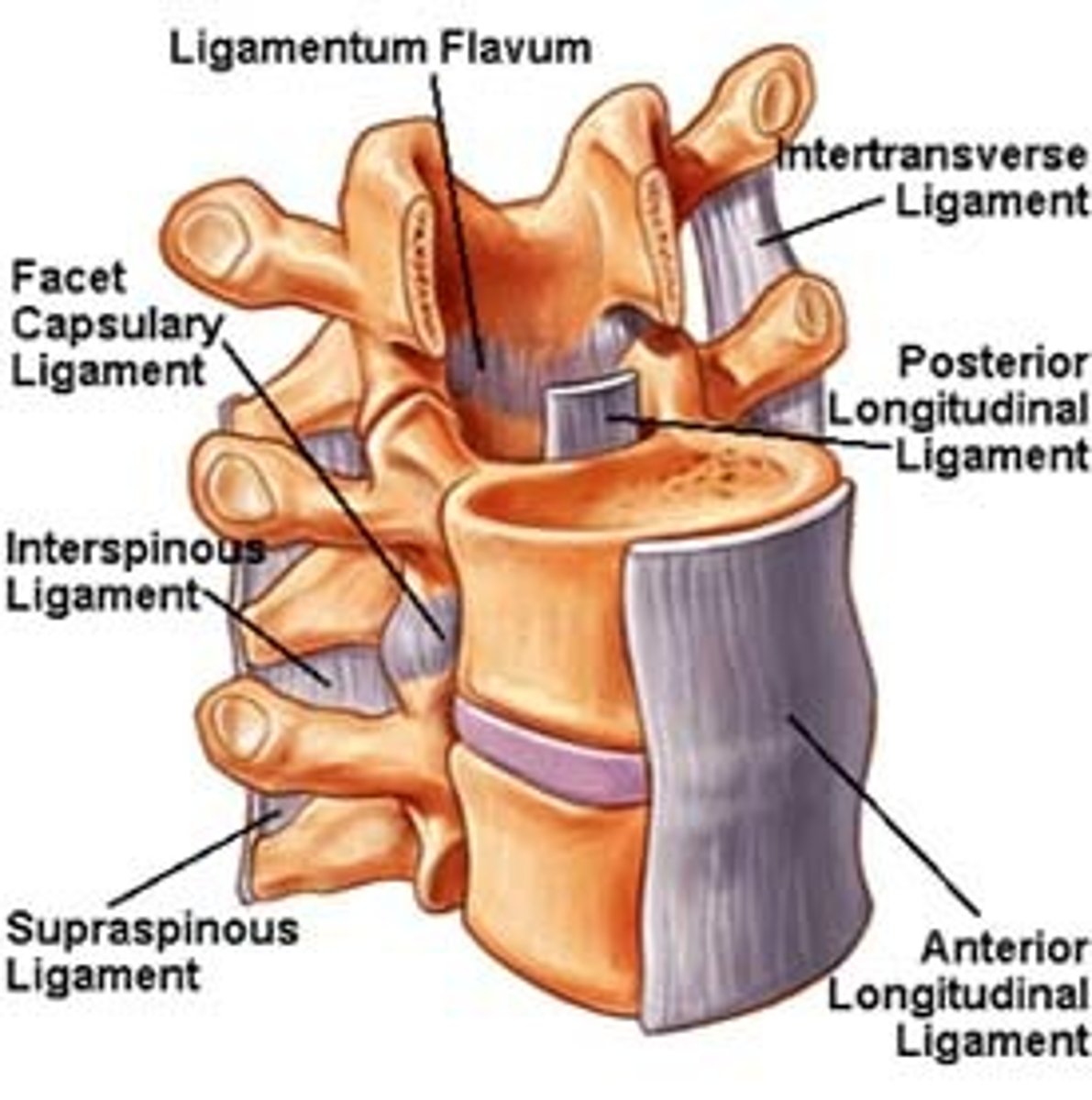
Vertebral joint LIGAMENTS
Facet capsulary ligament
posterior longitudinal ligament
anterior longitudinal ligament
*know alnar ligaments too
Disorders of the joints:
arthritis
-inflammation of a joint
bursitis
-inflammation of the bursa
bunion
-bony bump on base of toe
dislocations
-ends of bone out of position
Describe osteoarthritis:
common, usually develops with age
infection, injury, metabolic disorder
can be damaging over time
Rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disorder
no cure
goal of treatment is to lessen symptoms (low impact exercise and anti-inflammatory meds)
5 functions of the muscular system:
-movement
-stability (posture and tension)
-control of openings
-heat production (skeletal)
-glycemic control (Muscles absorb and store glucose which helps regulate blood sugar concentration)-
5 functional characteristics of muscles
excitability
conductivity
contractiblity
extensibility
elasticity
Excitability:
the ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Conductivity:
the ability to receive a stimulus and transmit a wave of excitation (electrochemical activity)
Contractility:
the ability to shorten forceably when stimulated; exerts a pull
Extensibility:
the ability to be stretched or extended without being damaged; can still be contracted while in full stretch
Elasticity:
the ability to bounce back to original length
What are muscles made of?
proteins
Muscles function to convert ______ energy into ________ force.
Chemical; mechanical
The chemical energy muscles use to function is obtained from _____ and _________.
ATP; creatine phosphate
What is a single skeletal muscle encased by?
connective tissue (epimysium)
What is inside connective tissue?
muscle, fascicles, muscle fibers (muscle cells)
What 4 things are included in the muscular system?
muscle tissue, connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves