BPK 241 Lecture 10
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms

Upper Arm Bones
Humerus
Shaft (with bicipital groove)
Head, neck & tubercles
Condyles & epicondyles
Coranoid fossa (anterior)
Olecranon fossa (posterior)
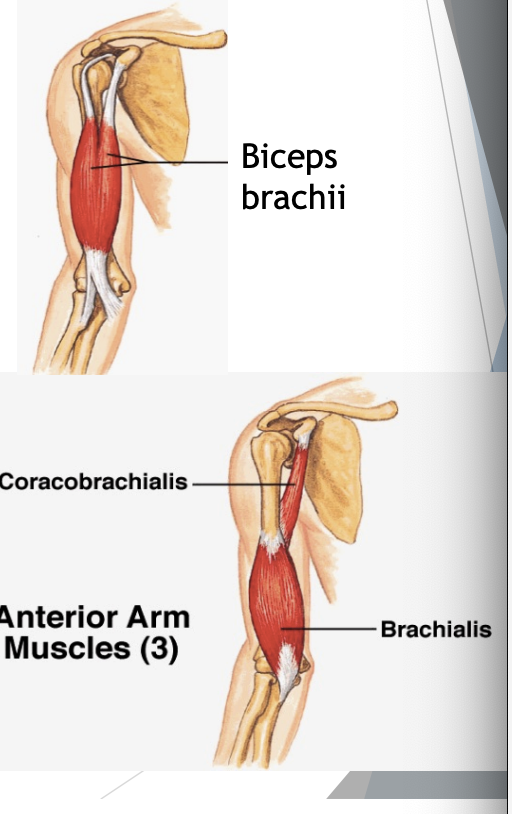
Muscles of the anterior compartment
Biceps brachii
O = supraglenoid tubercle, coracoid
I = radial tuberosity, forearm fascia
F = forearm flexion at elbow, supination (supinator magnus), assists shoulder flexion
Brachialis (starts at ½ of shaft)
O = anterior surface of humerus
I = coracoid of ulna
F = flexion of forearm at elbow
Coracobrachialis
F = assists flexion of arm at shoulder
All three innervated by muscolocataneus nerve
How many attachments of bicep brachii to humerus?
None
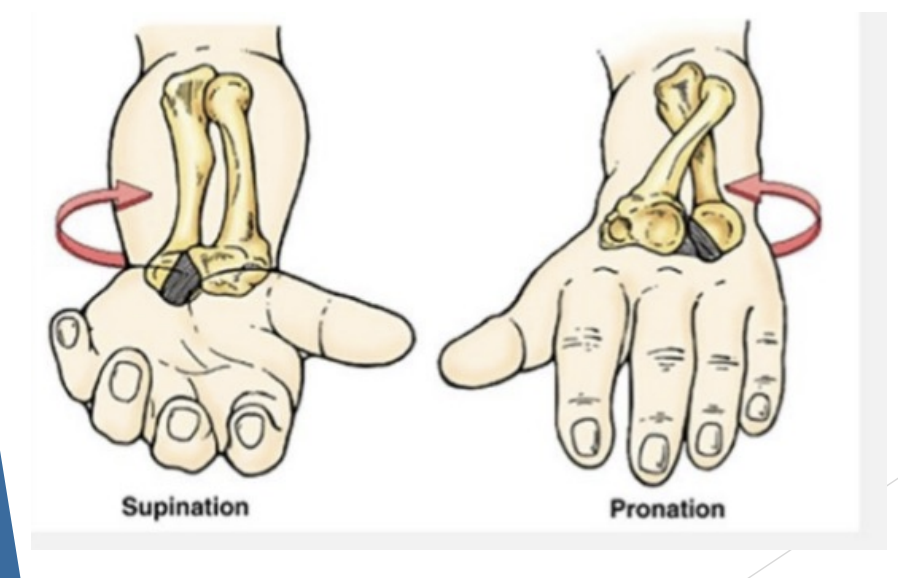
Movements
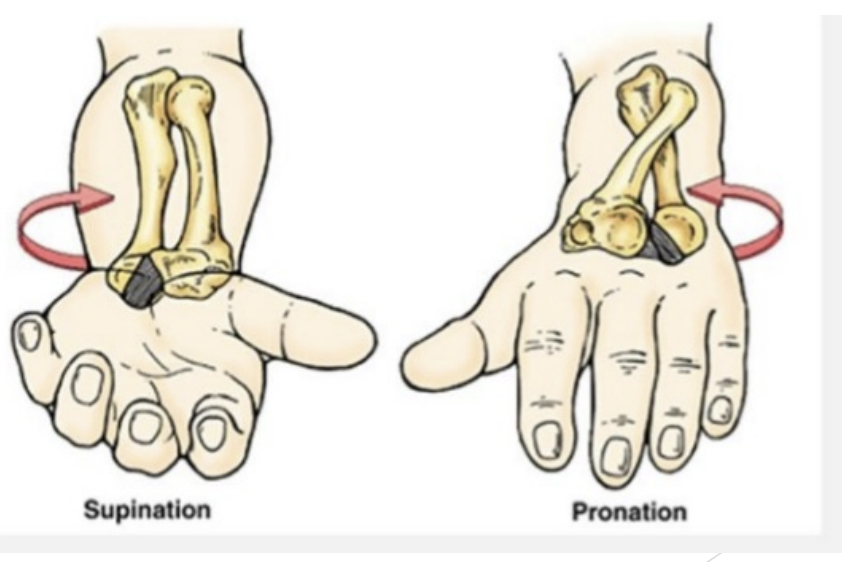
Forearm pronation & supination
Ulna is locked, doesn’t move
Radius rotate around ulna allowing pronation
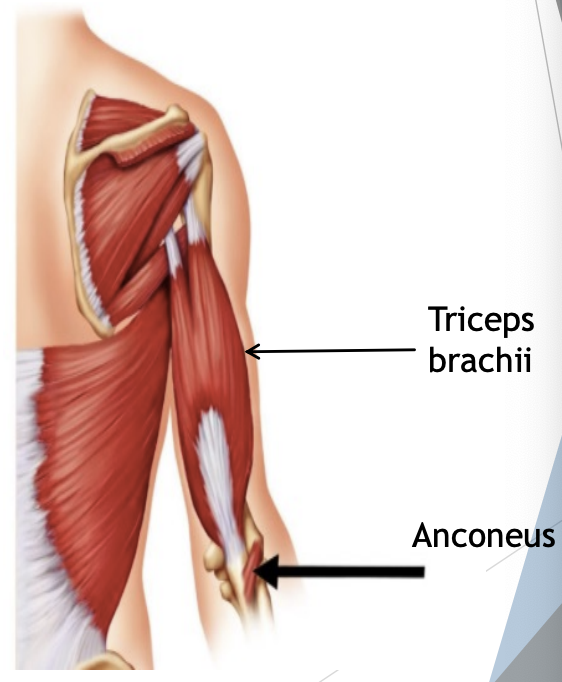
Posterior Compartment muscles
Triceps brachii
O = infraglenoid tubercle, upper lateral & lower medial halves of the posterior shaft of humerus
