AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.13: Amino acids, proteins and DNA
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the two functional groups present in amino acids? (1)
- Amine group (-NH₂)
- Carboxylic acid group (-COOH)
What is unique about the side chain (R) in amino acids? (1)
The alkyl side chain (R) is different for each amino acid
What is a zwitterion, and at what pH does it form? (1)
- A zwitterion is a molecule with both positive and negative charges.
- It forms at neutral pH
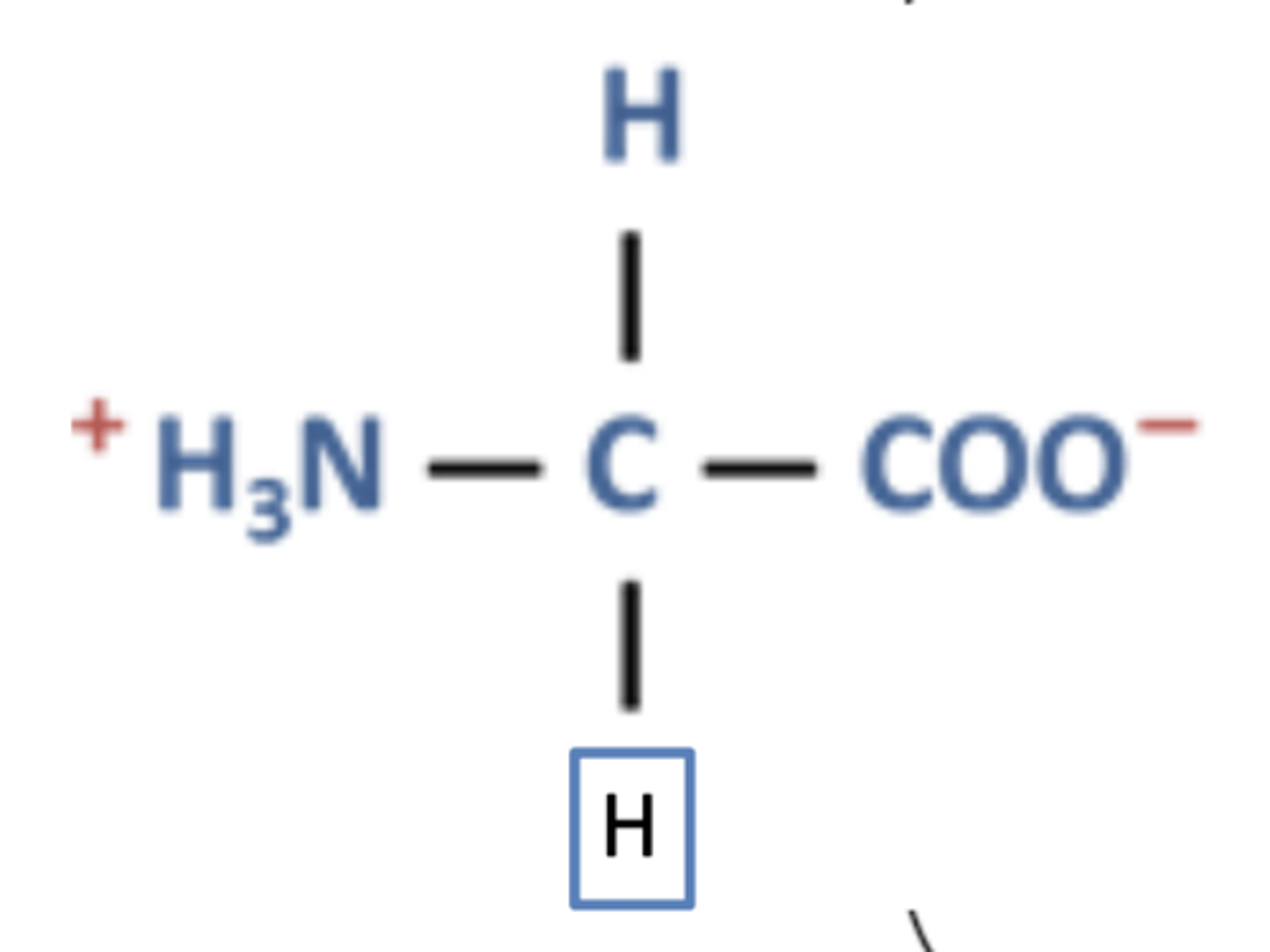
Why are zwitterions solid at room temperature? (1)
Due to strong ionic interactions between molecules
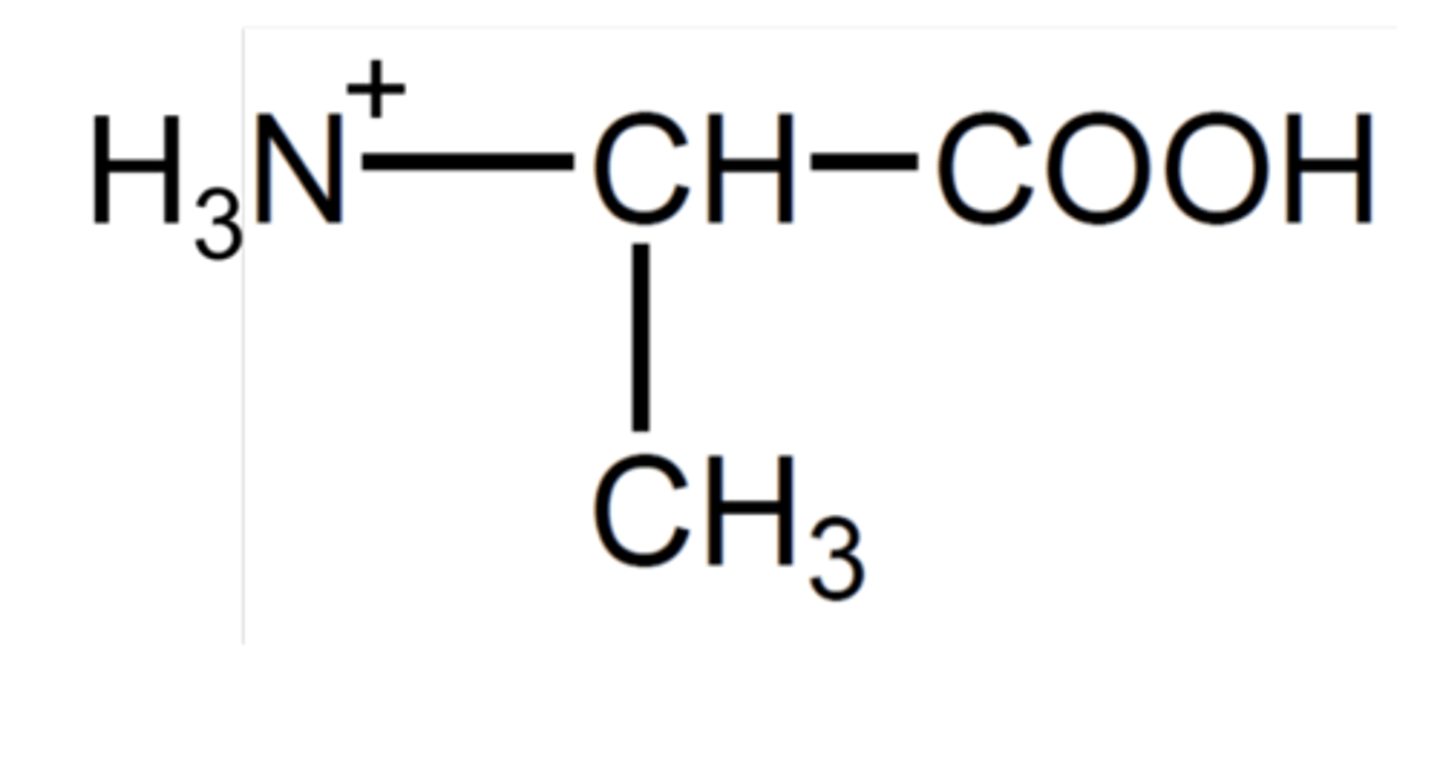
How does the amine group react with acids? (1)
The amine group is protonated by acids
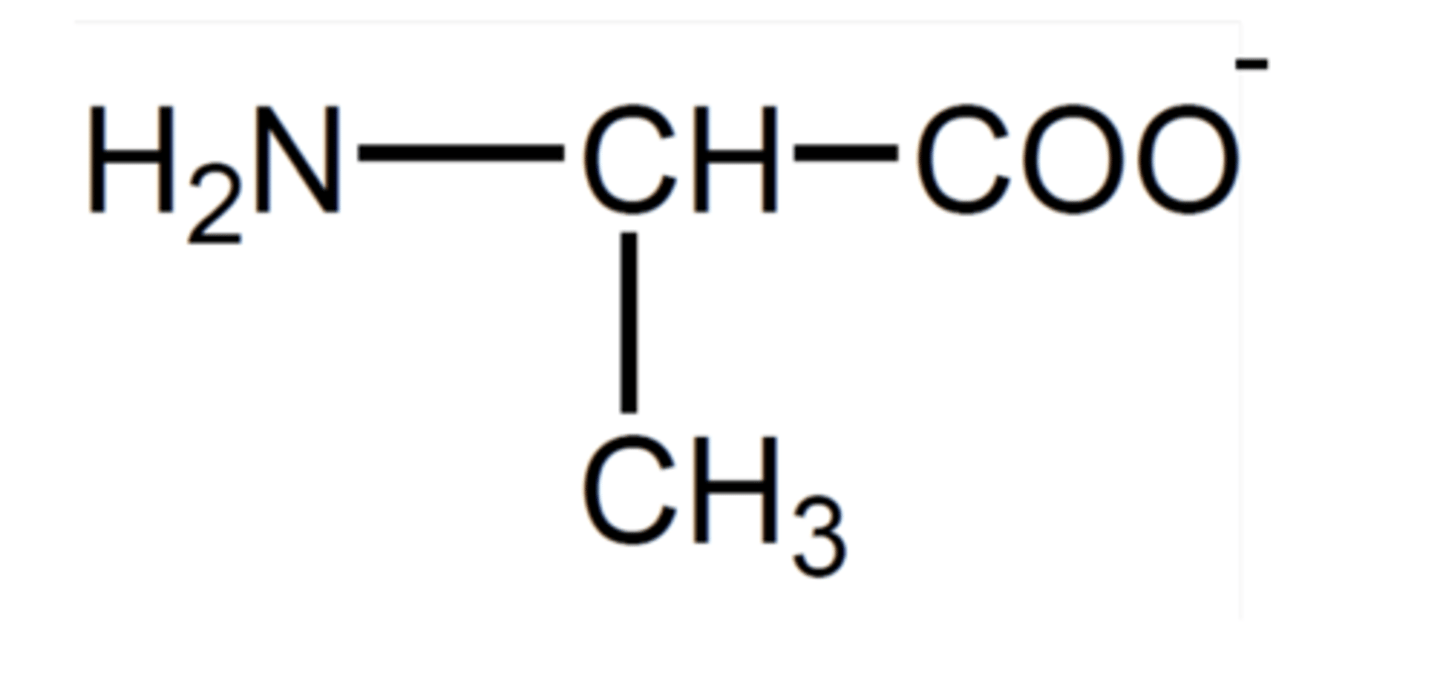
How does the carboxylic acid group react with bases? (1)
The carboxylic acid group is deprotonated by bases
What reaction occurs between the carboxylic acid group and alcohols? (1)
- The carboxylic acid group reacts with alcohols to form esters
- With an acid catalyst
