A&P test 5 chapters 12 and 13 review
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
functions of the central nervous system (CNS)
process and coordinate sensory data, motor commands, and higher brain functions
functions of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
deliver sensory information to the CNS, and carry motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems
components of the CNS
spinal cord, brain, blood vessels, and neural and connective tissues
components of the PNS
all neural tissue that isn't part of the CNS
Which nervous system controls skeletal muscles?
central nervous system (CNS)
function of neuroglia (glial cells)
support and protect neurons
oligodendrocytes
1 of 4 types of neuroglia. small cell bodies with few processes that contact the other neuron cell bodies
ependymal cells
1 of 4 types of neuroglia. form epithelium called ependyma, and line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain (these do a lot with cerebrospinal fluid)
microglia
1 of 4 types of neuroglia. smallest and least numerous, with many fine-branched processes. migrate through neural tissue and clean up cellular debris, etc
What are the most abundant class of neuron in the CNS?
interneurons (located between sensory and motor neurons) (distribute sensory information and coordinate motor activity, also involved in higher functions)
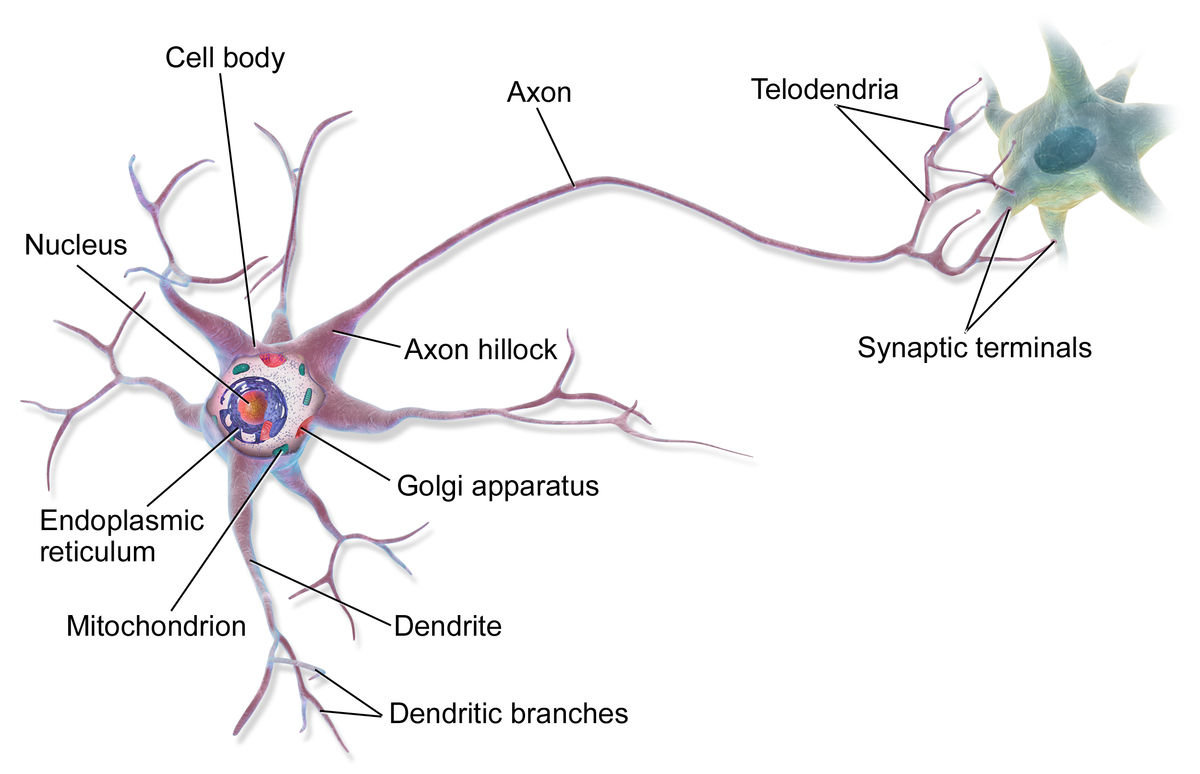
telodendria
fine extensions of distal axon
passive channels
AKA leak channels. they are always open and their permeability changes with conditions
active channels
AKA gated channels. most are closed at resting potential, but all open and close in response to stimuli
all-or-none principle
the initiation of action potential (if a stimulus exceeds the threshold amount, the action potential is the same, no matter how large the stimulus is) (the action potential is either triggered or it isn't)
action potential
electrical signals that transport information through the nervous system
type A fibers
a classification of axon. myelinated, large diameter, HIGH speed (140 meters per second), carry rapid information to and from the CNS (ex. position, balance, touch, and motor impulses)
type of neurotransmitter released from Cholinergic synapses
acetylcholine (ACh)
cholinergic synapses
any synapse that releases ACh
type of neurotransmitter released from Adrenergic synapses
norepinephrine (NE)
the effect that a neurotransmitter has on the postsynaptic membrane depends on what?
the receptor of the neurotransmitter (not the neurotransmitter itself)
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials (EPSPs) occur when:
sodium channels open in response to a stimulus, depolarizing the postsynaptic membrane and making its charge more positive
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials (IPSPs)
hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane (when its charge becomes more negative)
neuroglia
glial cells, support and protect neurons, account for about half of the volume of the nervous system
In the spinal cord, white matter is separated into ascending and descending tracts organized as what?
columns (anterior, posterior, lateral)
ascending tracts
carry information to the brain
descending tracts
carry information to the spinal cord
spinal meninges
specialized membranes that isolate the spinal cord from its surroundings, protect the spinal cord, and carry blood supply
What is the name for the outward projections from the central gray matter of the spinal cord?
gray horns
Ventral spinal nerves are: motor, sensory, both, or neither?
motor
Dorsal spinal nerves are: motor, sensory, both, or neither?
sensory
Which muscle areas does the cervical plexus innervate?
neck, thoracic cavity, diaphragmatic
Which muscle areas does the sacral plexus innervate?
posterior thigh, lower leg, foot
plexus
network of nerves
Ways to classify reflexes
by early development, by type of motor response, by complexity of neural circuit, and by site of information processing
functions of tendon reflexes
prevent skeletal muscles from developing too much tension and tearing or breaking tendons
flexor reflex
type of withdrawal reflex (moves body part away from pain or pressure stimulus) (ex. pulling your hand away from a hot stove)
reciprocal inhibition
allows the flexor reflex to work by inhibiting the stretch reflex of the antagonistic (extensor) muscle
dura mater
outer layer of spinal cord, touch and fibrous
arachnoid mater
middle meningeal layer of the spinal cord, covered by arachnoid membrane
pia mater
innermost meningeal layer of the spinal cord, mesh of collagen and elastic fibers, bound to underlying neural tissue
meningitis
viral or bacterial infection of the meninges
epineurium
outer connective tissue layer of spinal nerves, dense network of collagen fibers
perineurium
middle connective tissue layer of spinal nerves, divides nerve into fasicles (axon bundles)
endoneurium
inner connective tissue layer of spinal nerves, surrounds individual axons