Uncomplicated Pregnancy (Pearls) (Smarty PANCE)
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
What presents with amenorrhea, N/V, breast changes, basal body temperature changes, and skin changes?
Pregnancy
What is the definition of a "term" pregnancy?
A pregnancy that lasts 37 to 42 weeks is called a "term" pregnancy. When labor starts before 37 weeks, doctors call it "preterm" labor.
When can Braxton Hicks contractions start occurring?
28 weeks plus
"False labor" (also sometimes referred to as "Braxton-Hicks contractions") is defined as regular or irregular painful contractions that are not associated with cervical dilation.
When is an US performed in pregnancy?
5-6 weeks
What produces b-hcg in pregnancy?
The placenta as well as all types of trophoblastic tissue
How often does b-hcg double?
In the first four weeks of a viable pregnancy, hCG levels will typically double about every two to three days. After six weeks, the levels will double about every 96 hours.
When can b-hcg be detected in serum?
8-11 days after conception
When does b-hcg peak?
10-12 weeks
When can b-hcg be high?
Twins and trophoblastic dz
When does b-hcg decrease in pregnancy?
2nd-3rd trimester
when is b-hcg low?
Threatened or missed abortion
What is Naegele's rule?
EDC = LMP + 7 days - 3 mos + 1 yr
When is the uterus palpable?
At approximately 12 weeks gestation the uterus becomes large enough to be palpable just above the pubic symphysis. At 16 weeks gestation, the fundus of the uterus can be palpated at the midpoint between the umbilicus and the pubic symphysis.
How many extra calories should a pregnant woman eat a day? When breastfeeding?
300 extra calories while pregnant
500 extra calories while breastfeeding
What causes weight gain in pregnancy?
● Uterus
● Uterine contents - fetus and placenta
● Increase in blood volume
● Extracellular fluid
What is the average amount of extra water retained?
6.5 L (3.5L in uterus & 3.0L blood volume and breasts)
What is the average weight gain in pregnancy?
27.5 lbs (25-35 lbs)
Recommended weight gain is based on pre-pregnancy weight:
● Underweight BMI less than 18.5 28-40 pounds
● Normal Weight BMI 18.5-24.9 25-35 pounds
● Overweight BMI 25.0-29.9 15-25 pounds
● Obese BMI greater than or equal to 30.0 11- 20 pounds
What is the non-pregnant normal caloric intake?
2,300 kcal/day
What is the pregnant caloric intake?
2,600 kcal/day
What is the breastfeeding caloric intake?
500 kcal /day (2800 kcal day)
How much does the baby usually weigh in pregnancy?
3,500 g (7.71 lbs)
How much does the placenta, amniotic fluid and uterus weigh in. pregnancy?
900 g (1.98 lbs)
How much does the blood volume and interstitial fluid weigh in pregancy?
1200 g (2.6 lbs)
How much does breast enlargement account for in pregnancy?
400 g (0.88 lbs)
How much does maternal fat weigh in pregnancy?
1600 g (3.5 lbs)
When does increased cardiac output occur in pregnancy? how?
20-24 weeks gestation
● decrease systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
● increased stroke volume
● increased HR by ten beats/min
● increased preload
What kind of murmur is present in most pregnant women?
Systolic murmur due to physiologic changes
What happens to the point of maximal impulse (PMI) in pregnancy? why?
Displaced laterally b/c increase in L ventricular size
What causes the increase in blood volume in pregnancy?
Increased estrogen stimulates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which increases aldosterone, which in turn increases Na and H2O absorption
What occurs due to the rise in venous pressure? (3 things)
● Dependent pedal edema - increase venous pressure + dec osmotic pressure
● Varicose veins in legs and vulva
● Hemorrhoids
What are the RBC changes in pregnancy? (2 things)
● Inc plasma volume accounts for anemia
● Inc utilization of iron
What are the blood changes in pregnancy? (3)
● Inc WBC
● Plt dec
● Dec concentrations in all clotting factors
What are the GU changes in pregnancy? (kidney size, GFR, renal pelvis, BUN and Cr, CrCl)
● Kidneys enlarge
● Inc GFR - 40-65^
● Renal pelvis dilates
● BUN and Cr dec
● Cr clearance inc
T/F proteinuria and hematuria are not normal in pregnancy?
● True - protein loss should not exceed 300 gm in 24 hrs
● Mild glucosuria can be normal, but GDM should not be ignored
What happens to the ureters during pregnancy? Why?
Dilate due to smooth muscle relaxation due to inc progesterone
What happens to the bladder during pregnancy?
● Inc bladder capacity initially
● Inc urethral length
● Incontinence
What is the best test of kidney function in pregnancy?
Creatinine Clearance (CrCl)
What changes occur in the mouth during pregnancy? (2)
● Gums may become soft, slightly swollen, and prone to bleeding easily (epulis)
● Inc salivation
What are the stomach changes that occur during pregnancy?
● Displaced upward
● LES relaxes
● Increased GERD
What are the changes that occur in the gallbladder during pregnancy? (2)
● Contractility is reduced => inc residual volume and stasis
● Inc cholesterol => inc cholesterol stones
What are the changes that occur in the colon during pregnancy?
