Intro to BioChem Exam 2
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
End of Module Quizzes 3 and 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
A glycosidic link is chemically an _____.
Ether
Which of the following is not a homoglycan?
Heparin
The three most common homoglycans found in nature are cellulose, starch and __________.
Glycogen
Glycogen is:
Main carbohydrate reserve of animals
How many stereoisomers are possible for an aldohexose
16
Both glycogenesis and glycogenolysis are controlled primarily by the interplay between the two hormones insulin and ________.
Glucagon
The presence of which of the following molecules indicates that the cell has sufficient energy reserves?
ATP and Citrate
In glycolysis ________ moles of NADH are produced per mole of glucose consumed
2
Cellulose is indigestible to most animals because:
Animals lack the enzymes required to hydrolyse the b links of the cellulose
Glycoproteins lack which of the following groups typically found in proteoglycans?
Uronic acids and Sulfate groups
The accumulation of AGEs is linked to which of the following diseases?
Atherosclerosis
Arthritis
Diabetes
All of the above are correct
Under stressful conditions epinephrine is released from the adrenal medulla. The release of epinephrine has which of the following effects on glucose metabolism?
Glycogenolysis is stimulated
Glycogenesis is inhibited
Adenylate cyclase is activated
All of the above are correct
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
Is an indicator of high cellular glucose concentration
Which of the following polysaccharides is known to bind the largest amount of water?
Heparin
Glycoconjugates result from the covalent linkage of carbohydrate to proteins or _________
Lipids
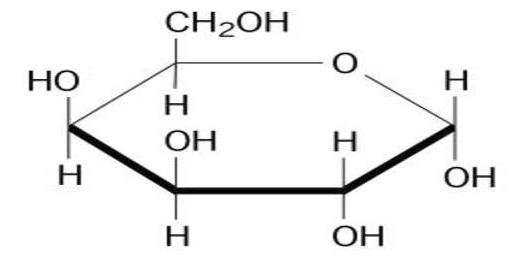
The name of this sugar is...
D-Galactose
An enzyme family called the _________ catalyzes the phosphorylation of hexoses in the body.
Hexokinases
Carbohydrate is thought to enhance the stability of protein molecules by:
Protecting the underlying protein from the action of proteolytic enzymes
Reaction of an amino acid with C1 of a cyclic aldose produces which of the following linkages?
Glycosidic
The preferred energy source of the brain is __________.
Glucose
Which of the following carbohydrates is a nonreducing sugar?
Sucrose
The binding of insulin to receptors on the surface of muscle cells stimulates which of the following processes
Glycogenesis
Lactose intolerance arises from
The inability of intestinal enzymes to cleave the lactose
In glycoproteins carbohydrate is most often linked to threonine, asparagine or __________.
Serine
Which of the following is required for the conversion of UDP-glucose to glycogen?
Glycogen synthase and Branching enzyme
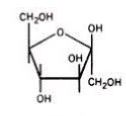
Name this sugar....
D-Fructose
Which of the following yields N-acetyl-D-glucosamine on hydrolysis.
Chitin
Which of the following sugars contains a b-1,4-linkage?
Cellulose
The most abundant organic substance on earth is ______
Cellulose
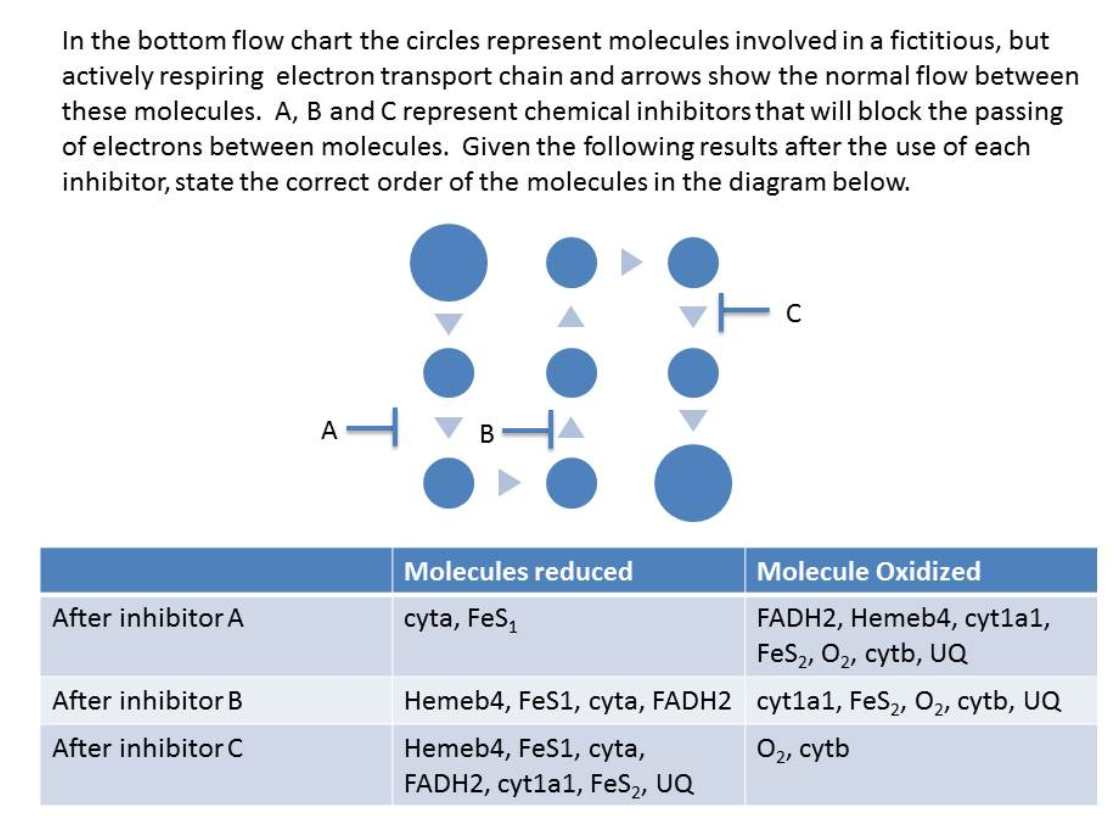
FeS1, cyta, HemeB4, FADH2, cyt1A1, FeS2, UQ, cytb, O2
How many malonyl molecules will need to be made to synthesize a 20 carbon long fatty acid?
9
Plasma lipoproteins transport _______ through the blood from one organ to another.
Triacylglycerols
Phospholipids
Cholesteryl esters
All of the above are correct
