Midterm 2 combined
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
Load
A force exerted by a weight
Tension
opposing force from muscle contraction
slow oxidative
aerobic, low power, fatigue resistant, sustained activity
slow myosin ATPase + SERCA activity
small diameter
high capillary density
high myoglobin content
more prominent color if applicable
fast glycolytic characteristics
anaerobic glycolysis, produce high power, rapid contractions, use low mitochondria, myoglobin, & capillaries
prone to fatigue, ideal for short bursts of energy
large diameter
pale color if applicable
Muscle fatigue
inability to contract even when muscle is receiving stimulus
muscle fiber starts fatigue when running low on ATP
Motor unit
single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates, which work together to produce muscle contractions
each muscle fiber is innervated by only one neuron
one motor neuron can innervate up to hundred of muscle fibers
when one lower motor neuron fires, all the muscle fibers in a motor unit contract tg
one muscle contains many motor units
Flexion
is the bending of the biceps
flexors shorten
Extension
extension of the biceps
extensors shorten
isometric contraction
builds tension in muscle, tension=load, first phase, lift & counterbalance weight
concentric contraction
muscle shortens, tension>load, second phase
eccentric contraction
muscle lengthens (generate tension while lengthening, elongating), tension<load, third phase
Factors affecting muscle tension
Number of motor units recruited
Frequency of stimulation of each motor unit
Resting sarcomere length before contraction
Size of muscle fibers in the motor units
How is motor unit recruitment used to regulate muscle tension?
regulates muscle tension by CNS, small, weaker motor units are activated first, then larger & stronger forces are added as force is needed
more motor units being activated —> more tension
how is action potential frequency used to regulate muscle tension
If APs are far apart in time, there’s 2 separate twitches
If APs are closer, second contraction begins before first relaxation finishes (temporal summation)
More motor units getting activate means …
more tension
Single muscle twitches
If the APs are far apart in time, we observe 2 diff twitches
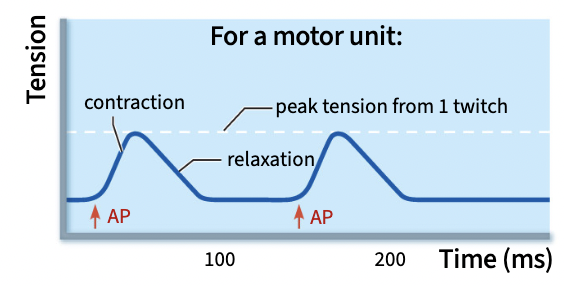
Temporal summation
If the APs are closer, the second contraction begins before the first relaxation finishes
contractions build open each other, refractory period is shorter than the time it takes the muscle to fully relax
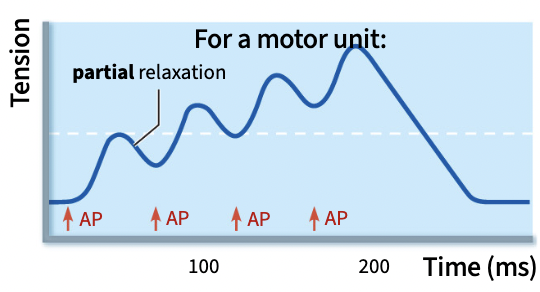
unfused tetanus
if frequency is higher still, muscle reaches this steady state, allows muscle to maintain a constant tension, go back & forth btwn partial contraction & relaxation
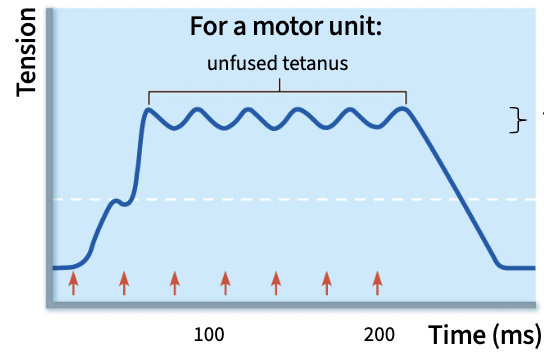
Fused tetanus
if frequency is super high, muscles reaches this rly rare, no relaxation, rapid fatigue stage,
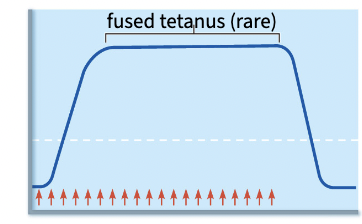
the larger the muscle fibers within a motor unit, the more _______________
tension they produce
Muscle fiber size influences tension by increasing _______________ and therefore the total ___________________
the number of sarcomeres & force-generating potential
how does the length-tension relationship and muscle fiber size influence the generation of muscle tension?