● Displaced laterally and superiorly
● Hypoperistalsis - constipation
● Appendix displaced upward and laterally
What causes hemorrhoids in pregnancy? (2)
● Constipation
● Elevated venous pressure in LEs
What are the skin changes that occur in pregnancy?
● Chloasma or melasma - brown patches
● Striae gravidarum
● Linea nigra
● Angiomas
● Palmar erythema
● Nails become brittle
● Hair thickens
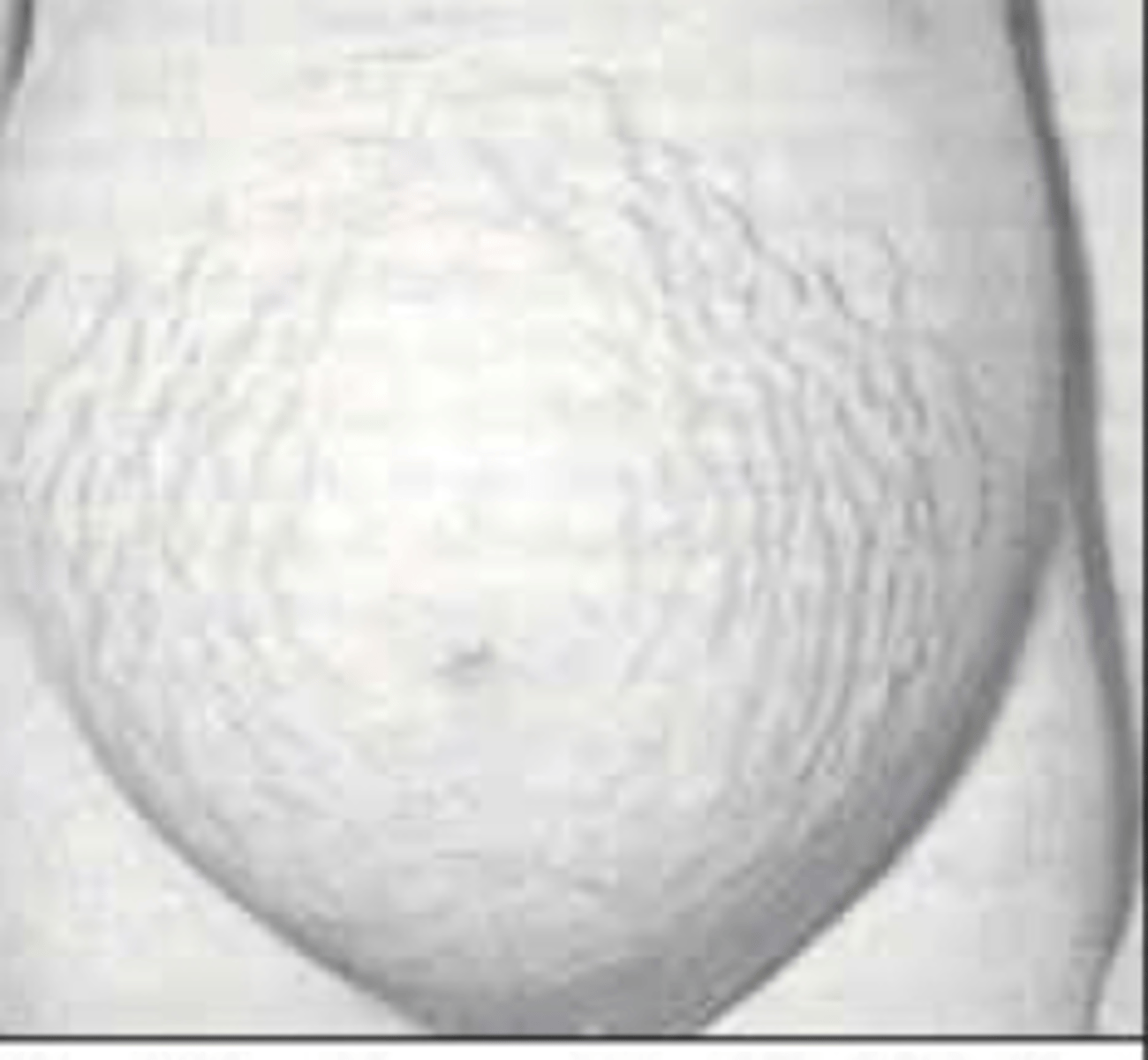
linear scar like lesions form over abdomen, breasts, buttocks and/or thighs in response to weakening of tissues during pregnancy
Striae gravidarum (stretch marks)
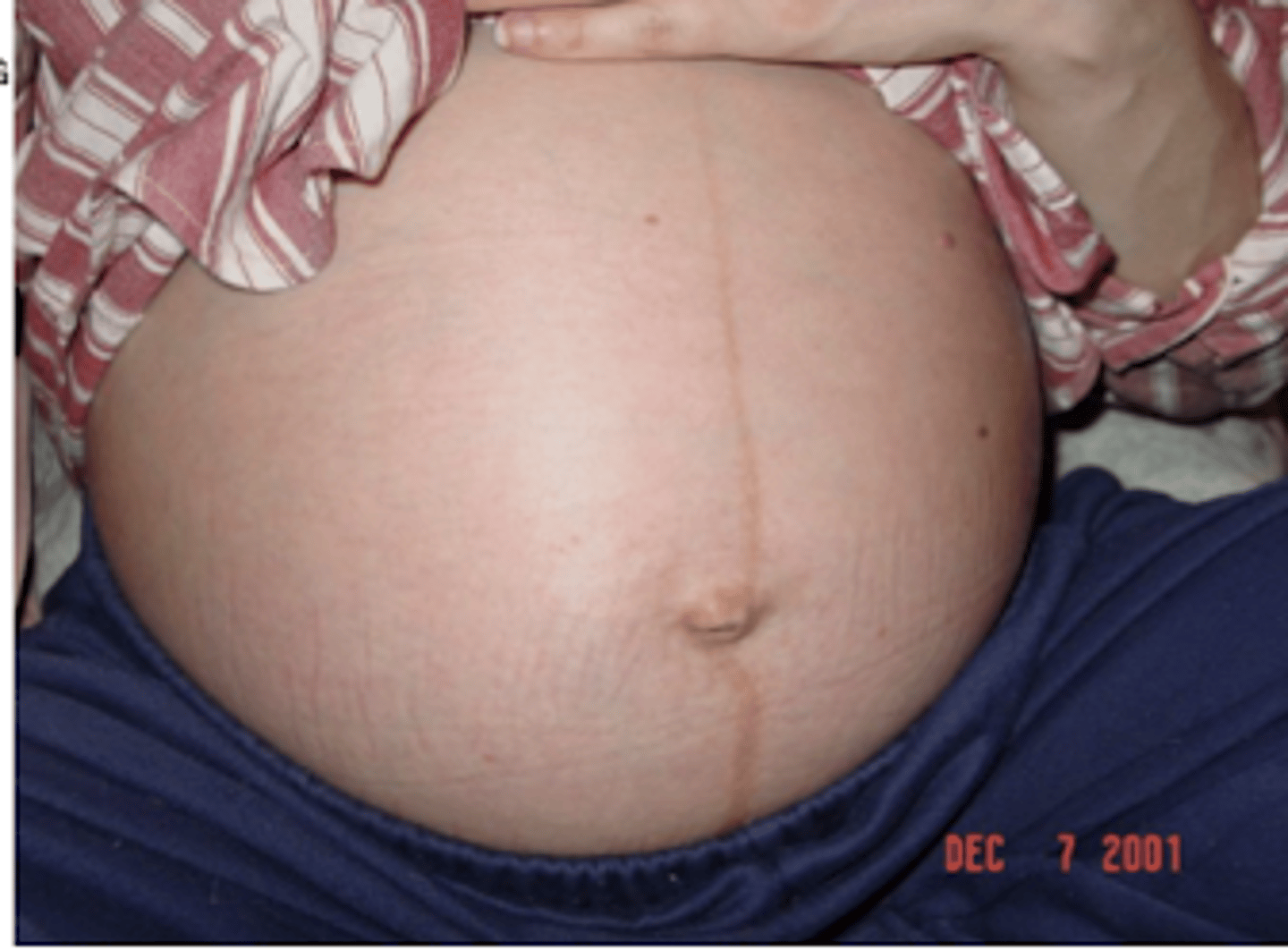
A dark line appearing on the abdomen and extending from the pubis toward the umbilicus
Linea nigra
What are the connective tissue changes that occur in pregnancy? (cervix, spine, joint, gait, abd, muscle)
● cervix softens
● progressive lordosis
● Inc joint mobility of SI, sacrococcygeal, pubic
● Waddle gait
● Diastasis recti
What are the breast changes that occur during pregnancy? what is giantomastia?
● Enlarge 2-3x - hyperplasia of breast tissue
● Inc fullness, tenderness, tingling, nodular
● Striae
● Increase mammary vascularization
● Colostrum - accumulates in alveoli
● Areolae - inc diameter, darker, erectile
● Gigantomastia - life-threatening breast enlargement
What are the cervical changes that occur during pregnancy? (4)
