L3-Bond enthalpy(1.4 kinetics)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Bond energy:
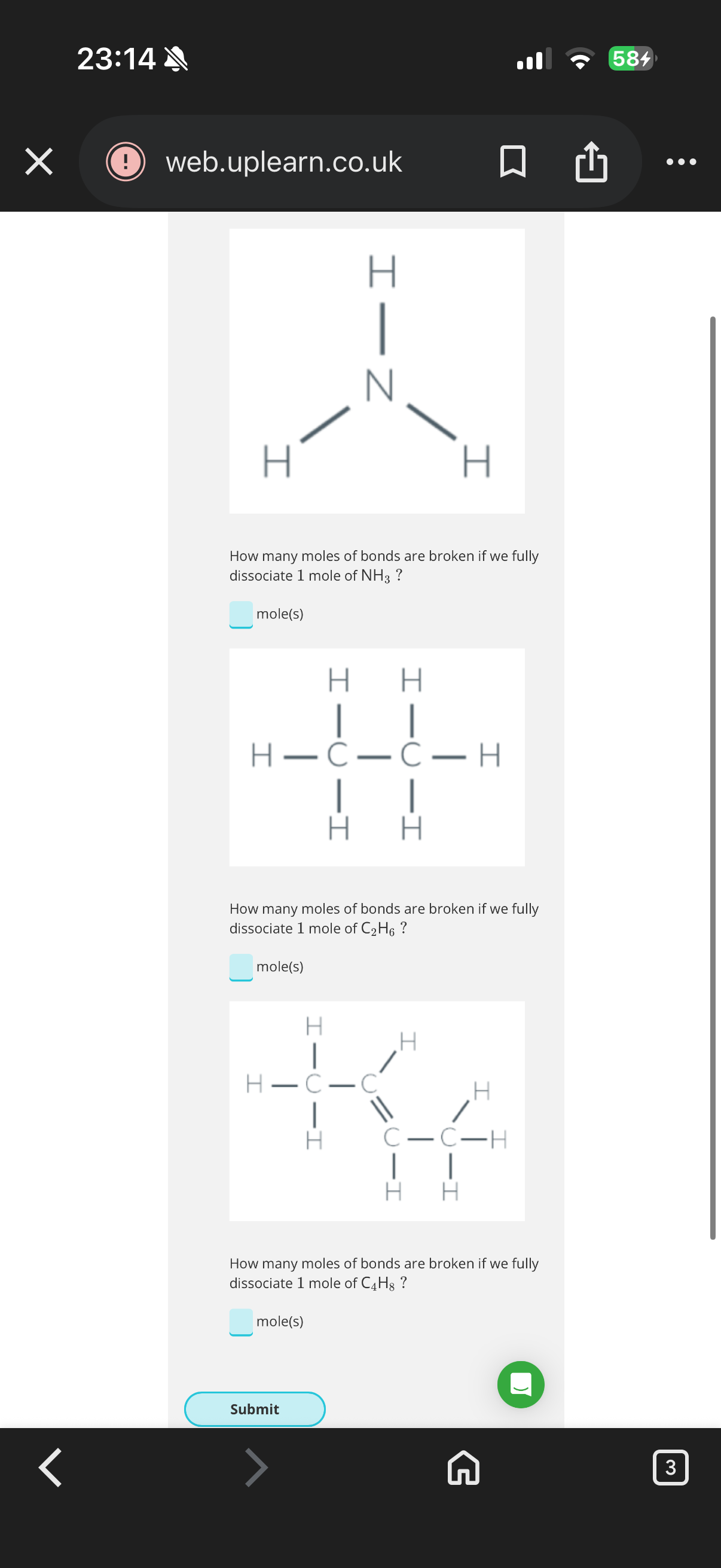
1.To break the two C=O bonds in CO2 we need to…
2.It always requires energy from the surroundings to break a bond between atoms, and breaking bonds is always...
It takes …3? to break the bonds between atoms which means that it’s …4?. When atoms split from a molecule, we say that they…5?.
Working with a molecule of bonds:
6.If it takes 7.24×10−19J to break one hydrogen bond, how much energy does it take to break one mole of hydrogen bonds?
Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
7.How many CH bonds does a CH4 molecule contain?
8.Answer image q?
Instead of looking at the enthalpy change when one bond is broken, we look at the enthalpy change when one …9? of bonds is broken.
