excipients for powder mixtures
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
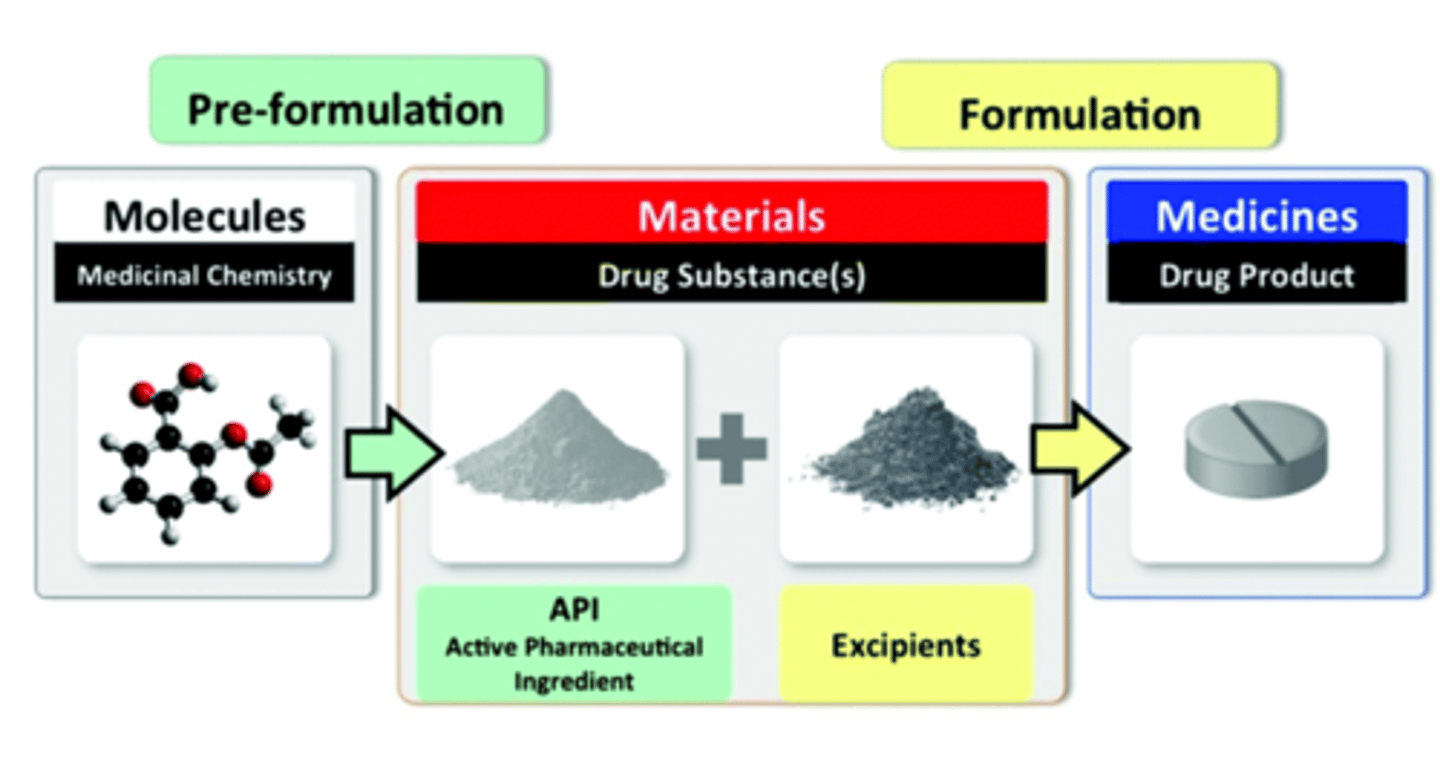
what are excipients? what is their role?
- all other components of a drug formulations than the active drug
- there are integral components of a medication, designed to protect, support, or enhance the stability, bioavailability or patient acceptability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API)
what are the ideal excipient properties?
- stable and reproducible (safe)
- no unwished interaction with drug
- pharmacologically inert
- desired functionaility
- cost effective
what can excipients be added to formulations for?
do NOT treat the disease, but improve patient's condition
1. to improve manufacturability (increase bulk, improve flow or mixing properties)
2. to protect, support, or enhance stability, bioavailability or patients acceptability - things to extend shelf life
3. to assist in product identification - by flavour, colour and smell
4. to enhance any other attribute of the overall safety, effectiveness or delivery of the drug during storage or use
how are excipients chemically diverse? what are examples?