Softening and cyanosis due to inc vascularity, edema
hypertrophy, and hyperplasia
What are the vaginal changes that occur during pregnancy? (3)
● Inc in thickness of the mucosa
● Loosening of connective tissue
● Hypertrophy of smooth muscle
What are the endocrine changes that occur during pregnancy? (pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid hormones)
● Pituitary gland enlarges - inc PRL and GH
● Increase thyroid - stimulated by the placenta, hypothyroidism
● Parathyroid hormone decrease
What are the neuro changes that occur during pregnancy?
● Memory decline
● Difficulty sleeping
● Fewer hrs of sleep
What symptoms should be asked about during pregnancy?
● Hyperemesis gravidarum
● Frequent urination
● Pica
● Breast soreness
● Varicose veins
● Joint/hand/back pain
What condition occurs when the placenta implants over the cervical os?
Complete previa/total previa
What condition occurs when the placenta implants less than 2 cm from the cervical os?
Marginal previa
What presents with bright red blood, extremely painful, poor tracing?
● Placental abruption (abruptio placentae)
What is the obstetric visit schedule?
● 8-28 weeks Q4 weeks
● 28-36 weeks Q2 weeks
● 36+ weeks - Q1 week
How is the fundal height measured?
Symphysis pubis to superior fundus
When is the fundus at the umbilicus during pregnancy?