Add energy from the surroundings
endothermic 3. Energy 4.endothermic. 5.dissociate
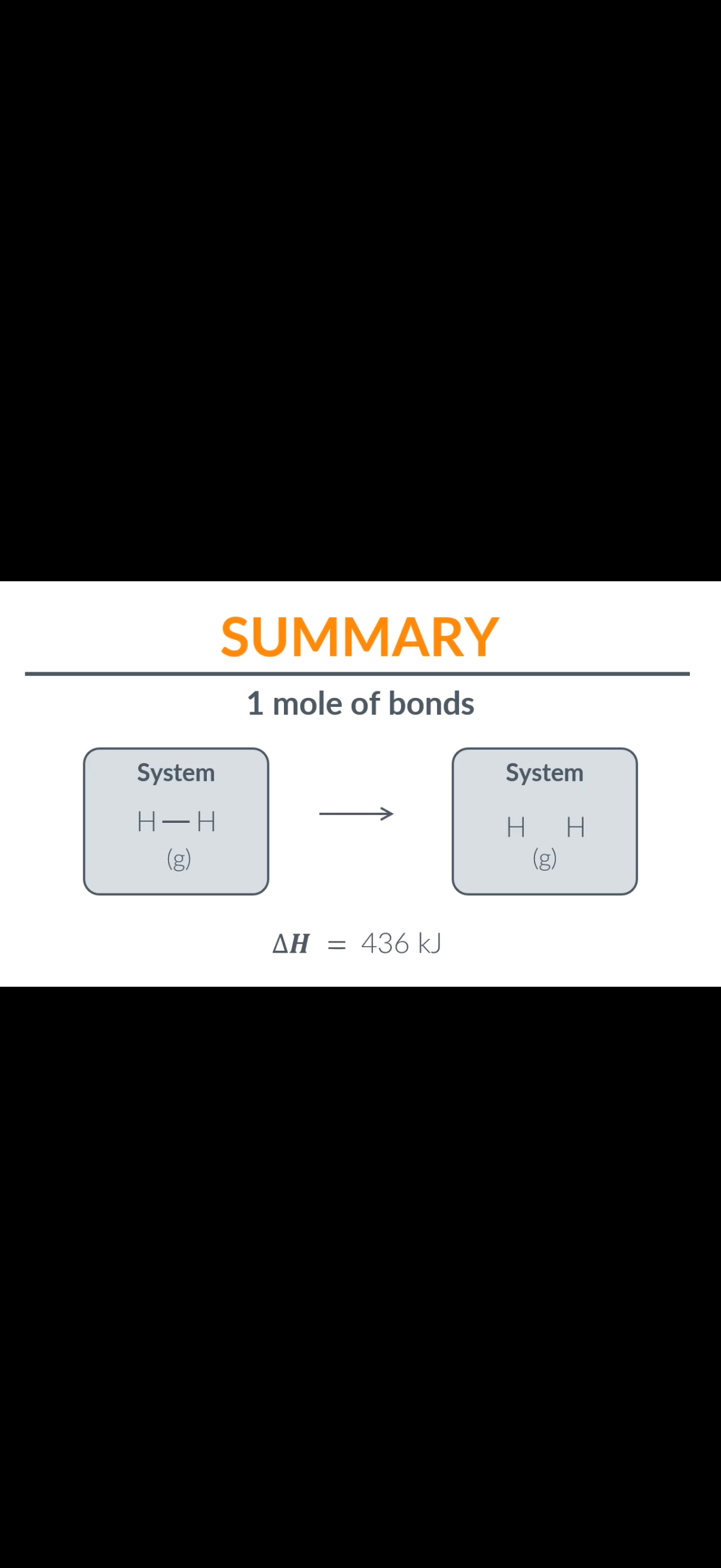
436KJ (Explanation-The energy required to break a single hydrogen bond is given as Ebond =7.24×10-19J.The number of bonds in one mole of a substance is given by (Na)Avogadro's number.
•To find the energy required to break one mole of bonds, multiply the energy required per bond by Avogadro's number.
Emole=Ebond×NA
𝐸mole=𝐸bond×𝑁𝐴
Emole=(7.24×10-19J/bond)×(6.022×10*23bonds/mol)
𝐸mole=(7.24×10−19J/bond)×(6.022×10*23bonds/mol)
Emole≈435992.8J/mol
𝐸mole≈435992.8J/mol then divide by 1000
Four. 8. 3 then 7 then 11
mole
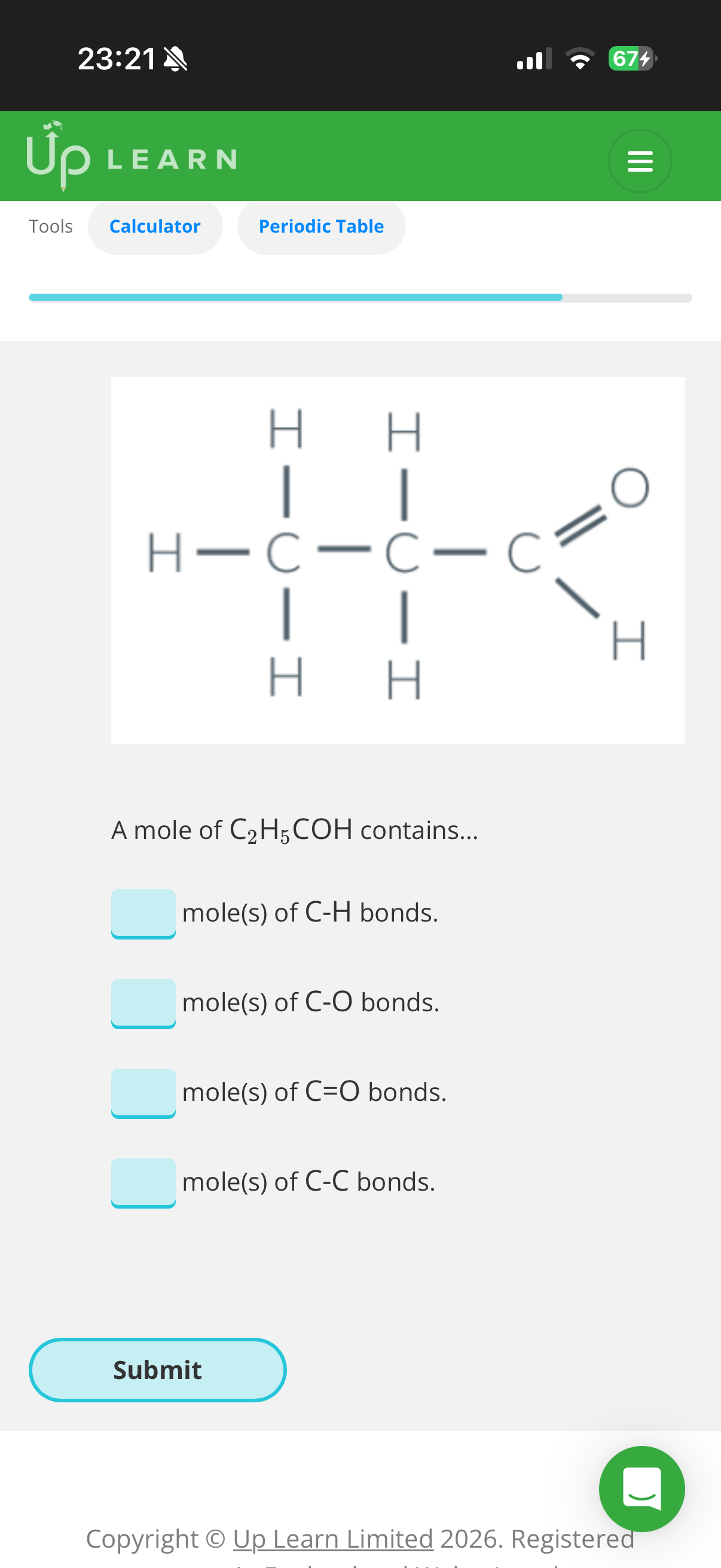
1.Answer image q?
