A3 alkenes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
addition to alkenes
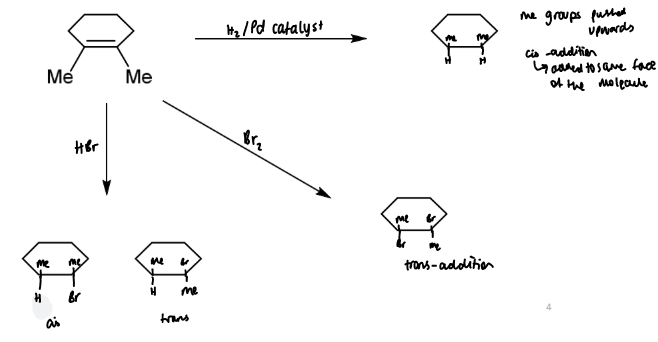
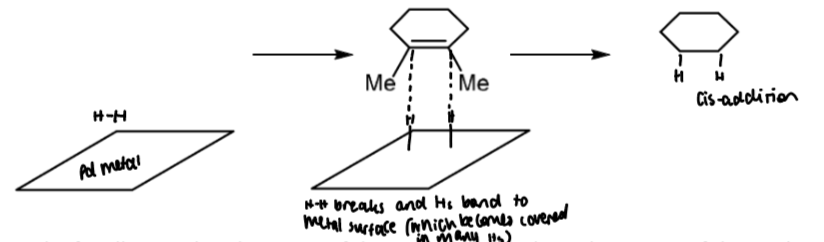
catalytic hydrogenation (alkenes)
hydrogen does not react spontaneously but will react in the presence of a catalyst
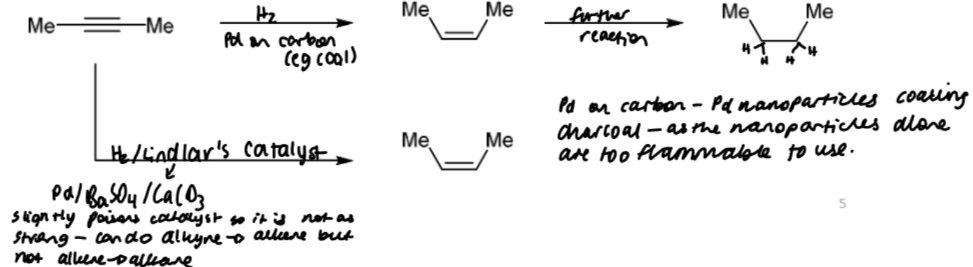
catalytic hydrogenation (alkynes)
similar to alkenes but the extent of the reaction depends on the activity of the catalyst
Lindlar’s catalyst is strong enough to hydrogenate alkynes but not alkenes. this means alkyne → alkene must be the easier step of the process.
bromination of alkenes
bromine is an electrophile (Br-)