Optimal resting length is a maximum possible tension (peak)
Overly contracted: lower length in graph, little tension
Overly stretched: too loong, little tension
Autonomic Nervous system
neurons that innervate our internal organs
self-governing
many ANS organs are under antagonistic control by ….
sympathetic & parasympathetic divisions
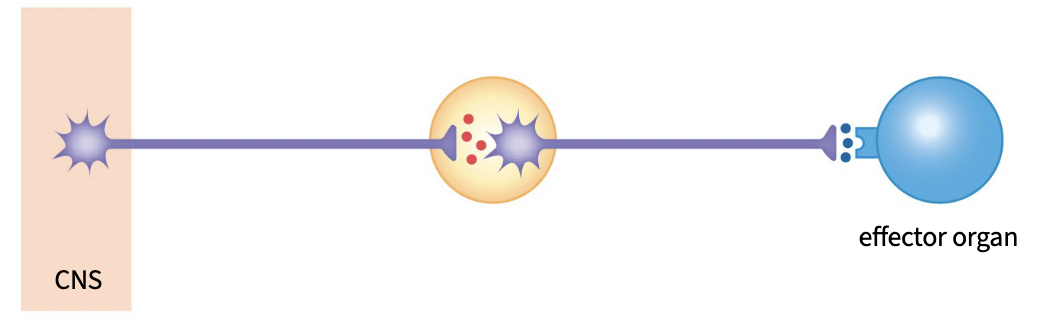
Label (L to R)
preganglionic neuron, autonomic ganglion, postganglionic neuron, neuroeffector junction, effector organ (like smooth or cardiac muscle)
neuroeffector junction
synapse btwn postganglionic neuron & effector neuron
steps of neuroeffector junction function
Action potential arrives
Depolarization opens VG Ca2+ channels
Ca2+ triggers vesicle exocytosis
Neurotransmitter binds receptor
Neurotransmitter diffuses away after
some timeVaricosity reuptakes neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter is recycled for the future
Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions differences
1. neurotransmitter used at each synapse
2. preganglionic neuron’s point of origin in the CNS
3. location of the autonomic ganglion
neurotransmitters and receptors involved in the sympathetic
preganglionic: acetylcholine & nicotinic receptor
postganglionic: norepinephrine & adrenergic receptor (ionotropic)
neurotransmitters and receptors involved in the parasympathetic
preganglionic: acetylcholine & nicotinic receptor
postganglionic: acetylcholine & muscarinic receptor (metabotropic)
vagus nerve
consists of 80% of a parasympathetic axons
part of vagus nerve that innervate upper body (above hip), originates from:
brain stem
part of vagus nerve that innervate lower body (hip & below), originates from:
sacral region of spinal cord
part of sympathetic NS that innervate upper body (above hip level), originates from:
thoracic part of spinal cord
part of sympathetic that innervate lower body (hip & below), originates from:
lumbar region of spinal cord
distance of sympathetic & parasympathetic to spinal cord
SNS: near, form sympathetic chain
PSNS: far, close to target organ
adrenal glands
where some preganglionic neurons synapse in & produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions
consist of chromaffin cells (post ganglionic)
what type of control is the smooth muscle making up blood vessels under?