20 weeks
What is indicated by a larger uterus? (2)
● Multiple, GDM
What is indicated by a smaller uterus?
interuterine growth restriction (IUGR)
When are fetal heart sounds first heard using doppler? Fetoscope?
● Doppler at nine weeks
● Fetoscope at 15-16 weeks
What is a normal fetal heart rate?
120-160 beats per minute
What is an indication of fetal well being?
Kick counts - pattern of movement over a given time
What does the Leopold maneuver determine?
The Leopold maneuvers are used to palpate the gravid uterus systematically. This abdominal palpation method is low-cost, easy to perform, and non-invasive. It is used to determine the fetus's position, presentation, and engagement in utero:
● Fetal direction
● Position of fetal back and small parts
● Presenting part of the fetus
What is the softening of the cervix (occurs 4-6 weeks)?
The Goodell sign is a probable sign of pregnancy, characterized by softening of the cervix.
● A positive Goodell sign occurs due to increased blood flow noticed in the cervix during the first 4 to 8 weeks of pregnancy, which can also give the vaginal part of the cervix a bluish appearance (Chadwick sign).
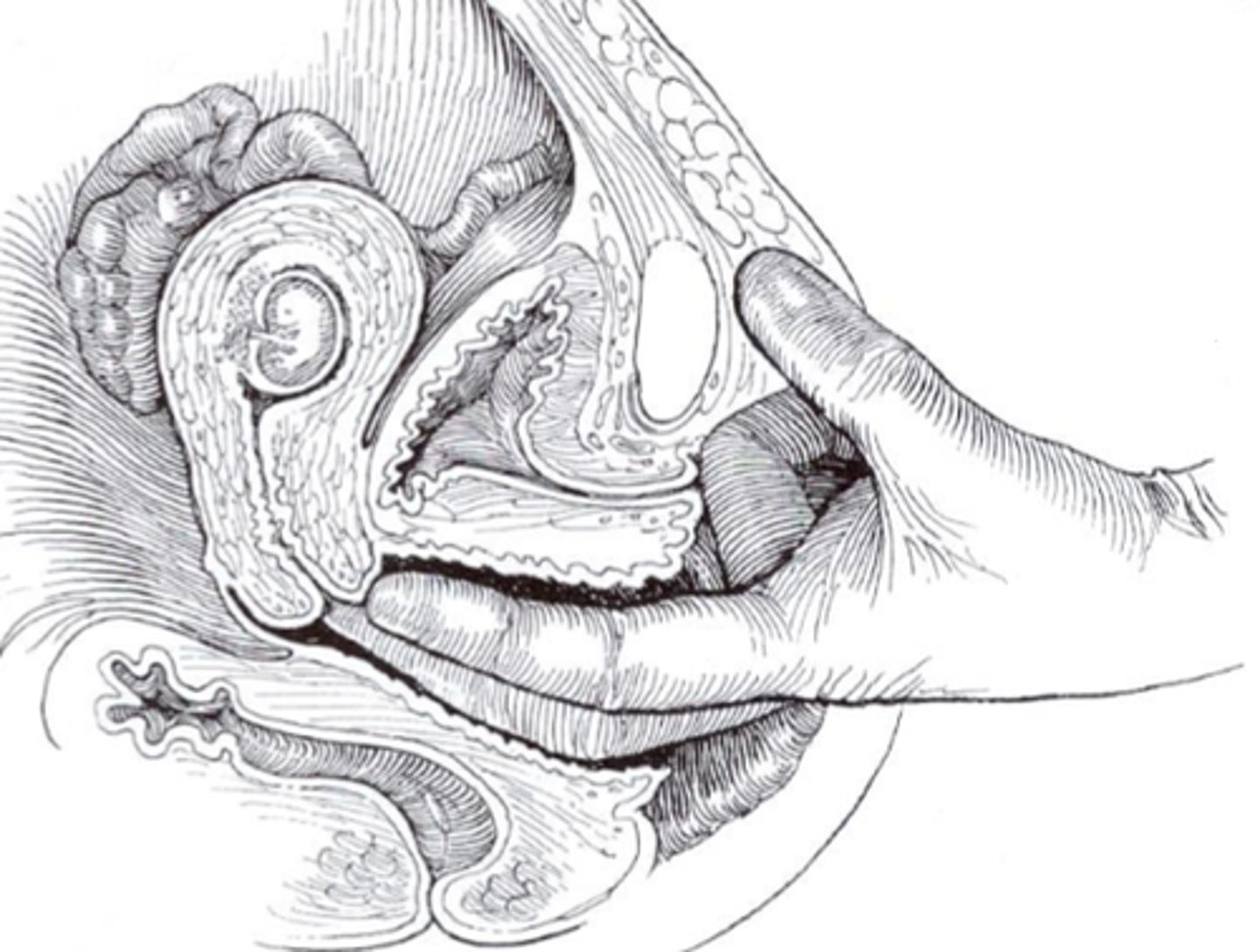
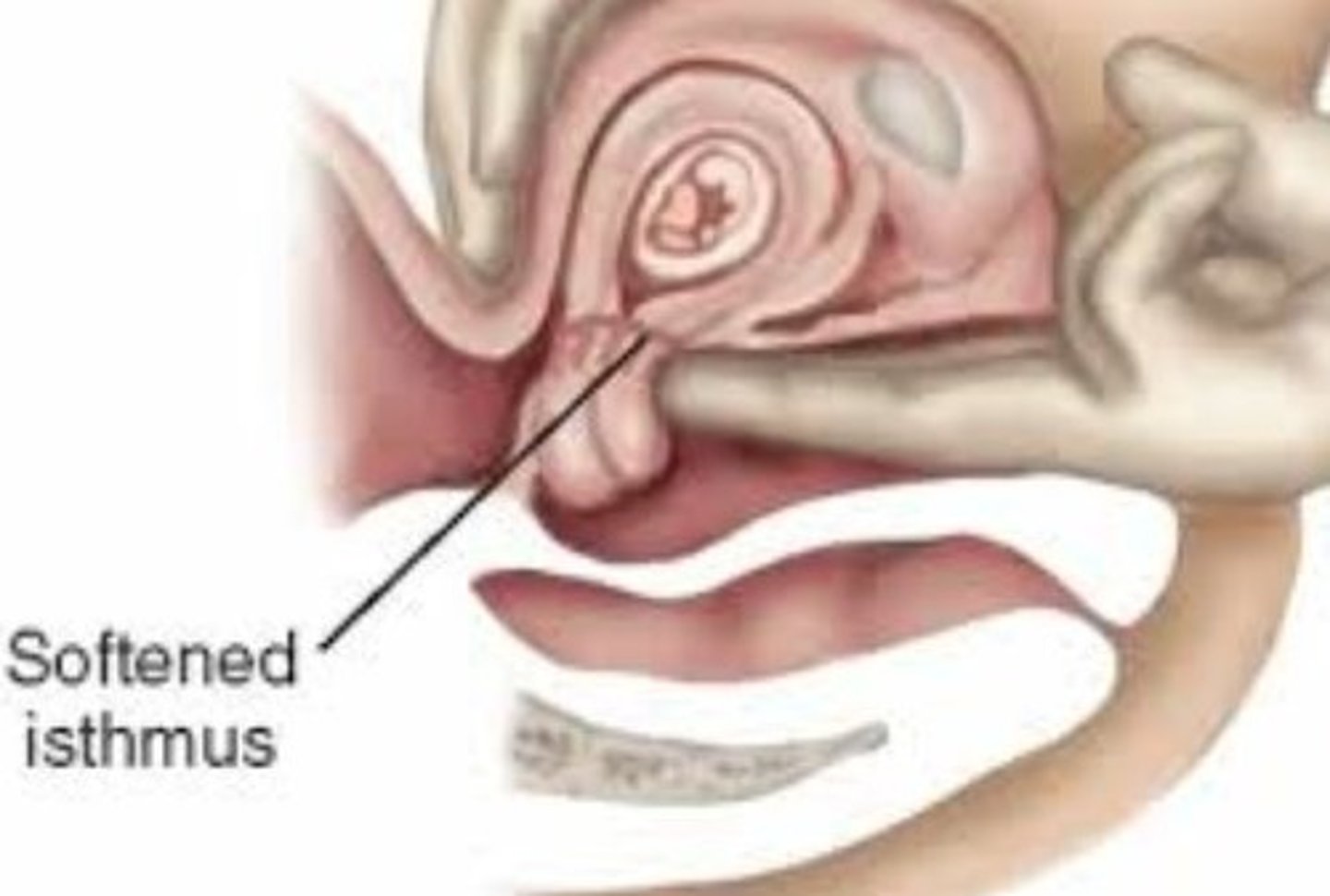
What is the softening of the uterine isthmus at 6-8?
Hegar sign is a non-specific indication of pregnancy that is characterized by the compressibility and softening of the cervical isthmus (i.e., the portion of the cervix between the uterus and the vaginal portion of the cervix).
Name given to the vascular congestion and bluish color of the vagina/cervix. This is an early sign after conception at 8-12 weeks?
The Chadwick sign is a non-specific, early sign of pregnancy that is typically characterized by a bluish discoloration of the cervix, vagina, and vulva. The Chadwick sign can typically be observed as early as six to eight weeks after conception, and commonly disappears shortly after birth.
