parasitism
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what percent of animals are parasites?
>50%
what is phoresis, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism?
phoresis- two symbionts travel together
- no harm
- no physiological or biochemical dependence
e.g. Fierasfer spp. which live on holothurians
mutualism- - no harm
- association is not obligatory (some dependence)
e.g. sunfish expose fins to seabirds
Commensalism - usually only one partner benefits
- no harm
- association is not obligatory (some dependence)
e.g. sea anemone and hermit crab
Parasitism - one partner lives at the metabolic
expense of its host, harm, obligatory dependence
what is parasitism in population terms?
Parasites are aggregated in
the host population
2) Large numbers of parasites
may kill their host.
3) A parasite has a higher
reproductive rate than its host
what is a facultative parasite?
can become parasitic if accidentally
ingested or enter an orifice/wound.
what is a definitive, intermediate, paratenic, reservoir host?
definitive- parasite reaches sexual maturity
intermediate- parasite develops & often reproduces asexually
paratenic-parasite undergoes no development but remains
infective to another host.
Reservoir-animal that harbours a parasite which can be
transmitted to humans
what is the difference between urban cycle and sylvatic cycle?
urban-domestic animals, sylvatic- wild animals
what is the difference between a mechanical and biological vector?
mechanical- no development, biological-development /replication
what is a major difference between macro and microparasties?
macro- transmission dependent upon specific transmission stages
what kind of disease is tuberculosis
bacterial
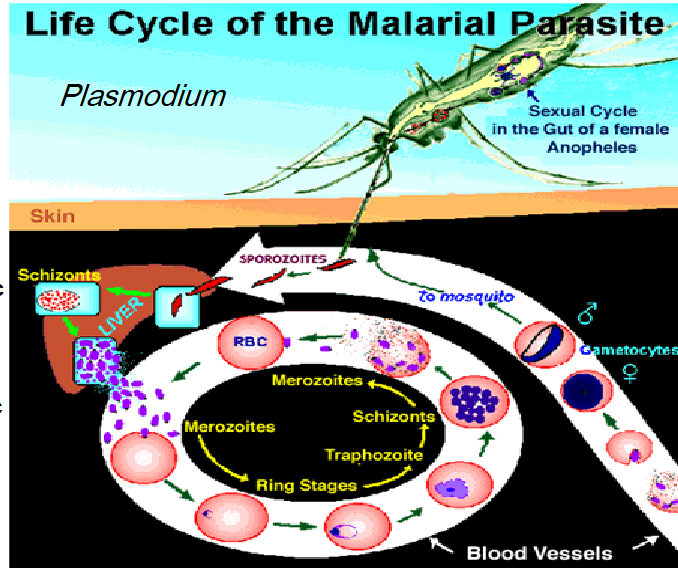
what are the stages of the life cycle of malarial parasite?
sexual- gametes fuse, form a sporocyst, inside which develops 1000’s sporozoites
Pre-erythrocytic cycle (liver) Asexual
Post-erythrocytic cycle (blood) Asexual & gamete formation - haemozoin (waste product)
what are some examples of macroparasites?