Bond dissociation enthalpy:
2.To find the bond dissociation enthalpy for the carbon-hydrogen bonds in a molecule of methane we’d need to…
3.What is bond dissociation enthalpy?
Mean bond enthalpies measure the enthalpy change when …4? of bonds is broken, taken as an …5? from a …6? of different compounds.
7.The enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions, where all substances are in their standard state.”
What enthalpy is the definition referring to?
8.The enthalpy change when one mole of a bond is broken to give separated atoms with everything in the gas state.”
What enthalpy is the definition referring to?
9.The enthalpy change when one mole of bonds is broken, taken as an average from a range of different compounds.”
What enthalpy is the definition referring to?
2.Break all the bonds of one quarter of a mole of CH4 which would be in a gaseous state.
3.the enthalpy change when one mole of a bond is broken to give separated atoms with everything in the gaseous state.
1 mole. 5. Average 6.range
Enthalpy of formation
Bond dissociation enthalpy
Mean bond enthalpy
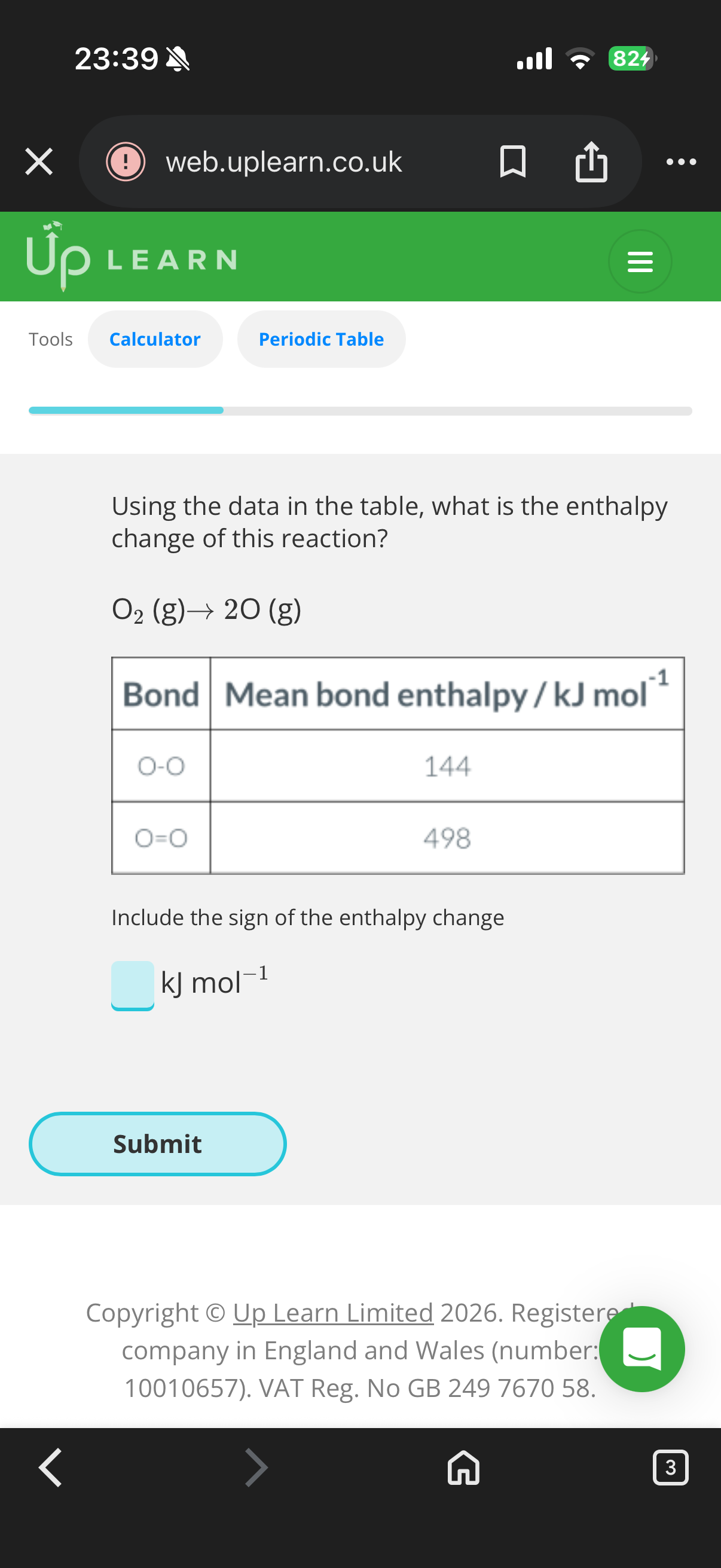
+498KJ Mol-1(endothermic reactions break bonds are and positive)
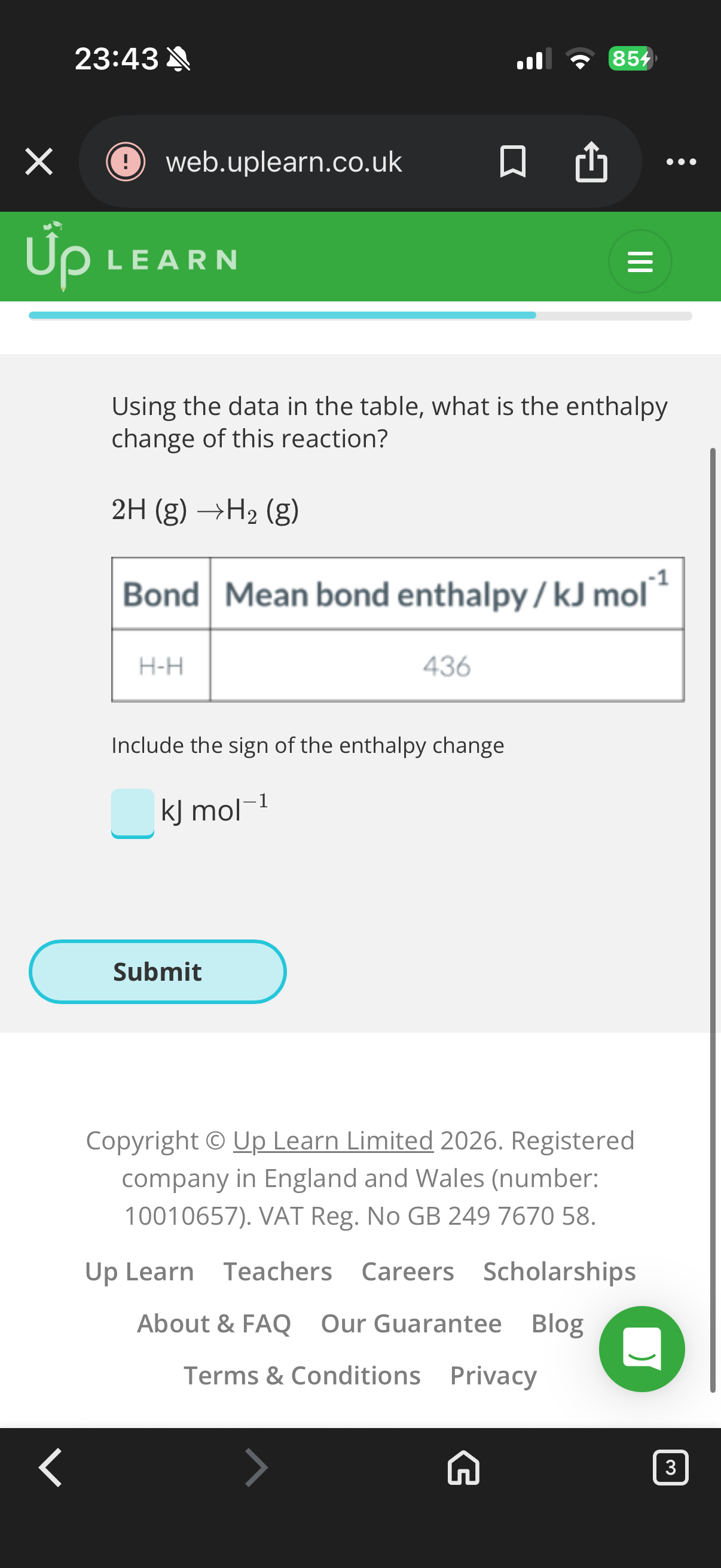
Exothermic reactions form bonds and are negative

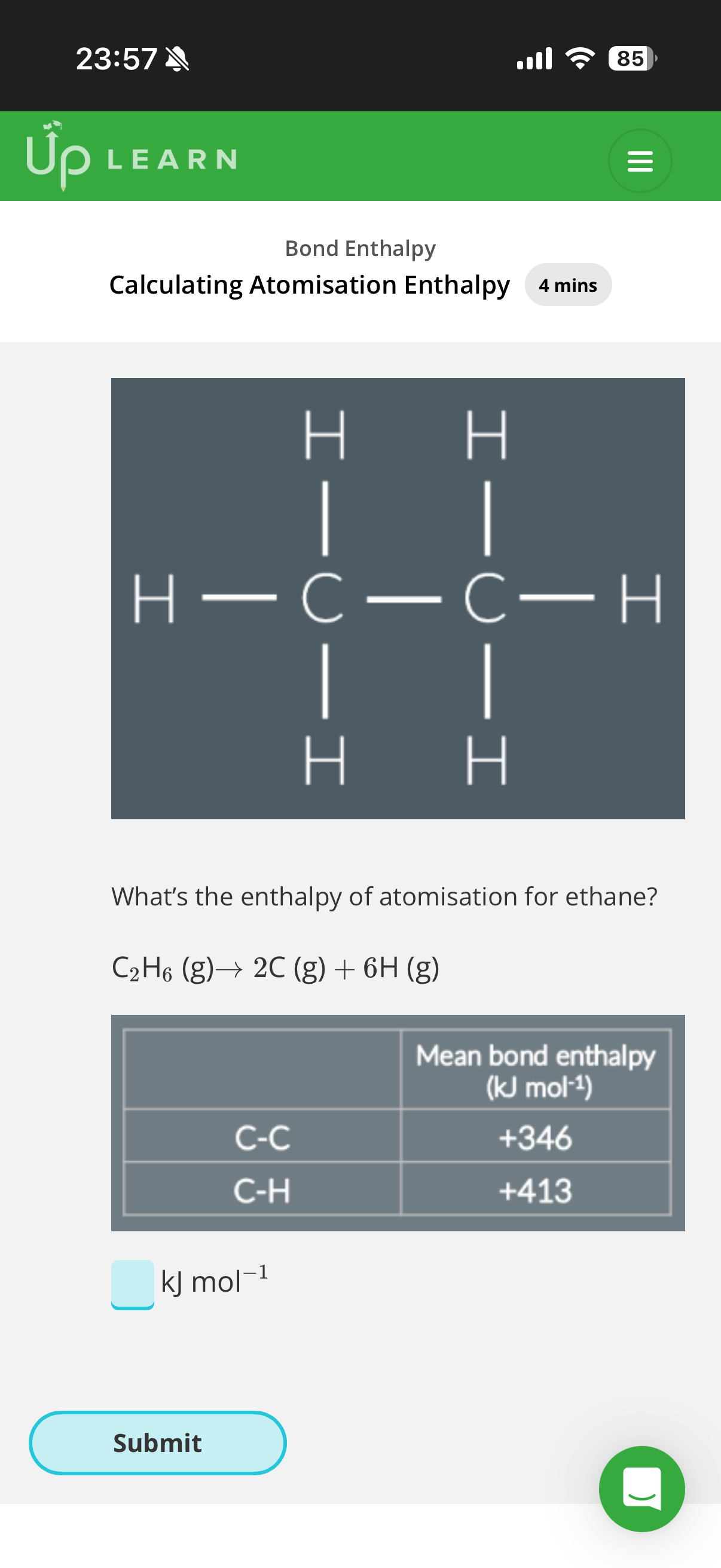
Calculating atomisation enthalpy:
1.What is the enthalpy change for this reaction?
