Chapter 2.1: Biomolecules & water
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Iron
element which is responsible in transporting oxygen and electrons in various human systems
monomer
a molecule which can be covalently bonded to a similar or identical molecule to create a polymer
AA
carbohydrates
nucleotides
Lipids are not considered monomers since they do not join to make polymers
Carbohydrates
(C H2 O)n formula
Each carbon is technically “hydrated“ with a water
n-1 hydroxyl groups
1 carbonyl group
red, black, blue, white, yellow, orange
List the colors in order separated by a comma for spacefilling/ball and stick diagrams
oxygen
carbon
nitrogen
hydrogen
sulfur
phosphorous
organic compounds
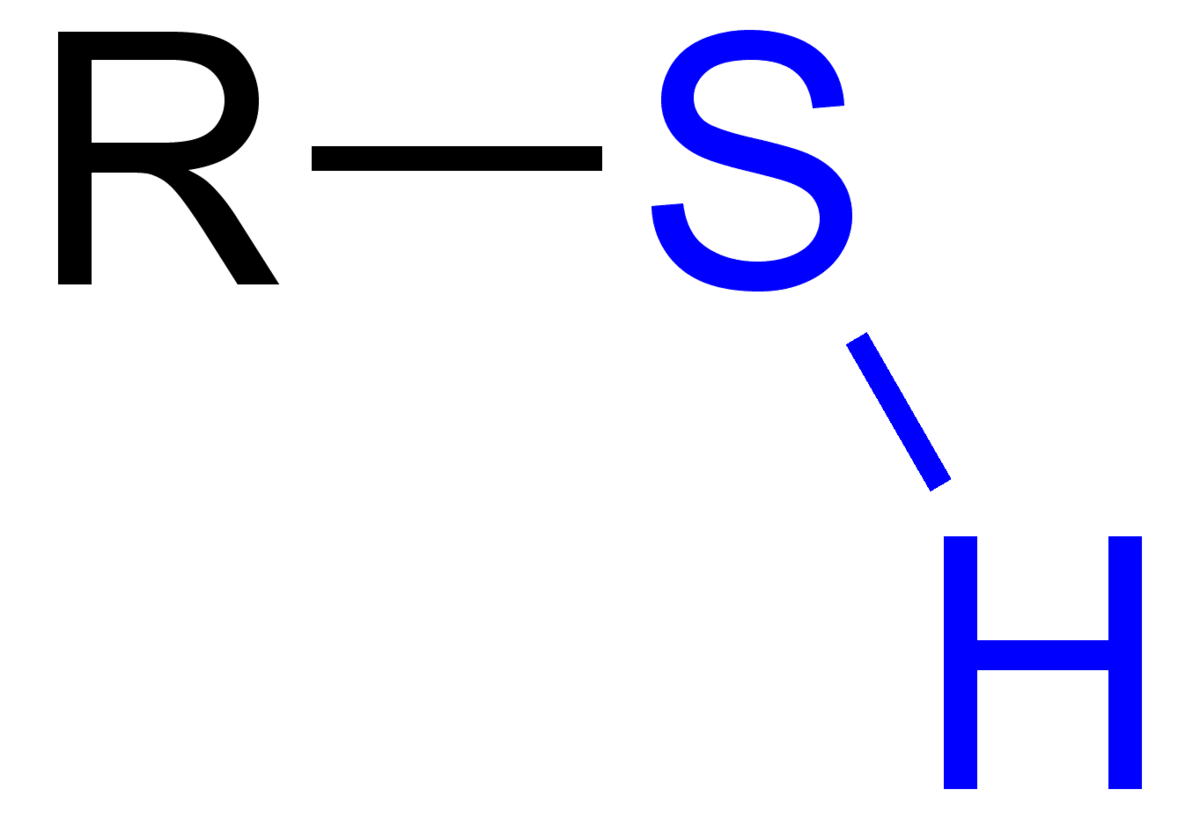
thiol
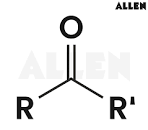
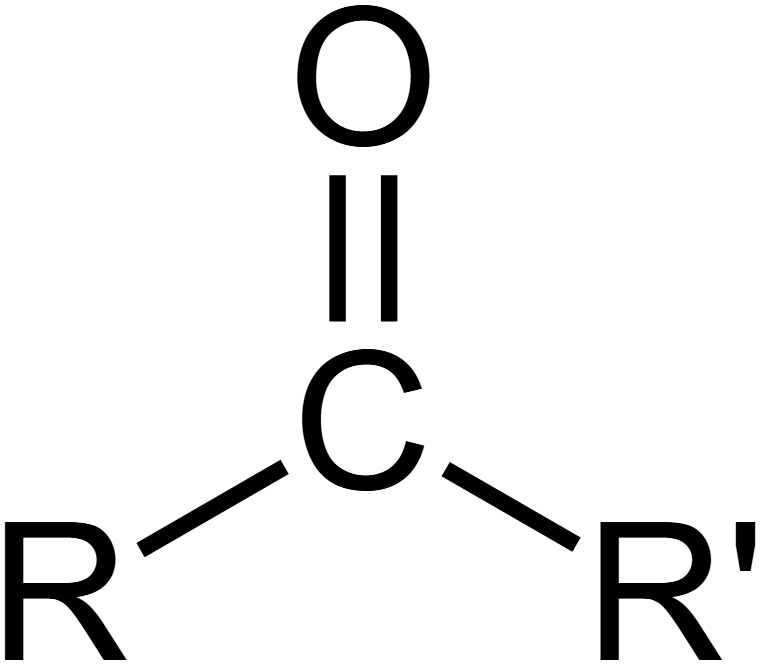
ketones
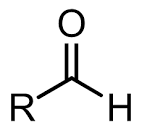
aldehydes
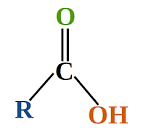
carboxylic acids
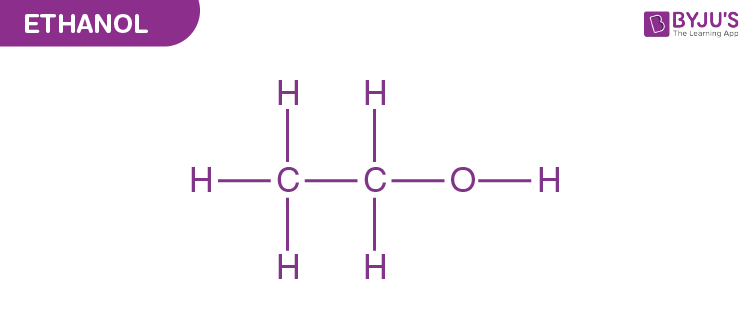
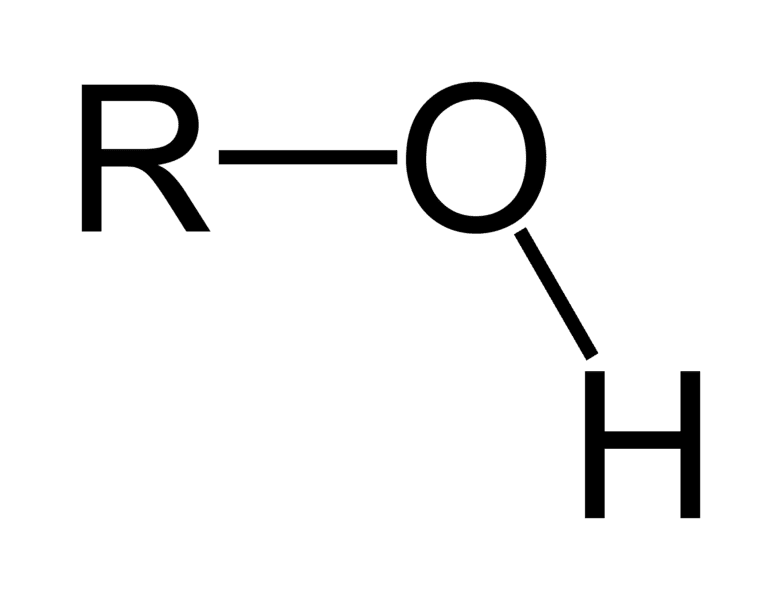
alcohol
amines
thiol - organic compound
organic compound
alcohol - organic compound
aldehyde - organic compound
organic compound