(flatworms) Platyhelminths: Monogenea- Entobdella, Trematoda-Schistosoma, Cetsoidea-tapeworms
Nematoda(round worms)- Trichinella
Arthropoda
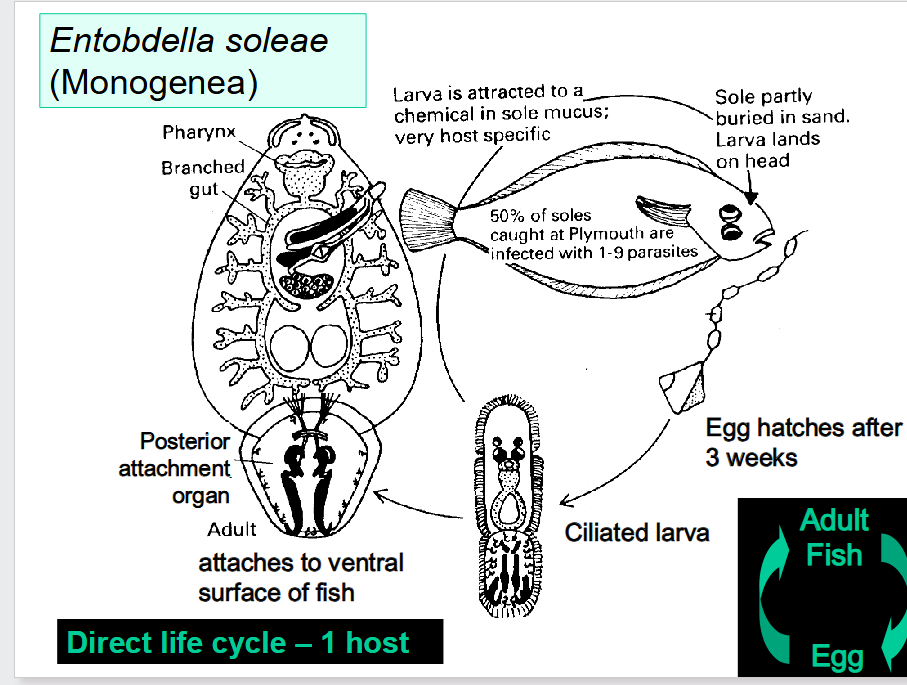
what is the life cycle of Entobdella solae
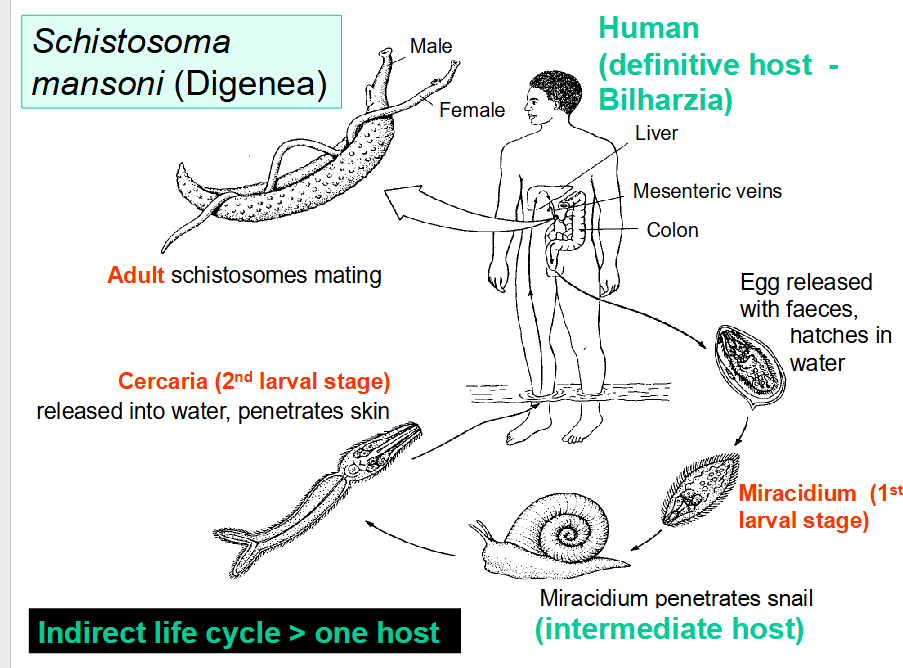
what is the life cycle of Schistosoma Mansoni
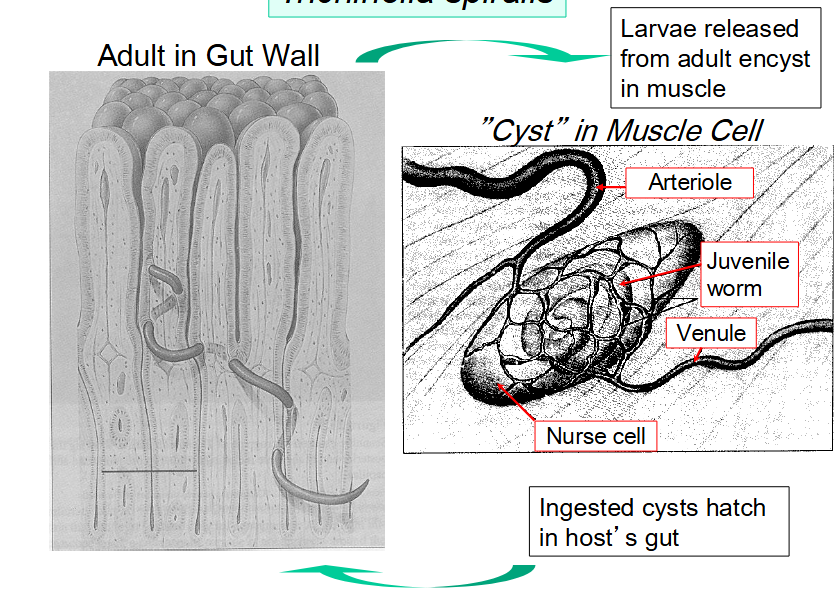
what is the life cycle of Trichinella spiralis
what are the characteristics of phylum platyhelminthes
-acoelomates, triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical
monogenea- direct life cycle
digenea- indirect (intermediate host)
cestoidea-indirect
what are the characteristics of Nematoda
endoparasites most with indirect life cycle
what do ideal parasites need
attachment
nutrition
evasion of immune response
reproduction
how do monogenean, digenean and cestode attach?
monogean-opistorhaptor (worm length <1mm-3cm)(has suckers, clamps, hooks/glands)
digenean- oral & ventral suckers (worm length 0.1mm-8cm)
cestode-scolex (worm length 2mm-40m)
what are the different methods of getting nutrition in macroparasites?
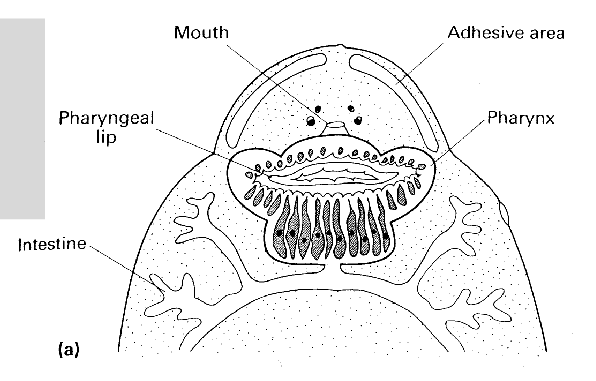
-surface browsing (entobdella)
-blood feeding (polystoma)
-bulk tissue feeding (Fasciolia juveniles)
-nutrient uptake across the body wall (cestode)