I = olecranon of ulna
F = extension of forearm at elbow
Anconeus
O = lateral epicondyle
I = olecranon of ulna
F = assists triceps brachii
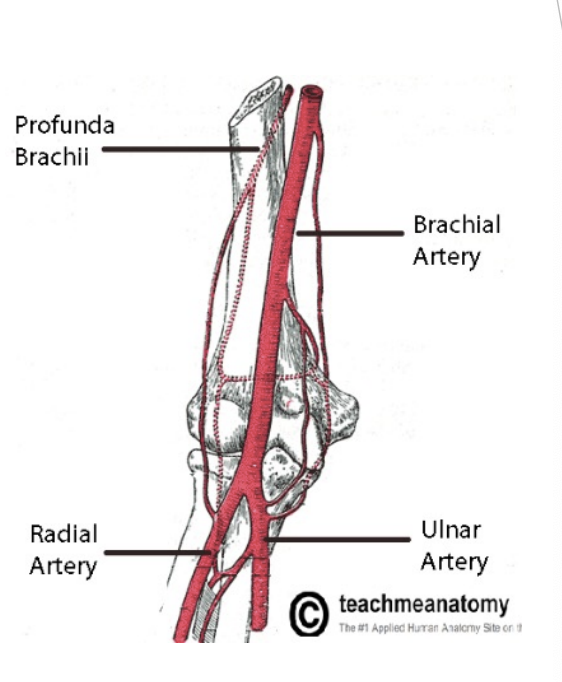
Arteries
Brachial artery
Anteromedial in upper arm
Moves laterally and anteriorly at elbow to form ulnar and radial artery
Profunda artery
Stops to exist beyond the elbow
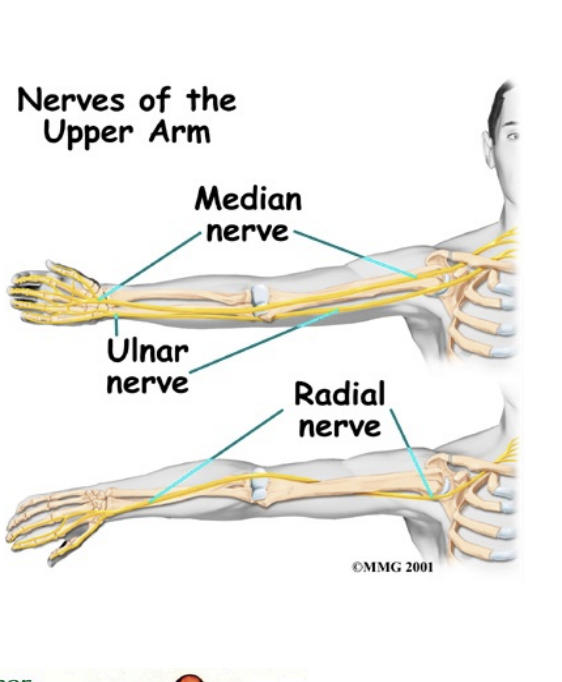
Nerves
Muscocutaneous
Median
Ulnar
Radial
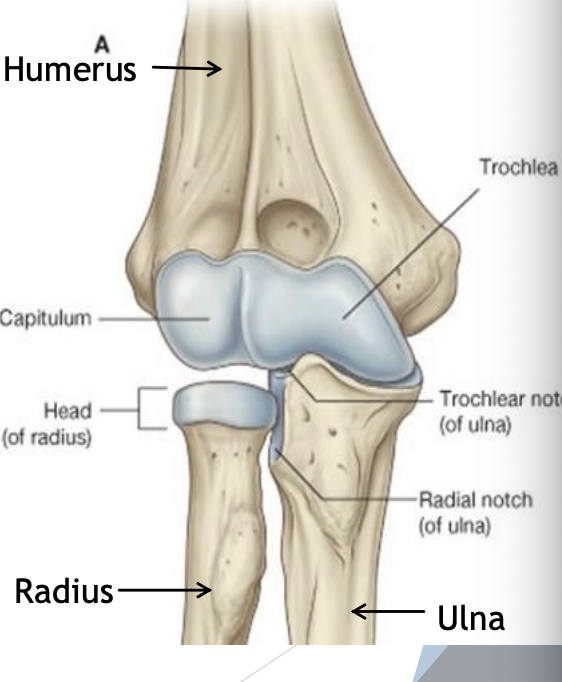
Elbow Bones
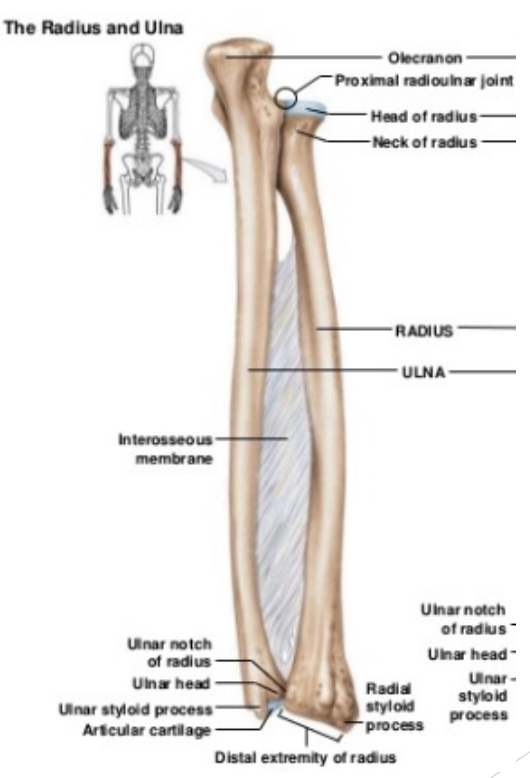
Radius (lateral forearm bone)
Head
Articulates with capitulum
Articulates with radial notch of ulna
Distal articulation with ulna
Interosseous membrane between shafts of radius and ulna
Ulna (medial forearm bone)
Trochlear notch (ulna) articulates with trochlea (humerus)
Olecranon process (posterior)
Coronoid process (anterior)
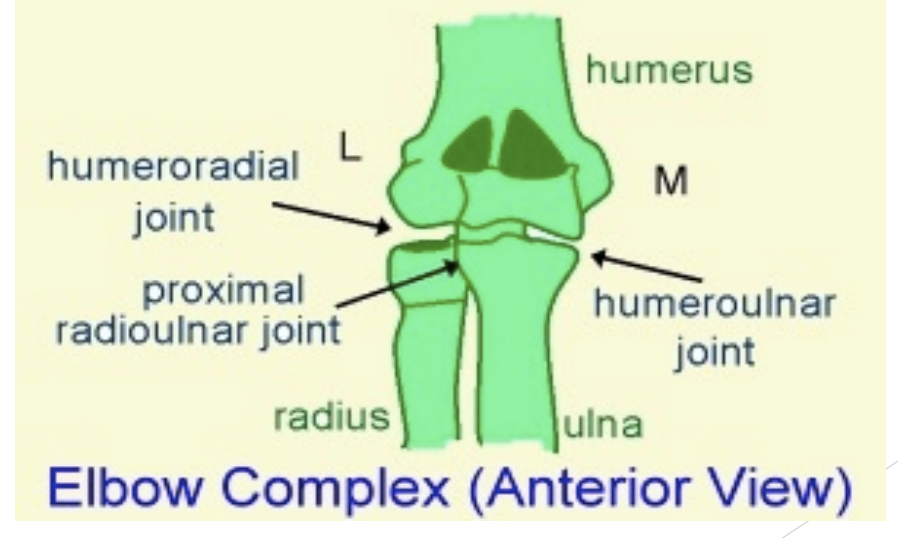
Joint type
Synovial and Hinge
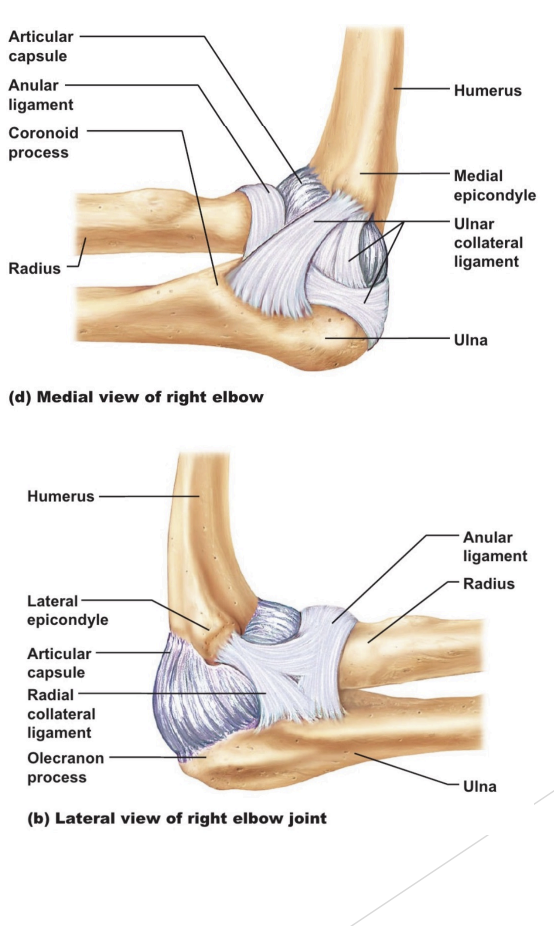
Ligaments
Capsular
Medial (ulnar) collateral - prevent valgus movement
Lateral (radial) collateral - prevent varus movement
Annular ligament