sympathetic control
3 subtypes of adrenergic receptors
alpha 1
beta 1
beta 2
bind E & NE
characteristics of alpha 1
expressed by: smooth muscle
promotes contraction
cause vasoconstriction, blood vessels tighten, increase bp, happens by catecholamines like NE & E
characteristics of beta 1
expressed by: cardiac muscle
promotes contraction
increase heart rate & contractility, increasing cardiac input & bp
characteristics of beta 2
expressed by: smooth muscle
promotes relaxation
causes vasodilation, widens blood vessels to increase blood flow to tissue
similarities & differences of smooth muscle and skeletal muscle in contraction
like: contraction is triggered by an increase in cytosolic Ca2+
unlike: no AP is required for contraction, Ca2+ comes from both SR & extracellular space, has less Ca2+ stored in SR
mechanisms where calcium can enter smooth muscle cells, explain
Hormone/NT pathway
a. hormone/NT bind to GPCRs, GPCR activate second messenger, second messenger opens Ca2+ channels linked to G-protein pathways, —> Ca2+ entry
b. hormone/NT bind to GPCRs, GPCR activate second messenger, second messenger opens Ca2+ channels in SR, —> Ca2+ release in cytosol (intracellular)
Mechanical Stretch Pathway
mechanical stretch opens mechanically gated Ca2+ channel —> Ca2+ entry
how does Ca2+ cause smooth muscle contraction
cytosolic Ca2+ concentration rises
Ca2+ binds calmodulin
Ca2+- calmodulin complex activate MLCK
MLCK phosphorylate myosin light chain (enhance ATPase activity, hydrolyze ATP), myosin & actin form cross-bridges
what does ATP hydrolysis do in muscle contraction
Reset crossbridge cycle
Energize myosin
Baseline ATPase activity is very low & must be enhance for contraction to occur
How does Ca2+ cause muscle relaxation
cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations falls
pumped out of cell
pumped into SR thru SERCA
Ca2+ unbind from calmodulin, MLCK inactivates
MLCP dephosphorylates myosin light chain
Myosin ATPase activity decreases, & myosin returns to an inactive state
balance between _____________ and _______________ activity is one of the main regulators of contraction
MLC kinase & MLC phosphatase
MLC kinase activity is enhanced by the ___________
Ca2+ calmodulin complex
MLC phosphatase activity is regulated by various ____________
G-protein-coupled pathways
Both alpha 1 & Beta 2 are …
GPCRs
more ca2+ will lead to ______ of myosin light chain
more, so much that it eventually caps off
more Ca2+ —> more phosphorylation —> more tension
how autonomic regulation through the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors influences smooth muscle contraction
PKC phosphorylates & opens Ca2+ channel (TRPC) —> Ca2+ entry
G protein pathway leads to opening of Ca2+ channels on membrane
SR binds IP3 gated Ca2+ channels —> Ca2+ release intracellu