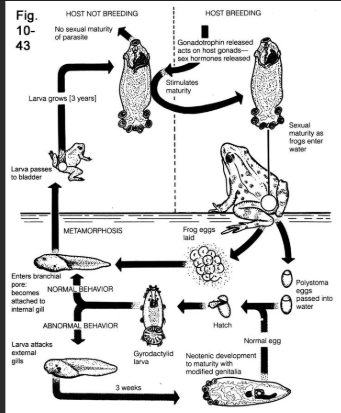
in Polystoma integerrimum, what is the difference between a slow growing adult and neotenic adult (dimorphic life cycle)
slow growing- 3yr to mature in frog bladder (1cm)
neotenic- 3 weeks to mature in tadpole gills (1/3 of size)
due to haematoiden crystals in neotenic gut (too much in blood)
what are some problems w blood feeding
Waste products of blood digestion
Lack of B vitamins
Clotting agents
Exposure to the host’s immune system
what are some morphological adaptations for nutrition?
increased SA: microthrix- in cestodes, microvilli- monogeneans, surface folds-all groups
modified mouthparts- cutting plates, penetration stylets in N. Americanus
what are some physiological and behavioural adaptations of these PARASITES?
1)Symbiotic micro-organisms to counteract Vitamin B
deficiency e.g. human body louse
2) Production of anticoagulants e.g. nematodes
3) Release of endogenous (parasite) enzymes &
binding of exogenous (host) enzymes
4) Acidification of the host’s gut through secretion of H+
5) Migration along the host’s gut
what is cross immunity?
immunity between species and genera
(although immunity is usually species-specific).
what are the 2 types of incomplete resistance?
