Human Nutrition.
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
balanced diet
Provides sufficient energy. Provides molecules for metabolism and nutrients in correct quantities.
necessary food groups
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
water
dietary fibre
minerals
vitamins
food functions funcitons
carb - Source of energy. Provide energy for respiration in cells
protein - growth and repair of tissues
lipid - insulation and energy storage
vitamins - needed in small quantities to maintain health
minerals - needed in small quantities to maintain health
fibre - provides bulk/roughage and helps food to move through the stomach and intestines
water - needed for chemical reactions to take place. regulates body temperature.
vitamin C
forms an essential part of collagen protein, which makes up skin, hair, gums and bones
maintains healthy skin and gums
deficiency of VC is called scurvy
vitamin D
helps the body absorb calcium and so required for strong teeth and bones
deficiency of vitamin D is called rickets. rickets causes weak and soft bones, as well as deformities
can lead to osteoporosis later in life if u dont have enough calcium
iron
required to make haemoglobin
for transport of oxygen
prevent iron-deficient anaemia
* ingestion - taking in of substances * digestion - breakdown of food * absorption - the movement of nutrients (small food molecules and ions) from the wall of the intestine into the blood * assimilation - uptake and use of nutrients by cells * egestion - the removal of undigested food from the body as faeces
mouth and salivary glands in digestive system role
The teeth in the mouth break down food into smaller pieces. This is to increase the food's surface area for the action of of amylase enzymes in chemical digestion. The salivary glands produce amylase, which breaks down starch into maltose. The tongue shapes the food into a bolus and is lubricated by saliva, so it is easier to swallow.
oesophagus
Tube that connects the mouth and stomach.
Uses wave-like contractions/peristalsis to push the food down without relying on gravity.
stomach
The stomach mechanically digests food by churning actions. The muscles in the lining of the stomach contract to physically squeeze and mix the food with hydrochloric acid. This breaks it down into smaller pieces and liquefies it.
chemically digests food using pepsin enzymes, which chemically digest proteins
hydrochloric acid killing harmful microorganisms in food and denatures enzymes in bacteria
providing an acidic pH for optimum enzyme activity
small intestine
duodenum (first section) - where food coming out of the stomach finishes being digested by enzyme secreted here and from the pancreas.
the pH here is alkali. 8-9
ileum (second section) - where absorption of food molecules take place. long and lined with villi to increase the surface area over which food absorption can take place
large intestine
water is absorbed from the remaining material to produce faeces
faeces is stored in the rectum and removed through the anus
pancreas
produces all three digestive enzymes; amylase, lipase. protease
secretes an alkaline fluid (pancreatic juice) to raise the pH of the small intestine and provide an optimum pH for enzymes there
bile raises the pH of the small intestine
amino acids not used to make proteins r broken down here (deamination) this produces urea
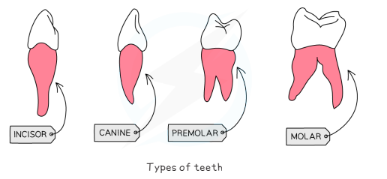
canines – pointed for tearing, holding and biting
premolars and molars – larger, flat surfaces with ridges at the edges for chewing and grinding up food
produced in the salivary glands and pancreas. acts in the mouth
\----------------------------------
maltase breaks down maltose to glucose on the membranes of the epithelium lining the small intestine
proteases
proteases break down proteins into amino acids.
pepsin breaks down protein in the acidic conditions of the stomach
trypsin breaks down protein in the alkaline conditions of the small intestine
produced by the pancreas - trypsin
produced in the pancreas and acts in the duodenum
how r villi adapted for absorption
microvilli on the surface of the villi further increase the surface area for the absorption of nutrients. to increase rate of absorption of nutrients
the wall of each villus is one cell thick. this reduces the diffusion pathway and there is a short distance for active transport
lacteal runs through the centre of the villus to transport fatty acids and glycerol away from the small intestine in the lymph
Well supplied with a network of blood capillaries to maintain good concentration gradient. Capillaries absorb glucose and amino acids.
(For structure diagrams say:
Thin epithelium. One cell thick to reduce diffusion pathway and increase diffusion rate. Epithelium has microvilli to increase surface area for absorption)
lacteal functions
absorbs, fatty acids (and glycerol)
transports, fats / fatty acids, into, lymph(atic) vessels
importance of microvilli
large surface area
allow, increased rate of / fast, absorption of nutrients