- inorganic salts
- carbohydrates
- synthetic materials
- oils
- natural products
what determines the property of excipients?
some excipients can play different role depending on concentration
what is the function of an anti-tacking agent?
prevents stickiness or tackiness of polymeric film coating on tablets
e.g talc, glyceryl monosterate
what is the function of binder?
substances used to cause adhesion of powder particles in tablet granulations
e.g ethylcellulose, starch, hypromellose.....
what is the function of colorant?
added for esthetic and identification purposes - which is important for children, to increase acceptability. (eg, strawberry is pink, banana is yellow)
however some people are allergic
what is the function of diluent?
acting as a bulking agent to achieve adequate capsule fill volume or tablet size; reduces drug particle cohesion
it is diluting drug in bulk of excipient - to allow size and compaction
e.g lactose, mannitol, starch
what is the function of disintegrant?
promotes rapid break up of the capsule or tablet upon contact with the aqueous fluid (eg GI fluid) which results in increased SA of drug exposed to fluid and faster dissolution - as a drug should be released drug quickly to be absorbed
e.g starch, cellulose, pregelatinised starch
what is the function of film coating polymer?
PROTECTS - provides an immediate release coating for tablets or provides a modified release coating for tablets or pellets/beads - depending on the polymer chosen
e.g hypromellose, Eudragit
what is the function of glident?
improves powder flow during processing when filling capsule shells or compressing tablets
e.g colloidal silica, silicon dioxide, mag silicate, talc
what is the function of lubricant?
prevents adherence of powder to tablet press or encapsulating equipment by reducing friction - helps flow
e.g mag sterate, stearic acid
what is the function of opacifier?
improves the stability of light sensitive drugs
e.g titanium dioxide
what is the function of plasticiser?
enhances flexibility of film coating added to hot melt extrusion formulations to lower the glass transition temperature of the polymer and facilitate processing
what is the function of surface active agent?
enhances wetting of drug by the aq fluid (eg GI), thus improving dissolution of poorly water soluble drugs
solubilises an otherwise water insoluble drug
their inclusion in a coating composition may also homogenise the coating liquid used on tablets and enhance spreadbility
what are the most popular excipients in powder mixtures?
- lactose (monohydrate/anhydrous/spray dried)
- starch (natural/pre-geletinised)
- cellulose (powdered/microcrystalline) - not that sustainable due to extraction methods
- talc
- colloidal silicon dioxide
- magnesium sterate
what are the considerations for using lactose as an excipients?
- most studied and best understood excipient
- problematic for lactose-intolerant individuals
- maillard reaction - instability with primary amine-containing drugs - as sugar and proteins react
- turns tablets from white to brown, therefore coating is used
what can starch be used for as an excipient?
- binder
- disintegrant (primarily)
- anti-adherent
- lubricant
what can powdered cellulose be used for as an excipient?
- capsule filler (diluent) - primarily
- tablet binder
- tablet disintegrant
- tablet glidant (depends on conc)
it is incompatible with strong oxidising agents and slightly hygroscopic
what is microcrystalline cellulose be used for as an excipient? what exactly is it and how is it obtained?
- adsorbent
- anti-adherent
- binder/diluent - primary use, in wet granulation and direct compression as smaller particle size and easier dose uniformity
- tablet disintegrant
it is partially depolymerised cellulose obtained through controlled acid-hydrolysis and spray dried
- it is porous, hygroscopic and crystalline
- usually more expensive
what is talc primarily used for as an excipient? what are the considerations?
- used primarily as glidant, anti-adherent and lubricant in solid dosage forms
- may contain traces of aluminium silicate and iron
- purity varies with geographical source
- must be free of asbestos and carefully used - there is a contamination risk due to the natural sources (there was a case of cancer from this)
- mineral and extras to be used cosmetically
what is colloidal silicon dioxide primarily used as and excipient? what are its properties?
- primarily used as glidant - coats larger particles to reduce cohesion
- also used as tablet disintegrant and adsorbent
- it is a fine powder that helps flow
- it has a very high specific surface area
- practically insoluble in water and organic solvents
- forms colloidal dispersion in water
- also used as tablet disintegrant and adsorbent
what is magnesium sterate primarily used as an excipient? what are its properties?