What reaction can the amine group undergo with acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides? (1)
Acylation reactions
What are two amino acids bonded together by a peptide bond called? (1)
Dipeptide
What are three amino acids bonded together by a peptide bond called? (1)
Tripeptides
What are many amino acids bonded together by a peptide bond called? (1)
Polypeptides
What is the primary structure of a protein? (1)
The sequence of amino acids covalently bonded to form the polypeptide chain
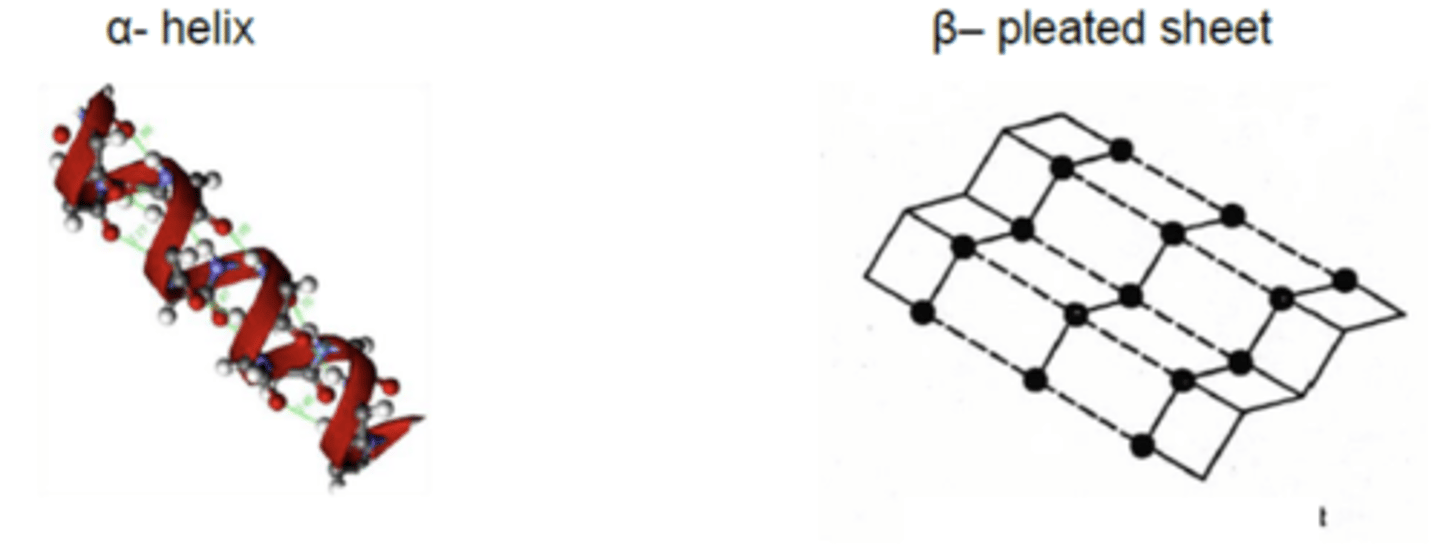
What is the secondary structure of a protein formed by? (1)
Hydrogen bonding between backbone atoms
What are the two examples of secondary structure of a protein? (2)
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in the tertiary structure of a protein? (2)
- Hold the polypeptide chains together
- By forming between the C=O group of one amino acid and the N-H group of another
What causes disulfide bridges to form in proteins? (2)
- Through the oxidation of two cysteine amino acids
- Resulting in a covalent bond between their sulfur atoms
What are enzymes? (2)
- Enzymes are proteins with an active site that is stereospecific
