Derangements in Tonicity (I)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
why does tonicity matter?
1) cells/enzymes function optimally at physiologic osmolality- cytoplasm contains particles in solution
2) rapid shifts of water in/out of cells causes injury (especially neurologic)
definitions- osmole, osmolality, osmolarity, meq, tonicity

osmolarity v tonicity
-osmolarity describes solution (units of concentration)
-tonicity describes behavior of solution (unitless)
-hypoosmolar solutions are always hypotonic
-isoosmolar and hyperosmolar solutions may be hypo, iso, or hypertonic
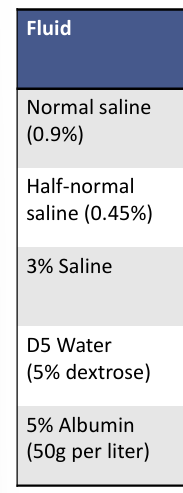
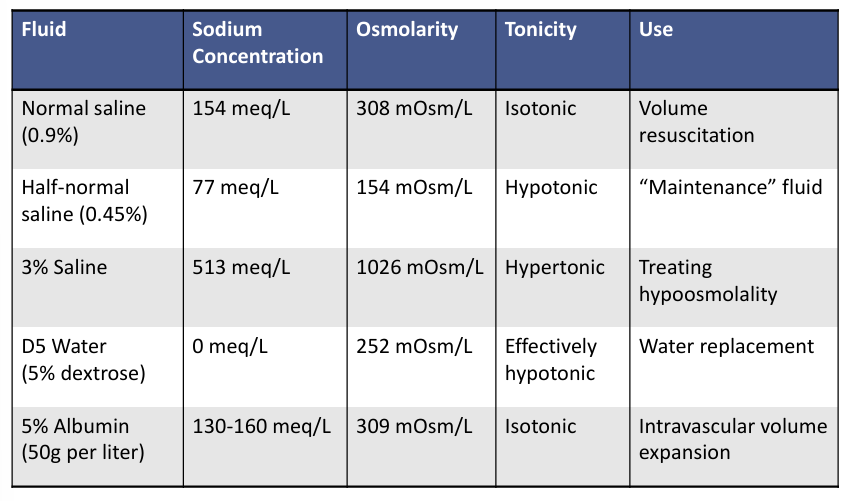
IV fluid therapy- fluid, sodium concentration, osmolarity, tonicity, use
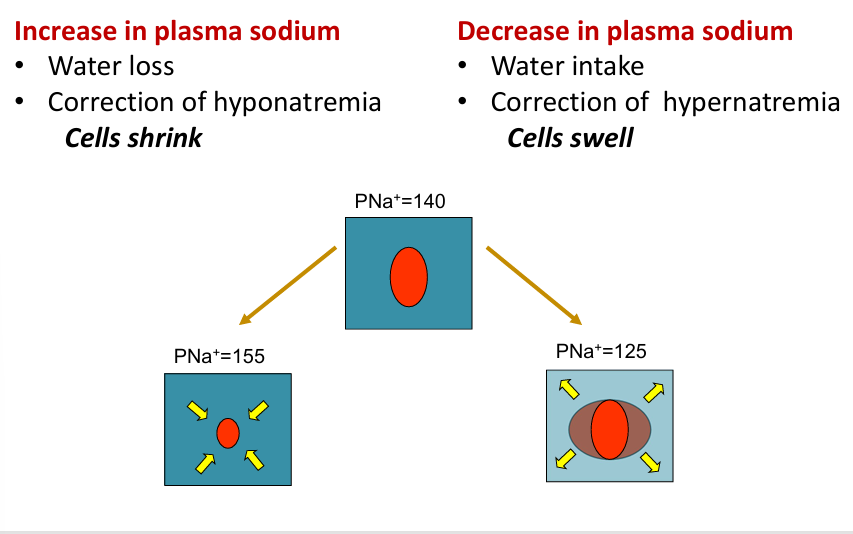
why does tonicity matter?- increase and decrease in plasma sodium
intra/extracellular osmolality key concepts