- primarily used as a lubricant
- coats larger particles to reduce friction
- greasy to touch, cohesive and adherent
- high specific surface area - small particle size
- almost insoluble in ethanol, ether and water
- hydrophobic, excessive amounts will retard drug dissolution
- incompatible with strong oxidising agents e.g strong acids and alkalis, iron salts
- causes asprin degredation by increasing solubility and hydrolysis by elevating pH
what are the differences in excipient in omeprazole gastro-resistant and orodispersable?
- gastro-resistant (usually 1st choice) contains a enteric coating, hypromellose acetate succinate, which is a polymer that only dissolves in the intestine at above pH 5
- orodispersable should disperse in mouth on tongue and taste nice, therefore has flavourings and also miccrocrystalline cellulose which is a disintegrant
what can excipients modify?
without excipients, drug may not work
they improve:
- drug absorption
- improved bioavaliability
- inhibition of efflux in GIT
- reduced bioavailability
- drug stability - inhibition of drug degredation
- use of antioxidants to reduce oxidative degredatioon
- use of chelating agents to sequester oxidation-inducing metal ions (eg Cu2+ and Fe2+)
what are ways that excipients contribute to improving solubility of pharmaceutical products?
- solubilisation - excipients such as surfactants enhance drug solubility by forming micelles
- complexation - excipients like cyclodextrins form inclusion complexes with poorly soluble drugs, improving solubility and dissolution rate
- amorphous solid dispersion - excipients like polymers formulate amorphous solid dispersions which prevent drug crystalisation and promote rapid dissolution (crystals are less soluble)
- pH modification - excipients like buffering agents alter GI pH, optimising drug solubility and absorption at specific sites
surfactactants can form micelles and solubilise hydrophobic drugs
what are examples of excipients in complex drug products?
- release modifiers
- suspending agents/viscosity modifiers
- solubility/bioavaliability enhancers
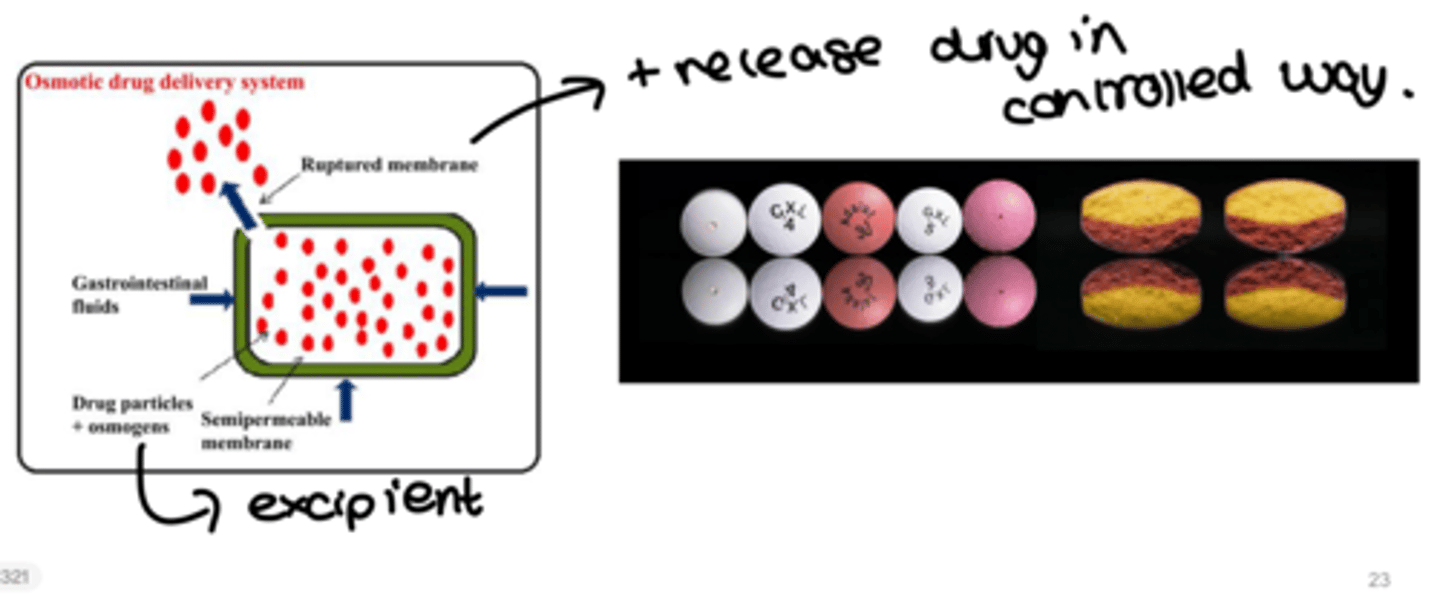
what is OROS?
