nutrition and disorders of the heart and blood vessels
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
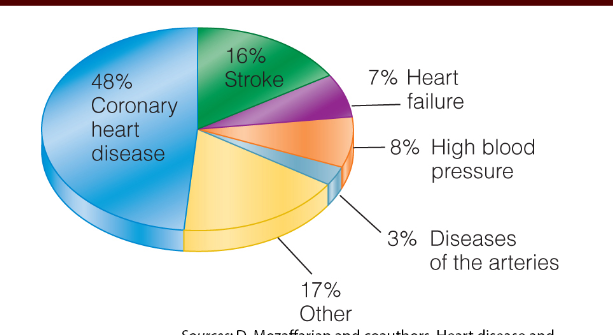
• Accounts for about __% of deaths in U.S
31%
what the leading cause of death worldwide`
cardiovascular disease
most common form of CVD and what is it due to
coronary heart disease
atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries restricting blood flow
what is a myocardial infarction
heart attack
sudden reduction in coronary blood flow
what is a stroke
blocked blood supply to brain tissue
other forms of CVD other than CHD
hypertension
heart failure
peripheral artery disease
what can CHD and atherosclerosis called
myocardial infarction
stroke
what happens in atherosclerosis
the artery walls become progressively thickened due to plaque accumulation
percentages of deaths from CVD in the US
what is plaque
fat deposits. fibrous connective tissue, and a small muscle cell
what does atherosclerosis arise from
injuries that cause injury to the inner arterial wall
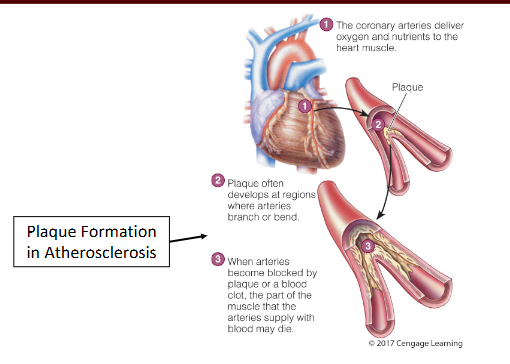
where does plaque often develop
at regions where arteries branch or bend due to a disruption in the blood flow in those areas
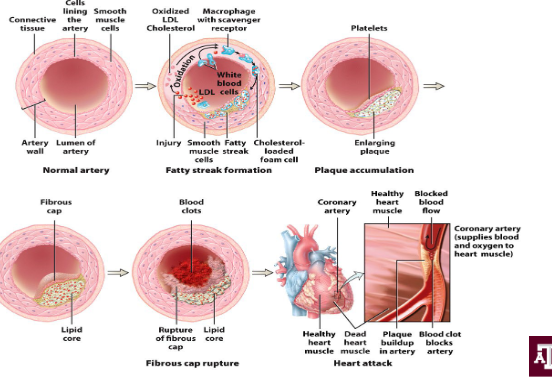
the process of atherosclerosis
the subtle damage initiates an inflammatory response that is going to attack immune cells and increase the permeability of the vessel wall
then LDLs will slip under the endothelial cells of the artery and become oxidized by local enzymes are start to accumulate
eventually the plaque will thicken and harden
consequences of atherosclerosis
plaque can rupture and promote blood clots
and they interfere with blood flow
narrow lumen of artery
blood clots can lead to enlarged thrombus (blood clot), embolism (blood clot gets stuck in a narrow artery blocking blood flow), ischemia(reduced blood flow)
obstructed blood flow in coronary arteries (angina pectoris (pain) or heart attack)
peripheral artery disease (causes pain and weakness in legs and feet bc lack of blood flow)
kidney disease or kidney failure
aneurism
what is a blood clot called
a thrombus
what is the most common cause of an aneurism
atherosclerosis
what is an aneurism
a sack like abnormal dilation of a blood vessel’s walls
if it ruptures = massive bleeding and death
causes of atherosclerosis
inflammation (direct damage to the artery wall or material penetrating the surface of the vessel)
shear stress (stress of blood flow through arteries damaging them) /hypertension
abnormal blood lipids (when LDL is high, they are taken up in susceptible regions in the artery wall where they are prone to oxidation)
cigarette smoking (nicotine are toxic to endothelial cells. also it causes induction of chronic inflammation and vasoconstriction)
diabetes mellitus (hyperglycemia leads to accumulation of advanced glycation end products - AGEs)
age and gender (risk seen in men older than 45 and women over 55. risk in women post menopause)
tell me how abnormal blood lipids cause atherosclerosis
when blood lipid levels are high
when LDL is high, they are taken up in susceptible regions in the artery wall where they are prone to oxidation.
