Zool 110 Lec: Non-Avian and Avian Dinosaurs (Lec 34)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Class Aves
what class do birds belong to
1. Saurischians 2. Ornithischians
what are the two groups of dinosaurs (other than birds)
feathers and flight
birds are defined by _____ and _____
Ornithischian Dinosaurs (Bird-Hipped)
pelvis has ilium, ischium, and pubis, the pubis points backward and runs parallel with ischium
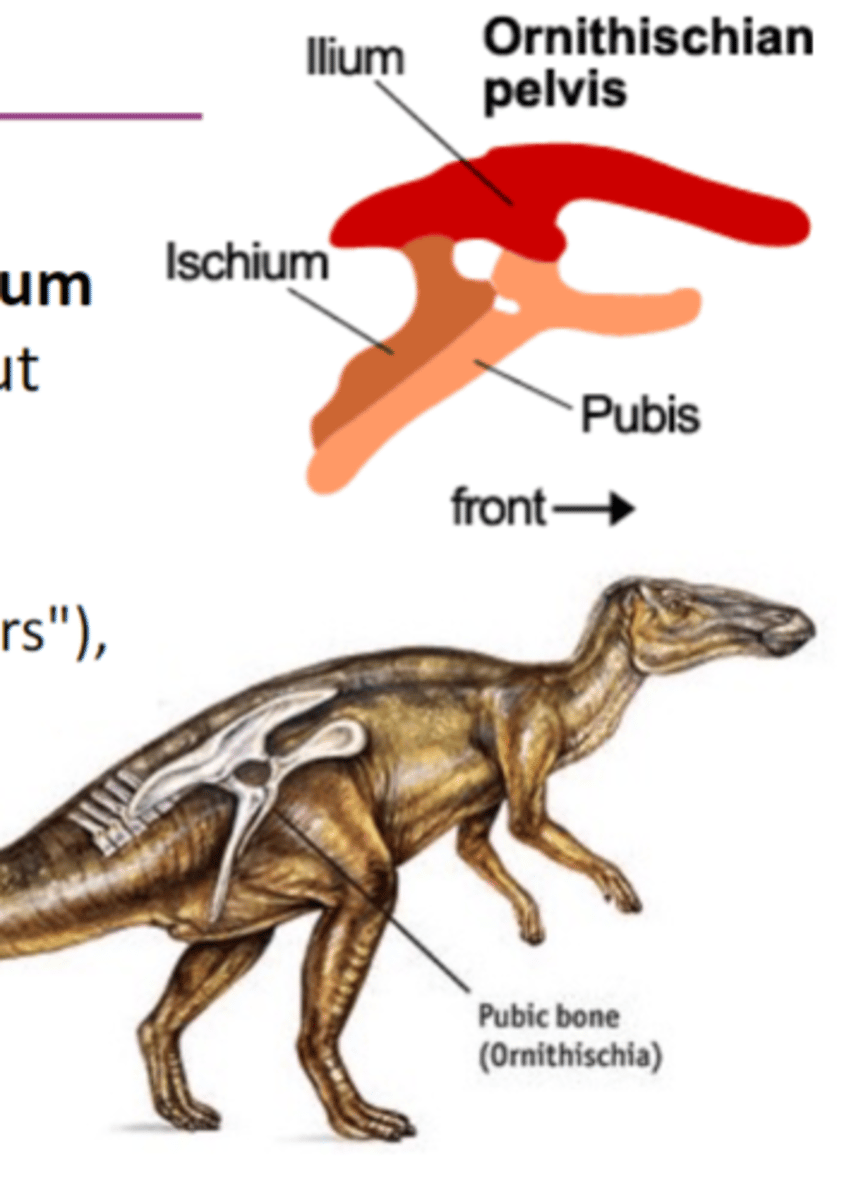
ornithopoda (hadrosaurs), iguanodontids, heterodontosaurs, hypsilophondontids, ceratopsia, anklyosauria, stegosauria, pachycephalosauria