NH3(g)→N (g)+3H (g)
Given the mean bond enthalpy of N-H is 391kJ mol−1.
2.Answer image q?
Steps to calculate atomisation enthalpy:
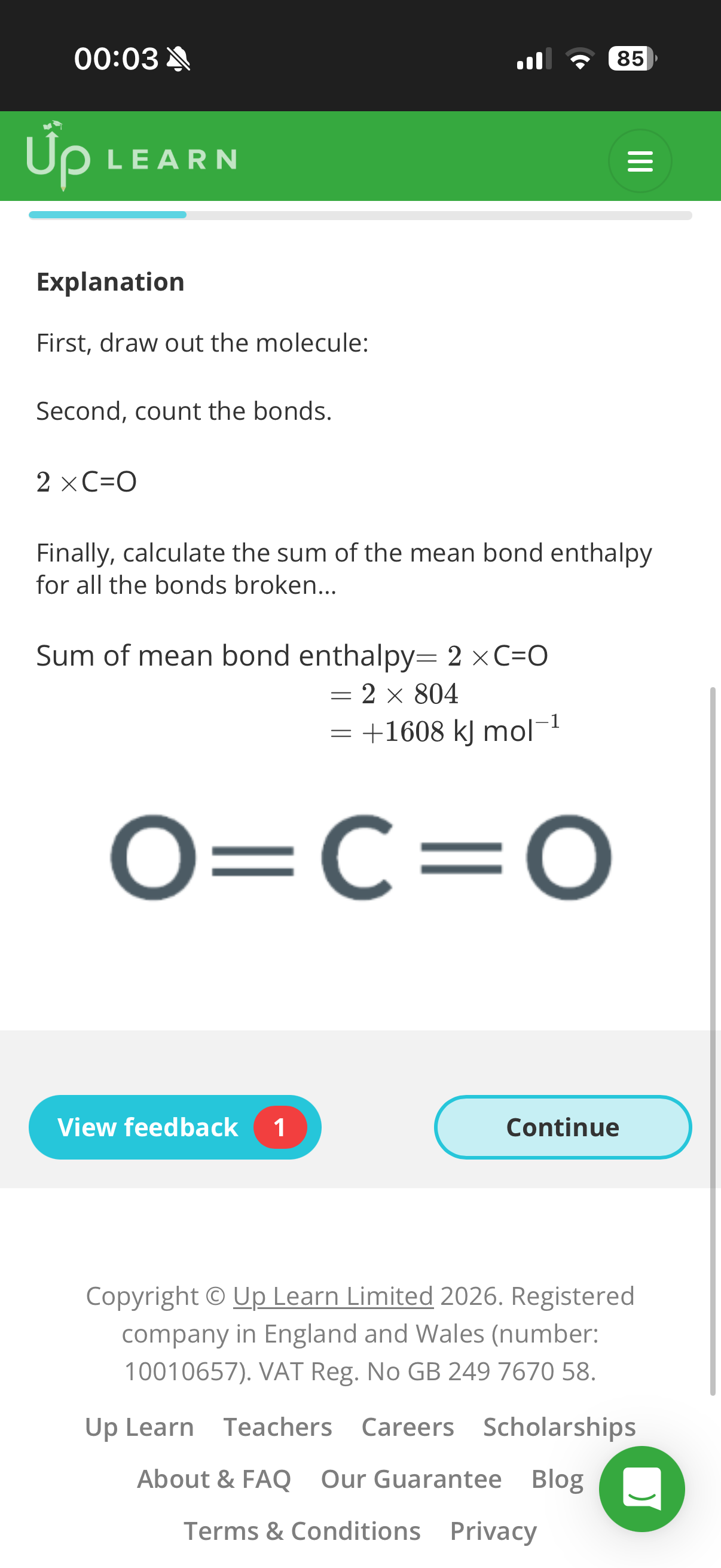
First, …3? the molecule.
Second, count the …4?.
Third, calculate the …5? of the mean bond enthalpy for all the bonds broken.
+1173KJ mol-1 (391X3)
Draw. 4. Bonds. 5. Sum
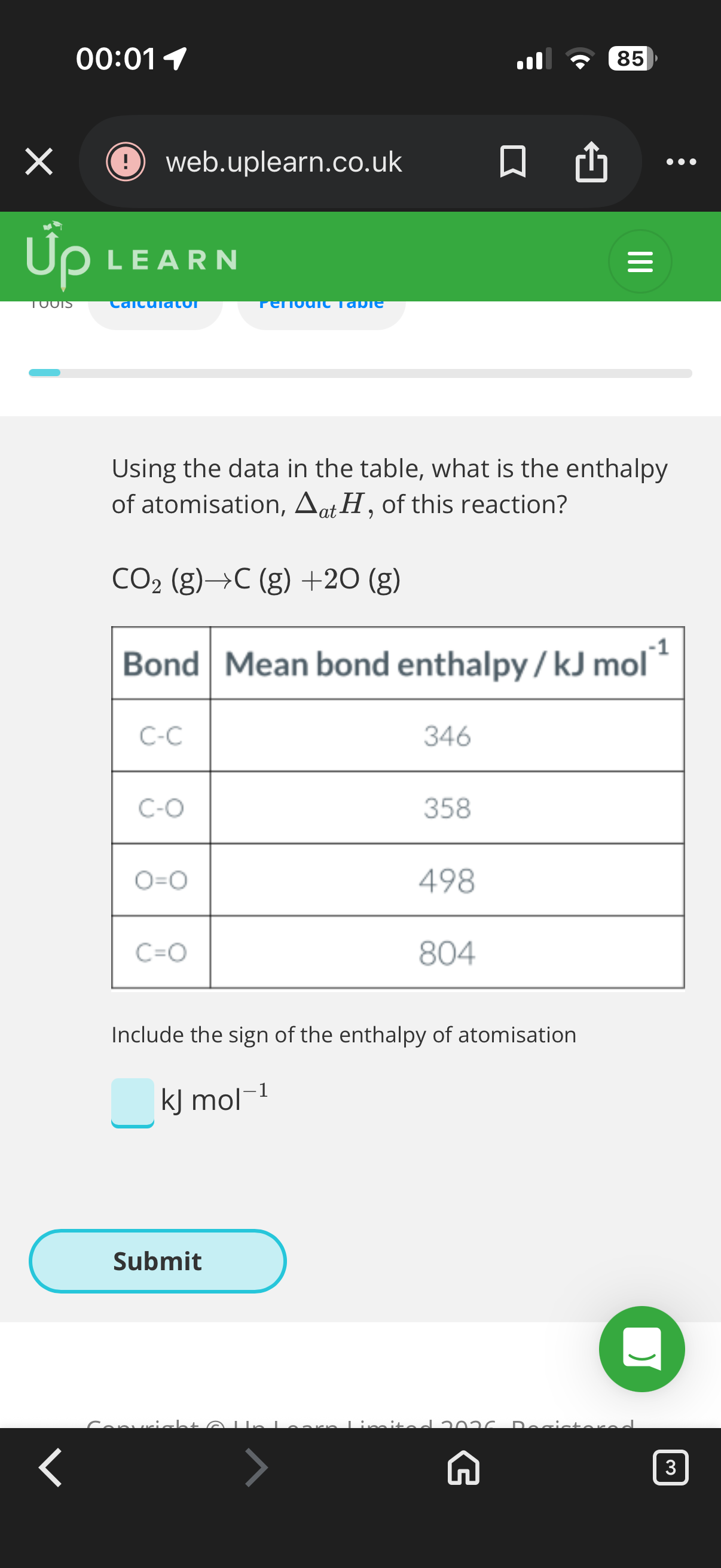

Answer image q
What is enthalpy of atomisation?