Ketone - organic compound
organic compound
carboxylic acid - organic compound
amine - organic compound
organic compound

Hydroxyl - Functional group
functional group
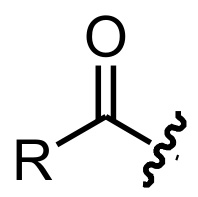
Acyl - functional group
carbonyl - functional group
functional group
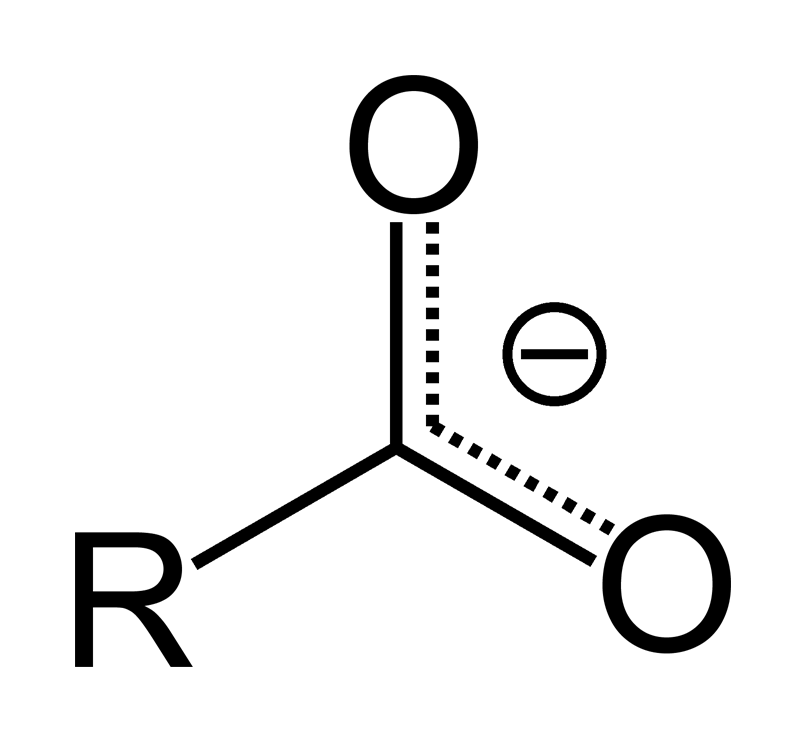
carboxylate - functional group
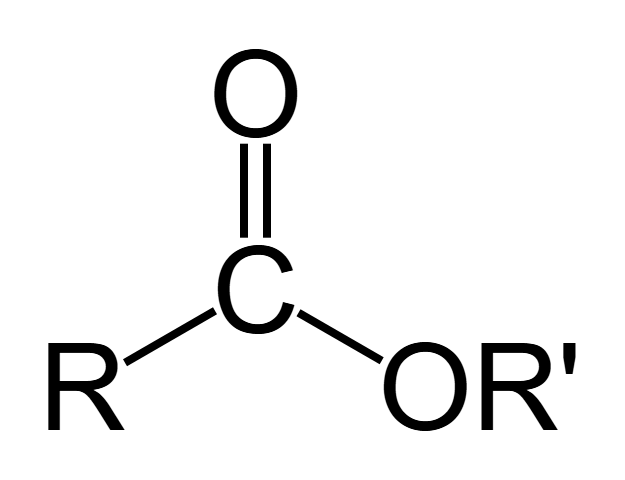
ester - functional group, linkage
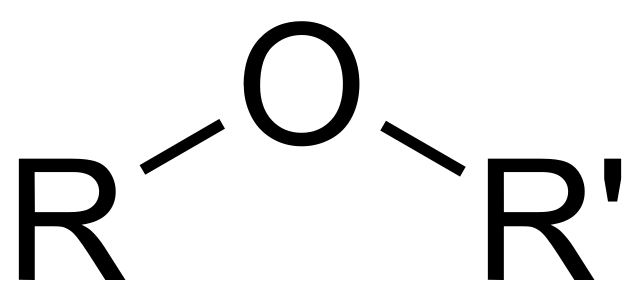
ether - functional group, linkage
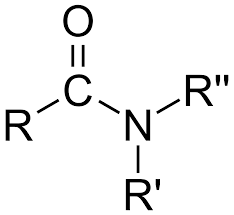
amide - functional group, linkage
sulfhydryl - functional group
functional group

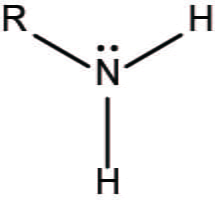
amino - functional group
functional group
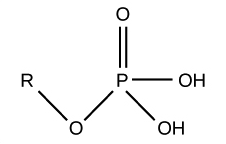
phosphate - functional group
can exist without H
4 oxygens
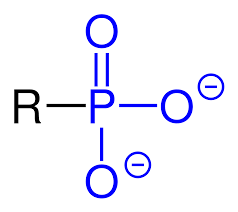
phosphoryl - functional group
3 oxygens
phosphate ester - functional group, linkage
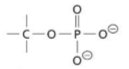
phosphoanhydride - functional group, linkage

residue
A monomer in a polymer
is referred to as a ____ since it loses a part of itself when bonding
polymer
