Atoms and Elements Review Packet Answer Key
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NGSS Chemistry 2024-2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What did John Dalton study
studied ratios in which elements combine in chemical reactions
Theory about atoms
all elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms
atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different
atoms of different elements combine in whole-umber ratios to form compounds
atoms of one element cannot be changed into atoms of another element through chemical means
J.J. Thomson discovered?
discovered cathode rays (electrons)
J.J. Thomson performed?
performed experienments that involved passing electric current through gases at low pressure
Who created plum pudding model of atoms
J.J. Thomson
What is plum pudding model of atom
atoms were solid with positive and negatives charges equally dispersed
Gold foil experiment, who?
Ernest Rutherford
gold foil experiment → shot alpha particles at gold foil
Ernest Rutherford concluded…
most alpha particles went through the gold foil and some were deflected
concluded that the atom was made up of mostly empty space except for a small, dense, positively charged center (nucleus)
Who made planetary model of the atom and what is it about
Neils Bohr
electrons arranged in concentric circles around the nucleus
Neils Bohr discovered ?
electrons in a particular path have a fixed energy, so the electron will not fall into the nucleus
Who made quantum mechanical model of atom and what is it about
Irwin Schrodinger
quantum mechanical model of the atom - only the probable location of an electron can be determined
Irwin Schrodinger used what
used quantum theory to solve a mathematical equation describing the location and energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom
describe how the periodic table is arranged
arranged by increasing atomic number
elements in the same group/family exhibit similar physical and chemical properties
periodic law
when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of the physical and chemical properties
describe metals
siny
conduct heat and electricity
ductile
malleable
describe alkali metals
shiny
most reactive metals
not found freely in nature
soft, can be cut with a knife
soluble in water
rapid reactions with oxygen and water
describe alkaline earth metals
gray-white luster
less reactive than alkali metals
harder than alkali metals
less soluble in water
less reactive than alkali metals
describe transition metals
exhibit typical metallic properties (ductile, malleable, luster, good conductors of heat and electricity)
describe metalloids
elements with properties of both metals and nonmetals
describe nonmetals
non lustrous
poor conductors of heat and electricity
describe halogens
very reactive (fluorine most reactive nonmetal)
not found freely in nature
describe noble gases
unreactive
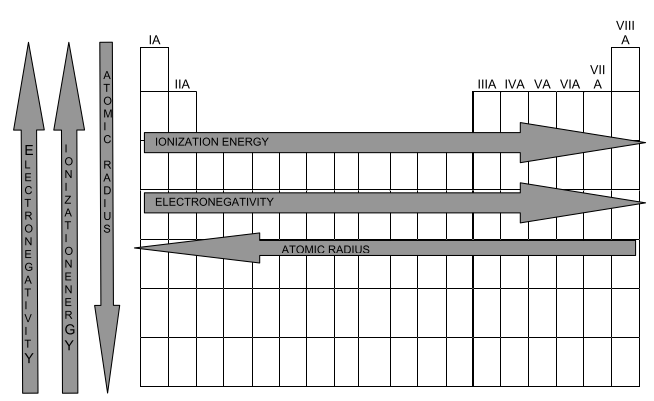
electromagnetically, ionization energy, atomic radius