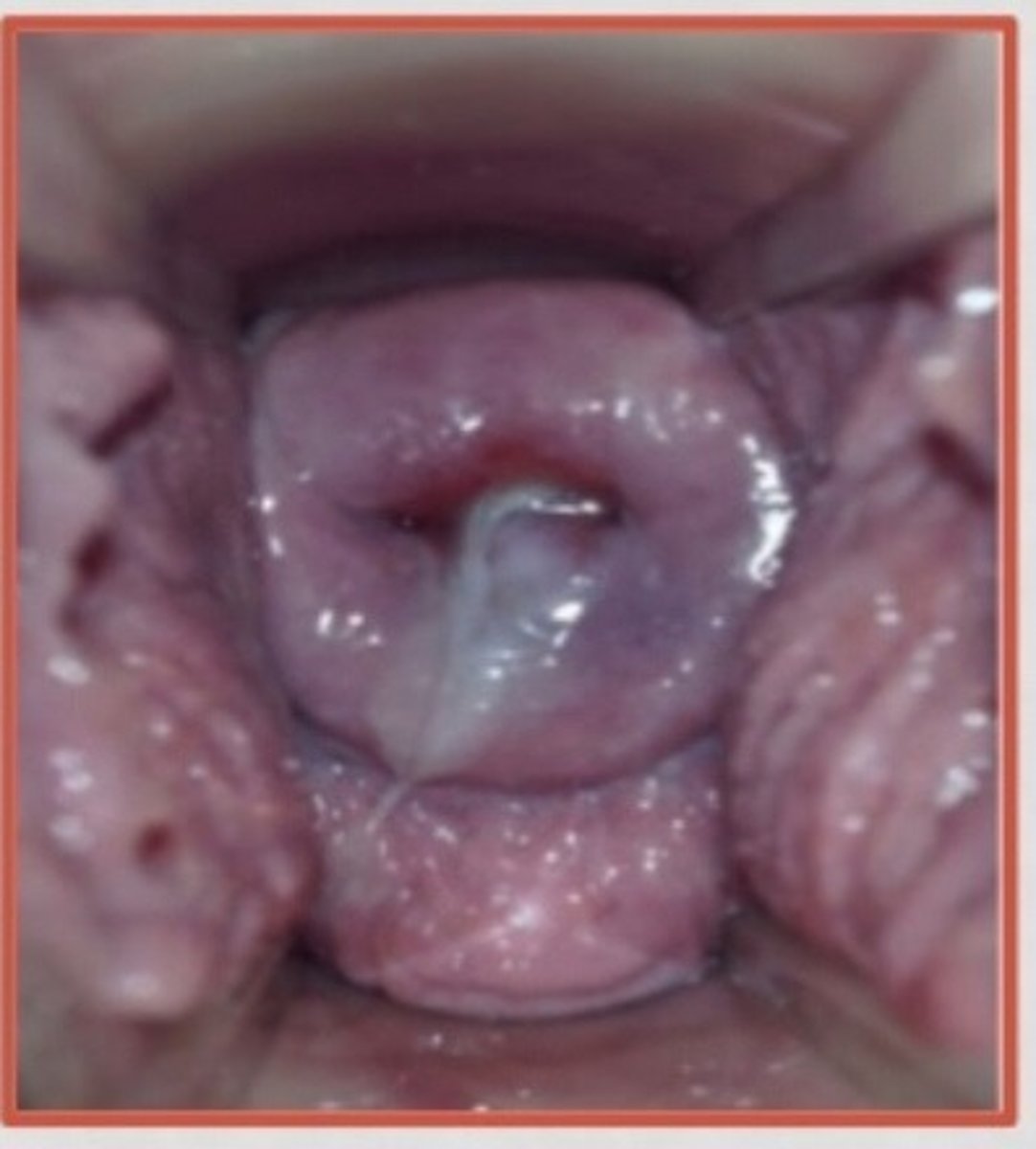
The characterized by the fundus flexing easily on the cervix? Occurs at 7-8 weeks?
McDonald sign is a probable sign of pregnancy characterized by an ease in flexing the body of the uterus against the cervix
What is fullness and softening of the fundus at the implantation site, 7-8 weeks?
Von Braun-Fernwald's sign is a clinical sign in which there is an irregular softening and enlargement of the uterine fundus during early pregnancy.
What labs are ordered at the initial prenatal visit?
● blood type (Rh+ or -)
● HgB (CBC)
● Rubella Ab
● Pap test
● STIs - G&C, RPR, HIV, Hep Band C
● PPD
● Thyroid, DM, ferritin
What is the purpose of the blood type and screen during pregnancy?
Prevention of fetal erythroblastosis and hemolytic disease of newborn (anemia and HF)
What is Rh sensitization?
In a mother with Rh-negative blood, the baby may have Rh-positive blood. If the two types of blood mix, the mother's body will make antibodies. This is called Rh sensitization. In most cases, this isn't a problem during the first time pregnancy. But in future pregnancies, sensitization could cause problems
Who gets Rh sensitization?
Rh sensitization during pregnancy can only happen if the mother has Rh-negative blood and the baby has Rh-positive blood. If the mother is Rh-negative and the father is Rh-positive, there's a good chance that the baby will have Rh-positive blood. Rh sensitization can occur.
What are the indications of RhoGAM?
Mom's blood type is RH negative - bc may make antibodies that cross over the placenta and attack baby's RBCs
What can cause sensitization to baby's blood type? (3)
● Spontaneous abortion
● Bleeding during pregnancy
● Bleeding at delivery
When is RhoGAM given?