Premunition - host recovers from disease & is resistant to
re-infection but some parasites remain & reproduce at slow
rate e.g. malaria.
Concomitant immunity - parasite elicits protection against
re-infection, but parasite itself remains unaffected by
immune response e.g. schistosomes
how does antigen polymorphism evolve in parasites?
e.g. seen in trypanosoma, malaria
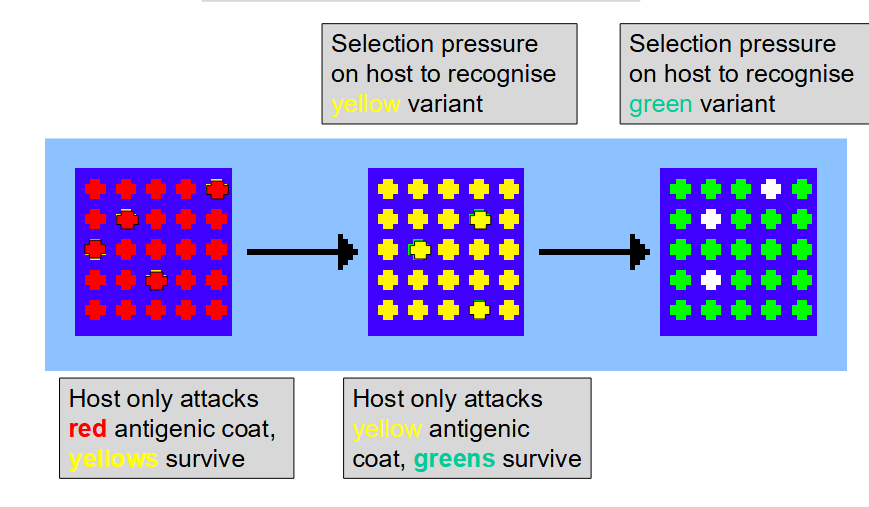
are parasites r-strategists or k-strategists
r, higher reproductive rate, can do asexual, parthenogenesis, sexual reproduction
what are some methods of avoiding immune response from the host?
1) Inaccessibility
2) Antigen disguise/mimicry
3) Antigen polymorphism e.g. Trypanosoma, malaria.
4) Shedding antigens e.g. Entamoeba (“Smoke screen”)
5) Immunomodulation of host (causing lymphocytes to
produce wrong cytokines, polyclonal B stimulation, inhibiting
macrophage activation) e.g. Leishmania causes cytokine
disruption.
6) Anticomplementary activity e.g. Entamoeba
what are the 3 methods of reproduction?
Oviparous - eggs released into the environment and develop outside
parent’s body e.g. Entobdella
Viviparous - embryos develop within parent’s body (no egg shell)
e.g. Gyrodactylus
Ovoviviparous - encapsulated embryos develop within parent’s body
e.g. Pseudodiplorchis (elongated uterus)
what are the pros to hermaphrodites?
Increases chances of finding a mate
2) Increases egg output
e.g. Taenia sagittata
(small worms > 2000 proglottids)
3) Potential for self-fertilization
what are the 2 types of sequential hermaphrodite?