During the production of mevalonate, a necessary molecule in cholesterol biosynthesis, reducing molecules are needed. Which reducing molecule(s) are used during the formation of mevalonate?
NADPH
Acetyl CoA that is consumed by the citric acid cycle is produced from which of the following biochemical pathways?
Glycolysis and Fatty acid oxidation
Lipolysis is used to
Degrade triacylglycerols
Glycerol from the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols is transported by the blood to the ____
Liver
Energy requiring transport mechanisms include
Primary active transport
Phospholipids are
Structural components of membranes and Surface active agents
The conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA is inhibited by ________.
Glucagon
Epinephrine
Palmitoyl-CoA
All of the above are correct
Phospholipids are
Structural components of membranes and Surface active agents
In addition to the prostaglandins and leukotrienes the autocrine regulators include:
Thromboxanes
Saturated fatty acids containing up to 16 carbon atoms are assembled in ________.
Cytoplasm
How many moles of NADH would be made if two moles of glucose proceeded all the way through aerobic respiration? (stopping after completing the citric acid cycle). Only fill in whole numbers for your answer.
Total number of NADH developed entered as a whole number = [____]
20
The role of very low density lipoproteins is
Transporting of lipids from liver to tissues
Cholesterol is a precursor of _________.
Aldosterone
Cortisol
Testosterone
Estrogen
All of the above are correct
_________ are the principal transporters of cholesteryl esters to tissues.
Low density lipoprotein
The myelin sheath
Surrounds nerve cell axons and Facilitates nerve impulse transmission
Which of the following molecules are a precursor to cholesterol synthesis?
squalene
Acetyl CoA that is consumed by the citric acid cycle is produced from which of the following biochemical pathways?
Glycolysis and Fatty acid oxidation
What is the systematic name of a fatty acid with the following abbreviation?
16:1cD9
cis-9-Hexadecenoic
Plasma lipoproteins transport _______ through the blood from one organ to another.
Triacylglycerols
Phospholipids
Cholesteryl esters
All of the above are correct
A membrane’s fluidity is largely determined by the percentage of
Unsaturated fatty acids
When triglycerides are mobilized from adipose tissue and used as fuel in other cell types. What is a common role for the glycerol molecules that are generated during this process?
They can enter glycolysis
Which of the following is not a function of phospholipases?
Energy storage
Prostaglandins are involved in _________.
Ovulation
Inflammation
Digestion
All of the above are correct
The basic structure of biological membranes is a consequence of the physical properties of _______.
Phospholipids
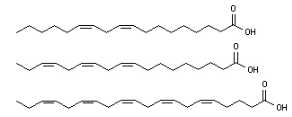
Which of the following fatty acids have the highest melting point considering that all double bonds are cis double bonds?
The top image
Which of the following is not a function of lipids
Energy storage
Components of biological membranes
Insulation
Source of acetyl-CoA
All of the above are functions of lipids
Prostaglandins are involved in _________.
Ovulation
Inflammation
Digestion
All of the above are correct
Have a double bond six carbon atoms from the methyl end of the chain