2.The enthalpy of atomization is the enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from the element in its standard state under standard conditions.

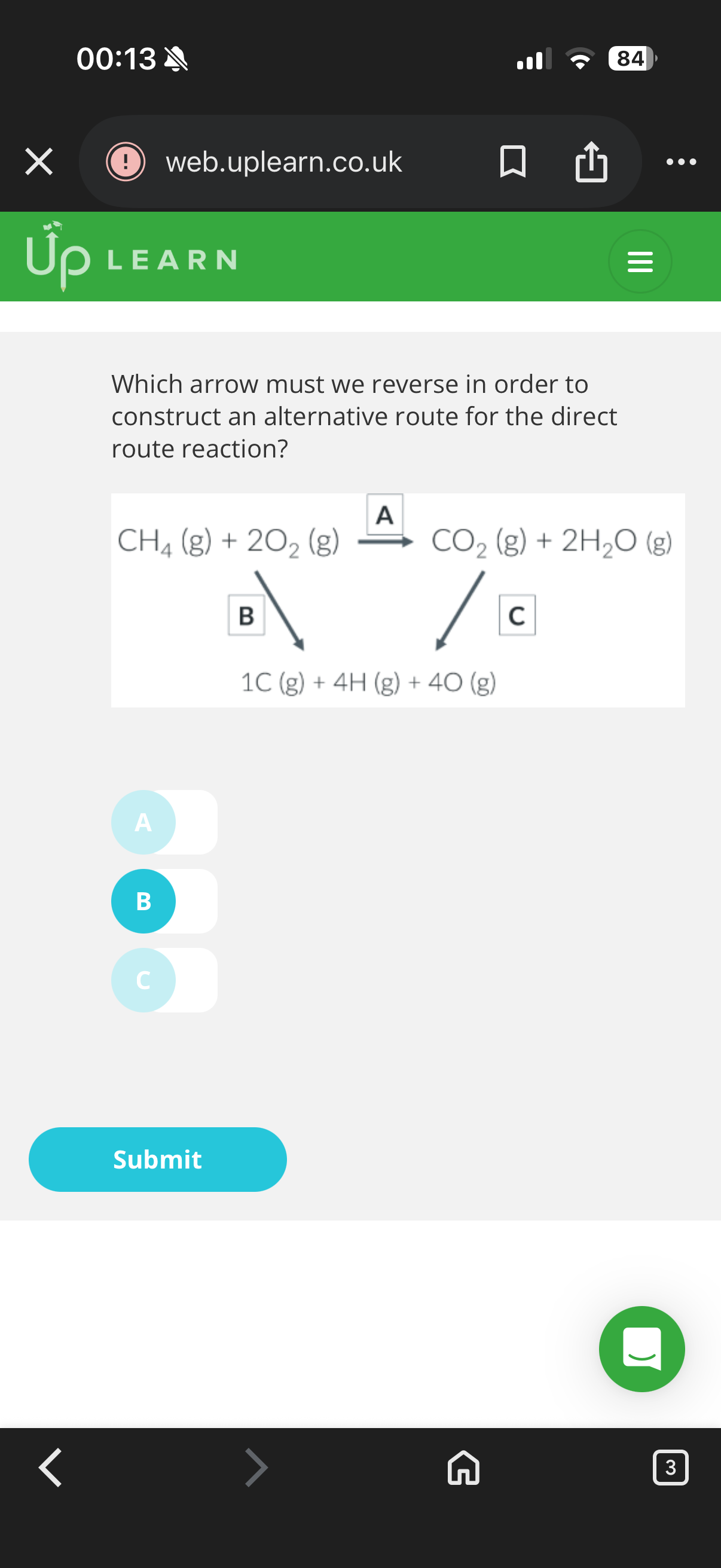
Bond enthalpy and alternative reaction routes:
1.Answer image q?
