Radioactive Waste
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Definition of High Level Wastes
Waste that contains a high level of radioactivity and generates significant amounts of heat through radioactive decay.
It gives off high amounts of radiation for a short time, or low amounts for a long time
Examples of High Level Wastes
Used uranium fuel rods
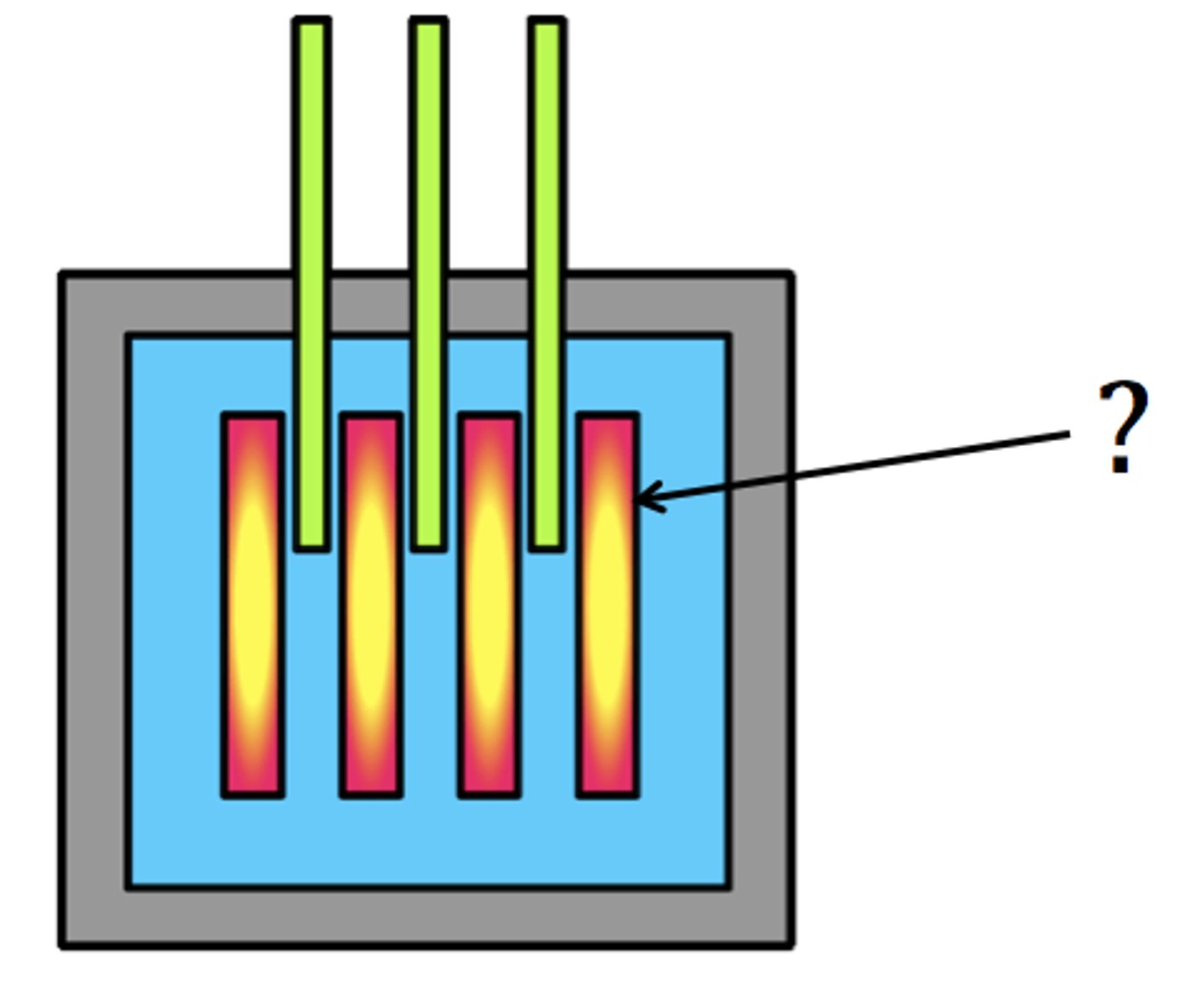
Why are used uranium fuel rods high level waste?
The split nuclei form highly radioactive isotopes
Definition of Intermediate Level Waste
Waste that has higher levels of radioactivity than LLW but does not generate enough heat through radioactive decay to require cooling.
Examples of Intermediate Level Wastes
Metal tubes surrounding the fuel rods that became radioactive in the reactor
Waste from decommissioning nuclear facilities
Definition of Low Level Wastes
Waste with low levels of radioactivity, posing minimal hazard. It generally includes materials contaminated with radioactive material or have become radioactive through exposure to neutron radiation.
Examples of Low Level Wastes
- Contaminated clothing, gloves, and equipment
- Waste solutions from used fuel reprocessing and storage
- Gases released from used fuel during storage and reprocessing

Which level waste is handled using vitrification?