wraps head of radius, allows radius to rotate, supinate + pronate
Moves across sagittal plane

Elbow Movements
Flexion & extension
Note: pronation & supination occur at radioulnar joints
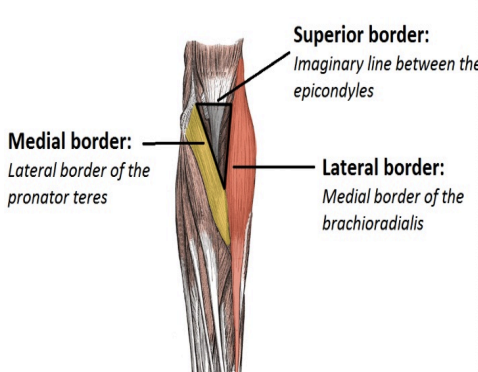
Cubital fossa
Anteriorly; inverted triangle
Contains median and radial nerve, brachial artery and its derivatives, and tendon of biceps brachii
Radioulnar Joints
Joint type
Synovial, pivot
Articulations
Proximal
Radial head and radial notch of ulna
Annular ligament
Distal
Ulnar styloid & ulnar notch of radius
Fibrocartilage disc, capsule, capsular ligaments
Notes: interosseous membrane
Radioulnar Joint Movements
Forearm pronation & supination
Radioulnar Joints: Active Muscles
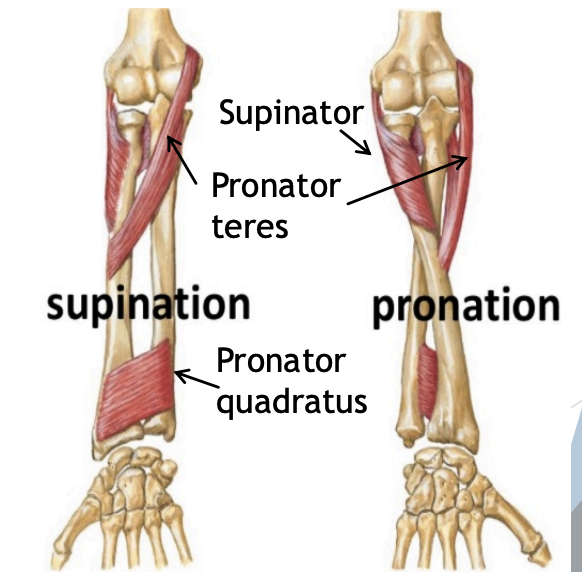
Supination
Bicep brachii (“supinator magnus”)
Supinator
Pulls elbow
Pronation
Pronator teres (proximal)
Pronator quadratus (distal)
Pulls forearm
From pronated or supinated to mid-range =
Brachioradialis - helps with mid-range supinate + pronate
Forearm Anterior Compartment
Superficial
Pronator Teres
Flexor Carpi Radialis (FCR)
Palmaris Longus
Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU)
Intermediate
Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS)
Deep
Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
Flexor pollicis longus (FPL)
Pronator quadratus
Pronator Teres
Rotate palm + pronate forearm
Innervated by median nerve
FCR
Metacarpals - attached to 2nd metacarpal
Innervated by median nerve
Palmaris Longus
Small muscle, 20% doesn’t have this
Innervated by median nerve
FCU
Attached to 5th metacarpal
Innervated by ulnar nerve
FDS
Send tendon to each finger, attaches to middle phalanges - flex wrist
Innervated by median nerve
FDP
Distal Phalanges
Half innervated by median nerve
Half innervated by ulnar nerve
FPL
Thumb
Innervated by median nerve
Pronator Quadratus
Distal forearm into pronation
Innervated by median nerve
Forearm Posterior Compartment
Superficial
Brachioradialis
Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL)
Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB)
Extensor digitorum (ED)
Extensor digiti minimi (EDM)
Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
Deep
Anconeus
Supinator
Abductor pollicis longus (APL)
Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
Extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
Extensor indicis (EI)
Brachioradialis
Helps with elbow flexion, supination, pronation to mid range
Innervated by radial nerve
ECRL
2nd metacarpal - radial deviation
Innervated by radial nerve
ECRB
3rd Metacarpal
Innervated by radial nerve
ED
Distal phalanges - extends fingers
Innervated by radial nerve
EDM
Pinky extension
Innervated by radial nerve
ECU
5th metacarpal, ulnar deviation, wrist extension
Innervated by radial nerve
Anconeus
Supinator, tricep extension
Innervated by radial nerve
Supinator
Supinates forearm
Innervated by radial nerve
Snuffbox muscles
APL, EPB, EPL
Innervated by radial nerve
EI
index finger
Innervated by radial nerve
Flexion of hand at the wrist
FCR, FCU, FDS, FDP, FPL
Extension of hand at wrist
ECRL, ERB, ECU, ED, EDM, EI, APL, EPB, EPL
Adduction (ulnar deviation) of hand at wrist
FCU, ECU
Abduction (radial deviation) of hand at wrist
FCR, ECRL, ECRB
Circumduction of the hand
Requires flexion, extension, abduction, adduction plus pronation & supination
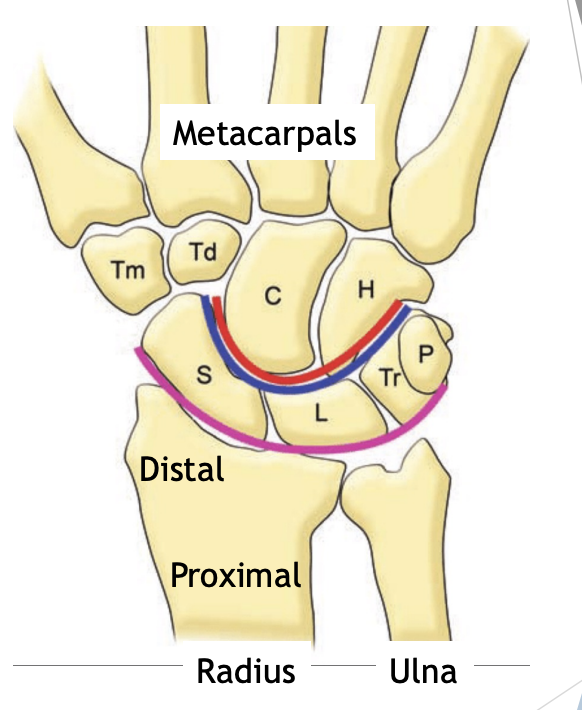
Wrist bones
Radiocarpal joint
Distal radius