-intracellular osmolality = extracellular osmolality (at steady state)
-outside world (illness, fluids, diet, etc) affects extracellular osmolality
-changes in extracellular osmolality rapidly equilibrate with intracellular by the movement of water- raising extracellular osmolality → water exits cells; lowering extracellular osmolality → water enters cells
-intracellular osmolality is largely dependent on potassium
-extracellular osmolality is largely dependent on sodium
osmolality and serum sodium
-osmolality depends on total body exchangeable sodium + potassium
-serum sodium is an excellent (though imperfect) surrogate for osmolality
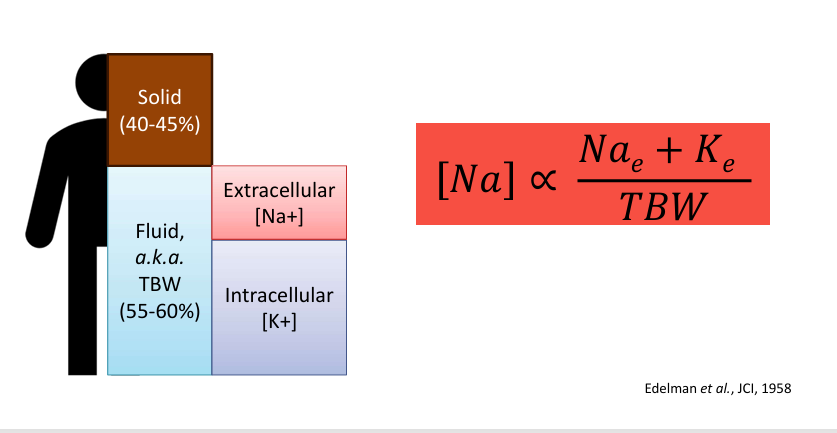
osmolality and relationship to sodium and potassium in serum and urine
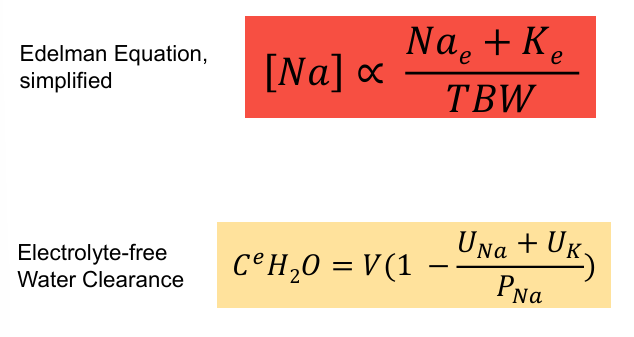
interpreting lab tests- serum osmolality, serum sodium concentration, urine sodium, urine osmolality