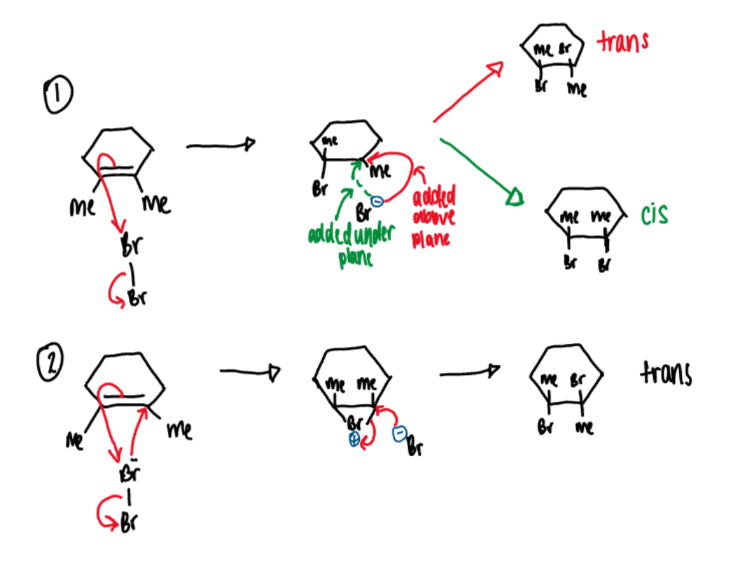
there are two possible mechanisms but only one is correct
mechanism 1 cannot be correct as only the trans isomer is actually observed to form. the only way in which the cis isomer cannot form but the trans can is for a bromonium ion to be formed as in mechanism 2
what is the positive charge on a carbocation
empty p orbital
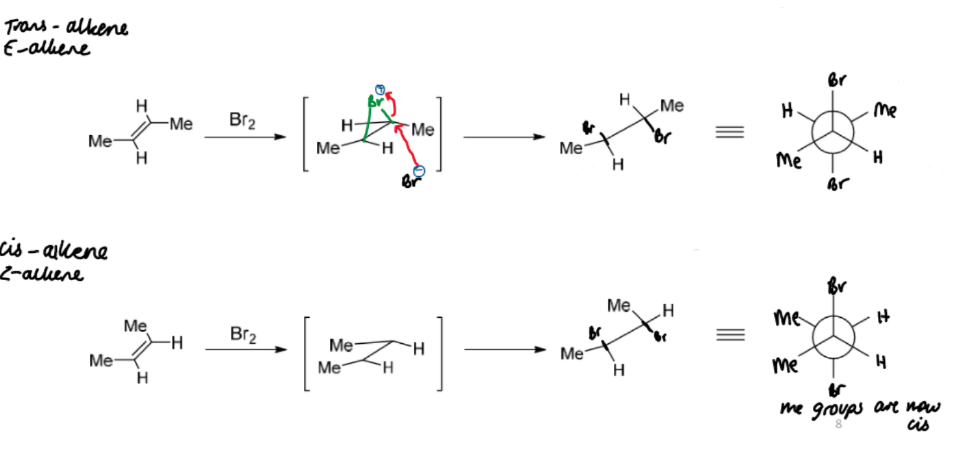
stereochemistry of bromination of alkenes
a single stereoisomer is produced which preserves the stereochemistry of the alkene with respect to the groups other than Br
this means the reaction is stereospecific
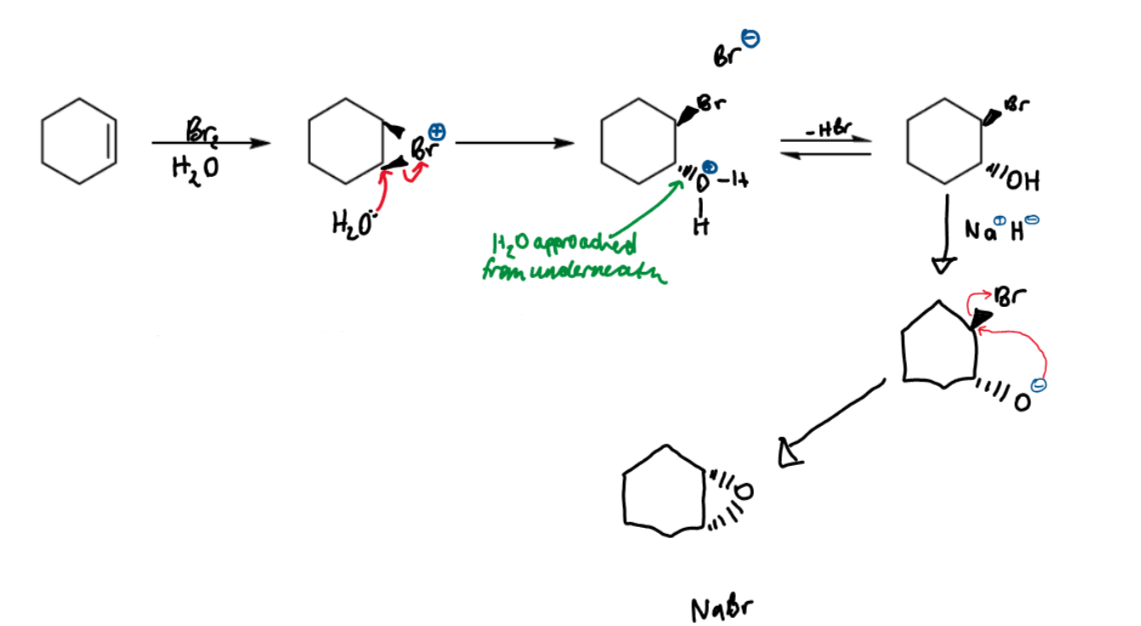