what are the groups of ornithischian dinosaurs
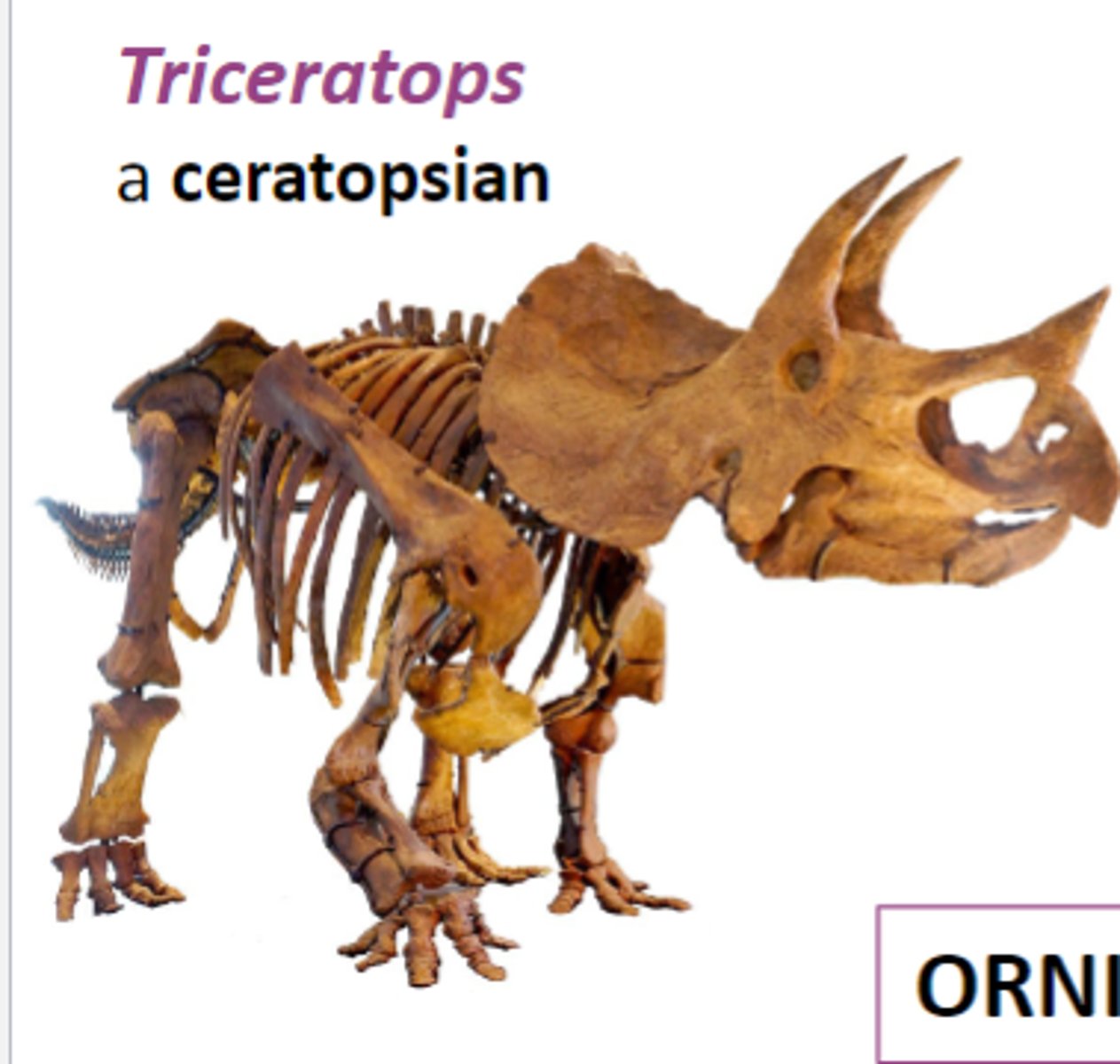
Triceratops
a ceratopsian
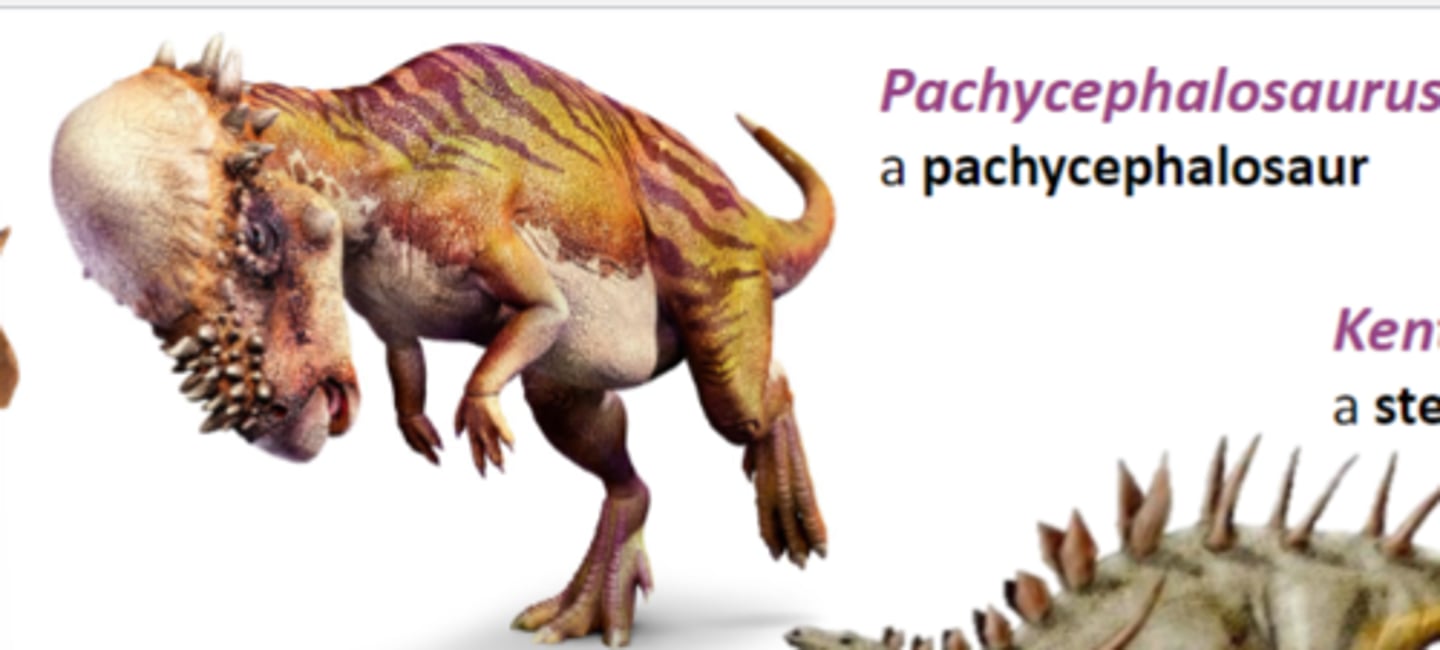
Pachycephalosaurus
a pachycephalosaur

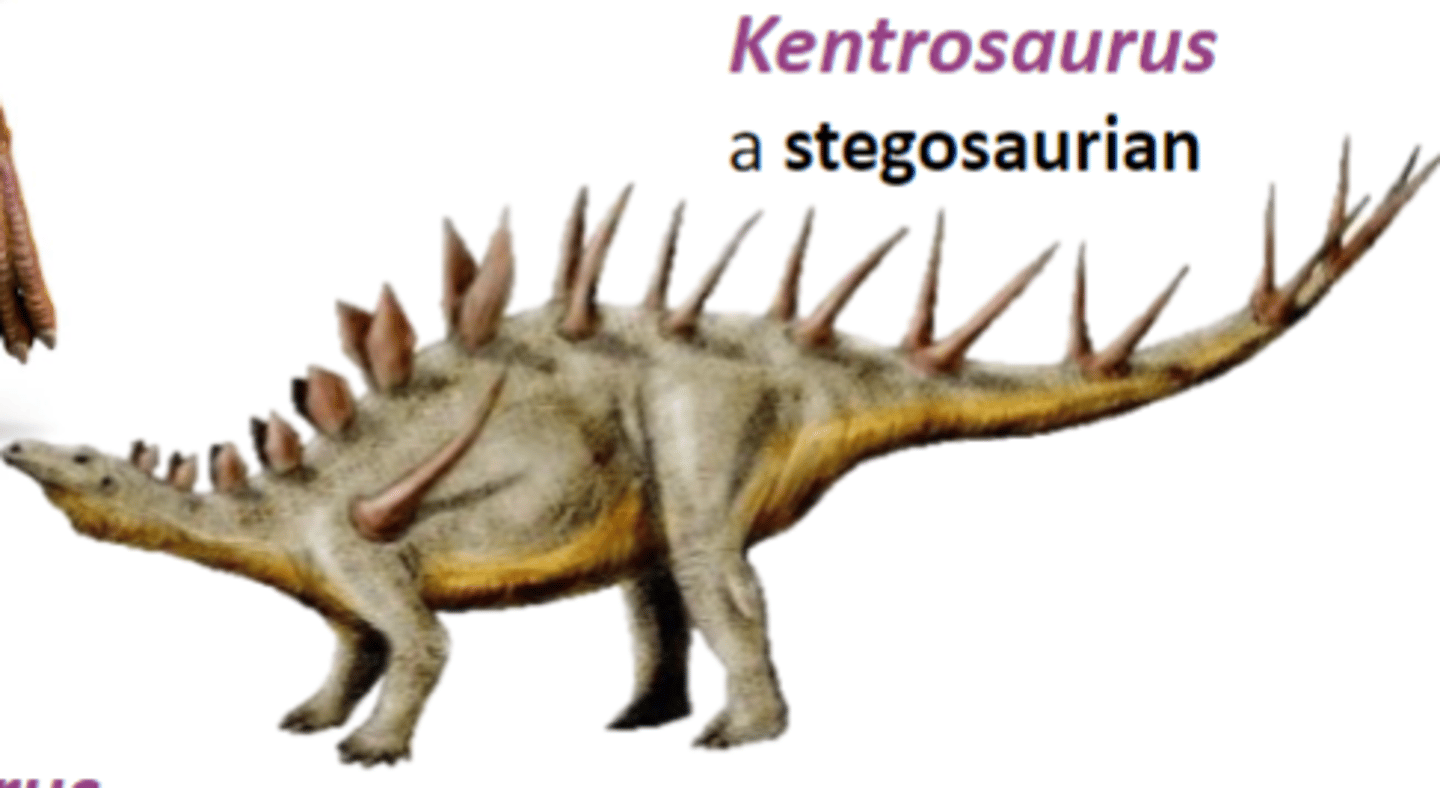
Kentrosaurus
a stegosaurian
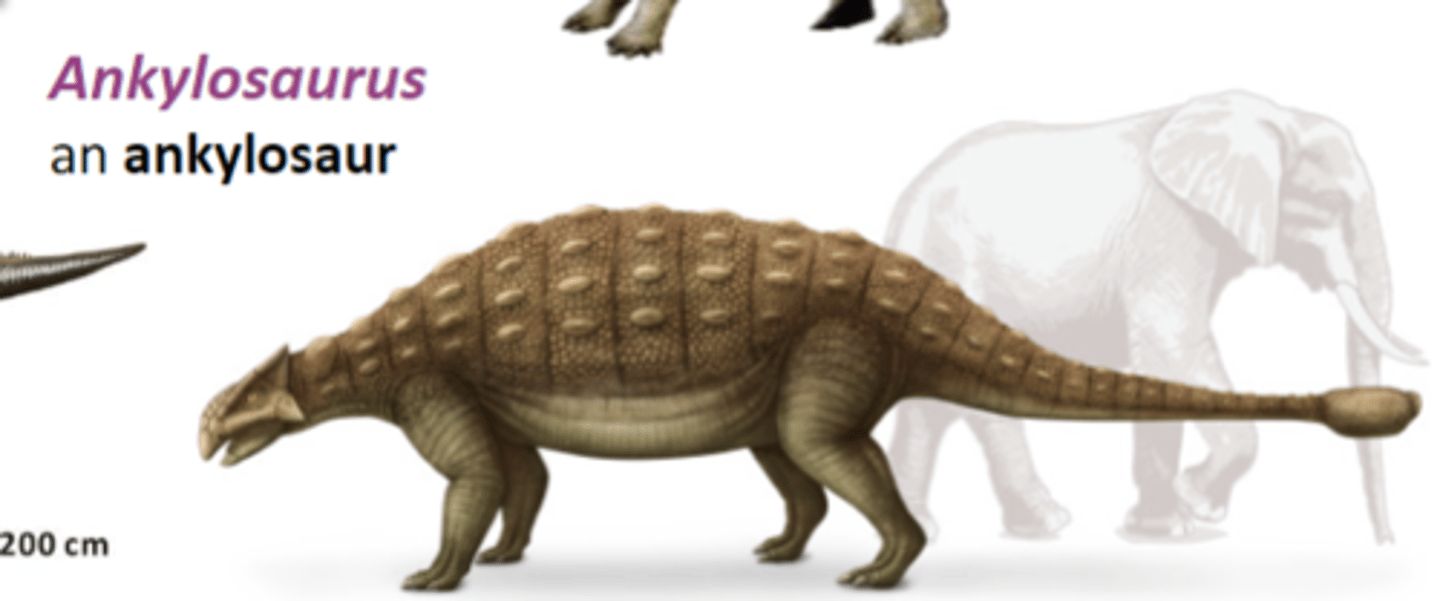
Ankylosaurus
an ankylosaur

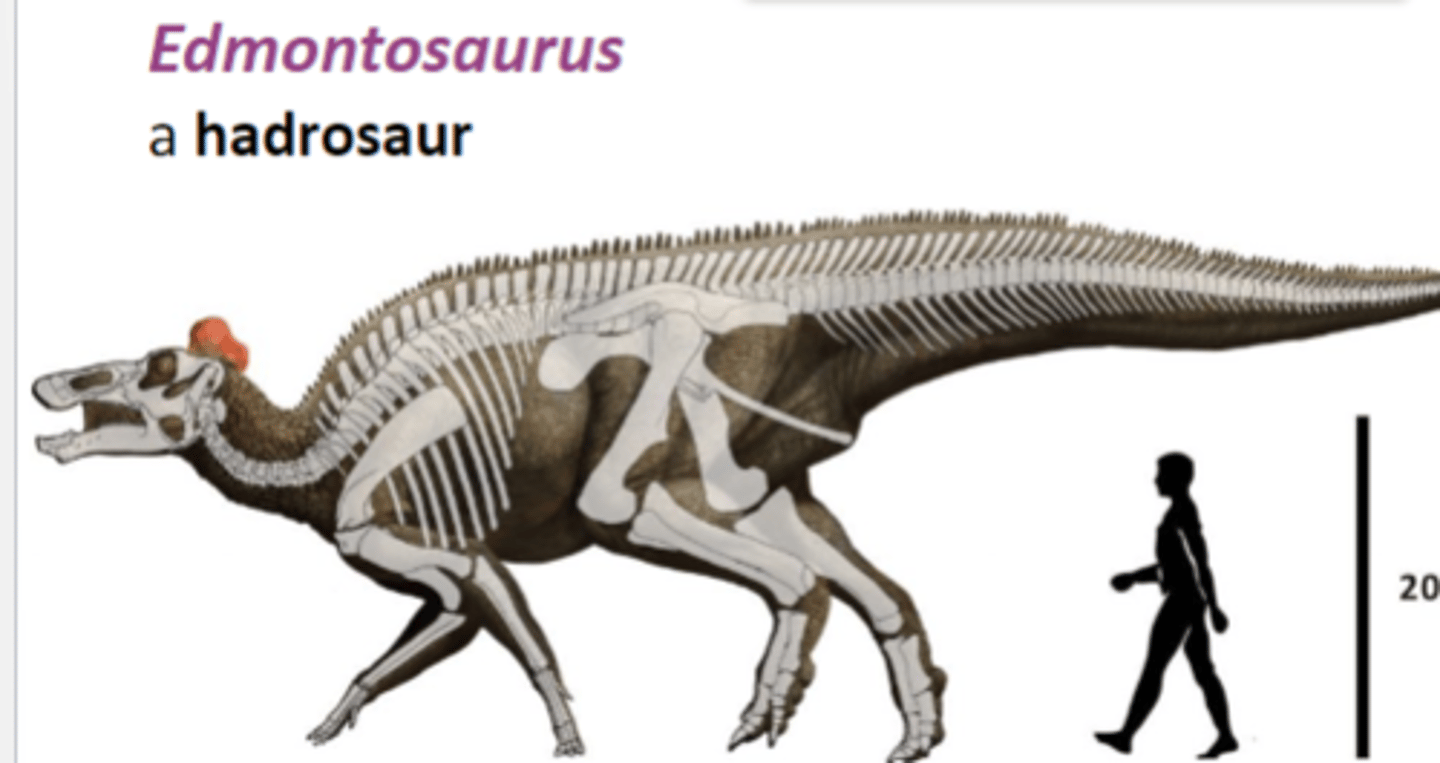
Edmontosaurus
a hadrosaur
Saurischian Dinosaurs (Lizard Hipped)
pelvis has an ilium, ischium, and pubis, grasping hand, asymmetrical fingers, more mobile neck, pubis at an angle to the ischium
