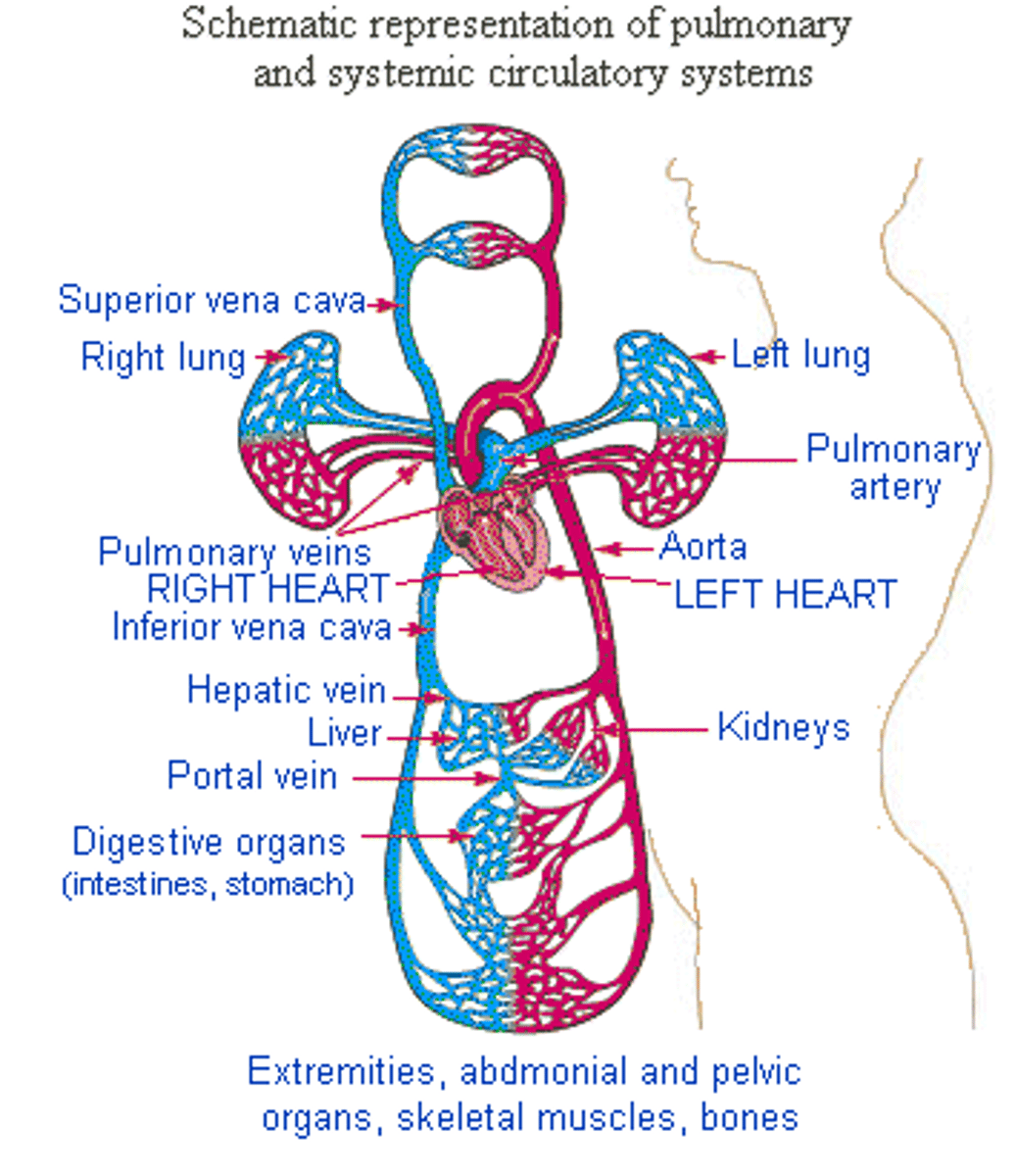
The Heart and blood vessels
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the pericardium?