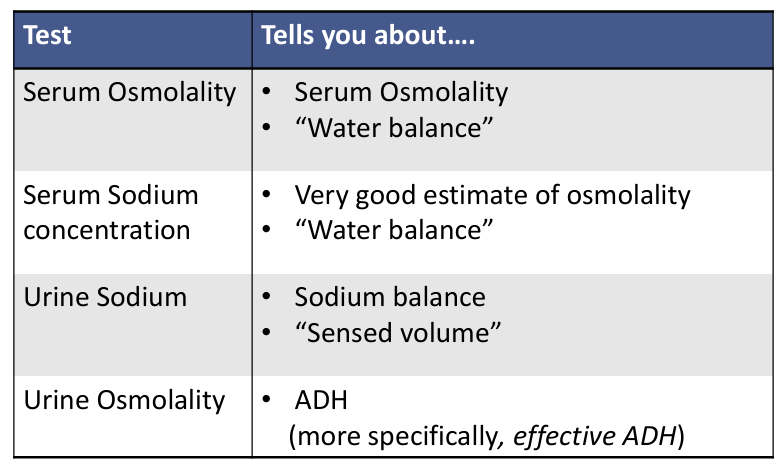
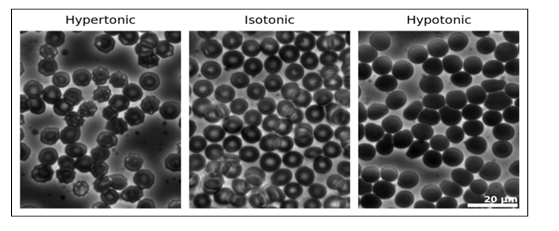
why does tonicity matter?- cell shrinking v swelling
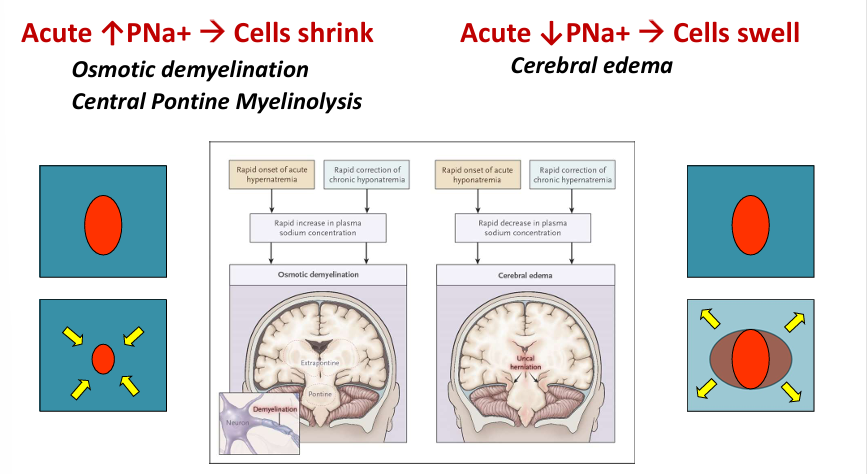
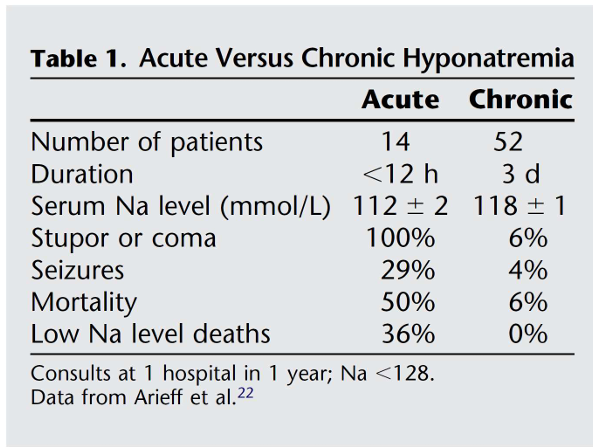
morbidity of hyponatremia
-mild chronic hyponatremia is associated with falls, unsteadiness, and attention deficits
osmotic demyelination syndrome
-complication of acutely raising serum osmolality (usually in setting of correction of severe hypoosmolality/hyponatremia)
-rare but morbid: mortality 40-50%
-biphasic:
1) initially- encephalopathy, seizures → recovery
2) days later- dysarthria and dysphasia, flaccid quadriparesis, oculomotor abnormalities, “locked-in syndrome”
hypernatremia
-always implies hyperosmolality
-three components to consider: water intake, water loss, solute intake
hypernatremia pathway
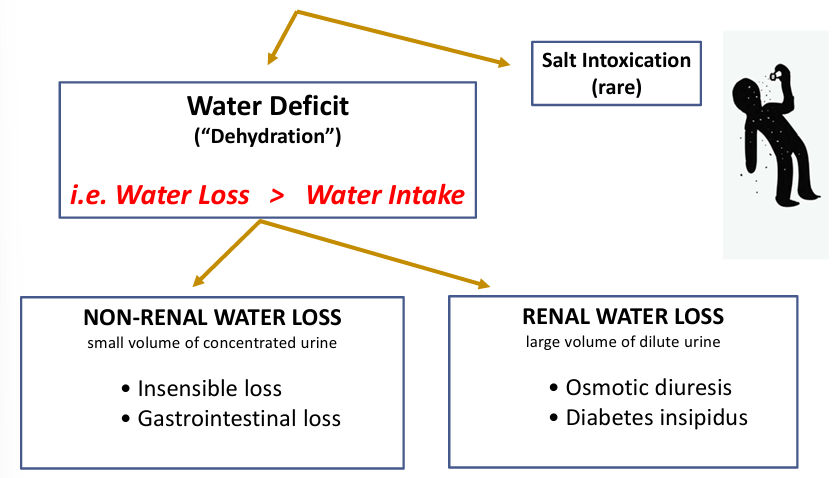
renal water loss- diabetes
-diabetes mellitus (“sweet”) = osmotic diuresis