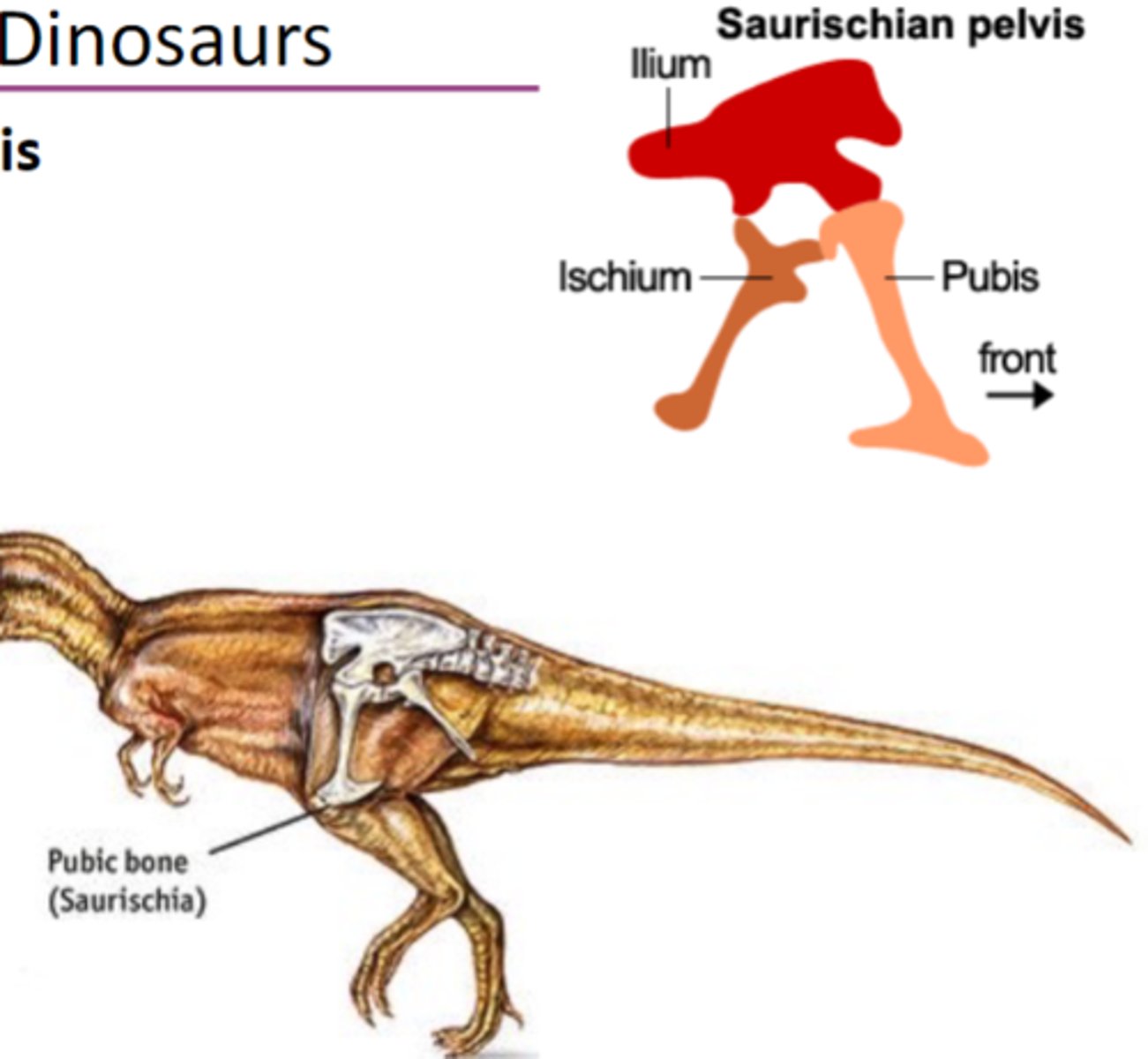
1. Sauropods 2. Theropods
what are the two major groups of Saurischian Dinosaurs
convergent evolution
the "bird-hipped" condition of ornisthischian dinosaurs is an example of what
Saurischian Dinosaurs
what group of dinosaurs are birds derived from
Notocolossus
a titanosaur
exaptation
the process in which existing structures take on new functions through descent with modification
feathers
what is exaptation within avian and non-avian dinosaurs
Ceolophysis
a theropod dinosaur
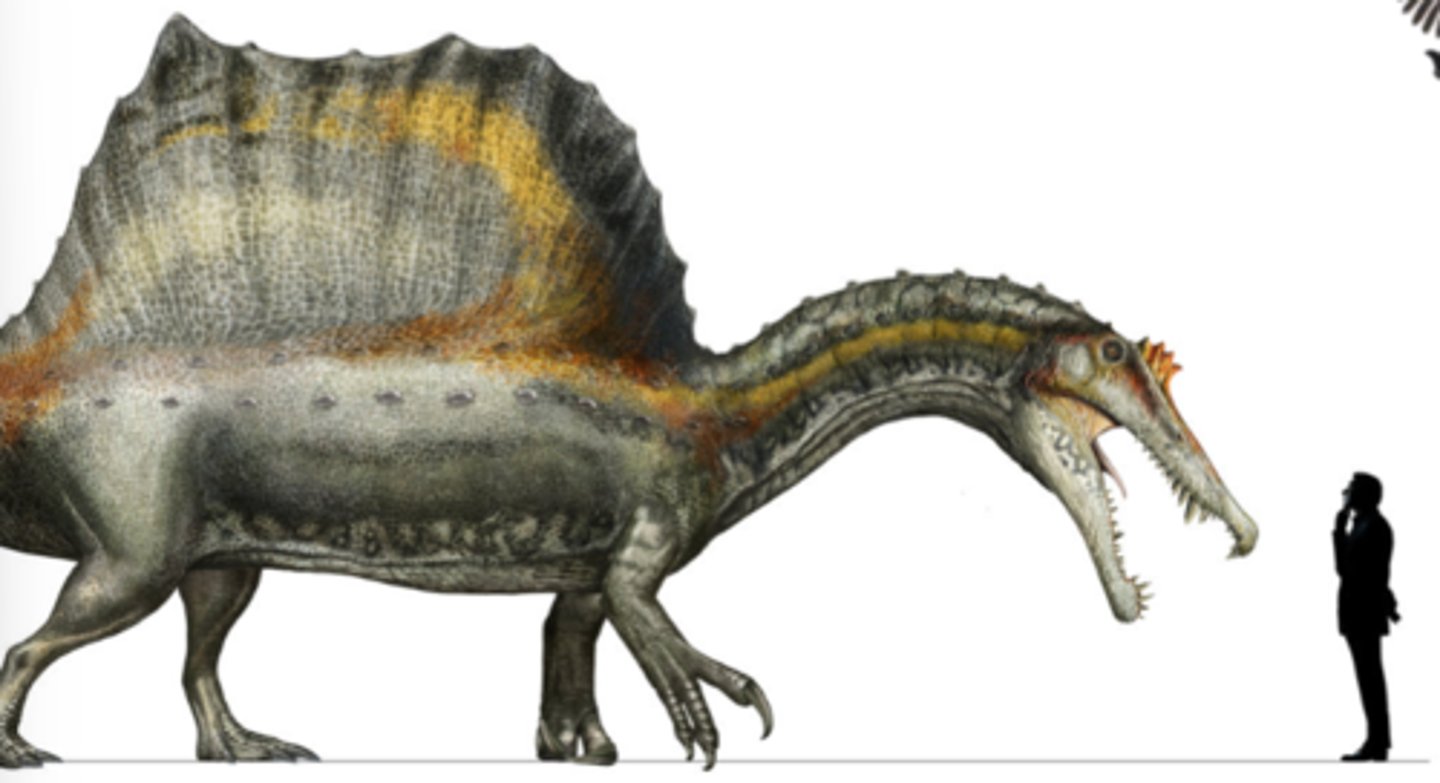
Spinosaurus
a theropod dinosaur