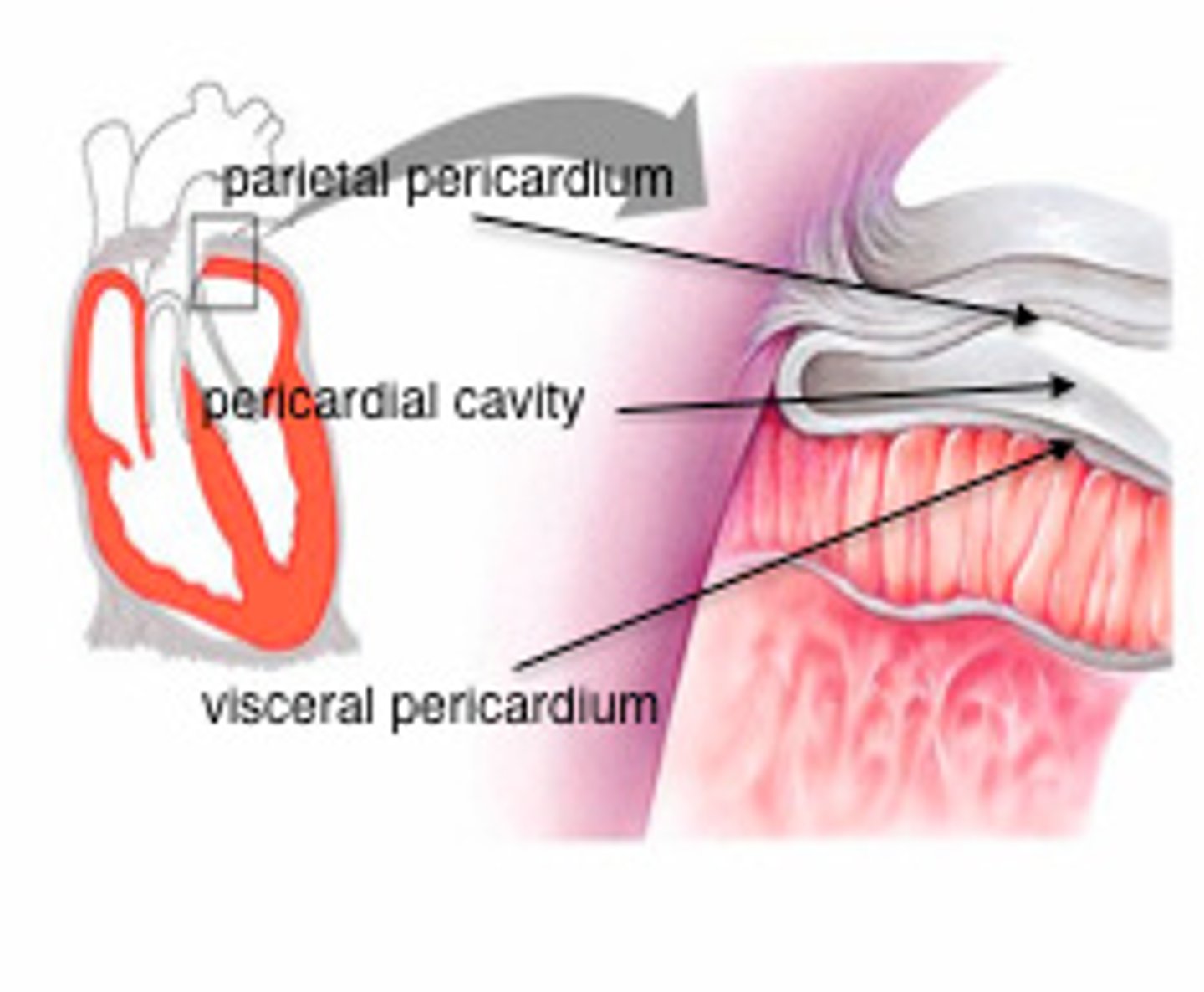
The pericardium is a serous membrane that lines the pericardial cavity, a double walled sac.
Functions of the pericardium.
-Reduces friction
-Keeps the heart contained in the chest cavity.
-Prevents the heart from overexpanding when blood -volume increases.
