A&P Chapter 5
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What does the integumentary system consist of?
Skin
Hair
Nails
Sweat glands
Sebaceous (oil) glands
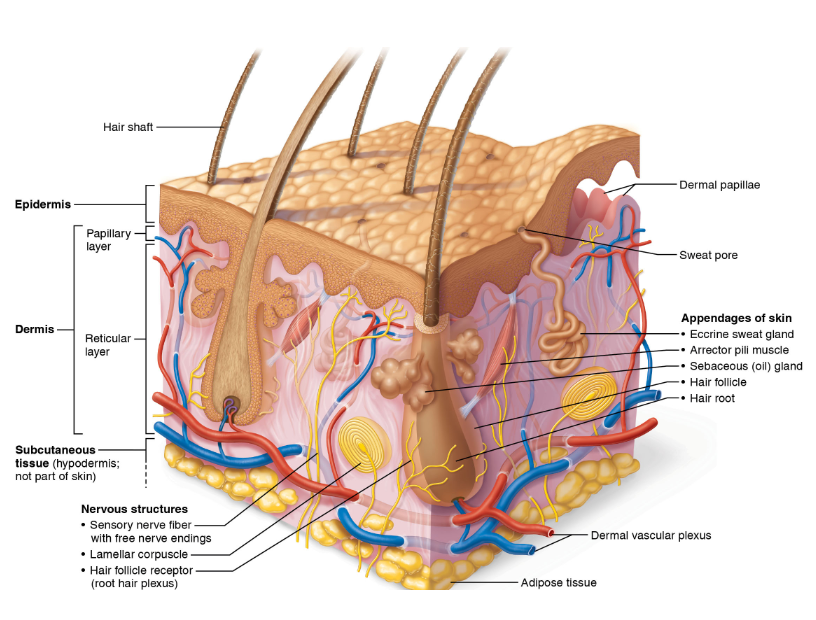
What is the epidermis?
Superficial region that consists of epithelial cells/tissue
True or False: Is the Epidermis Avascular
True; lacks blood vessels
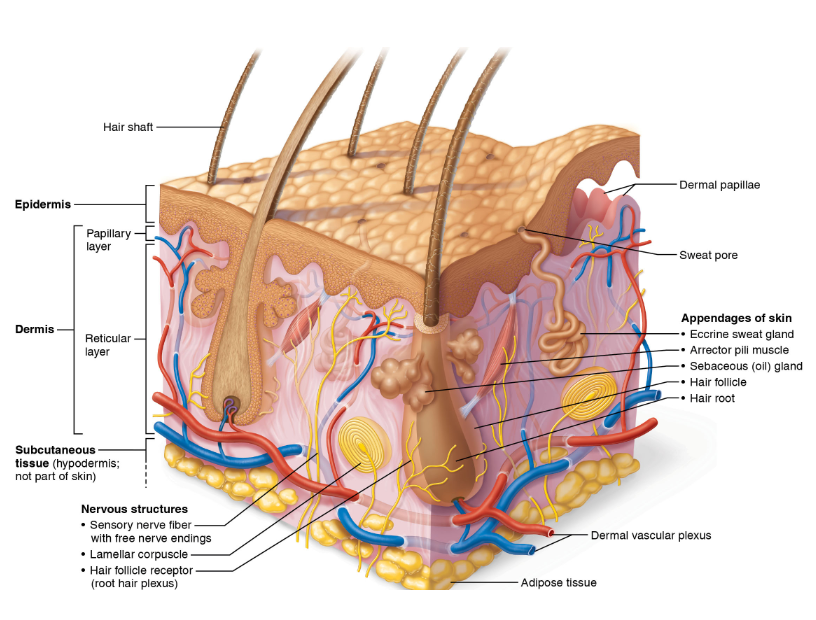
What is the dermis layer?
Underlies the epidermis, bulk of the skin, mostly connective tissue
True or False: Is the dermis layer Avascular?
False; Dermis layer is actually Vascular. Has blood vessels
True or False: Is the dermis layer Vascular?