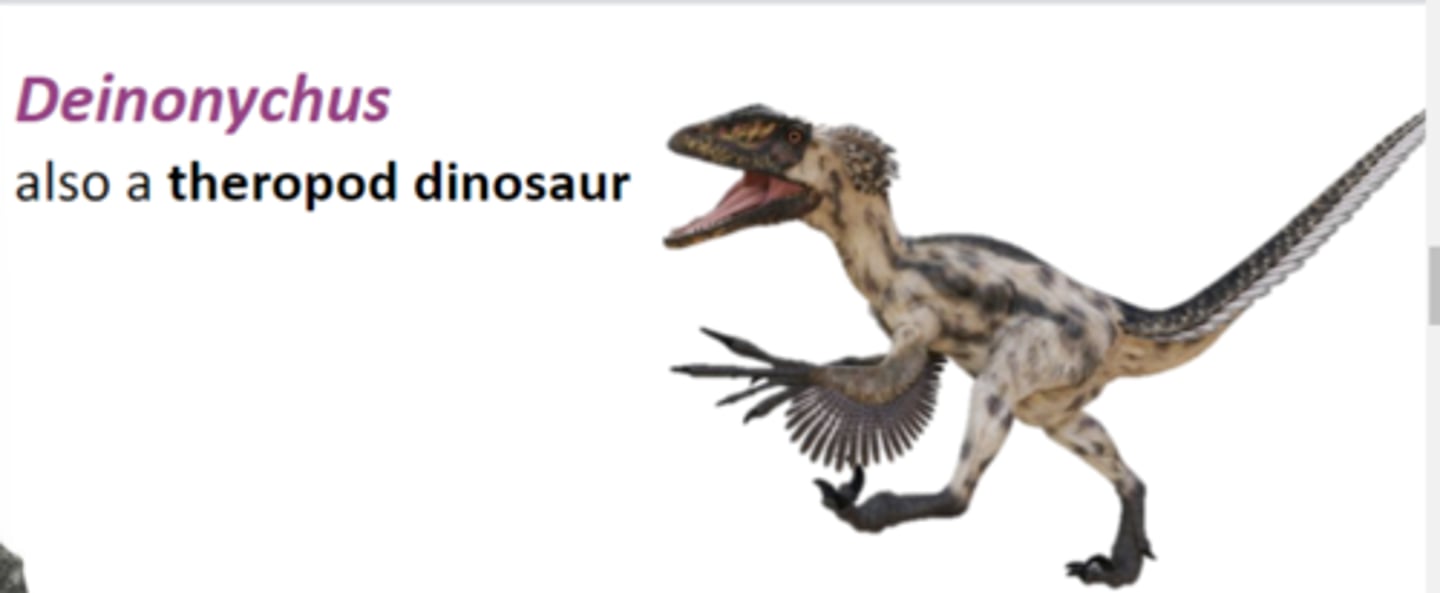
Deinonychus
a theropod dinosaur

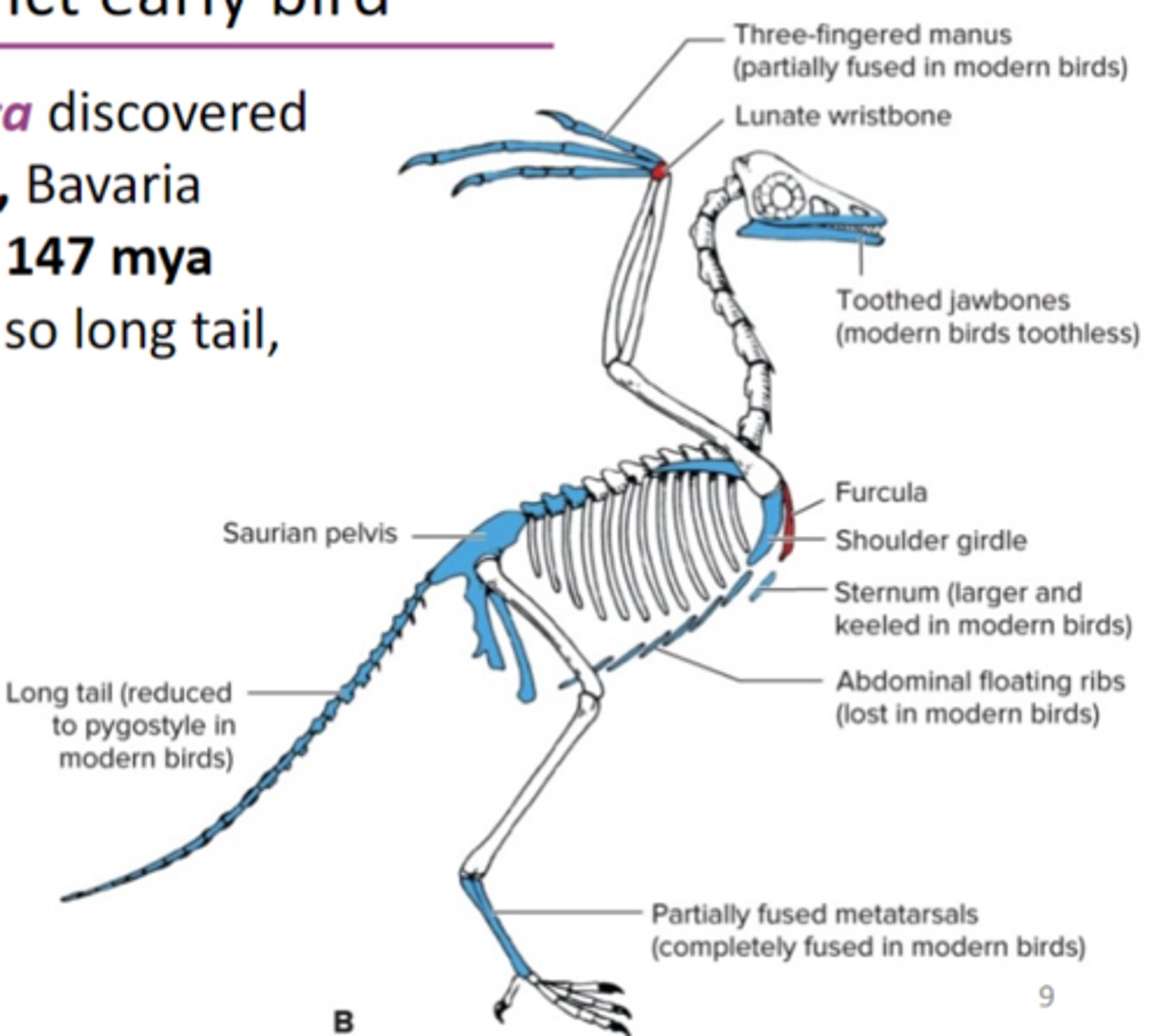
Archaeopteryx
an extinct early bird, famous fossil , special fused wrist bone (lunate wrist bone), and a fused wishbone (furcula)
theropod
current phylogeny puts birds as branch of _____ dinosaurs
1. feathers 2. furcula (wishbone) 3. pneumatic (hollow) bones 4. tridactyl foot with big toe pointed backward
bird features that had already evolved in dinosaurs
65 million
how many millions of years ago did the end-cretaceous mass extinction happen
Chicxulub Crater