-Limits heart motion
Name the two components/divisions of the pericardium
1. visceral pericardium aka epicardium (closest to the heart)
2. parietal pericardium ( lines the inner surface of the pericardial sac.
What is the name and function of the fluid between the two pericardium layers?
Serous fluid acts as a lubricant; and reduces friction between the opposing layers as the heart beats.
What is the function of the auricles?
also known as left and right atrial appendages. Functional the auricles serve as reservoirs for extra volume within the atrium chambers.
What is the function of the atria?
The atria receive blood returning to the heart from other areas of the body.
R atrium: receives deoxygenated blood returning to the heart from the superior and inferior venae cavae.
L atrium: receives oxygenated blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary veins.
What is the function of the superior and inferior vena cava?
The superior vena cava returns de-oxygenated blood from the head, neck, arm and chest regions of the body to the right atrium.
The inferior vena cava returns de-oxygenated blood from the lower body regions (legs, back, abdomen and pelvis) to the right atrium.
Which structure do the venae cavae open into?.
right atrium
What type of blood does the aorta carry?
oxygenated blood entering the systemic circulation.
What is the function of the pulmonary arteries?
Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the left and right lungs.
What is the function of the pulmonary veins?
Carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium so it can be transferred to the aorta
Where is the coronary sinus located and what is its function?
located in the right atrium; runs transversely in the groove between the left atrium and left ventricle, medial to the inferior vena cava opening.
Function: deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle itself drains into the right atrium via the coronary sinus.