reactions of bromonium ions
bromonium ions can also react with other nucleophiles
reaction with water gives a trans-bromohydrin
bromohydrins provide a synthetic route to epoxides
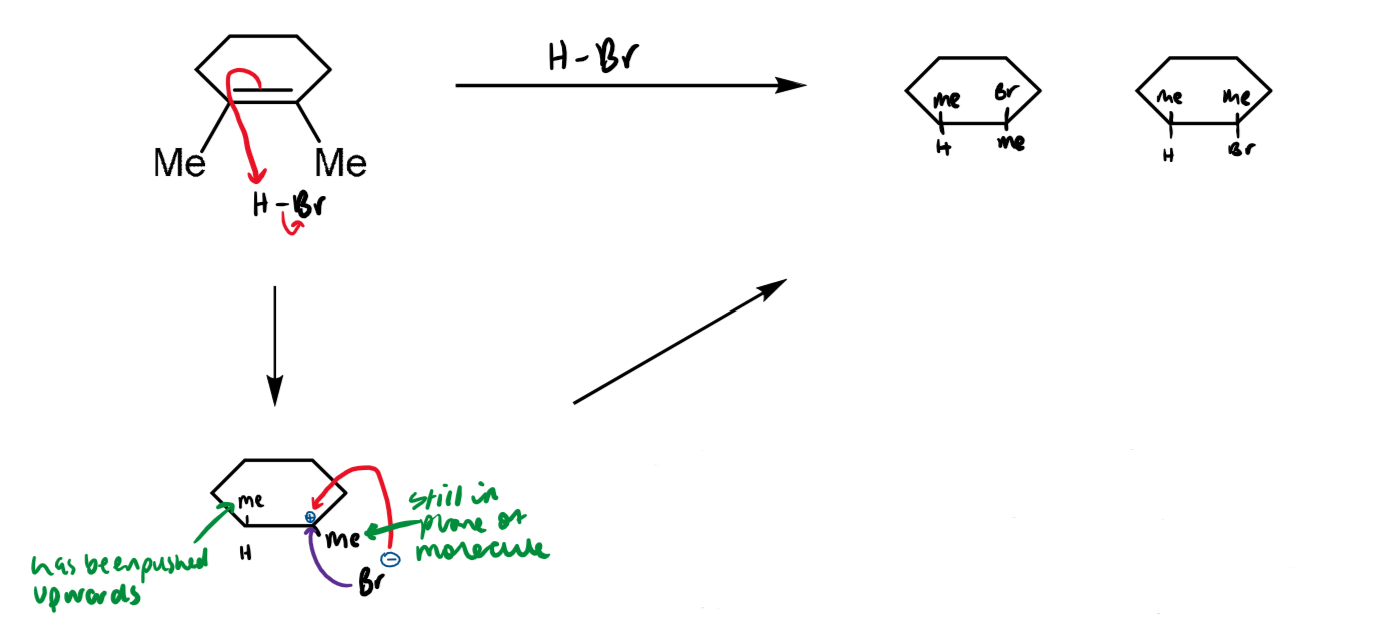
effect of unsymmetrical alkenes
unsymmetrical alkenes give unsymmetrical bromonium ions
the transition state has carbocationic character with the positive charge distributed between the two carbons, one of which can better stabilise the charge due to it the asymmetry. the nucleophile can attack at either carbon but the preferred product is the one in which the bromine ends up on the less substituted carbon.