osmotic-controlled release oral delivery system
what is oros composed of?
a compressed tablet core coated with a semi-permeable membrane through which delivery orifices are created using a laser beam or mechanical drill
they release the drug in a controlled way
what is unique about the delivery system of concerta?
it uses OROS that uses osmotic pressure to deliver methylphenidate through the small drill hole in the tablet at a controlled and predictable rate
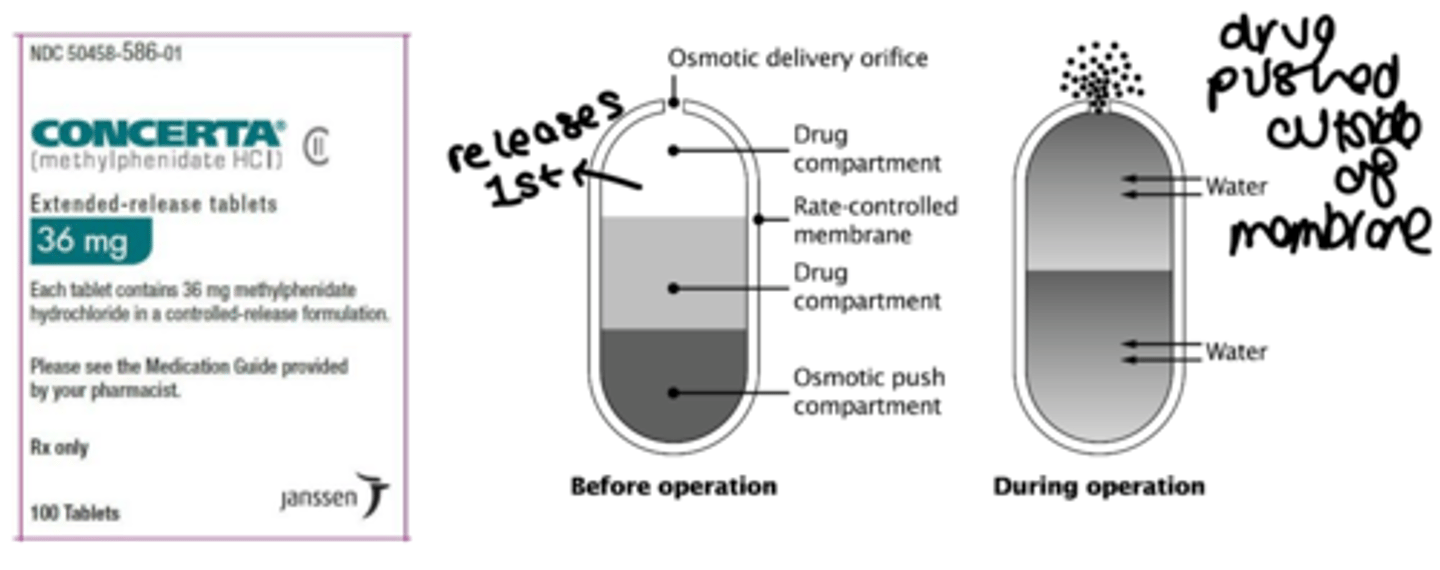
what are the release controlling excipients?
- water soluble hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC)
- the enteric coating methacrylate; polyacrylic acids; polyethylene oxide
what aspects of the release controlling polymer should be examined when targeting a specific release rate?
- molecular weight - an increase in mol weight generally slows the release
- pH dependancy - release controlling polymers that dissolve at specific pHs at a variety of rates allow formulators to select where in the GI tract release will occur
- processability - melting point, flowability and compactability must be considered as they may affect processing; particle size analysis provides clues
what are the applications of polymer blends in drug delivery?