Where are the atrioventricular (AV) valves found and what is their function?
Located between the atria and the ventricles. Function is to prevent backflow of blood into the atria.
What is the function of the chordae tendinae?
1- bring ventricular walls closer together during contraction preventing backflow
2- pull the semilunar valves open to allow ventricular ejection.
3- pull the AV Valves open during atriole systole.
4- prevent balloning of AV valves laflets back into the atria during ventricular systole,and to prevent AV valvular regurgtion.
Why is there a semilunar valve (pulmonary semilunar valve) at the base of the pulmonary trunk?
A semilunar valve is found at the base of the pulmonary trunk. This semilunar valve prevents blood from flowing back into the ventricles.
Name the structure that functionally divides the heart into left and right
Interatrial septum separates the left and right atria.
Interventricular septum separates the left and right ventricles.
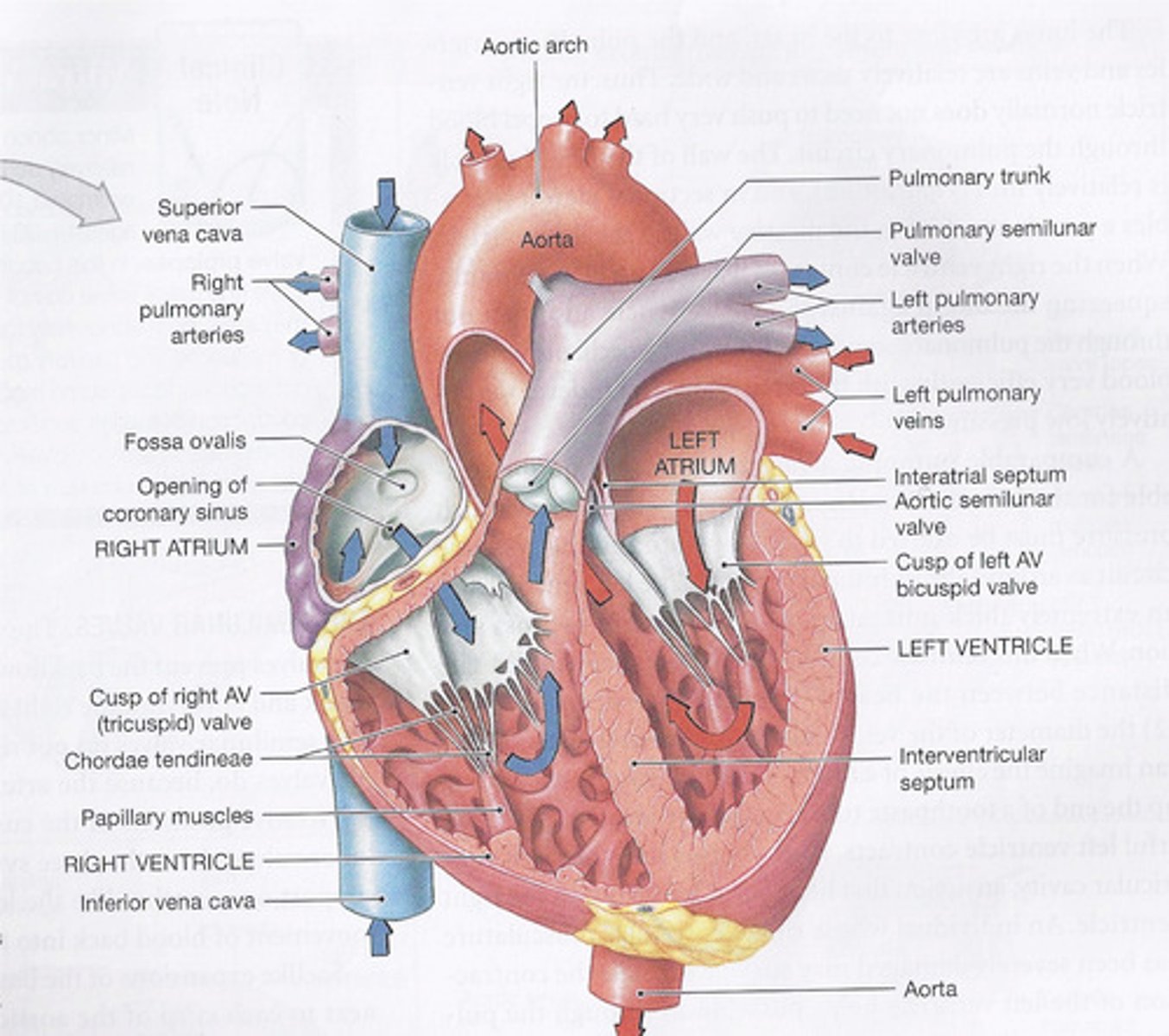
Name, in the correct order, all the structures that blood flows through on its journey from the superior and inferior venae cavae to the aorta.
deoxygenated blood at the superior and inferior vena cava enters in the R atrium also venous blood from the heart muscle itself enters the R atrium through the coronary sinus; goes through the tricuspid (R AtrioVentricular) valve; enters the R ventricle; pulmonary semilunar valve; L & R pulmonary arteries to the L&R lungs; oxygenated blood travels through pulmonary veins; enters the L atrium; bicuspid (L AV) valve; L ventricle; aortic semilunar valve; aorta.
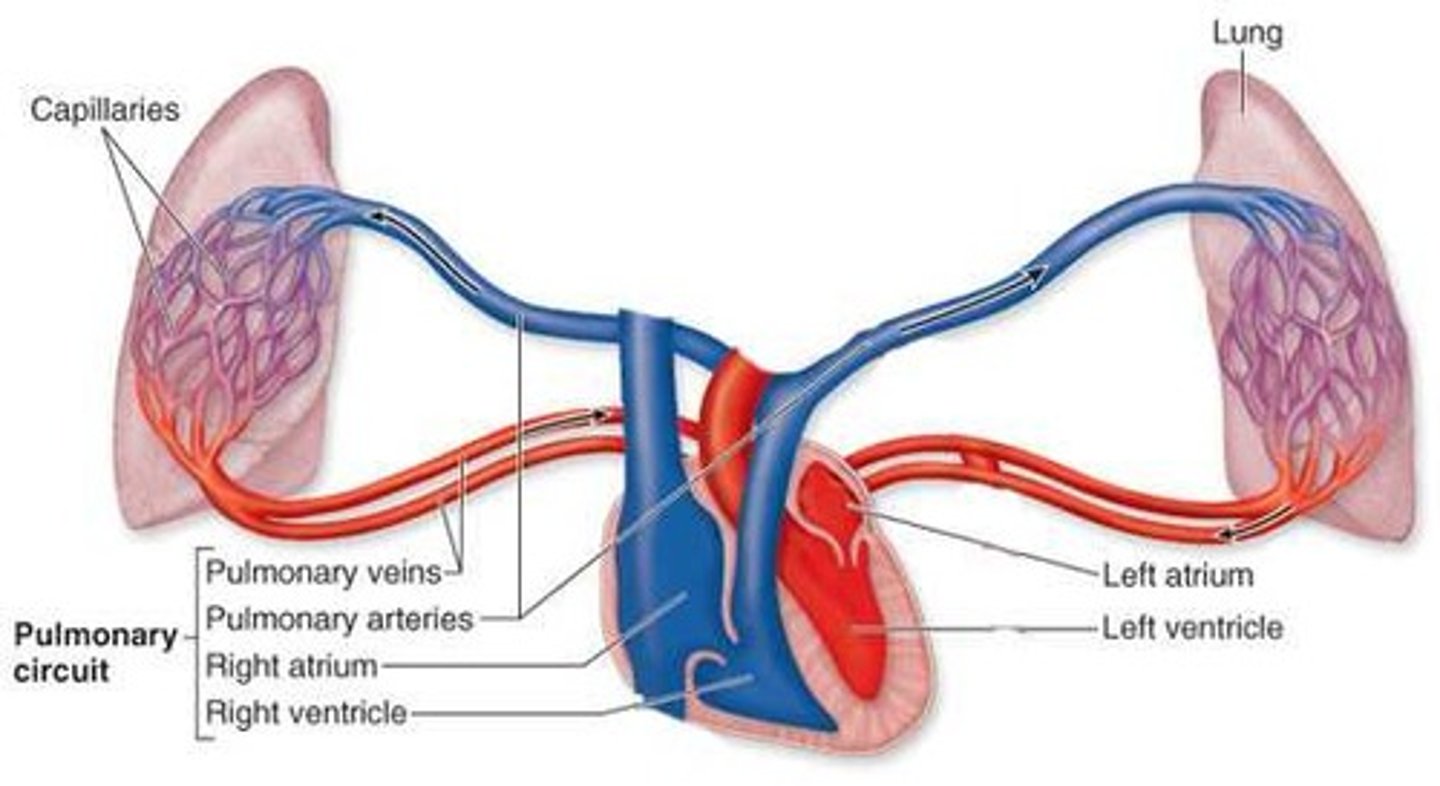
Pulmonary circulation
carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Coronary circulation
The left and the right coronary arteries arise from the base of the aorta and encircle the heart. Branches of these arteries supply the heart with oxygen and nutrients whilst the cardiac veins drain the venous blood into the coronary sinus which empties into the right atrium.