__ are created from monomers being linking together in one direction. All covalent bonds are in one direction.
has a reducing end and a non reducing end
directionality
refers to when all covalent bonds are in the same direction
peptide bond
a bond for amino acids into proteins
C - N bonded
Phosphodiester bond
a bond between nucleotides to create nucleic acid
5’ to 3’
glycosidic bond
a bond between monosaccharides to polysaccharides
donor, acceptor
A hydrogen bond requires a donor and an acceptor.
a hydrogen ___ is one where a hydrogen is bonded to a electronegative atom, while a hydrogen ___ is one where a lone pair on a electronegative atom accepts a hydrogen
donors can be N/S/O H
Acceptors can be N/S/O electron pair
3, 2, 2
water has __ HB
ice has __ - donors, and __ - acceptors
electrostatic forces
ionic interactions
weaker than covalent
intramolecular, rather than intermolecular
Hydrogen bonds
dipole dipole interaction
van der waals
Dipole dipole interaction
london dispersion forces
dipole - dipole interaction
between polar non-charged groups
weaker than HB
London dispersion forces
between nonpolar
weaker than DD
Hydrophobic effect
when a nonpolar substance is placed ina polar substance, the surrounding water molecules forces the nonpolar substance to clump and stick together
tendency of water to minimize contact with nonpolar substances
involves london dispersion forces
is not the nonpolar coming together, it is water moleculars pushing them together
driven by entropy
when nonpolar substance comes into contact with water, water cannot form hydrogen bonds. This disrupts the hydrogen bond system of water, thereby causing water to create this shell which is more ordered and prevents disorder. This in turn lowers entropy.
if multiple clumps of nonpolar substances appear, water will push it all into one clump. This is again driven by entropy since it minimizes contact with nonpolar substance, less water moleculars are in a cage like structure, therefore increasing entropy and making it more thermodynamically favourable.
amphipathic/amphiphilic
experiences both hydrophobic and hydrophilic effect
depends on how much of the molecule is hydrophobic/hydrophilic
micelle
example of an amphipathic molecule, where hydrophobic fatty acid tails point inside away from water, and hydrophilic heads point outside