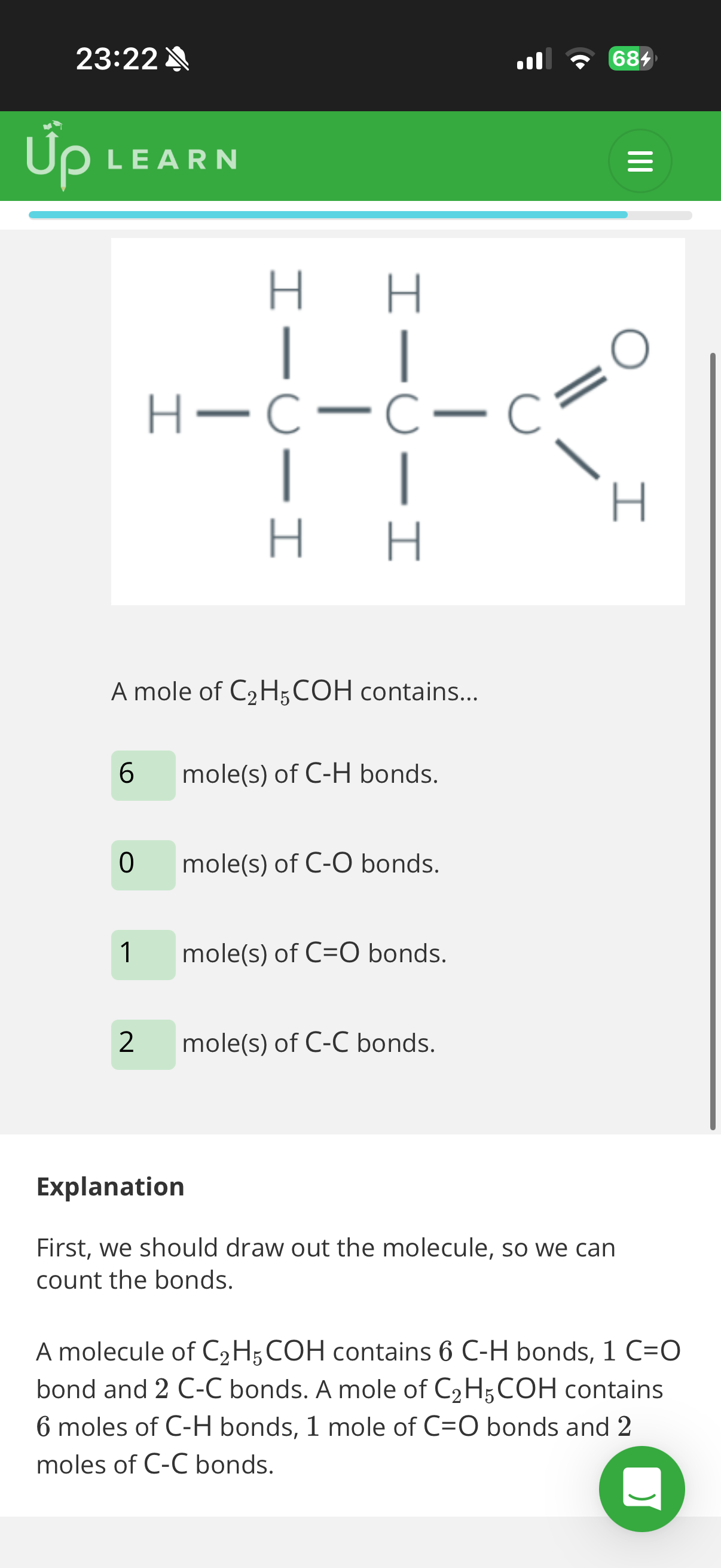
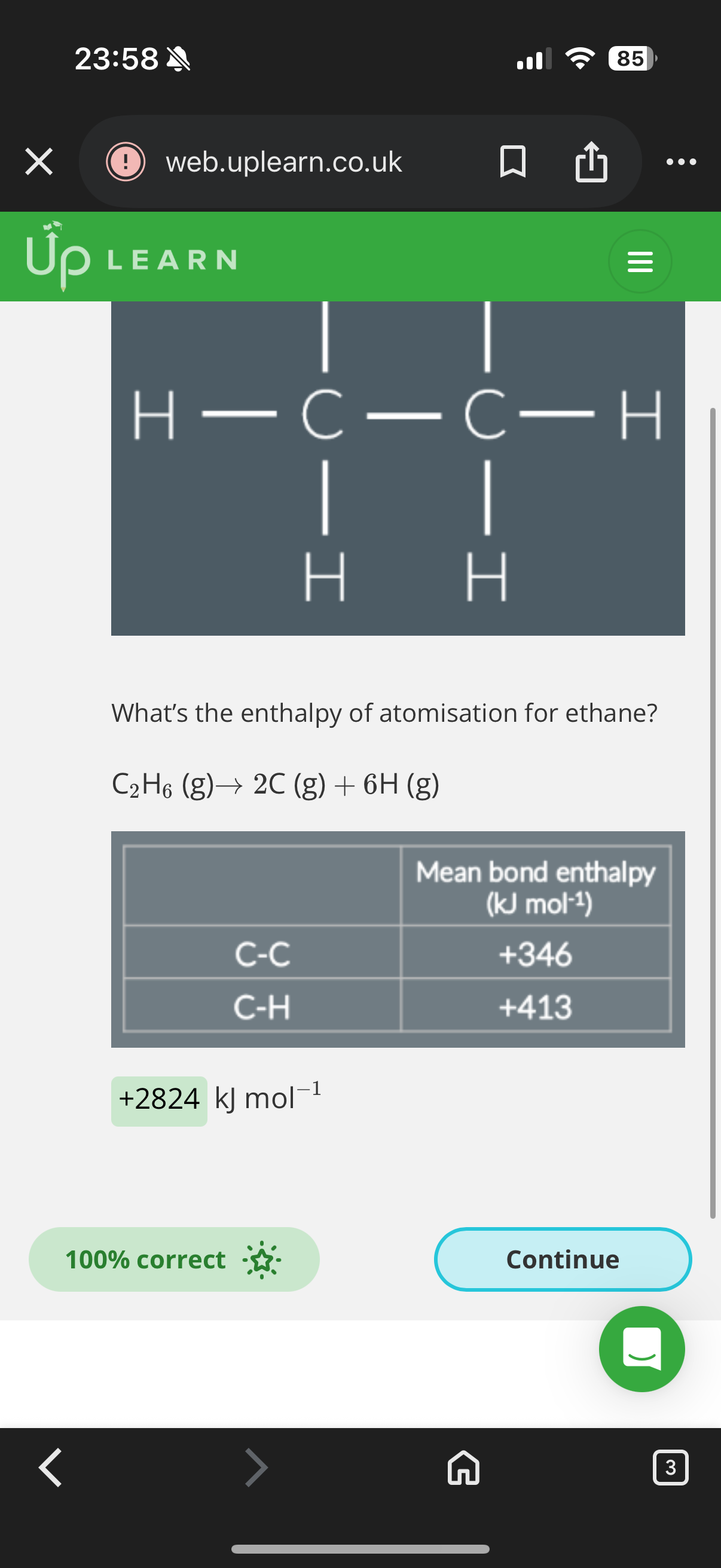
2.What’s the enthalpy of atomisation for methane(CH4-image)?