- controlled release
- excipients
- drug delivery systmes
- biodegradable systems
- solid dispersions
- capsule shells
- film coatings and oral films (allows amorphous to be stable)
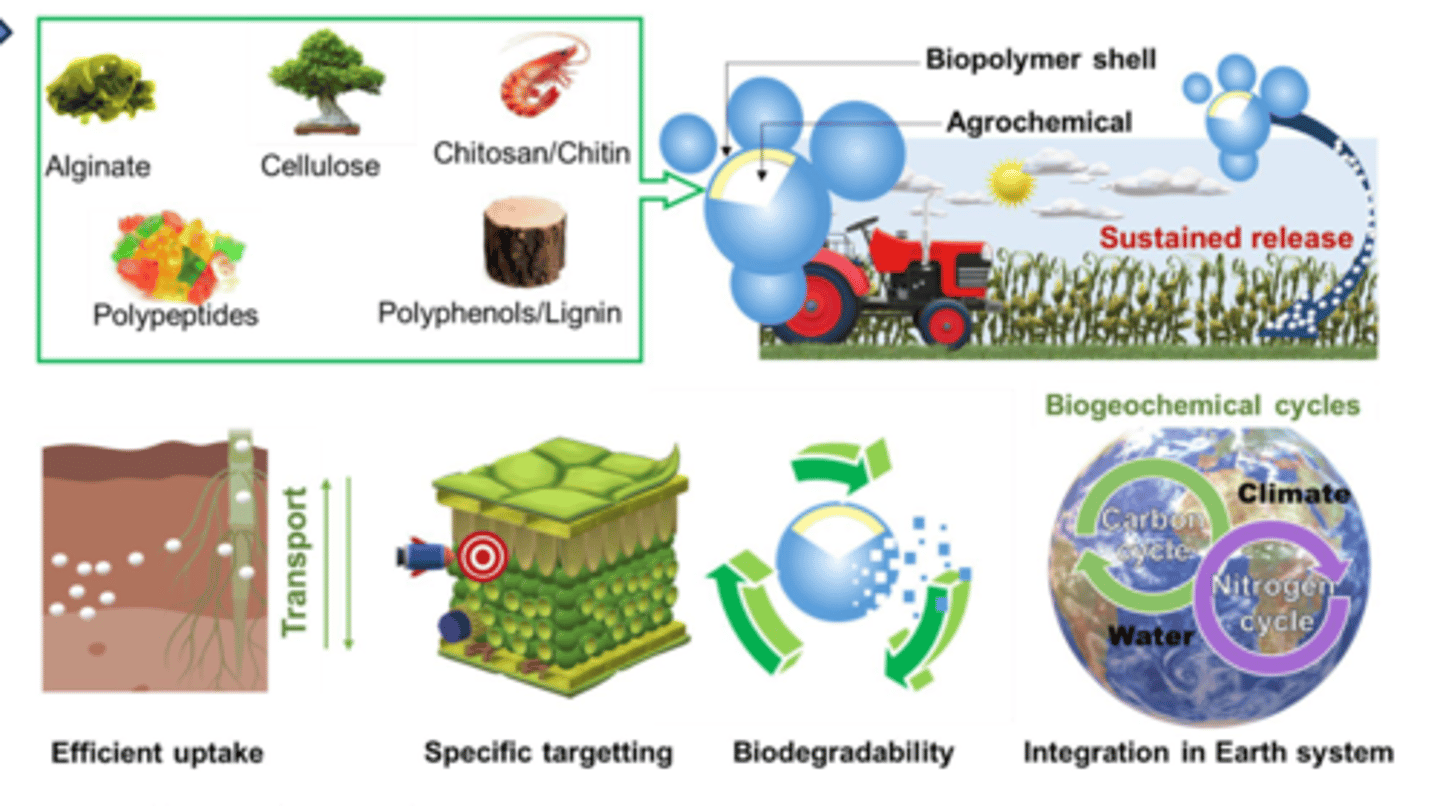
what are eco-friendly excipients for?
- designed to minimise environmental impact throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal
- these are often derived from renewable resources, are biodegradable and are produced using environmentally sustainable processes
what are biopolymers?
naturally occuring polymers derived from renewable sources such as plants, animals and microorganisms
- they are biodegradable and have lower environmental impact compared to synthetic polymers (eg PVP - involves the use of acetylene, ammonia and formaldehyde all of which are dangerous chemicals