Systemic circulation
takes blood to the whole body and returns to the heart through the inferior and superior vena cava.
Why are the walls of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk/arteries so thick compared to the venae cavae?
Arteries have thicker epithelium/muscular/elastic walls compared to veins, because they have to cope with a much greater pressure. The heart needs to pump blood at high pressures to ensure that the blood reaches all the cells of the body, from the brain to the toes. Thicker walls allow the arteries to cope with the pressure, instead of rupturing.
What is the artery in the interventricular sulcus called?
interventicular artery; supplies oxygenated blood to the heart.
What is the function of the coronary sinus?
Coronary sinus returns deoxygenated blood from the myocardium back to the r atrium.
What is the fossa ovalis?
The fossa ovals is located between the two atria in the interatrial septum and is an embryonic remnant of the foramen ovale.
Why is the left ventricle wall thicker than the right ventricle wall?
The left ventricle is more muscular than the right ventricle because it pumps the blood at a higher pressure.
The left ventricle pumps blood at a higher pressure because it has a further distance to travel, blood from the left ventricle goes to all areas of the body. The right ventricle only has to pump blood to the lungs which is a much shorter distance, therefore less pressure is required.
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
Function of the coronary arteries is to deliver oxygenated blood to the myocardium.
Why do the coronary arteries arise from the base of the aorta and not from the base of the pulmonary trunk?
purpose of the coronary artery is to supply oxygenated blood to the heart if the arteries raised from the base of the pulmonary trunk they would only have access to deoxygenated blood.