-diabetes insipidus (“tasteless”) = water diuresis
diabetes insipidus
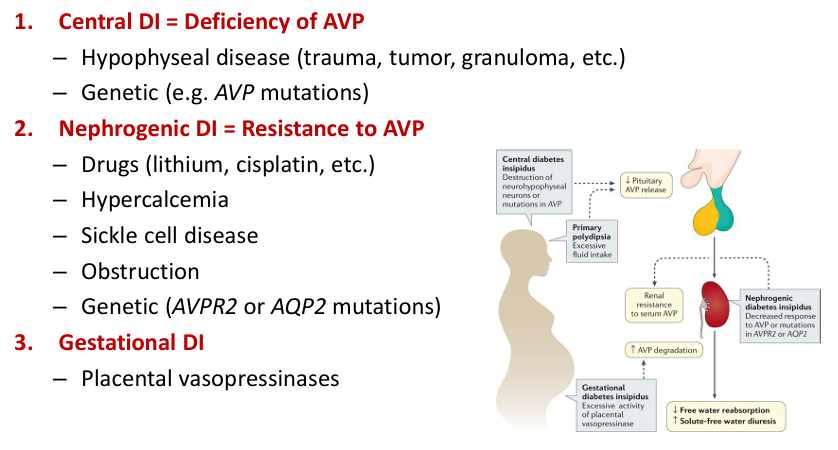
hypernatremia diagnostic approach
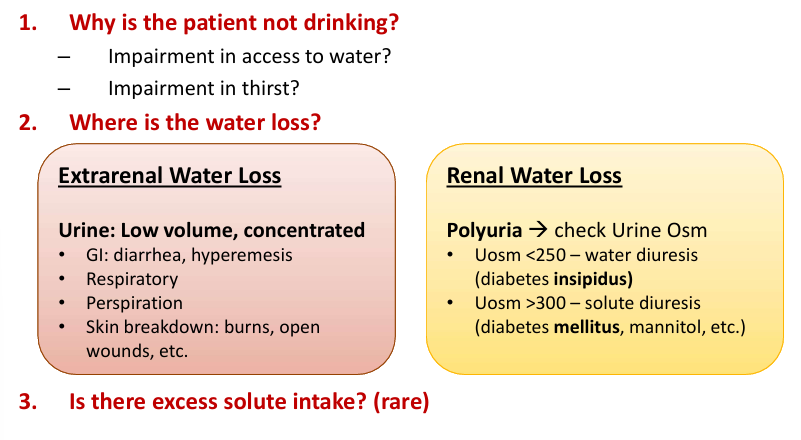
adaptation to hypernatremia
-chronic hyperNa leads to intracellular retention of “idiogenic osmoles”
-idiogenic osmoles raise intracellular osmolality to limit cell water loss
-can be generated as early as 4 hours after acute hypertonic challenge
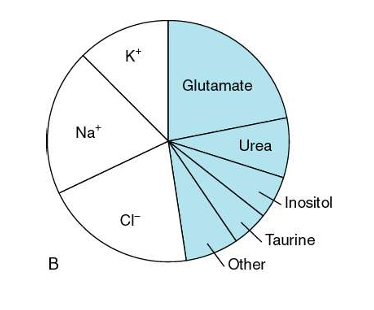
correction of hypernatremia

correction of hypernatremia in infants
-infants at risk of cerebral edema and seizures with rapid correction of hypernatremia/dehydration
-seizures virtually nonexistent if corrected <0.5 mEq/L/h
correction of hypernatremia in adults
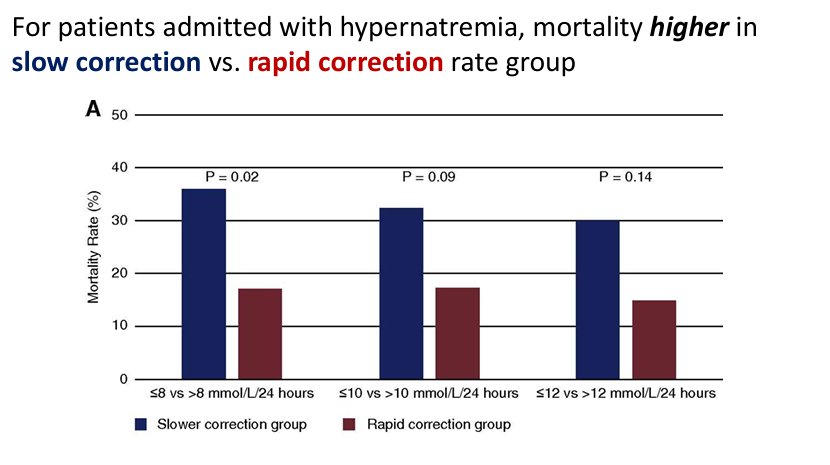
treatment and limits of correction of severe hypernatremia
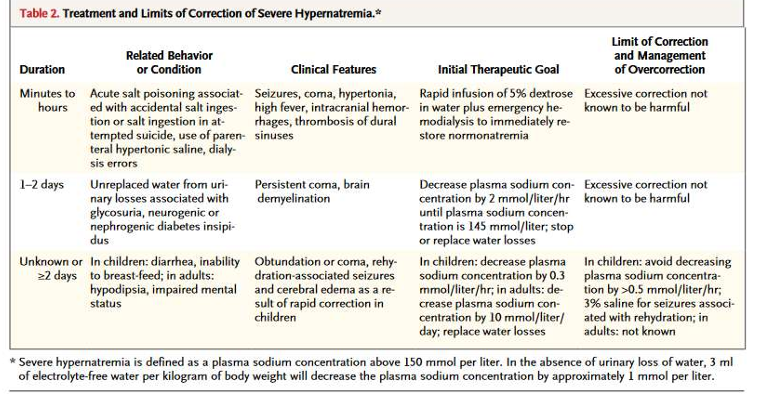
summary