Proximal carpal bones
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetal, pisiform
Distal carpal bones
Trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
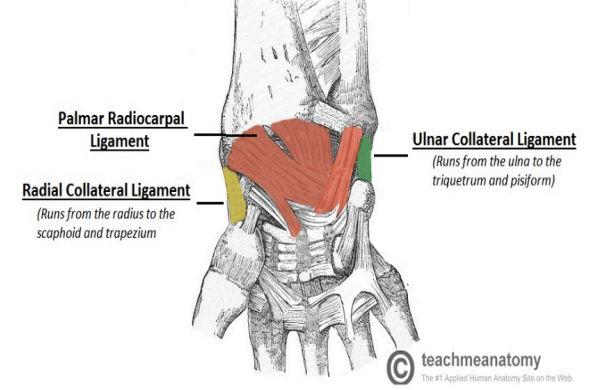
Wrist Ligaments
Capsular (anterior & posterior)
Collateral (medial & lateral)
Intercarpal
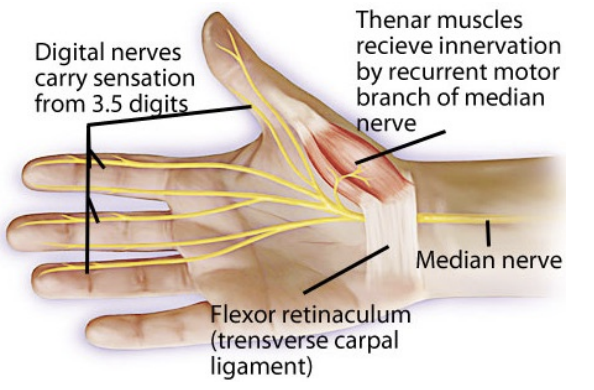
Retinacula
Hold tendon tight, posterior wrist gives support
Extensor
Flexor (N.B., roof of carpal tunnel)
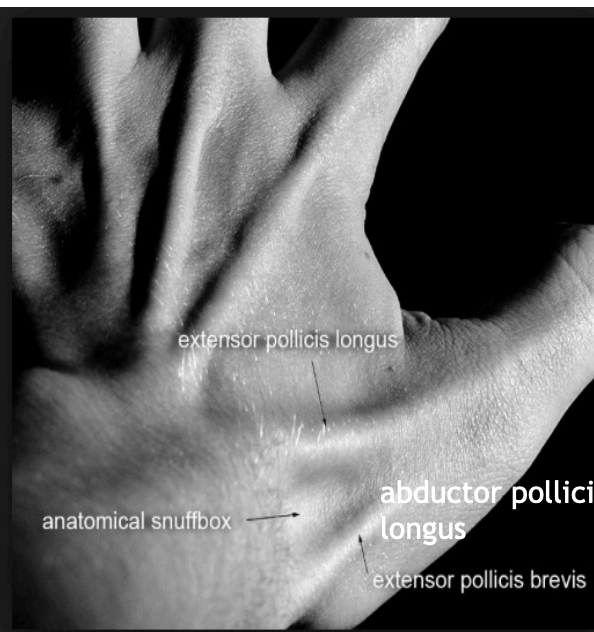
“Anatomical Snuffbox” of the wrist
Anatomy
Medially = Extensor pollicis longus (EPL) tendon
Laterally = Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB, Abductor pollicis longus (APL) tendons
Floor = scaphoid
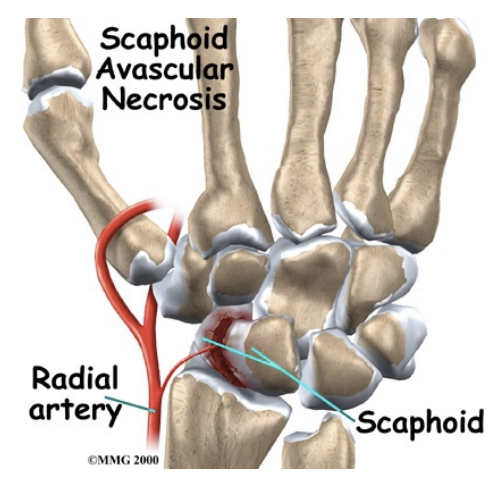
“Anatomical Snuffbox” of the wrist - Significance
Scaphoid bone
Narrow waist (fracture site)
Retrograde blood supply (not great blood supply)
Ischaemic (avascular) necrosis is common complication of untreated scaphoid fracture - degeneration of bone
Scaphoid necessary for full, pain-free wrist function
X-Rays do not show scaphoid fracture at first
Hence, tenderness in snuffbox? Assume fracture?