HLW
Which level waste is handled using encapsulation?
ILW
What is vitrification?
A method used to safely store radioactive waste by turning it into a solid, glass-like material.
This process prevents the waste from leaking into the environment in the future.
How does vitrification work?
1) Powdered radioactive waste is mixed with molten glass
2) This is poured into stainless steel containers and then sealed
3) The glass solidifies, encapsulating the waste
4) The steel containers are placed in cylindrical passages inside a concrete building.
5) The passages are ventilated to remove the heat of radioactive decay
Why is vitrification safe?
The glass structure locks in the radioactive particles so they can't dissolve in water or leak out.
Even if the glass shatters, the waste would remain encapsulated in the fragments.
What is encapsulation?
A method to safely store ILW by enclosing it in a solid material, like concrete or metal, to prevent it from leaking or coming into contact with the environment.
How does encapsulation work?
1) Hazardous wastes containing heavy metals (like arsenic, mercury, nickel, chromium residues) or ILW are mixed with a cement slurry
2) The mixture is poured into containers made of an impermeable and unreactive material
3) The solid cement encapsulates the waste, so it is immobilised
Where is HLW and ILW waste stored?
Sellafield, Cumbria, UK

What is the storage method for solid LLW?
Sealing solid LLW in thick polythene bags, inside steel drums, inside steel trucker containers in a concrete lined landfill site
Stored at Drigg (near Sellafield)
What is the storage method for liquid LLW?
Liquid LLW is filtered, undergoes ion exchange, and then discharged
What is the storage method for gaseous LLW?
It is filtered then released
How to monitor radioactive materials?
- Bq
- Gy
- Sievert
Becquerel (Bq)
Bq measures the activity of the source
Gray (Gy)
A measure of absorbed dose.
1 Gy is the absorption of 1 joule of radiation per kg of matter
Sievert
A measure of effective dose that allows for the differing effects of different types of radiation
Sievert Calculation
Number of sieverts = Number of Grays x a radiation weighting factor
The weighting factor for alpha radiation is 20
For gamma and beta radiation, it is 1
Monitoring Workers
Personal dosemeters
Photographic film badges which measure long term measure exposure
Air monitors
Contamination monitors

Personal dosemeters
They give a reading of current exposure
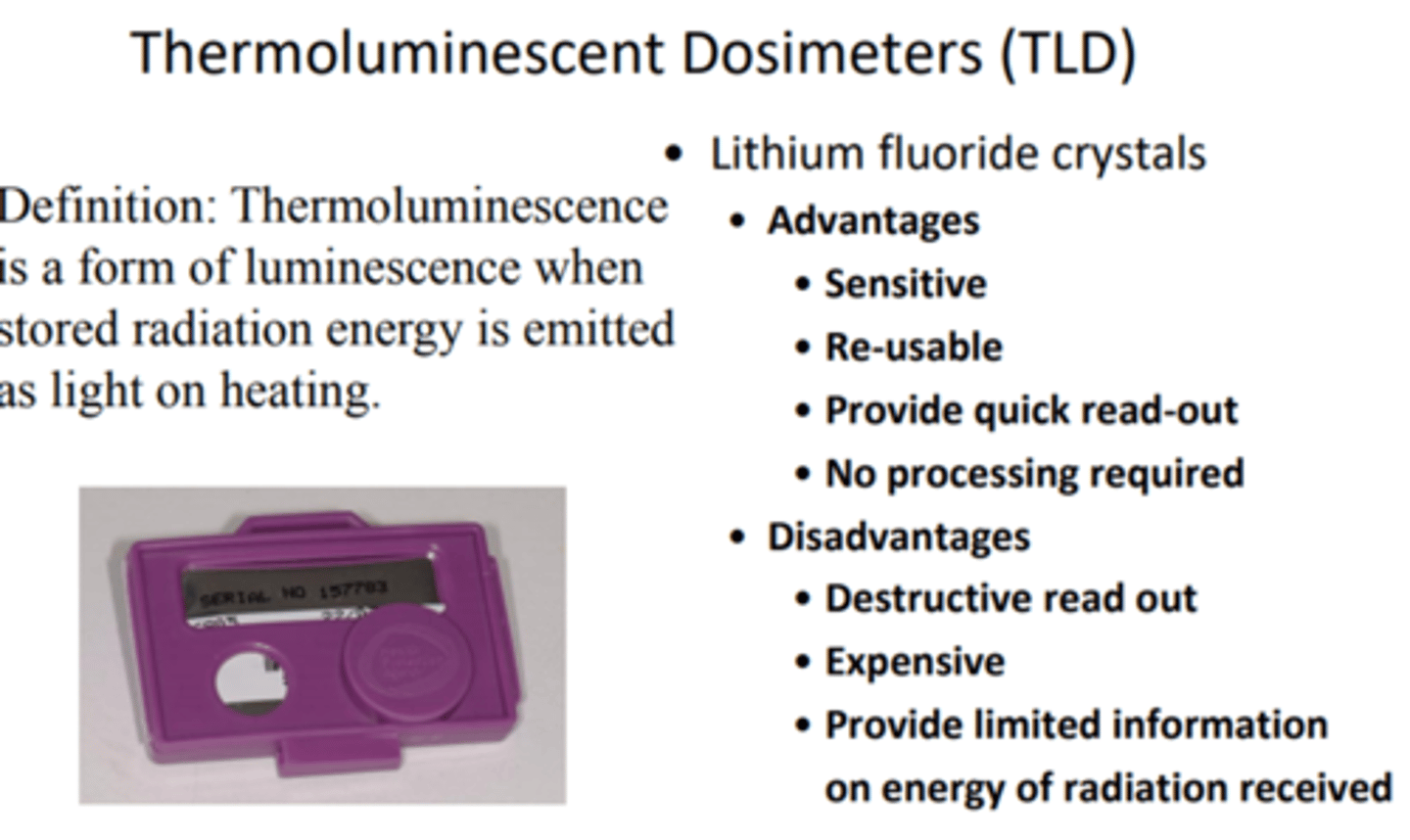
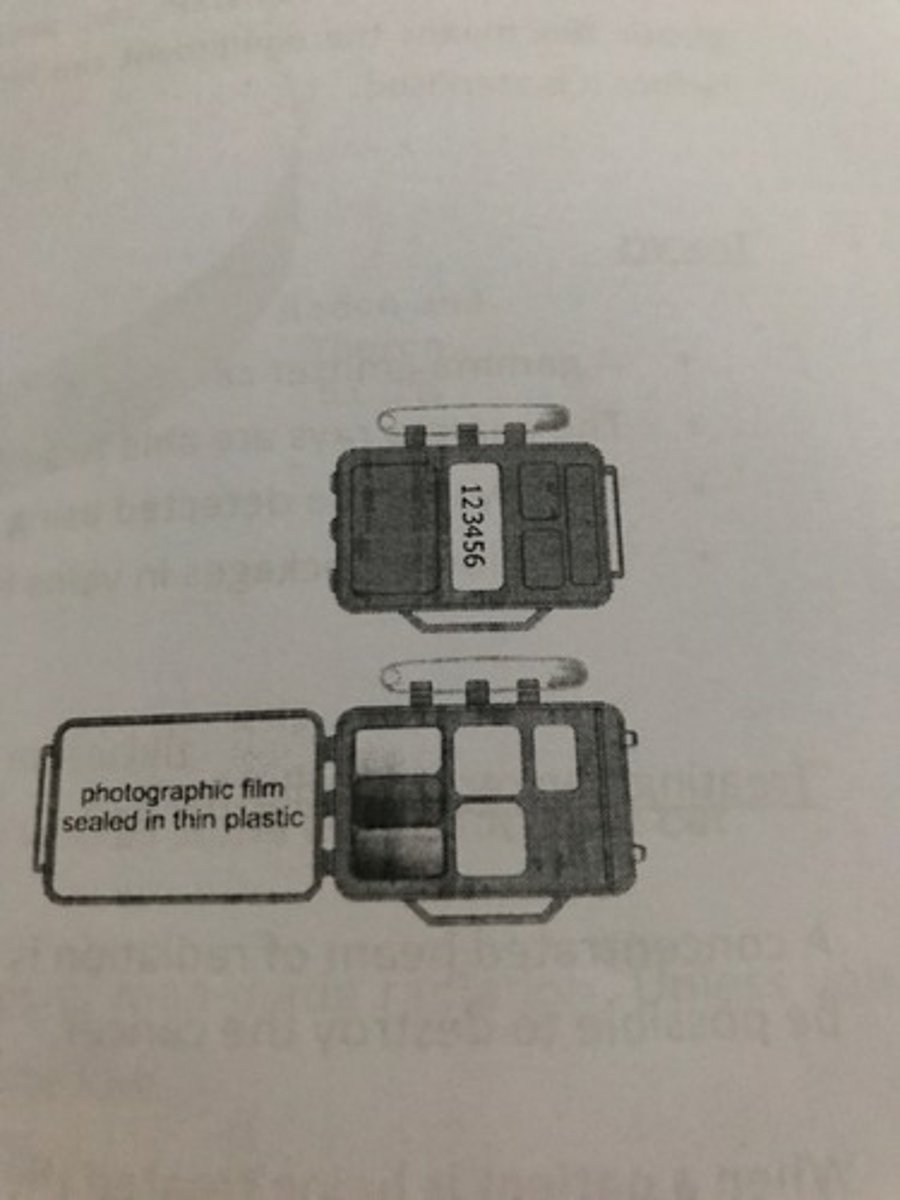
Photographic film badges
They measure long term exposure
Air monitors
They detect atmospheric particles, including alpha emitters

Contamination monitors
They monitor workers as they leave the premises and detect any contamination