protandry, protogyny
why would a parasite synchronise parasite and host reproduction
increases success of parasite transmission
what is the life cycle of Polystoma integerrium
what are the 4 ways of transfer
1) Contact Transfer e.g. Gyrodactylus (fish ectoparasite)
2) Ingestion of intermediate and/or paratenic hosts
- passive (e.g. ingestion) e.g. Trichinella spiralis
- active (modification of host behaviour)
e.g. Dicrocoelium dendriticum, Toxoplasma gondii
3) Release of egg/spores/cysts
4) Free living larvae
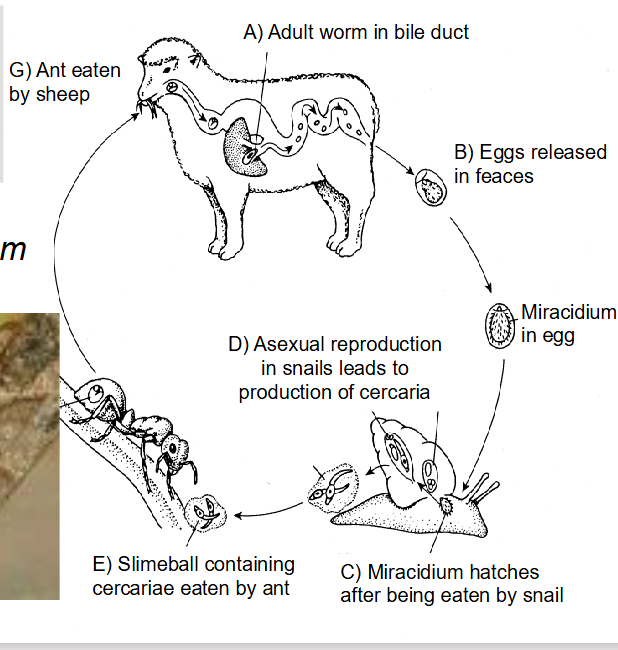
what is the life cycle of Dicrocoelium?
Toxoplasma gondii Life Cycle
Intracellular protist parasite, cats are definitive host
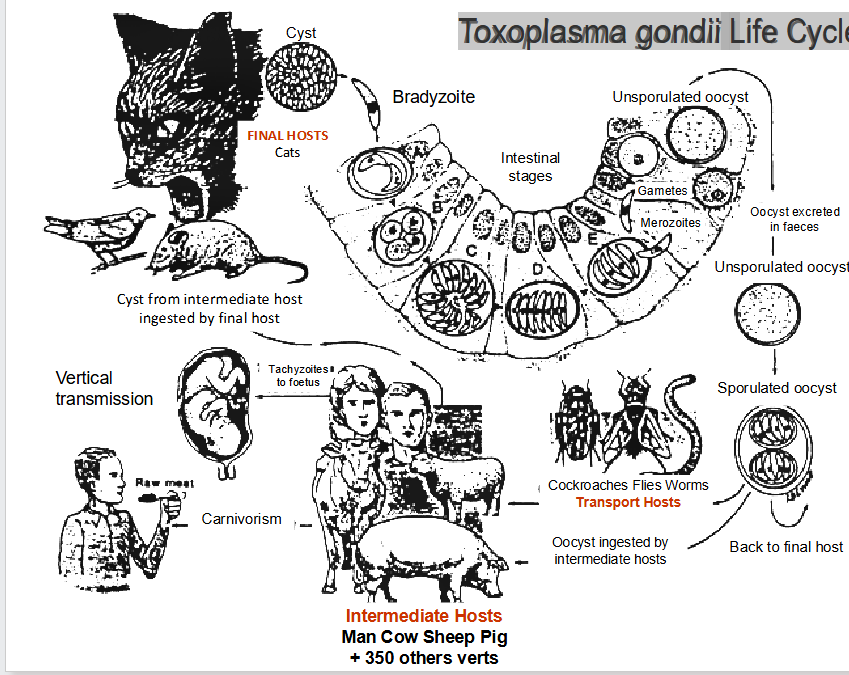
what % humans infected (toxoplasma?)
15-85% adult humans chronically infected = asymptomatic
what is the behavioural manipulation hypothesis
Behavioural manipulation hypothesis: a parasite will
specifically manipulate host behaviour essential for
enhancing its own transmission
• T. gondii infection converted the aversion to feline odours
into attraction
• But did not reduce learned fear, anxiety-like behaviour,
olfaction or non-aversive learning
what is the effect of Toxoplasma gondii on humans?
Infected males more impulsive, females more sociable,
Infected humans 6x more likely to be involved in road
traffic accidents
•More prone to feelings of guilt
•Infected women seem more intelligent, outgoing,
conscientious, sexually promiscuous & kind
•Opposite effect in men seem to cause opposite trends
-linked to schizophrenia- it increases dopamine production
for parasites to adapt what must they respond to?