evidence of an impact beneath the yucatan peninsula of Mexico
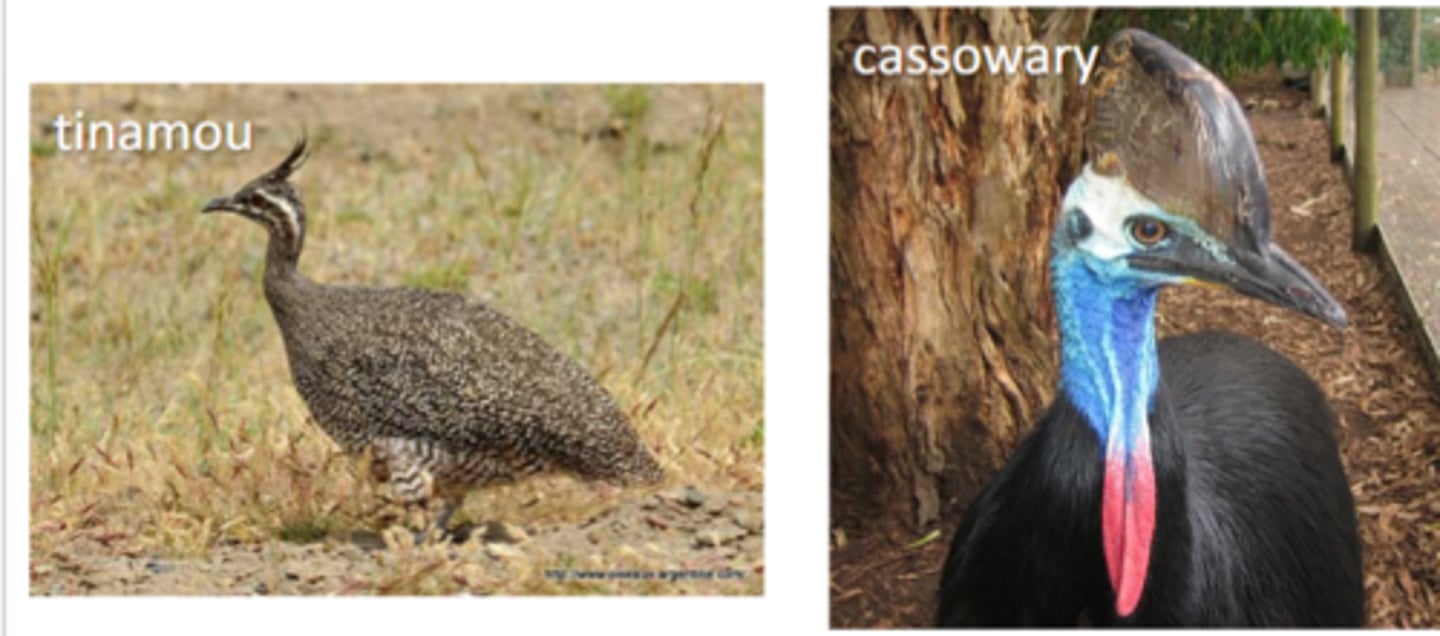
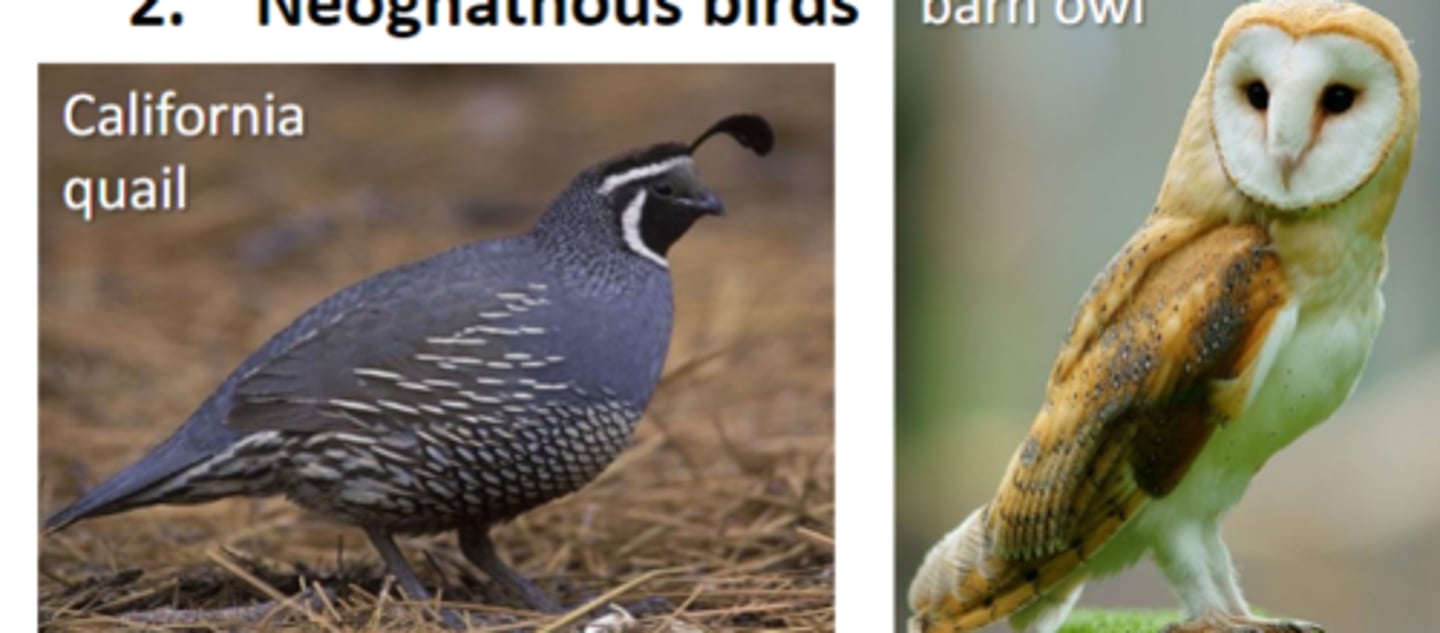
1. Paleognathous 2. Neognathous
what are the two groups of birds
Paleognathous birds

Neoghnathous birds
everybody else

pygostyle
reduced tail of birds
Bird Skeletal Anatomy
keeled sternum, furcula (wishbone), no teeth, foot with three toes, hollow, air-filled (pneumatic) bones
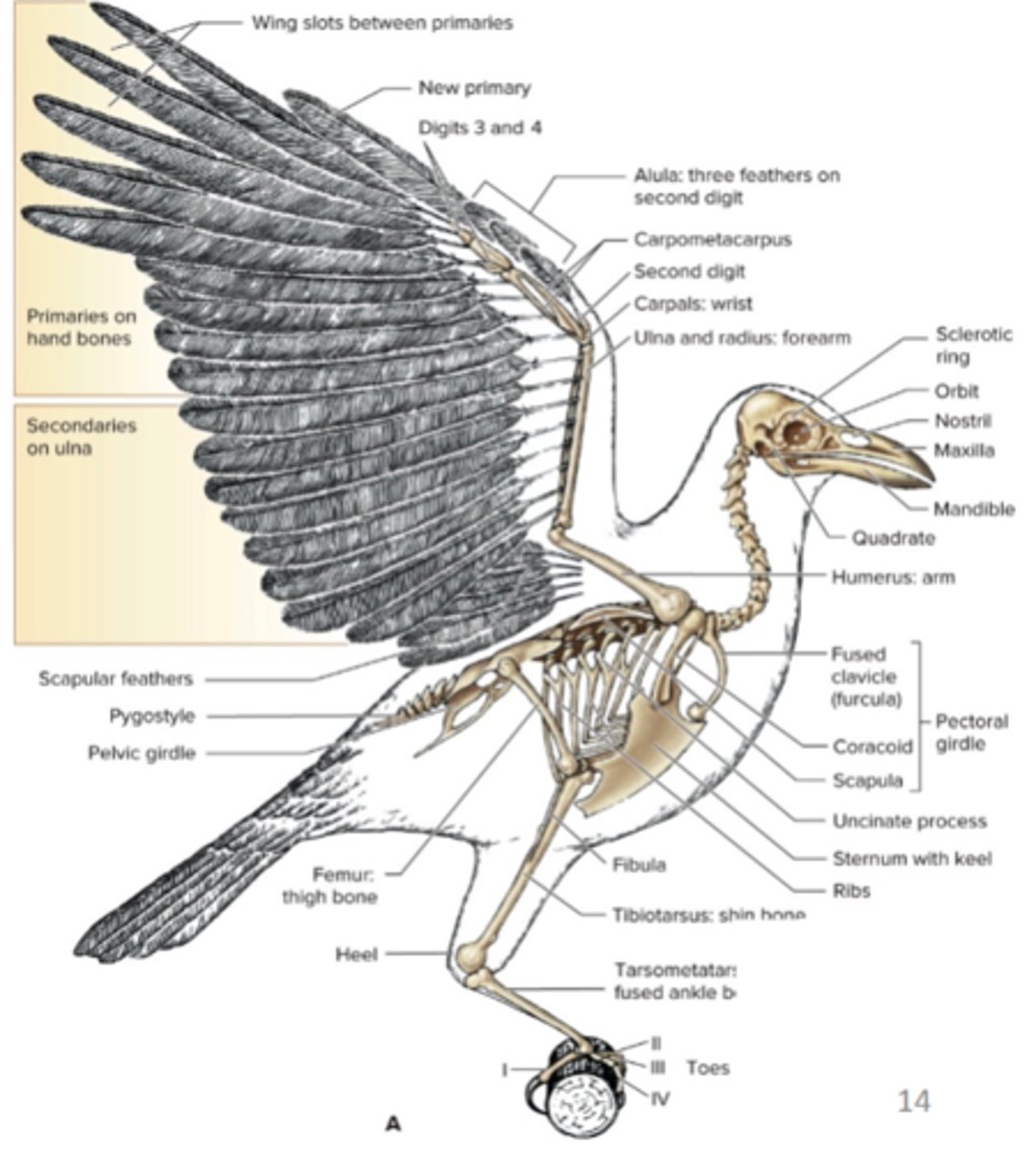
carpometacarpus, tibiotarsus, and tarsometatarsus
what are the fused bones of the bird skeleton
contour feathers