elevated levels of VLDL influences production of other atherogenic lipoproteins, promotes inflammation
tell me abt how HDL affects atherosclerosis
HDL protective bc they remove cholesterol from circulation and they inhibit inflammation
what to remember about LDL sizes
they come in all sizes
so super small and most dense LDLs can slip into arteries and are more atherogenic than the larger
atherosclerosis steps image
what is the most common type of CVD
coronary heart disease
what is coronary heart disease also known as
coronary artery disease
what does coronary heart disease lead to
angina pectoris
heart attack
sudden death
what is coronary heart disease
impaired blood flow through the coronary arteries
symptoms of coronary heart disease
pain in chest
SOB
weakness and fatigue
nausea
vomiting
abdominal discomfort
Angina pectoris symptoms are triggered by
exertion; subside with rest
Heart attack causes severe
pain; lasts longer; occurs without exertion
when do coronary heart disease symptoms arise
several years post condition
are men or women more likely to have a heart condition?
womenr
risk factors for coronary heart disease
modified with diet is highlighted

what do AHA and ACC reccomend with risk factors?
AHA/ACC recommend an assessment for risk factors of atherosclerotic CVD every 4-6 years in individuals from ages 20-79
they developed an online calculator
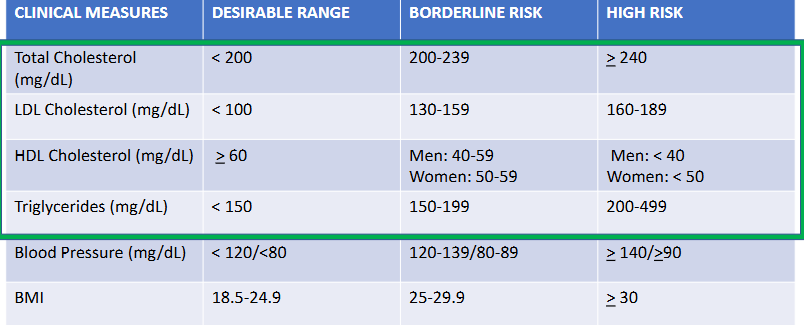
clinical measures in regard to evaluating your risk for coronary heart disease
clinicians review the lipoprotein profile or blood lipid profile, which include measures of total cholesterol, LDL, and HDL, and blood triglycerides
can also use the coronary artery calcium score which is obtained from a CT scan that evaluates the level of calcium content of plaque in the coronary arteries
levels of c reactive protein (marker of inflammation) may identify people as risk for CHD
ankle brachial index - ratio of bp measurements from the ankles and arms can find the presence of CHD
examples of lab and metabolic measures for CHD risk assessment
people with high risk of CHD are suggested to modify their lifestyle… how? (main features)
blood cholesterol-lowering diet, regular physical
activity (also not smoking) , and weight reduction
Balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains
tell me about the types of fats and regulating CHD
s
• Saturated fat…
• Replace with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (will lower LDL levels)
• (if you have high levels of LDLs) Consume <7% total kcal as saturated fat
• Polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat
• Replacing saturated with polyunsaturated fat associated with reduced morbidity, mortality from CHD
what fatty acids are beneficial for CHD risk
not omega 6 but omega 3!
limiting total fat intake, and types of fats with CHD suggestions
Total fat
• 25% to 35% of kcal
• 30% to 35% of kcal (if you have high triglycerides so that their carb intake isn’t excessive)
• Trans fats: keep intake as low as possible (will increase inflammation)
-Read food labels carefully
influence of dietary cholesterol on CHD
• Dietary cholesterol
somewhat unclear
• <200 mg/day for high-risk individuals
What are the recommendations for eggs and CHD risk?
eggs are not linked
undetermined
depends with healthy vs high risk people
soluble fibers and CHD
can reduce LDL levels by inhibiting cholesterol and bile absorption in the small intestines
Particularly soluble fiber found in in oats, barley, legumes, fruits
• Psyllium supplements effective in lowering cholesterol levels
Plant sterols and CHD
added to various food products (e.g., margarine, orange juice)
interferes with the cholesterol creation
• Supplied in dietary supplements
• ~2 g daily will lower LDL cholesterol by up to 10%
fish and omega 3 fatty acids in regards to CHD
also known as EPA and DHA
suppresses inflammation, lowers triglyceride levels and lowers blood clotting
fish is low in saturated fat and replaces meat dishes that have saturated fat!