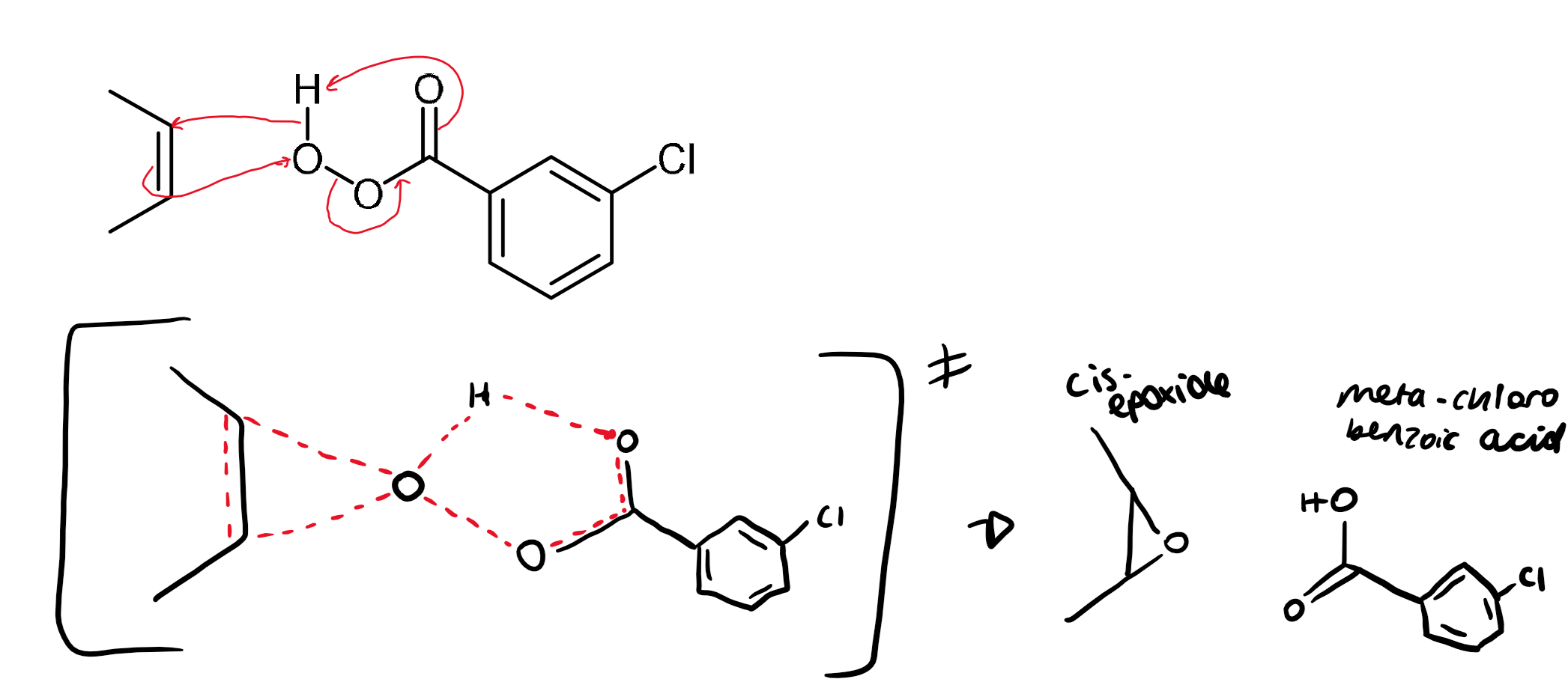
synthesis of epoxides from alkenes
epoxides can be synthesised from peracids which are carboxylic acids with an extra oxygen atom
the oxygen atom is electrophilic with a high energy O-O bond
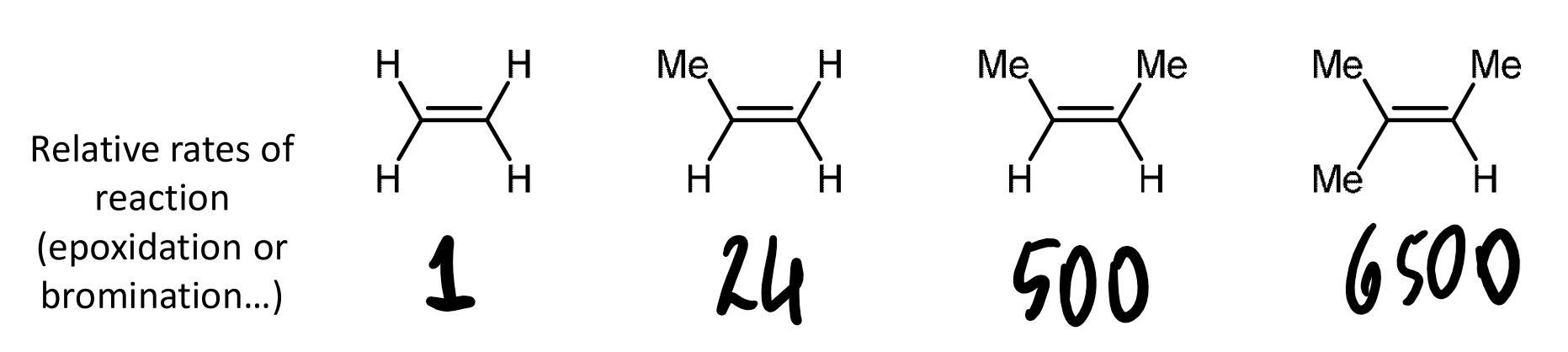
reactivity of alkenes
alkene is the nucleophile in the reaction
alkyl substitution on the alkene increases the rate of addition as a consequence of the inductive effect
the rate enhancements are quite substantial
EDG increases reactivity, EWG decreases it