give the bird shape (central quill that becomes the rachis/shaft, covered with barbs and barbules that form a vane)
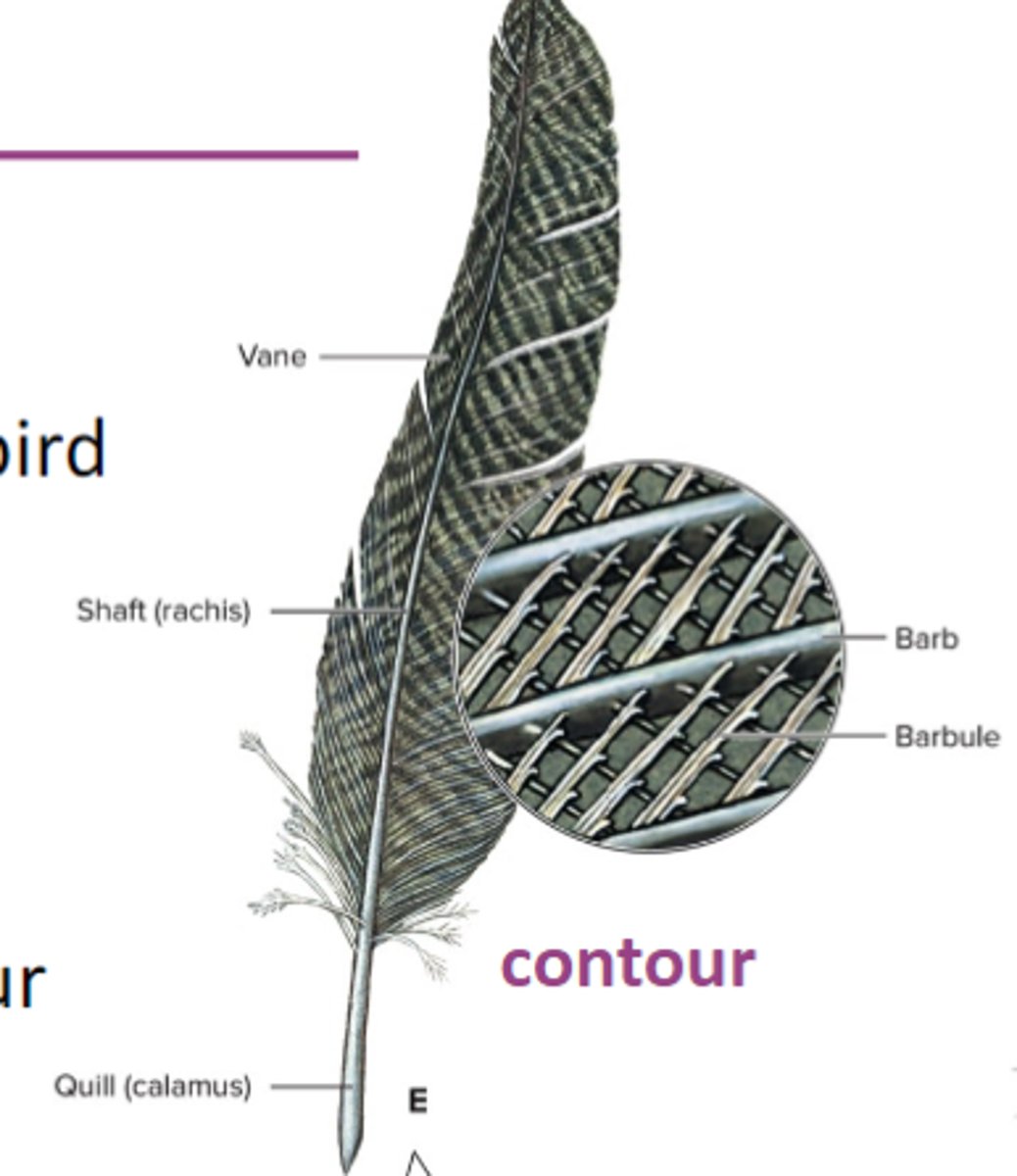
Flight feathers
contour feathers that extend beyond the body
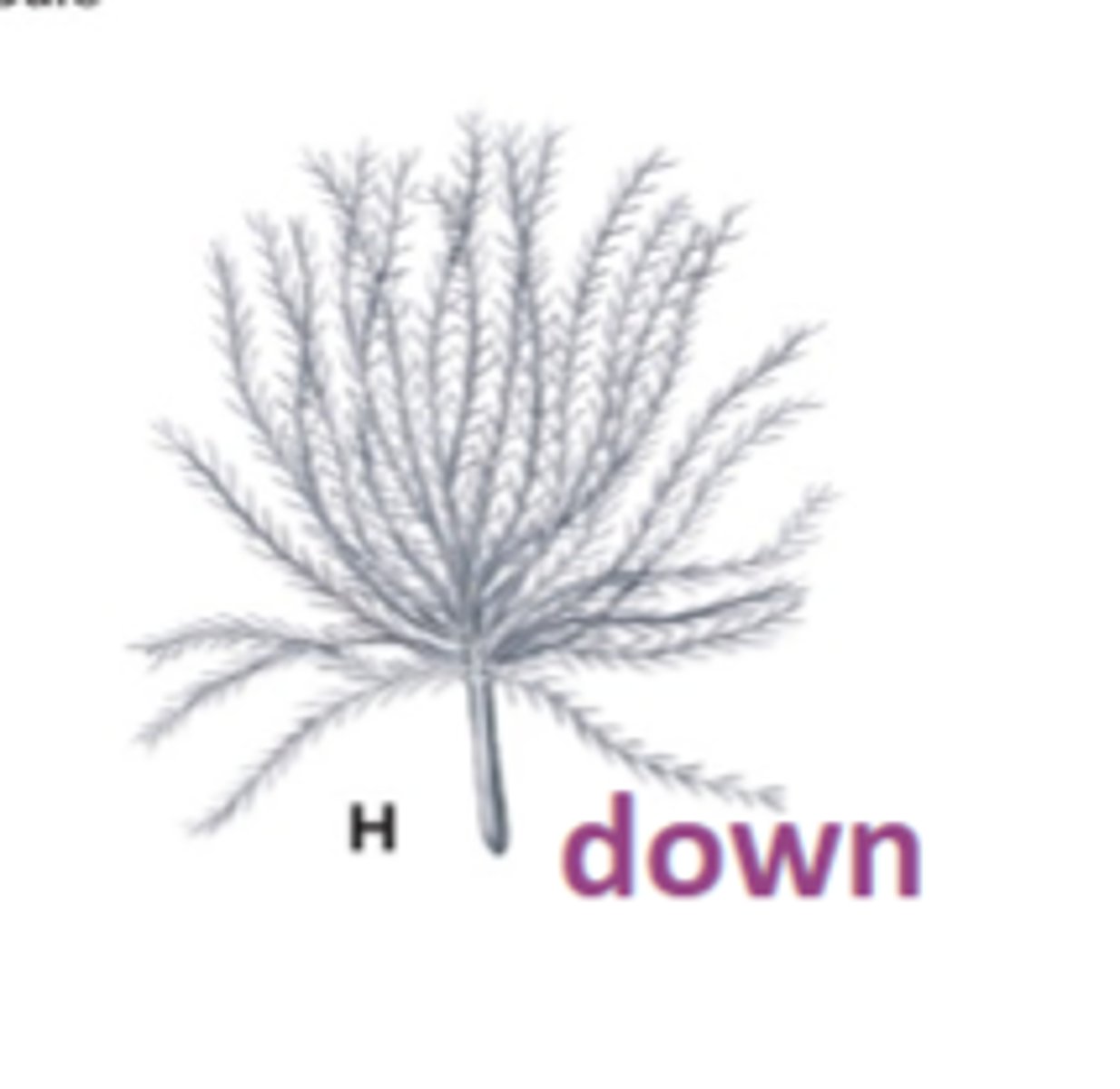
down feathers
feathers with no prominent rachis and no hooks on barbules, conserve heat
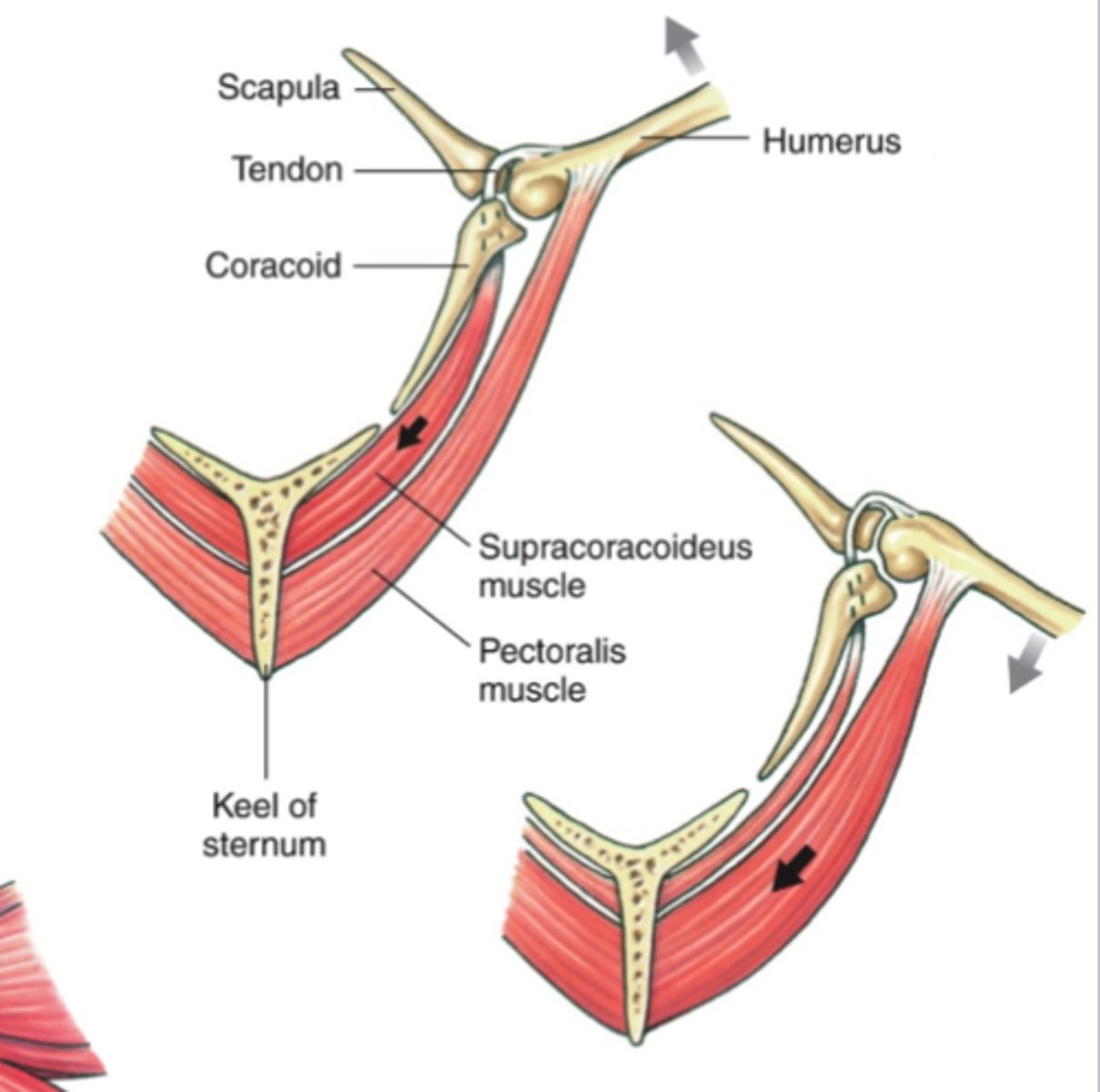
supracoracoideus (raises the wing) and pectoralis (depress the wing)
what are the two flight muscles
perching muscles
automatically tightening tendons close the toes down around a perch
diet
beak shapes reflect a birds ____
it is the most efficient respiratory system