AHA recommends 2 or more servings (3.5 oz) of fish per week,
with an emphasis on fatty fish
alcohol in regards to CHD
Light/moderate consumption
actually favorable
• 1 drink/day for women, 2/day for men
blood pressure and preventing CHD
Blood pressure reduction
• DASH eating plan (low-sodium, healthful diet)
• Reduce sodium intake (minimally-processed foods)
(sodium increases it and potassium lowers it)
physical activity and reducing CHD
40 min/session, at least 3-4 days/week
can reverse a number of risk factors
smoking and reducing CHD
Smoking cessation
• CHD incidence drops to levels near those of nonsmokers within 3 years
weight change and reducing CHD
Weight reduction (if obese)
• goal is to lose 5-10% of initial weight over 6-12 months
• Additional loss to acceptable weight
how to motivate your patients to manage their lifestyle changes
setting reasonable goals, practical sugesstiobs
vitamin supplementation and CHD risk
Vitamin supplementation and CHD risk
• B vitamin supplements and homocysteine
• Elevated levels of homocysteine associated with increased risk for CHD
-Amino acid produced during conversion of methionine to cysteine
-B-vitamins associated with this conversion include:
-Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12 and folate (low intakes of these leads to higher blood homocysteine concentrations so some patients eat a lot of these in hopes to reduce homocysteine but it says there is not correlation)
• Will B-vitamin supplements lower homocysteine?
• Yes, but.....
• No risk reduction for heart attacks noted
Antioxidant supplements (may inhibit atherosclerosis bc stress can cause it)
• Not recommended for heart disease prevention - inconsistent results (no proof)
what is hypertriglyceridemia
elevated blood triglyceride levels
who is hypertriglyceridemia common in
Common in people with diabetes mellitus, obesity,
metabolic syndrome, genetics, etc.
what is severe hypertriglyceridemia
(triglyceride levels are >500 mg/dL)
• Fatty deposits in skin
• Acute pancreatitis
how many people does hypertriglyceridemia affect
1/3 of adults in the US
hypertriglyceridemia may coexist with
elevated LDL cholesterol
nutrition therapy to reduce hypertriglyceridemia
Control body weight
• Become physically active
• Restrict alcohol
• Limit intakes of refined carbohydrates
-Especially fructose and sucrose
• In extreme cases (i.e. triglycerides > 1000 mg/dL):
-Very low-fat diets may be necessary
-< 15% of kcal from fat
• Fish oil supplements and hypertriglyceridemia
-3-4 grams EPA and DHA (the fish) from supplements recommend (from the previous 1 gram per day)
-Caution for blood thinning
hypertriglyceridemia and HDL
hypertriglyceridemia means low HDL
individuals that cannot improve CHD risk with nutrition and lifestyle changes must
b prescribes one or more indications
nutriton can effect drugs!
Drug therapies for CHD prevention
statins
bile acid sequestrants
nicotinic acid
Anticoagulants and aspirin
• Blood pressure medications
• Nitroglycerin (vasodilator) relieves angina
• Be aware of diet-drug interactions
tell me abt statins
Statins (e.g., Lipitor or Crestor) will reduce cholesterolsynthesis in the liver
• NDI(nutrient drug interaction): Avoid grapefruit, red yeast rice
tell me about bile acid sequestrants
less effective than statins
Bile acid sequestrants (e.g., Colestid or Questran)
interfere with bile acid reabsorption in the small intestine
• NDI: May interfere with absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
tell me about nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid (high dose niacin) lowers triglycerides;
increases HDL; reduces LDL and lipoprotein(a) levels
• Need to monitor liver enzymes, flushing in skin… bc liver enzyme elevation
drug therapies given immediately after a heart attack
Thrombolytic drugs to break up clot
• Anticoagulants or aspirin
• Painkillers
• Medications that regulate heart rhythm and reduce blood
pressure
• no food or beverages except for Sips of water or clear liquids only until condition stabilizes
treatment of heart attack once they are able to eat
Hearth healthy, sodium restriction (2000 mg/day) initially
• Small portions if tolerated - slowly regaining strength
• Cardiac rehabilitation programs
-Exercise therapy
-Instruction about heart-healthy food choices
-Help with smoking cessation
-Medication counseling
4th most common cause of death in U.S.
stroke
A leading cause of long-term disability
stroke
what is stroke
Sudden death of brain cells due to impaired blood flow to
part of brain
3 types of stroke
Types (3)
• Ischemic strokes (18%)
-Obstruction of blood flow to brain tissue
-Common cause: atherosclerosis
• Hemorrhagic strokes (13%)
-Bleeding within the brain due to rupture of blood vessels
-more deadly 33% result in death within thirty days
• Transient ischemic attacks (TAI)
-Sudden, short strokes. May predict more severe events.
what percent of strokes are ischemic?