RhoGAM is given at 28 weeks and delivery (also miscarriage and bleeding during pregnancy)
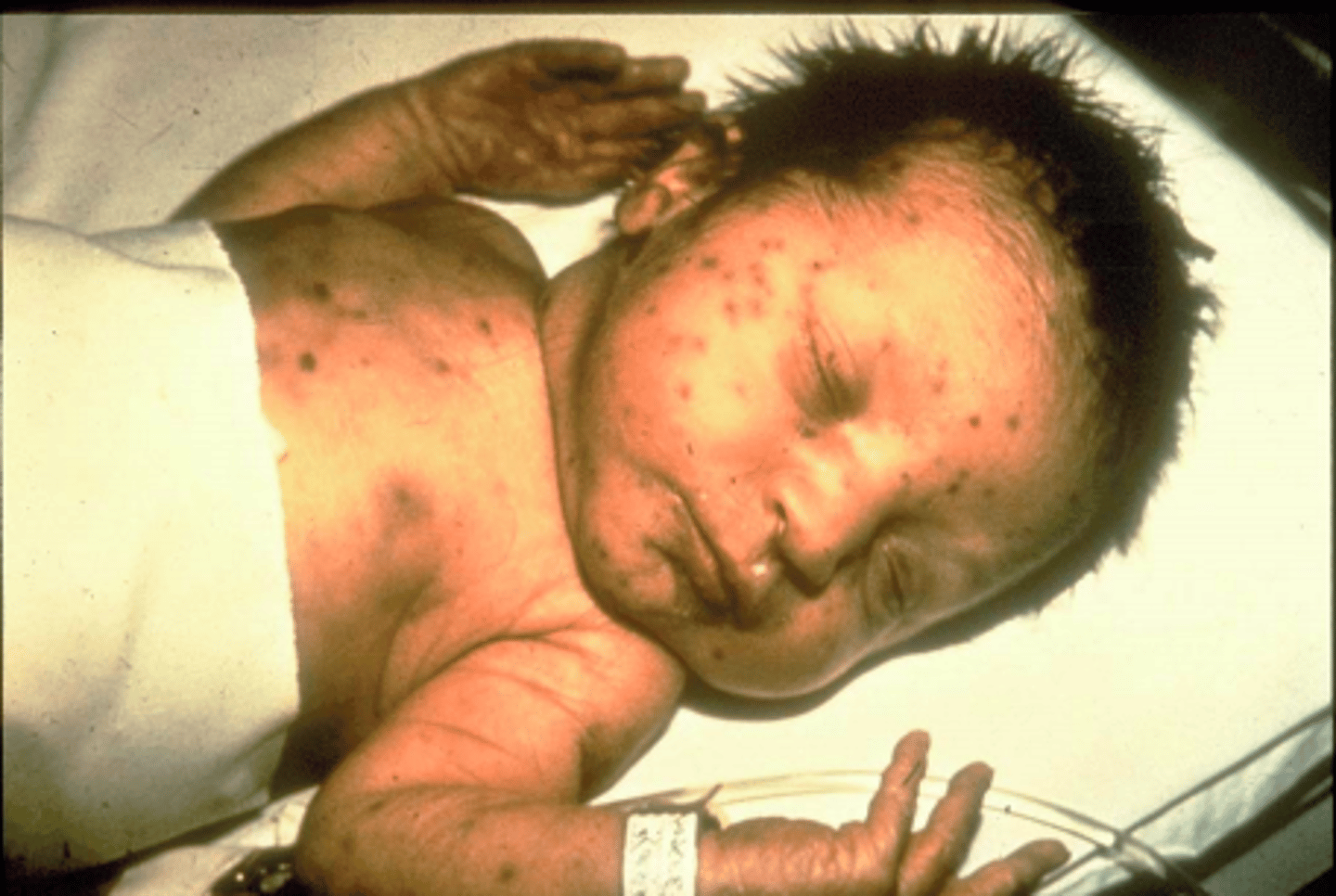
What presents with growth retardation; malformations of the heart, eyes or brain. Deafness and liver, spleen and bone marrow problems. Also, the baby has characteristic blueberry muffin appearance - thrombocytopenia purpura?
Congenital rubella syndrome aka hydrops fetalis
T/F MMR can't be given during pregnancy?
True
● It is safe for breastfeeding women to receive MMR vaccination. Breastfeeding does not interfere with the response to MMR vaccine, and the baby will not be affected by the vaccine through breast milk.
What are the indications for the MMR vaccine?
Children should get two doses of MMR vaccine, starting with the first dose at 12 to 15 months of age and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age.
● Nonpregnant women
● HIV infection w/ CD4 > 200
● Students, travelers, and household contacts of immunocompromised
● Healthcare personnel born after 1957 w/o evidence
● Adults who were vaccinated but at inc risk of a mumps outbreak
When is chorionic villus sampling performed?
10-12 weeks
Tay-Sachs, hemophilia and Down's syndrome can all be diagnosed by?