• Discontinuity in space (hosts – oasis in desert)
• Discontinuity in time (hosts are mortal)
• Host immunity
• Host evolution (host population modifies over time)
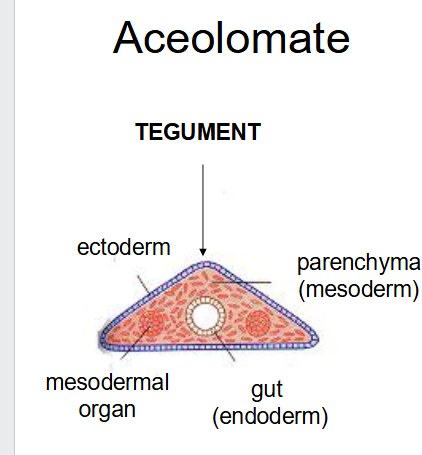
what have this body plan
-monogeneans
-cestodes (no gut)
-digeneans
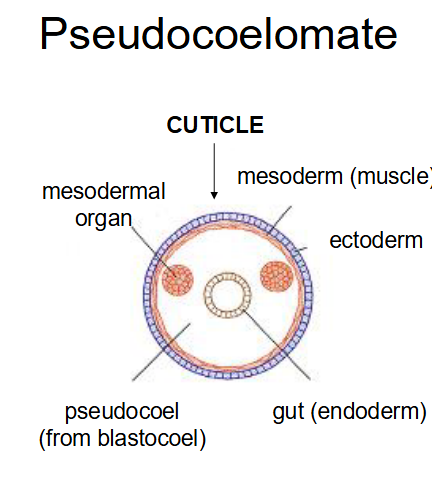
what have this body plan
-acanthocephalans
-nematodes
how did parasitism evolve?
preadaptation, then phoresis then facultative etc
how did Platyhelminths evolve?
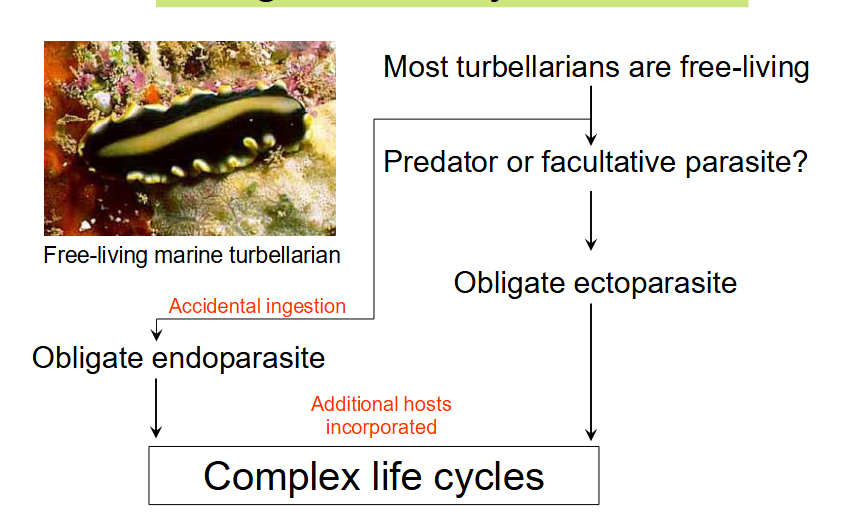
ever wondered y parasite life cycles r so goddamn complex?
-greater niche space for reproduction
-increase likelihood of transmission (having multiple intermediates in Dicrocoelium dendriticum)
what influence host-parasite associations?
-co-evolution
-host-switching
-continential drift and global events
-descent, colonisation, physical separation of populations
what are some of the oldest parasites?
• Digeneans in molluscs from the Miocene (10 mya)
• Tick (embedded in amber) from C. America 30
mya
• Copepods on marine fish 130 mya
• Helminths from shark 300 mya
• Monogeneans in placoderms 400 mya
• Parasite traces on trilobites 570 mya
oldest parasite is actually mitochondrion
what are some positives to parasites
-inverse relationship between allergies
and the presence of parasites
-maggots cleaning wounds
-whipworms may prevent Crohn’s disease (alter bacterial balance)
-probiotic worms perhaps prevent asthma