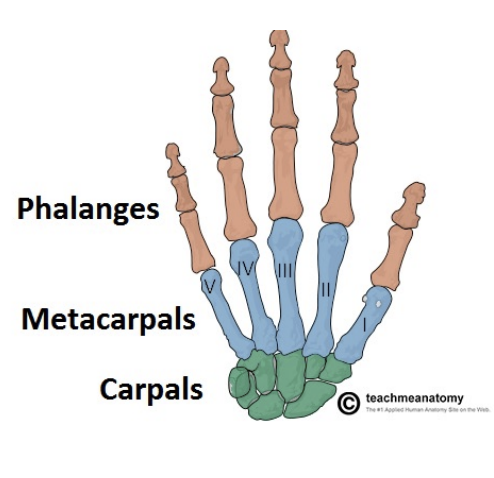
Hand Bones
Metacarpals I (thumb-side)
V (pinky side)
Phalanges (as in toes)
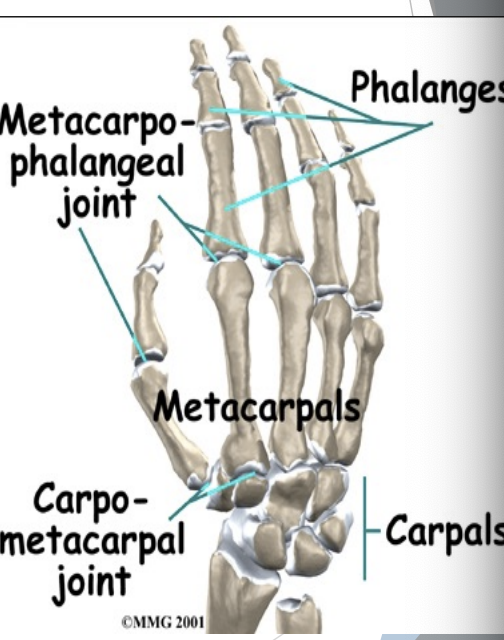
Hand Joints
Carpometacarpal
Metacarpophalangeal (MCP)
Interphalangeal (IP)
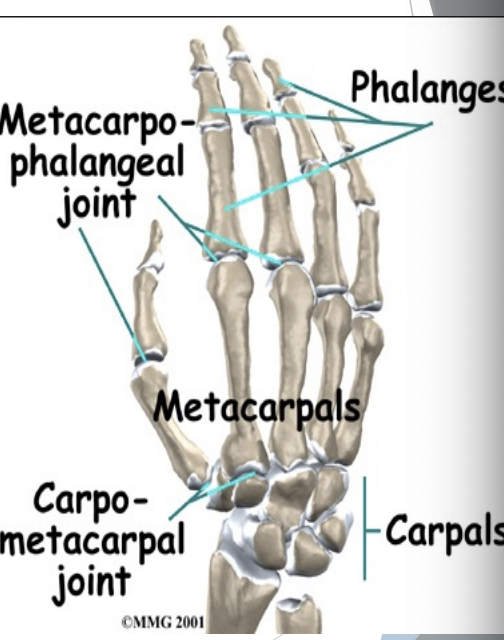
Carpometacarpal
Metacarpal II-V = gliding, minimal movement
1st Metacarpal with trapezium = synovial, saddle joint, flexion/extension, abduction/adduction & circumduction (opposition)
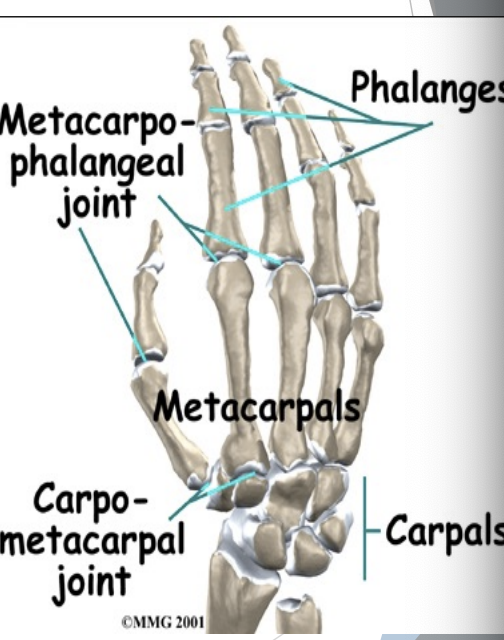
MCP
Primarily flexion/extension
Strong collateral ligaments
Strong flexor & extensor tendons
Some adduction & abduction
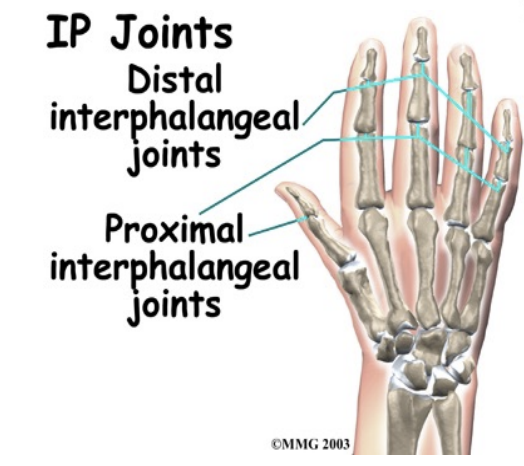
IP
Synovial joints
Flex & extend
Collateral ligaments
Intrinsic muscles of the hand
Thenar (thumb) eminence
Hypothenar (pinky finger) eminence