- Interacting only with one enantiomer
What is an enzyme-substrate complex? (1)
It is a complex formed when an enzyme binds to its specific substrate
What is the function of enzyme inhibitors? (1)
Enzyme inhibitors block the active site of enzymes and prevent their function
What are the components of a nucleotide in DNA? (3)
- A phosphate ion bonded to
- 2-deoxyribose (sugar), which is in turn bonded to
- One of the four bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, or thymine.
How are nucleotides joined together in DNA? (2)
- Nucleotides are joined together in a condensation reaction
- Forming a sugar-phosphate backbone and losing water during the process
What is cis-platin? (1)
Cis-platin is a square planar complex used in chemotherapy treatmen
How does cis-platin disrupt DNA replication? (1)
- Cis-platin bonds with guanine and disrupts DNA replication
- Which kills the cells
What happens to the chloride ligands in cis-platin when it binds to DNA? (1)
The chloride ligands are replaced by guanine base
How does the nitrogen atom of guanine interact with cis-platin? (1)
The nitrogen atom uses its lone pair to form a coordinate bond with the platinum in cis-platin
What happens when cis-platin reacts with water inside the body? (2)
- One chloride ligand is replaced by a water molecule
- Forming [Pt(NH₃)₂Cl(H₂O)]⁺ and Cl⁻ as a by-product
What is the reaction when cis-platin reacts with water inside the body? (2)
[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] + H2O → [Pt(NH3)2Cl(H2O)]+ + Cl-
Why can't trans-platin function like cis-platin? (1)
- The chloride ligands are on opposite sides of the complex
- Preventing effective interaction with DNA
What other fast-multiplying cells are affected by cis-platin treatment? (1)
- White blood cells
- Gametes
- Hair cells
What are the side effects of cis-platin treatment? (3)
- Immune system suppression
- Fertility issues
- Hair loss
Which nitrogen atoms on guanine can form a coordinate bond with cis-platin? (1)
Either of the nitrogen atoms with a lone pair NOT involved in bonding to cytosine
How can cis-platin be administered to minimise its side effects on healthy cells? (1)
Use in very small amounts or target the application to the tumour