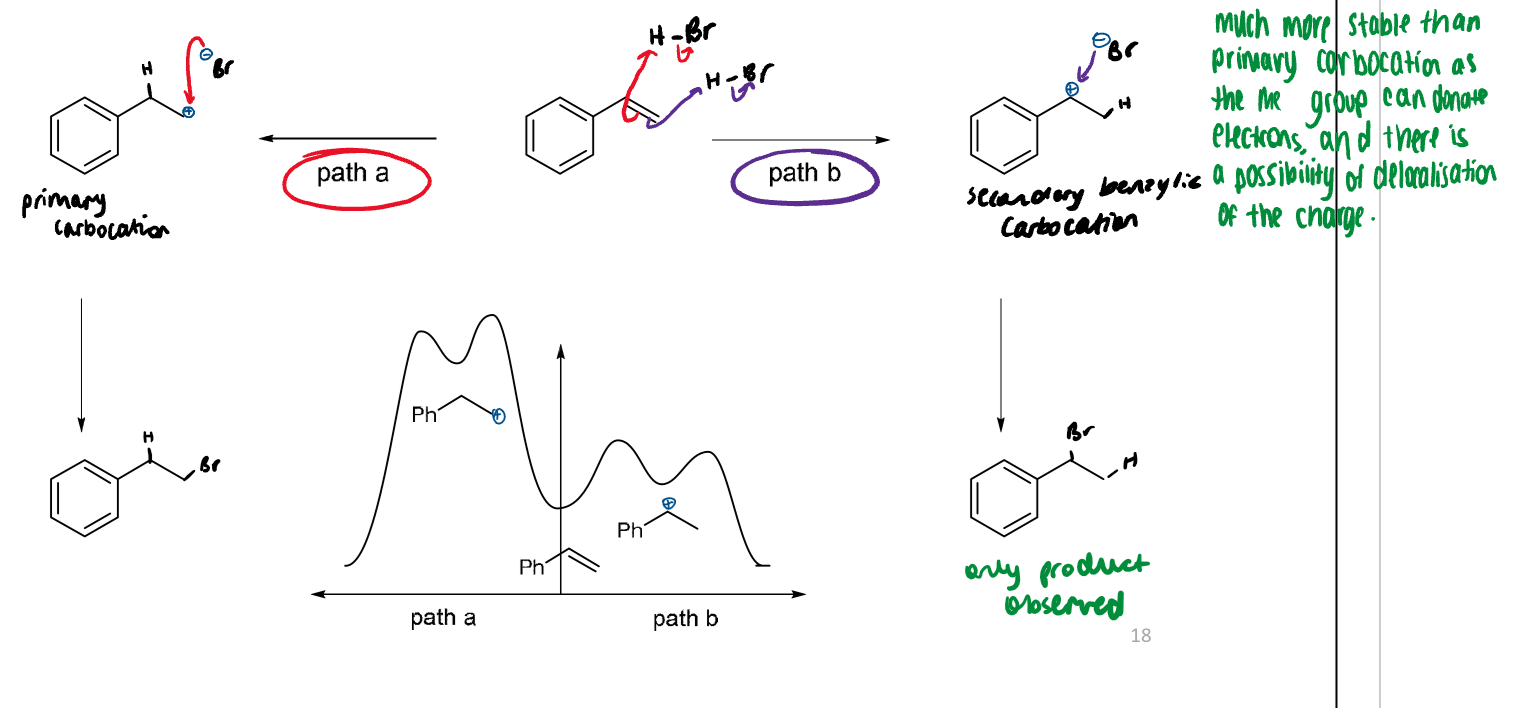
addition of H-X to alkenes
the reaction is not stereospecific, but it might be stereoselective so have some preference
if the alkene is not symmetrical this reaction is also regioselective (preference for a site of reaction) - see Markinov’s rule
markinov’s rule
addition of H-X to an unsymmetical alkene gives the more highly substituted product
this occurs because the most stable cation intermediate (lowest energy transition state) gives the most substituted product