what is special about the birds respiration system
homologous
is the evolutionary origin of wing structure homologous or analogous
two
how many full respiratory cycles are needed to move air through a birds respiratory system
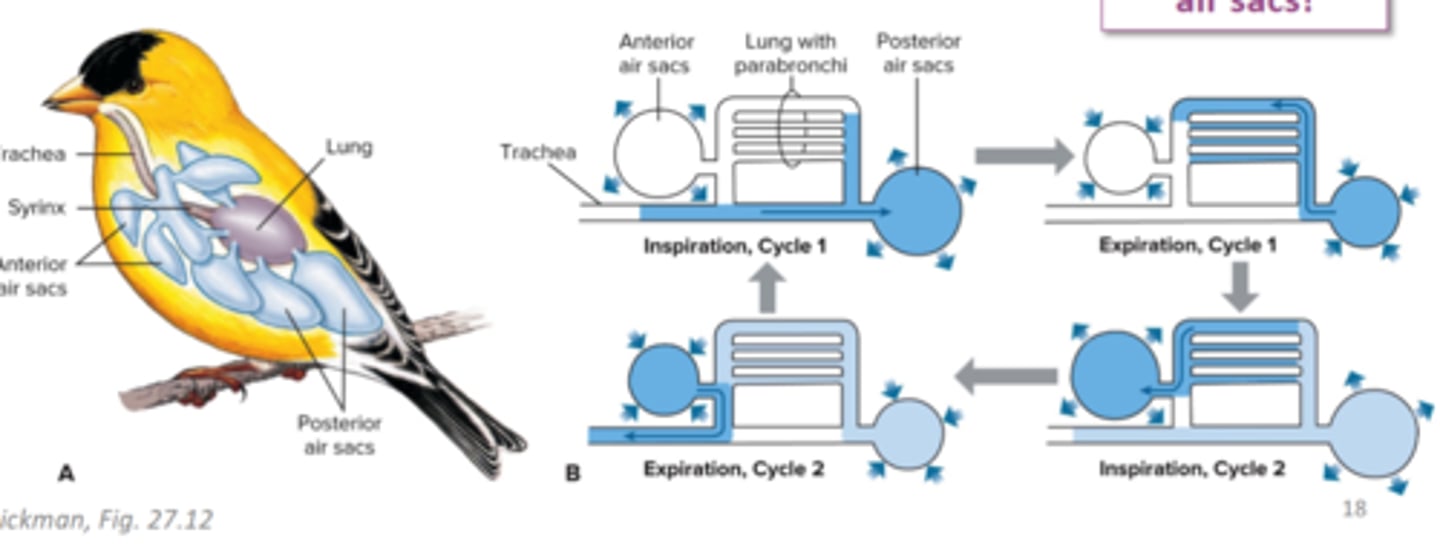
parabronchi
allow for continuous movement of air
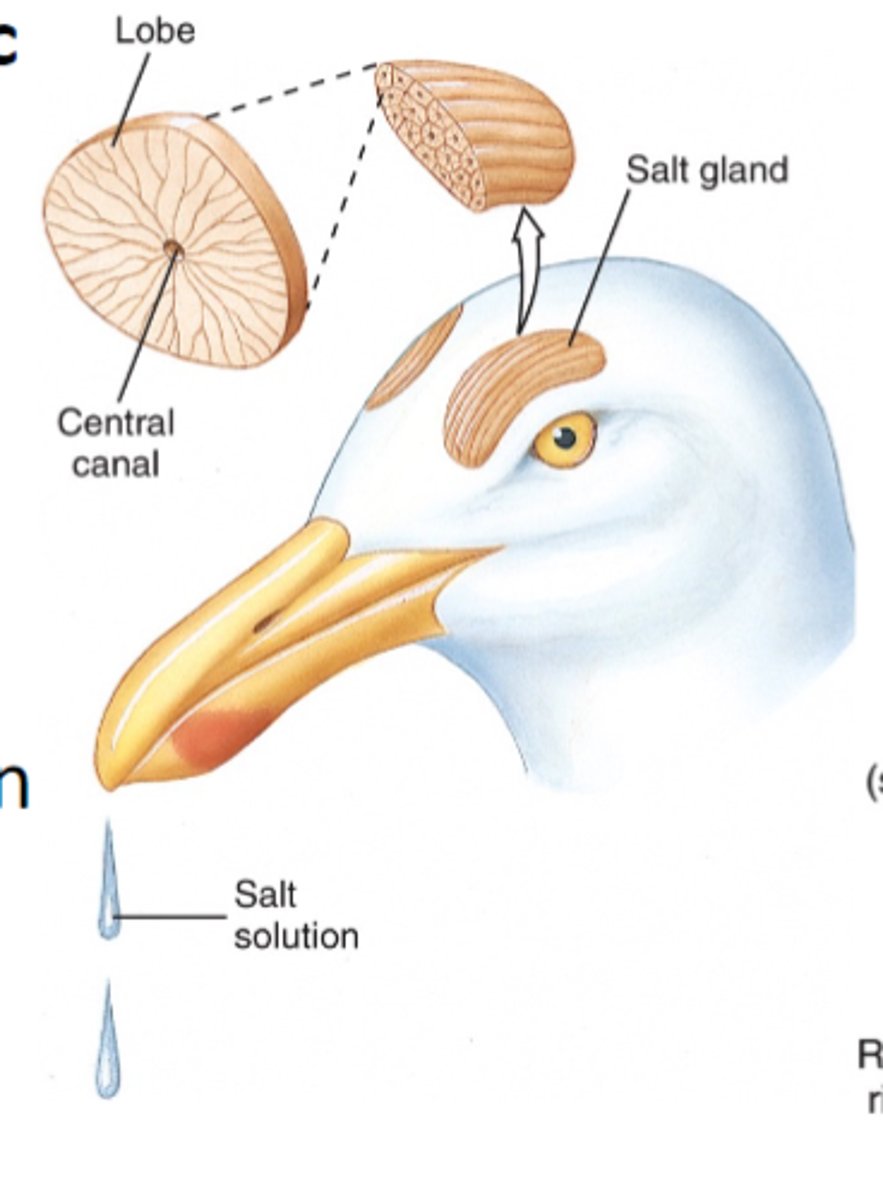
bird excretory system
excretion by metanephric kidneys in form of uric acid, salt glands may supplement kidneys in marine birds
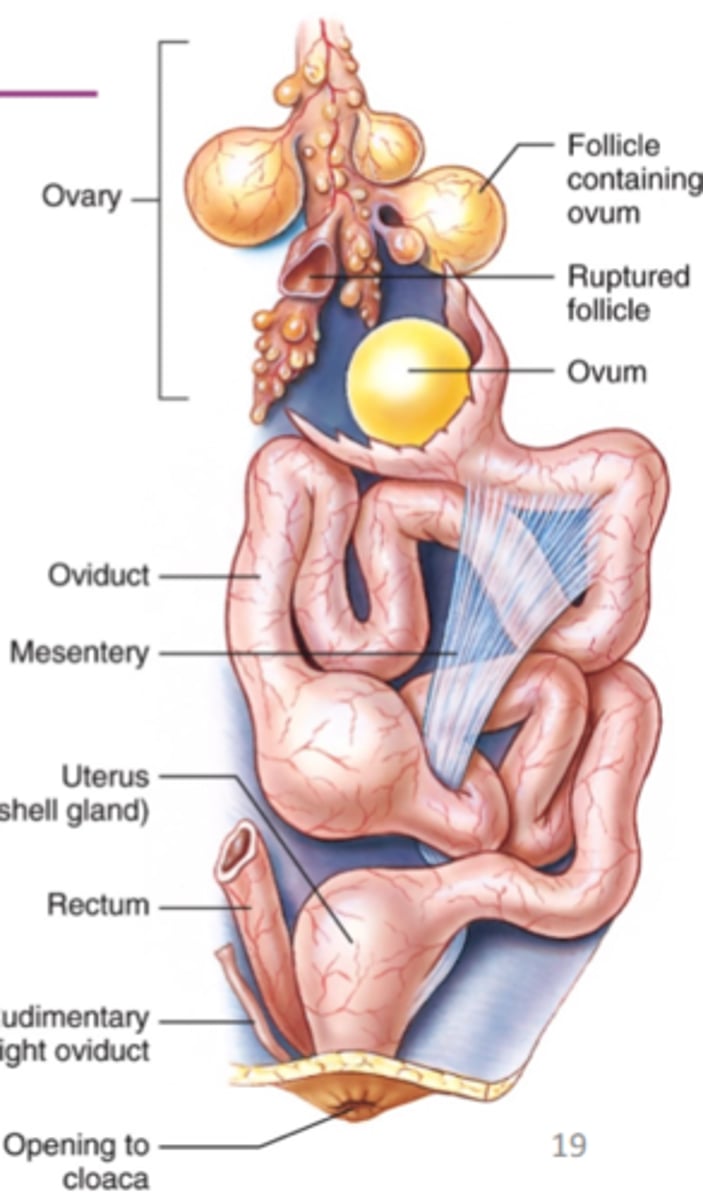
Bird reproductive system