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
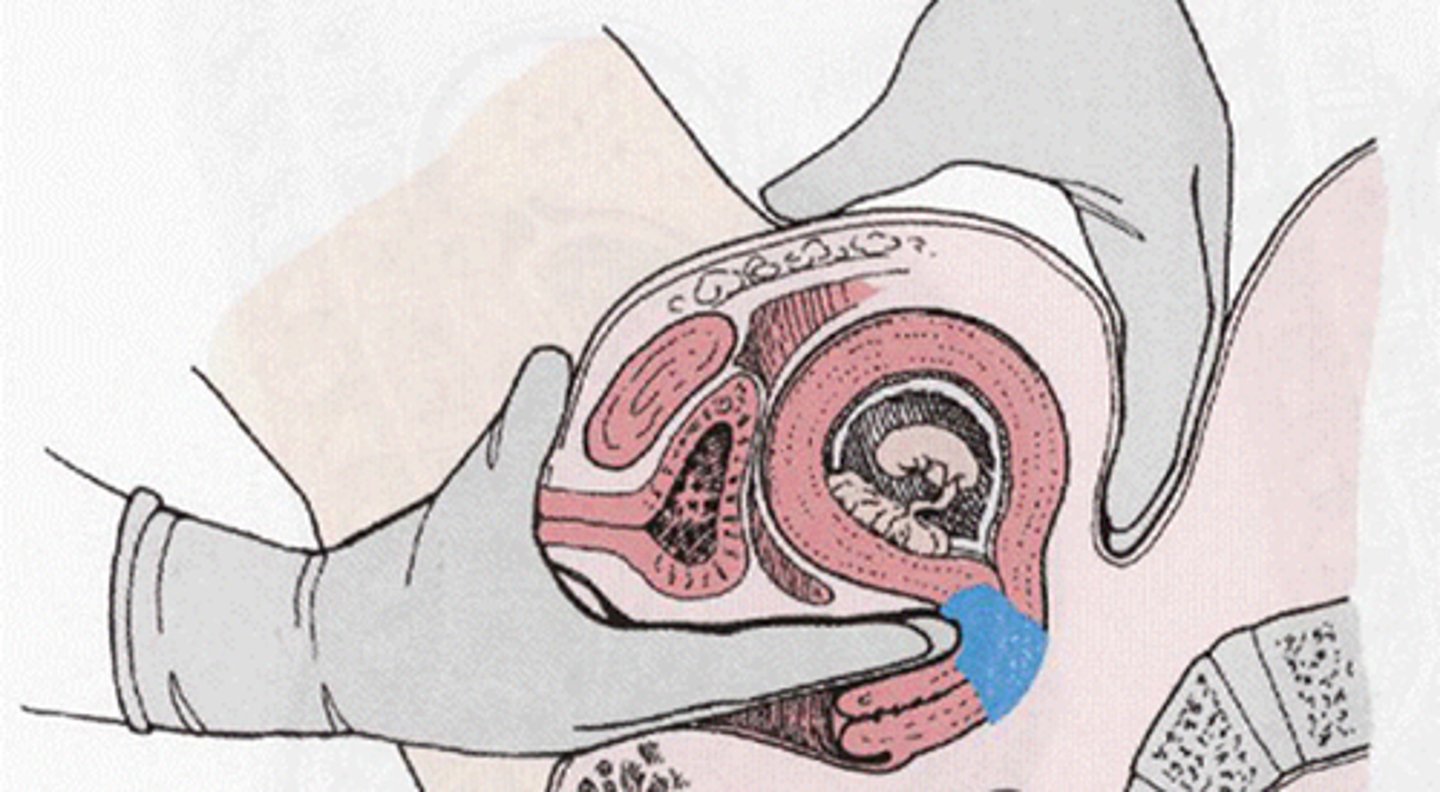
How is chornionic villus sampling performed?
Transabdominal or transcervical bx of placenta
Some reasons that a woman might elect to undergo CVS?
Some reasons that a woman might elect to undergo CVS are:
● Previously affected child or a family history of a genetic disease
● chromosomal abnormalities, or metabolic disorder
● Maternal age over 35 years by the pregnancy due date
● Risk of a sex-linked genetic disease
What conditions cannot be diagnosed by chorionic villus sampling? (2)
● Neural tube defects
● Lung maturity
What is associated with enlarged nuchal transulucency (> 3.0 mm)? (2)
Nuchal translucency is usually done between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy. An enlarged nuchal translucency is associated with fetal aneuploidy (often down syndrome) and structural malformations
When can non-invasive prenatal testing or cell-free DNA testing occur?
> 10 weeks - tests maternal blood using cells released from placenta
What conditions are screened for using non-invasive prenatal testing?
Trisomy 21, 18, 13, triploidy, and Turner syndrome (XO).
What is the "triple screen", maternal serum screen 3?
The Triple screen measures serum levels of AFP, estriol, and beta-hCG. It is performed during the second trimester to classify a patient as either high-risk or low-risk for chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defects)
What is the "quad screen", maternal serum screen 4?
The quad screen measures levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), beta-hCG, estriol, and inhibin A
What is the "penta screen", maternal serum screen 5?
AFP, beta-hCG, unconjugated estriol, inhibin A, and hyperglycosylated human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG-H)
What does an elevated AFP on triple or quad screening indicate? (3)
● The baby may be further along than originally thought
● Neural tube defect
● Twins
What does a low AFP on triple or quad screening indicate?
Down's Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
What does an low estriol on triple or quad screening indicate?
Down's Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
What presents with a low U-estriol, AFP, and elevated bhcg and inhibin A
Down's Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
What presents with an low u-estriol, AFP, Bhcg, and inhibin A
Edwards (Trisomy 18)
What presents with an elevated AFP?
Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
When is amniocentesis done?
15-20 weeks
What can an amniocentesis detect? (2)
● chromosomal abnormalities (confirmation of NIPT findings, CF)
● neural tube defects
● fetal lung maturity
● infection
What conditions cannot be detected on amniocentesis?
Birth defects like cleft palate, club feet
What are the diagnostic criteria for gestational diabetes?
● 1 hr GTT > 130
● The 3 hr GTT - draw fasting, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 3 hr specimens - If 2+ are elevated GDM dx