Why does the blood need to bypass the lungs in the foetus?
The lungs in a fetus are not functional - gas exchange is performed via the placenta and the mother excretes the waste.
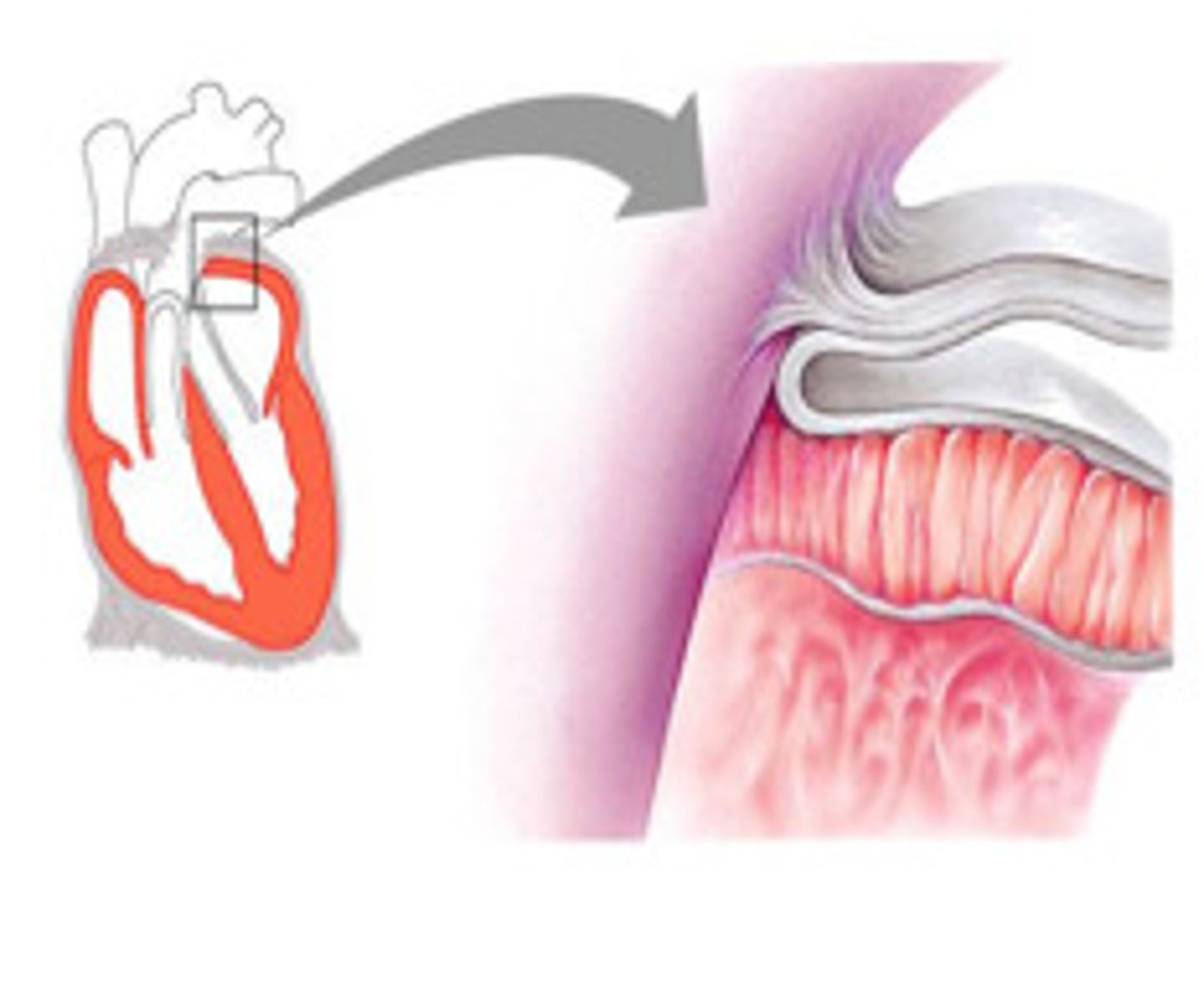
pericardium question
identify the pericardium cavity, parietal pericardium & visceral pericardium
pericardium answer
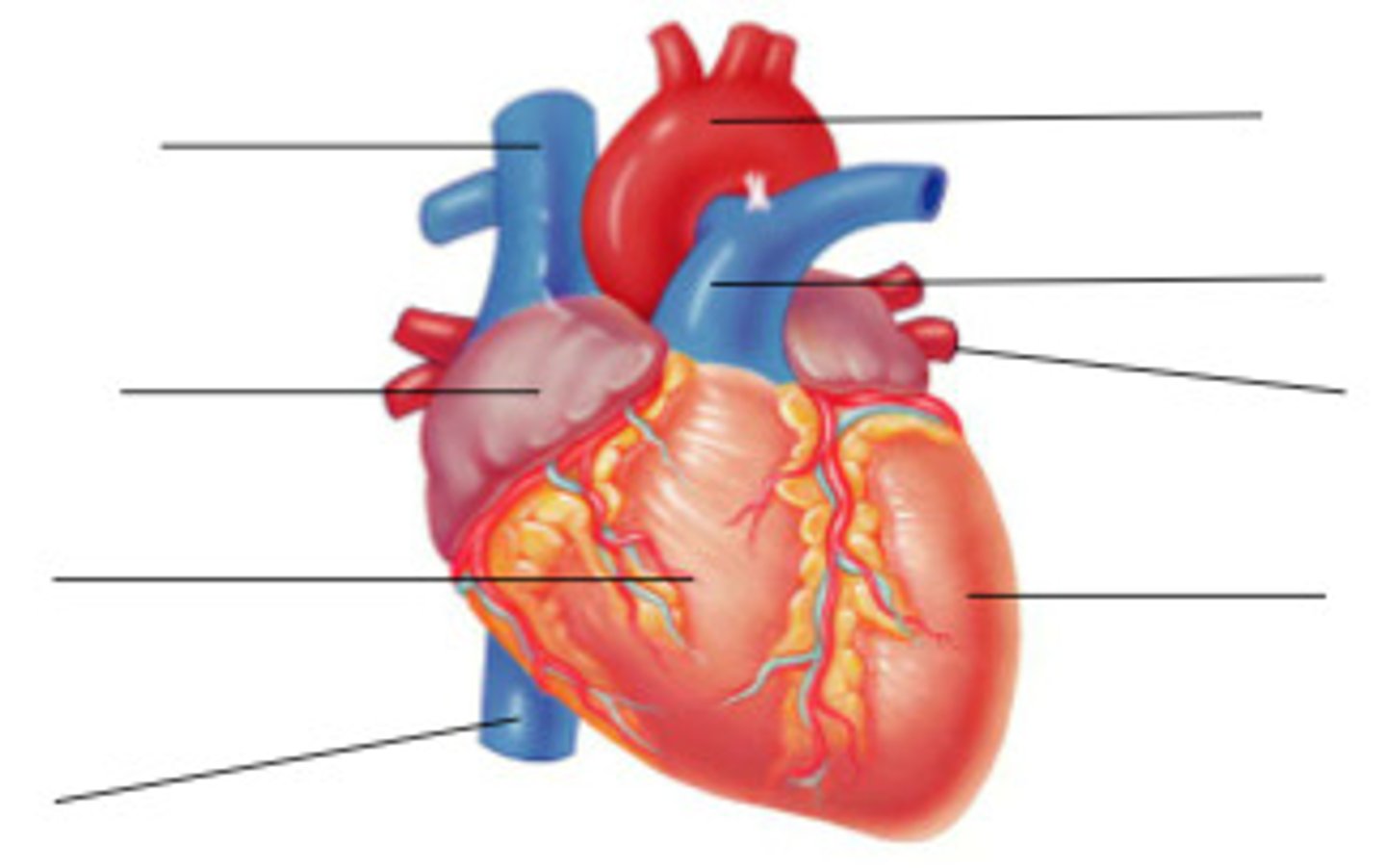