Dorsal & Palmar interosseous muscles (DABS & PADS)
Lumbricals
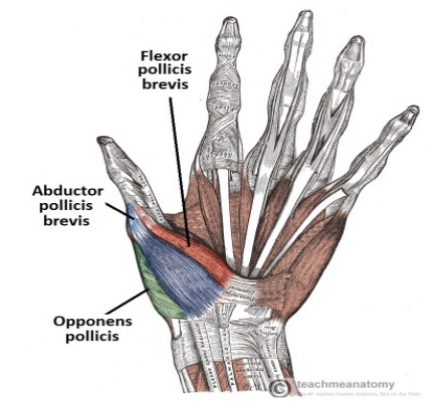
Thenar (thumb) eminence
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis (APB)
Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB)
Innervated by median nerve
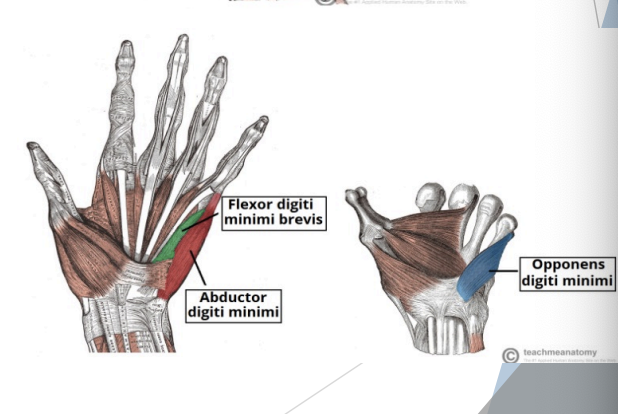
Hypothenar (pinky finger) eminence
Opponens digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi
Innervated by ulnar nerve
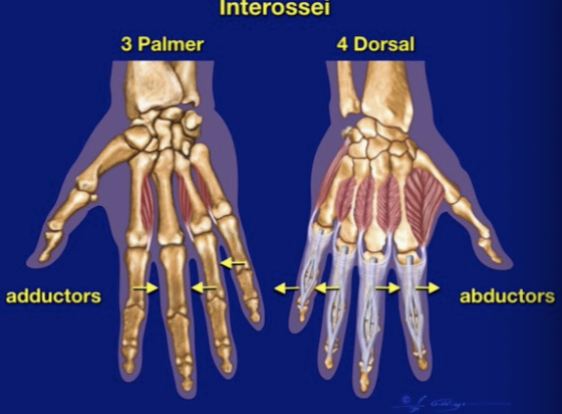
DABS & PADS
Innervated by ulnar nerve
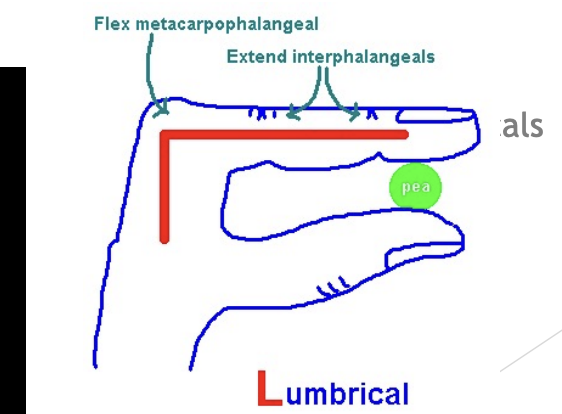
Lumbricals
Innervated by median nerve
Innervated by ulnar nerve
Puppet muscle
Innervation of Hand
All muscles in hand innervated by ULNAR nerve EXCEPT: ½ LOAF by median nerve
Thumb ½ of Lumbricals
Thenar eminence muscles (Opponens pollicis, Abductor pollicis, Flexor pollicis brevis)