how autonomic regulation through the beta-2 adrenergic receptors influences smooth muscle relaxation
PKA can phosphorylate SR & prevent binding to IP3
PKA activates MLCP
Characteristics of smooth muscle
contractile unit: actin & myosin
source for Ca2+ for contraction: extracellular fluid & SR
site of Ca2+ regulation: calmodulin in cytosol
branch of NS that regulate contraction: ANS
effect of stimulation by NS: contraction or relaxation
relative spd of contraction: slow
presence of gap junctions: yes, in some organs
Characteristic of Skeletal muscle
contractile unit: actin & myosin
source for Ca2+ for contraction: SR
site of Ca2+ regulation: troponin on thin filaments
branch of NS that regulate contraction: SNS
effect of stimulation by NS: contraction
relative spd of contraction: fast
presence of gap junctions: no
peptide/protein hormones
made of linked AA, large & hydrophilic
ex: insulin, glucagon, growth hormone, prolactin
steroid hormones
derived from cholesterol, small & hydrophobic
ex: cortisol, testosterone, estrogen, & progesterone
amine hormones
made of modified AA, small & hydrophobic/hydrophilic
ex: dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, thyroid hormone
catecholamine: adrenal gland, more hydrophilic, cell surface
thyroid gland: thyroid gland, more hydrophobic, intracellular
Peptide hormones characteristics
Source: most glands (pituitary, pancreas, & parathyroid )
Synthesis & storage: Made in rough ER, post-translational modifications in Golgi, stored in vesicles
Transport: soluble in blood, degraded after a few mins by enzymes
Mechanism of action: Bind to cell-surface receptor, typically GPCRs
Steroid hormones characteristics
Source: adrenal glands, testes, & ovaries
Synthesis & storage: Made in smooth ER, diffuse out almost immediately
Transport: not soluble in blood, bound to protein carriers, shield hormone from degradative enzymes
Mechanism of action: Diffuse into cells & bind intracellular/ intranuclear receptors
exocrine gland
when contents are secreted into a duct
ex: sweat gland
hormone
chemical messengers secreted in bloodstream
nontropic hormone
hormone acts on peripheral target cells
tropic hormone
hormone that stimulate another endocrine gland to secrete its own hormone
hormones characteristics
endocrine system, hormones are released in body for general distribution, widespread effects, reacts more slowly, GPCRs or intracellular steroid receptors
neurotransmitters characteristics
nervous system, release NT at synapses onto specific target cells, local & specific effects, fast
endocrine gland
no duct needed, contents secrete directly to extracellular space
secrete hormones
ex: adrenal gland
Amine hormones characteristics
Source: adrenal & thyroid gland
Synthesis: Made in cytosol, from modifying AA like tyrosine
what part of the brain regulate hormone release?
hypothalamus
Simple endocrine reflex