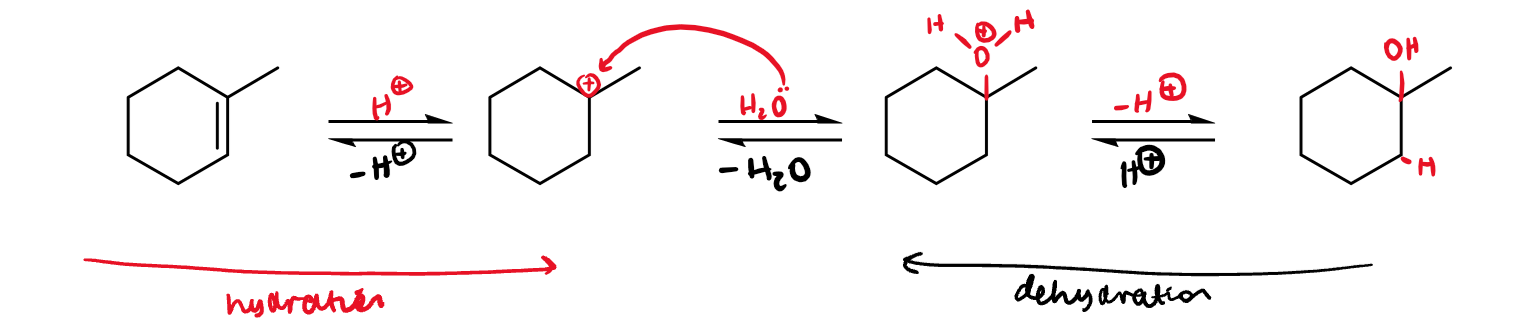
hydration of alkenes
addition of water in H-OH format
dehydration of tertiary alcohol is favoured entropically
primary/secondary (especially primary) require strong acid catalysts and heat to dehydrate, whereas tertiary dehydrate easily with mild acid catalysts
this is because tertiary carbocations are significantly more stable (in addition to entropic favourability)
tertiary alcohols also have no competing reactions, where other classes have E2 and oxidation to carbonyls