True; has blood vessels
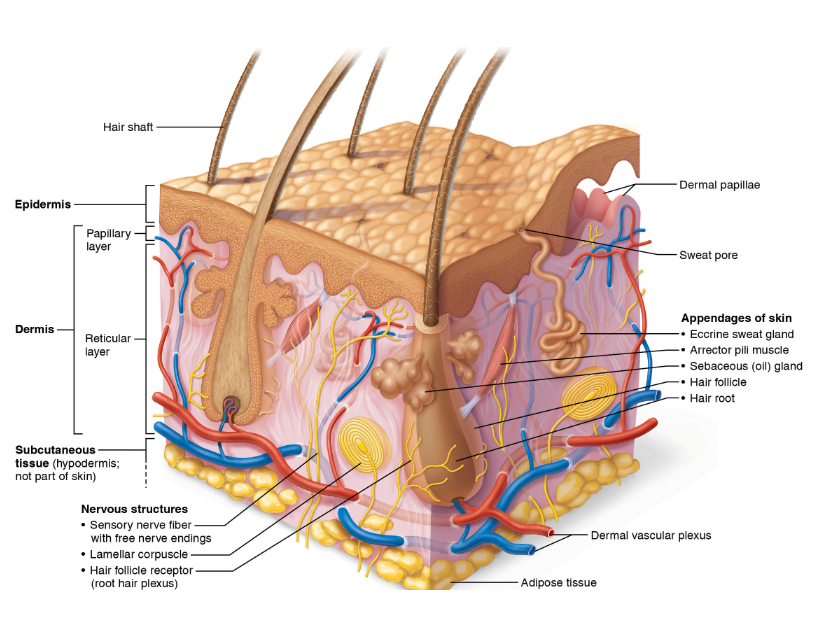
What is the hypodermis?
Subcutaneous layer, deep to skin.
True or False: The hypodermis is NOT apart of the skin
True; not apart of skin but shares similar functions
What is the hypodermis consist of?
Adipose tissue, helps absorbs shock and insulates
The epidermis is mostly?
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What are the 4 cell types in the epidermis?
Keratinocytes, melanocytes, dendritic cells, and Tactile (Merkel) cells
What are keratinocytes?
Produce keratin (protein that gives skin its protective properties)
Most cells of the epidermis
Connected by desmosomes
What are melanocytes?
Spider shaped, located in the deepest layer of the epidermis
Produce the pigment melanin, which is packaged into melanosomes
What are dendritic (Langer hans) cells
Star shaped
Macrophages in the deep epidermis
Ingest foreign objects
Key activators of the immune system
What are Tactile (Merkel) cells?
Spikey shaped
Sensory receptors that sense touch
Think skin has how many layers?
5
Thin skin has how many layers?
4
What are the 5 layers of the skin?
Stratum Basale
Stratum spinsosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
Stratum corneum
What is the stratum basale?
Deepest epidermal layer
Firmly attaches to dermis
Has stem cells that divide all the time (produces 2 daughter cells)
1 daughter cell goes to the surface, takes 25-45 days
Cells die as it gets closer to the surface
Other daughter cells stays in layer as stem cell
10-25% of layer is made of melanocytes
What is the stratum spinosum (prickly layer)
Several layers thick
Pre-keratin filaments attach to desmosomes
Allows for resist to tension and pulling
Among the keratinocytes there are also melanosomes and dendric cells
What is the stratum granulosum layer (granular layer)
4-6 cells thick, a thin layer
Cell appearance changes
Cells flatten, nuclei and organelles disintegrate
Keratinization occurs
Cells obtain keratohyalin granules to help from keratin fibers
Cells also gain lamellar granules that slow water loss
Cells above this layer die
Due to being far away from capillaries
What is Keratinization?
Cells fill with keratin
What is the stratum lucidum layer (clear layer)
Only in thick skin
Has thin and translucent 2-3 rows of clear, flat , dead keratinocytes
Lies superficial to stratum granulosum
What is the stratum corneum layer (horny layer)
20-30 rows of flat dead cells
¾ of epidermal thickness
Cells may be dead but function to
Protect deeper cells from environment
Prevent water loss
Protect from abrasions and penetrations
Acts as a barrier
What is apoptosis?
Cell death
What cells make up the dermis?
Fibroblasts
Macrophages
Sometimes mast cells and WBC
The dermis contains _____, blood vessels, and ______ vessels
nerves, lymphatic
The dermis contains what layers?
Papillary layer
Reticular layer
What is the papillary layer?