endocrine cell (gland) directly senses a stimulus and responds by secreting a hormone, regulate hormone release, occur at the level of the gland
hypothalamus
main integrating center for hormone release, regulate
pituitary gland
regulates many of the organs of the body
anterior pituitary
linked to hypothalamus by blood vessels (portal system)
portal system
local blood vessel networks that connect 2 nearby structures
steps of hormone release in anterior pituitary
neurons in hypothalamus release hormones
hormones travel thru portal system to anterior pituitary
endocrine cells of anterior pituitary release their own hormones
posterior pituitary
axons from the hypothalamus extend directly into the
posterior pituitary
not a true gland, dont have its own hormone producing cells
steps of hormone release in posterior pituitary
neurons in hypothalamus make hormones
hormones are stored in vesicles in axon terminal
neurons release hormones to rest of body
Non-tropic hormones released in pituitary gland directly exert effect on…
tissues of the body
ADH/vasopressin
nontropic, posterior pituitary hormone that affects osmolarity, water secretion
simple endocrine feedback loop
take place at the level of the gland
substance being regulated is source of feedback
complex endocrine feedback loop
involve coordination by hypothalamus
tropic, the downstream hormone is source of feedback
nontropic, depends on specific hormone & specific effect achieved
adrenal gland medulla
synthesize epinephrine
adrenal gland cortex
synthesize cortisol
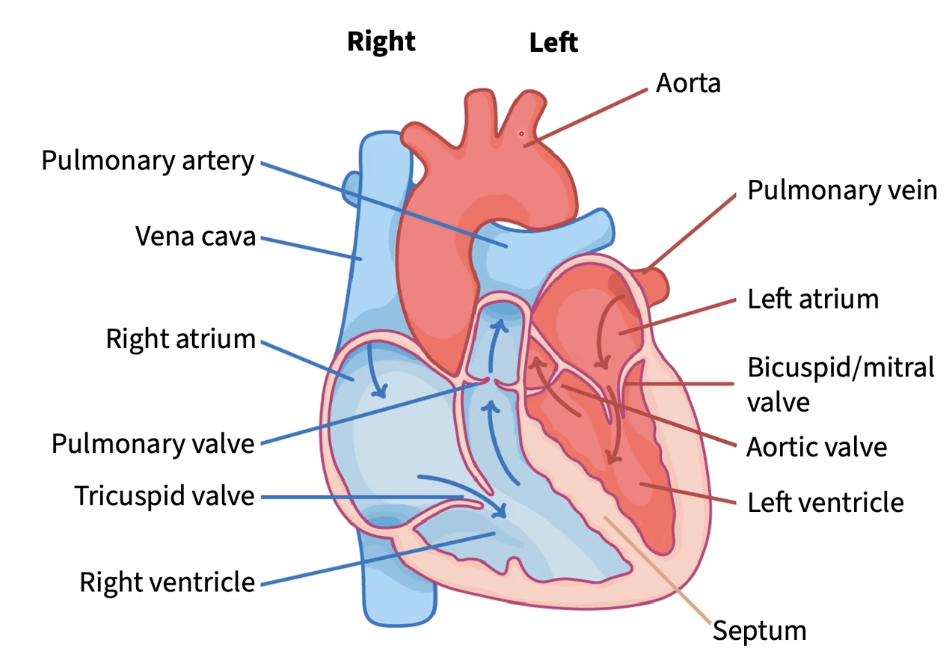
cardiovascular system 2 major divisions
systemic division & pulmonary division
pulmonary division
R side of heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange & returns blood to heart
systemic division
L heart, pumps oxygenated blood thru aorta rest of the body and return blood in oxygen derived state
heart in cardiovasc system
central pump, w/ R & L sides working in parallel
blood vessels in cardiovasc system
tubes that carry blood
ex: arteries, veins, & capillaries
blood in cardiovasc system
fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, & waste
valves
ensure unidirectional blood flow
fast oxidative glycolytic
aerobic & anaerobic, intermediate, higher tension contraction, moderate fatigue resistant contractions, moderate intensity
medium myosin ATPase + SERCA activity
medium diameter
medium capillary density
medium myoglobin content
more moderate color if applicable
arteries
carry blood from heart
aorta
largest artery
coronary artery
supply blood to heart muscle itself
vein
carry blood twds heart
vena cava
largest veins
vena cava splits into:
superior & inferior
each artery branches into many _________, which in turn branch into __________
arterioles & capillaries
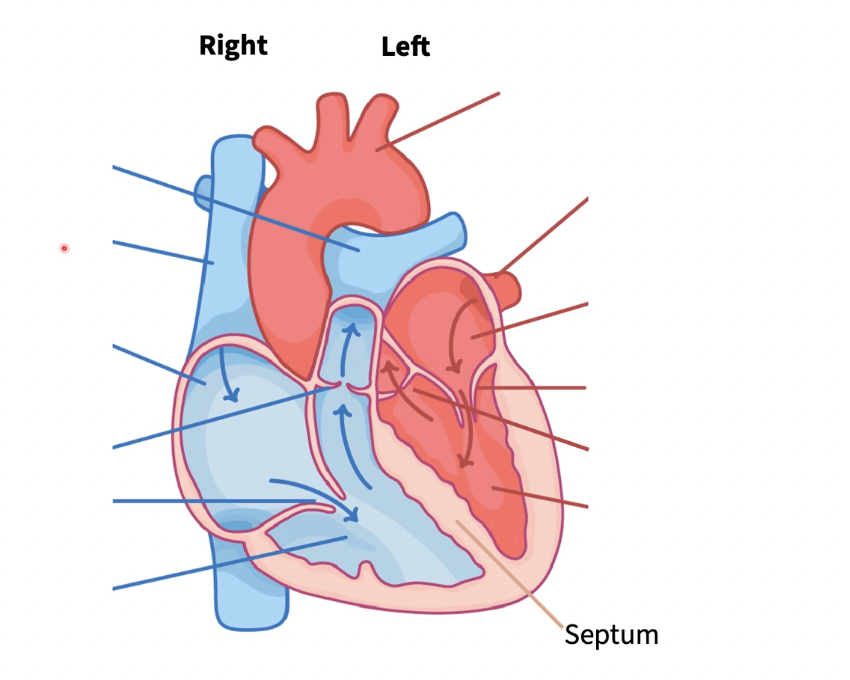
label (r to l)