it can be difficult to hydrate an alkene directly
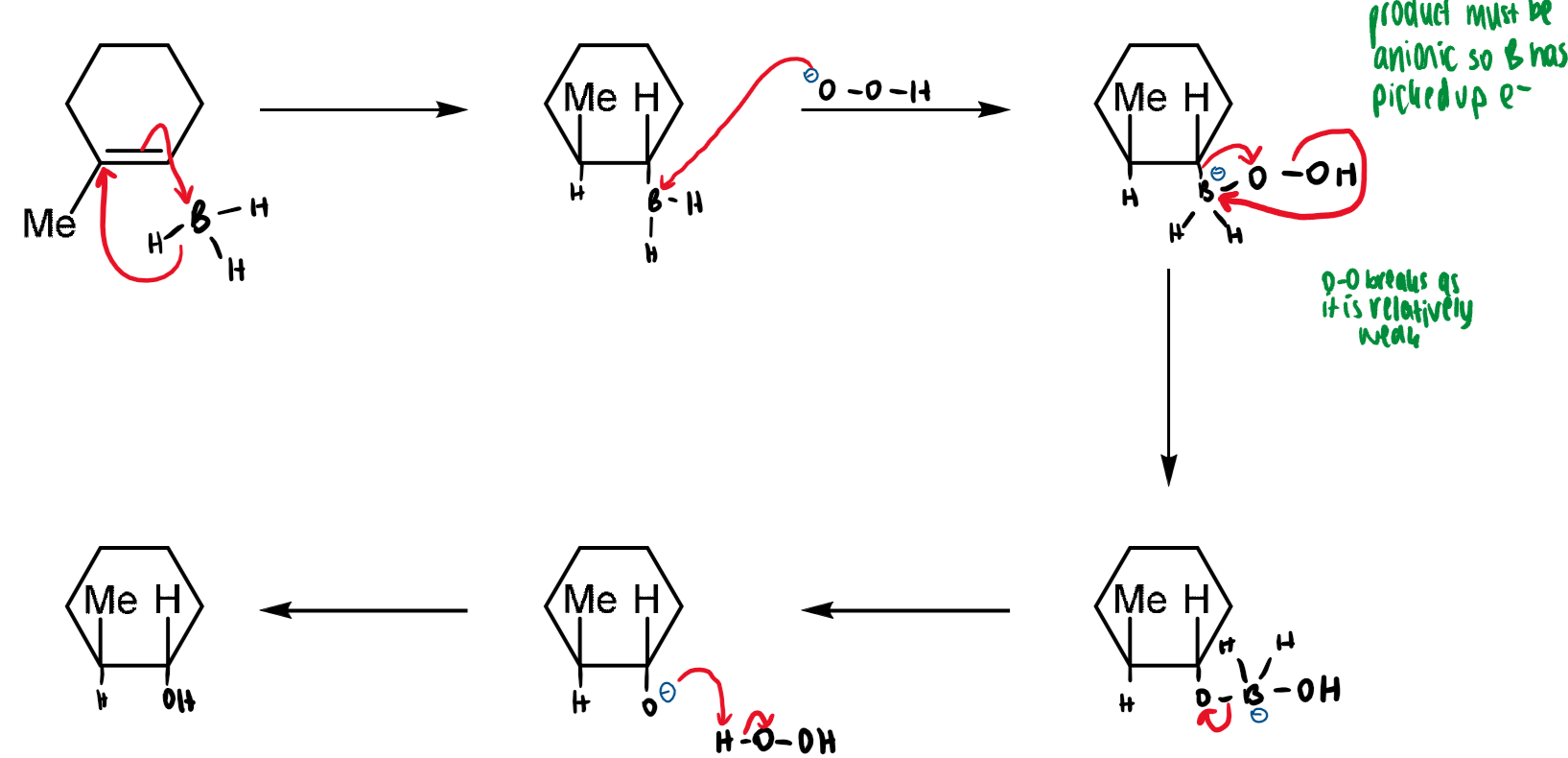
hydroboration
anti-Markinov addition to alkenes
this does not obey Markinov’s rule as there is no carbocation intermediate
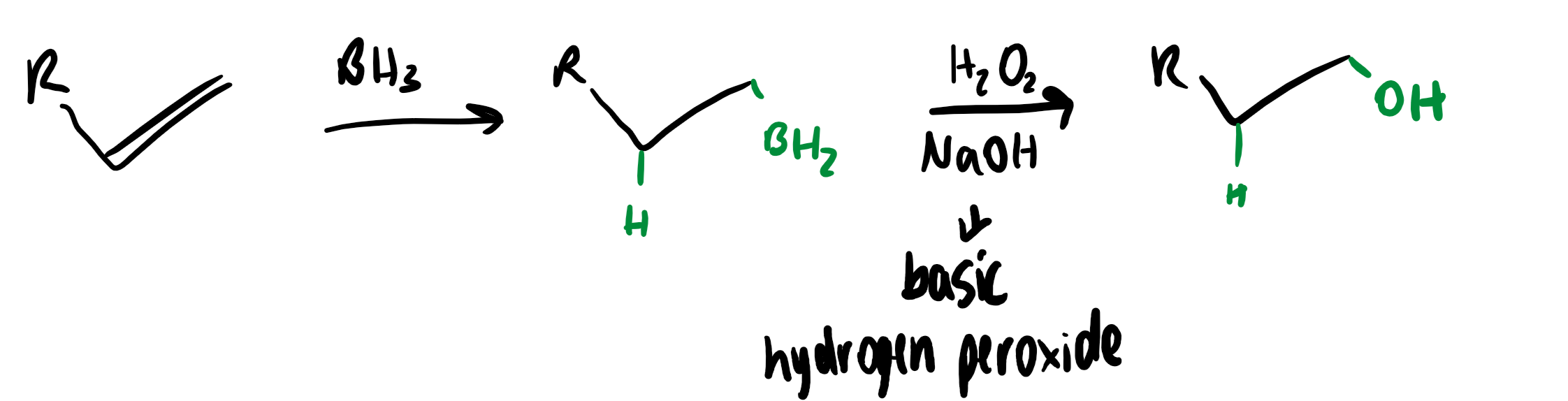
regio- and stereochemistry of hydroboration
hydroboration is a regioselective stereospecific cis-addition of boron and hydrgoen
boron attaches itself to the least hindered end of the alkene
alkyl migration is stereospecific - oxygen remains on the same face as boron