Superficial layer of areolar connective tissue, consists of loose, collagen and elastic fibers, and blood vessels
Contains Dermal papillae
In thick skin dermal papillae is on top of dermal ridges or friction ridges
Enhances gripping ability
Helps with sense of touch
Ridges leave unique fingerprint pattern
What is dermal papillae?
Superficial region of dermis
Sends finer like projections into epidermis
Projections contain capillary loops, free nerve endings, and touch receptors
What is the Reticular layer
Makes up 80% of dermis thickness
Contains coarse, dense irregular connective tissue
Elastic fibers provide stretch
Collagen fibers provide strength
Bind water, keeps skin hydrated
Contains Cleavage lines and Flexure lines
What is the cutaneous plexus?
Network of blood vessels between the reticular layer and hypodermis
What are cleavage (tension) lines?
Caused by collagen fibers running parallel to skin surface
Externally invisible
What are flexure lines?
Dermal folds at or near joints
Visible on hands, wrists, fingers, soles, toes
What pigments contribute to skin color?
Melanin
Carotene
Hemoglobin
What is melanin?
Pigment made in skin by melanocytes
Polymer of amino acids, tyrosine
Sent to shield DNA of keratinocytes from UV
More sun= more produced
2 forms: reddish yellow to brownish black
True or False: Skin color difference is due to the amount and form of melanin?
True
Moles and freakles are?
Accumulation of melanin
What is carotene?
Yellow to orange pigment
In palms and soles
Where does carotene accumalte?
Stratum corneum and hypodermis
What is hemoglobin (pigament)
Pink hue in fair skin
Low levels of melanin
What is cyanosis?
Blue skin color
Low oxygenation of hemoglobin
What is pallor?
Pale color
Anemia
Low blood pressure
Fear
Anger
What is erythema?
Redness
Fever
Hypertension
Inflammation
What is jaundice?
Yellow cast
Liver disorder
What are bruises?
Black and blue marks
Result of clotted blood beneath the skin
Sweat glands are also known as?
Sudoriferous glands
True or False: Sweat glands are on all skin surfaces
False: On all skin surfaces besides nipples and parts of external genital
What are the types of sweat glands?
Eccrine (merocrine)
Apocrine
What are Eccrine sweat glands
Most numerous type
Abundant on palms, soles, and forehead
Connect to pores
Coiled tubular gland
Function in thermoregulation
Regulated by sympathetic nervous system
Secrete sweat
What are Apocrine sweat glands
Confined to axillary and anogenital areas
Secrete thick milky sweat, contains fatty substances and proteins
Larger than eccrine glands
Start functioning at puberty
Function is unknown
What leads to body oder?
Bacteria breaking down sweat
What is ceruminous glands?
Lining of external ear canal; earwax
What are mammary glands
Secrete milk
What are sebaceous (oil) glands
Widely distributed
Develop from hair follicles, Secrete into hair follicles
Inactive til puberty
Stimulated by hormones
Secrete sebum
What are the functions of the skin?
Protection
Body temperature regulation
Cutaneous sensations
Metabolic functions
Blood reservoir
Excretion of wastes
What does Protection look like for the skin?
Exposed to the environment which can be harmful
Contains 3 different barriers
What are the types of barriers of the skin?
Chemical
Physical
Biological
What is a chemical barrier?
Secretes chemicals like sweat, sebum, defensin
Has acid mantle
Melanin is a chemical barrier against UV
What is acid mantle?
Low pH of skin retards bacterial multiplication
What is physical barriers of the skin
Flat, dead, keratinized cells of the statum corneum
Has some limited penetration to:
Lipid soluble substances
Plant oleoresins
Organic solvents
Heavy metals
Some drugs
What are biological barriers of the skin?
Epidermis has phagocytic cells
Dermis has macrophage
DNA absorbs harmful DNA radiation and converts it to heat
What is body temperature regulation?
Insensible perspiration
What is insensible perspiration?
Normal, resting body temperature, unnoticeable sweat
What is sensible perspiration
When body temperature rises, blood bessels dilate and increases noticeable sweat
What are cutaneous sensory receptors
Part of the nervous system
What are exteroreceptors?
Respond to stimuli like temperature and touch
What are free verve endings?
Sense painful stimuli
True or False: The skin holds up to 5% of total blood volume