87%
which type of stroke is most deadly
hemorrhagic stroke
more deadly 33% result in death within thirty days
stroke prevention
Recognize stroke risk factors: similar to those for heart disease
-Hypertension, elevated LDL, diabetes, smoking, physical inactivity
• Make lifestyle choices to reduce risk
• Medications
-Antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin)
-Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin [Coumadin])
neurological effects of stroke depend on
Neurological effects of stroke vary depending on area of the
brain that has been injured. May include:
• Difficulty speaking (dysphasia or aphasia)
• Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
• One-sided paralysis
in stroke
what is necessary to prevent brain damage?
early diagnosis and treatment
Preserve brain tissue and minimize long-term disability
• Ideally, thrombolytic drugs used within 4.5 hours after ischemic stroke
tell me about post stroke rehabilitation programs
Rehabilitation programs
• Start as soon as possible after stabilization
• Physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech and language pathology, and
kinesiotherapy
nutrition care post stroke
Focus: help patients maintain nutrition status and overall health
• Tube feedings may be needed until skills regained
definition of hypertension
Chronic elevation of blood pressure
• Primary or essential hypertension
• Cause is unknown
bp stats

what is a Primary risk factor for atherosclerosis and
cardiovascular diseases
hypertension
what is a primary cause of stroke and kidney failure
hypertension
how much of US adults does hypertension effect?
Affects about one-third of U.S. adults
an estimated __% of people with hypertension are
unaware that they have it
17%
in what race is hypertension prevalence higher?
african americans
Factors that influence blood pressure Blood
pressure depends on
Cardiac output: volume of blood pumped by the heart
• Peripheral resistance: resistance the blood encounters
in the arterioles
what is peripheral resistance affected by
diameter of arterioles and viscocity of blood
Physiological factors that influence blood pressure
Nervous system: regulates heart muscle contractions and arteriole
diameters
• Hormonal signals: may cause fluid retention or blood vessel
constriction
- Kidneys - control hormone secretion for vasoconstricion and retension of na and h2o
90-95% of hypertension cases the cause it….
znd what is this called
unknown
primary or essential hypertension
if hyperension is caused by a known physical or metabolic disorder it is called
secondary hypertension
Risk factors for hypertension
nearly 2/3ds of older individuals have hypertension
bp that is sensitive to salt?

Lifestyle Treatment of Hypertension***
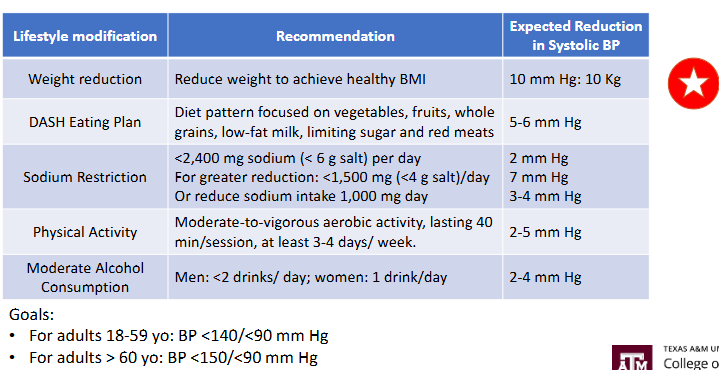
weight and hypertension treatment**
Weight reduction
• Blood pressure reduced by ~1 mm Hg per kg weight loss
Dietary approaches for blood pressure reduction***
more potassium, fiber, magnesium, and calcium

drug therapies for hypertension
Combinations of two or more medications usually required
• Most treatments include diuretics
• Lower BP by reducing blood volume
• Other medications:
• Calcium channel blockers
• Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
• Angiotensin-receptor blockers
what is heart failure
Heart’s inability to pump adequate blood
• Also called congestive heart failure results in buildup fluid
what dos heart failure lead to
Fluid accumulation in extremities and lungs
• Heart enlarges (to accomdate the extra workload by eventually will wekaen!)
causes of heart failure
Various causes
• Often a consequence of chronic hypertension or CHD
Leading cause of hospitalization in patients >65 years old
heart failure
Consequences of heart failure
left sided failure
right sided failure
effects food intake and level of physcial activity
cardiac cachexia
what is left sided heart failure
Left side of heart receives fluid from lungs (rich in oxygen)
• Buildup of fluid in the lungs, i.e., pulmonary edema
• Shortness of breath; limited oxygen for activity
what is right sided heart failure
Right side of heart receives fluid from peripheral tissues
• Fluid accumulation in the lower extremities (edema), and abdomen (ascites)