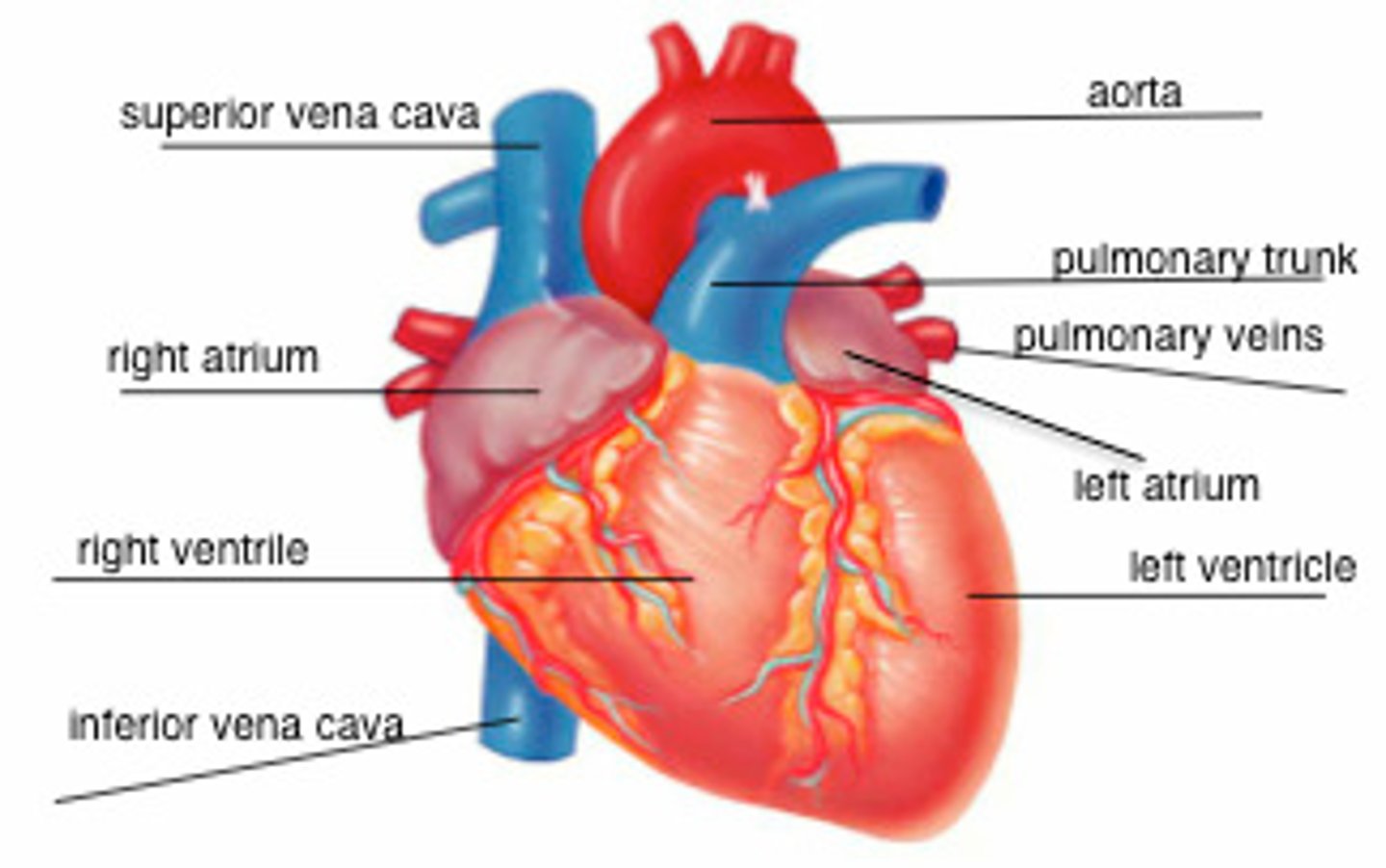
external heart anatomy question
label the diagram
external heart anatomy 2
Sectional anatomy of the heart and path of blood flow.
Pulmonary circulation
Systemic circulation