ovary typically present on left side only, enlarges during reproductive season
1. pterosaurs 2. bats 3. birds
flapping (powered) flight evolved three times independently in what three vertebrates
angle of attack and camber
what two features generate lift
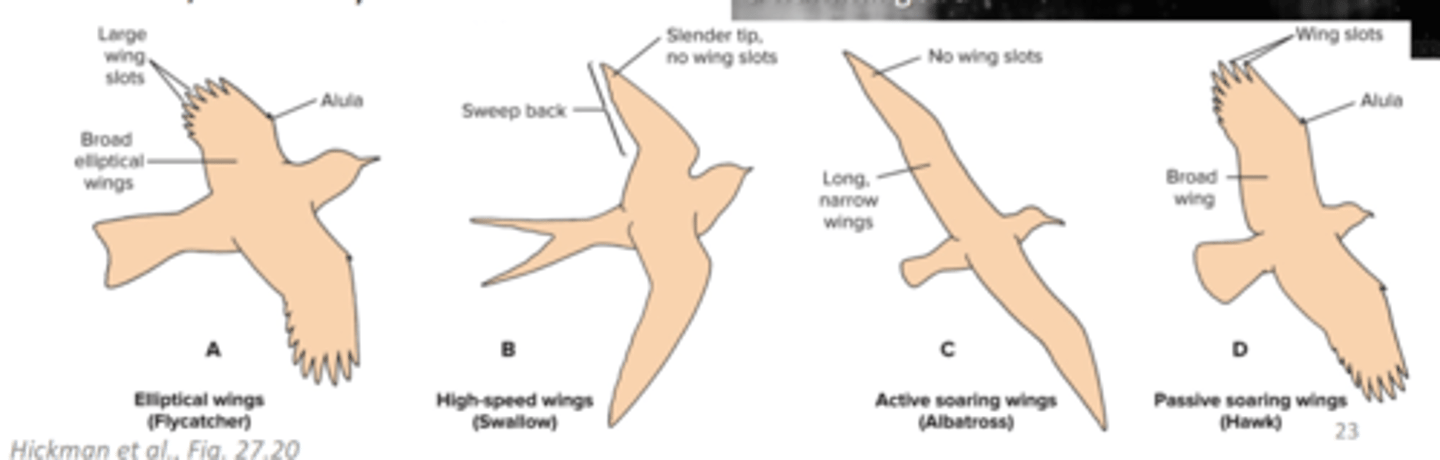
1. Elliptical (songbirds) 2. High speed (ducks and swallows) 3. Dynamic soaring (albatross) 4. High-lift or passive soaring (hawks and vultures)
what are the four types of wing forms
oviparous
are birds oviparous or viviparous
deforestation, pesticides, lead poisoning, and housecats
what are the major threats to birds