Given the mean bond enthalpy of C-H is +413kJ mol−1
3.What’s the enthalpy of atomisation for 2 moles of O2?
Given the mean bond enthalpy of O=O is +498kJ mol−1
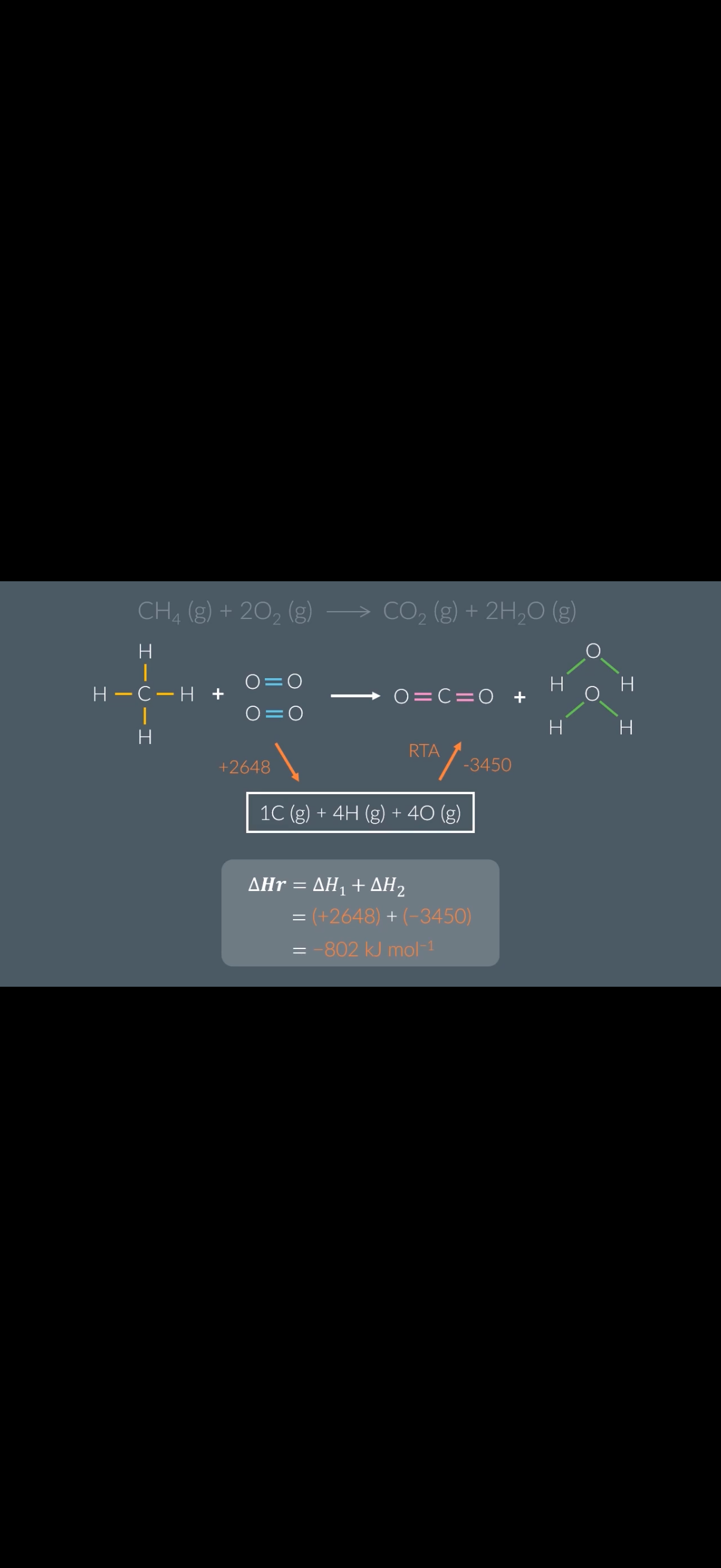
4.What is the enthalpy of atomisation for the starting reactants?
5.What’s the enthalpy of atomisation for the final products of this reaction?
Mean bond enthalpy of C=O: +799kJ mol−1. Mean bond enthalpy of H-O: +463kJ mol−1
Steps to work out the alternative route reaction for bond enthalpies:
1.Write out a full …5? for the direct route of the reaction.
2. Design an …6? reaction route using the enthalpy of Atomisation
.
3. Create a …7? ,noting down which arrow was reversed.
4. Calculate the enthalpy of …8? for the products and reactants.
5. Add the values to the thermochemical cycle, checking the …9?.
6. Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction by …10? together the values.
1.C. 2. 1652 KJ mol-1 (413X4)
+996KJ mol-1 (
2×(+498kJ mol−1)2648 kj mol-1 (1652+996)
3450kJ mol−1
Explanation-The final products of this reaction are one mole of carbon dioxide for every two moles of water.
•To atomise one mole of carbon dioxide, we must break two moles of C=O double bonds.
•2×(+799kJ mol−1)=+1598kJ mol−1
To atomise two moles of water, we must break four moles of H-O bonds.
•4×(+463kJ mol−1)=+1852kJ mol−1
•So, the enthalpy of atomisation for the final products is
+1598kJ mol−1+1852kJ mol−1=+3450kJ mol−1
5.equation. 6.alternative. 7.thermochemical cycle 8.atomisation. 9. Signs. 10. Adding
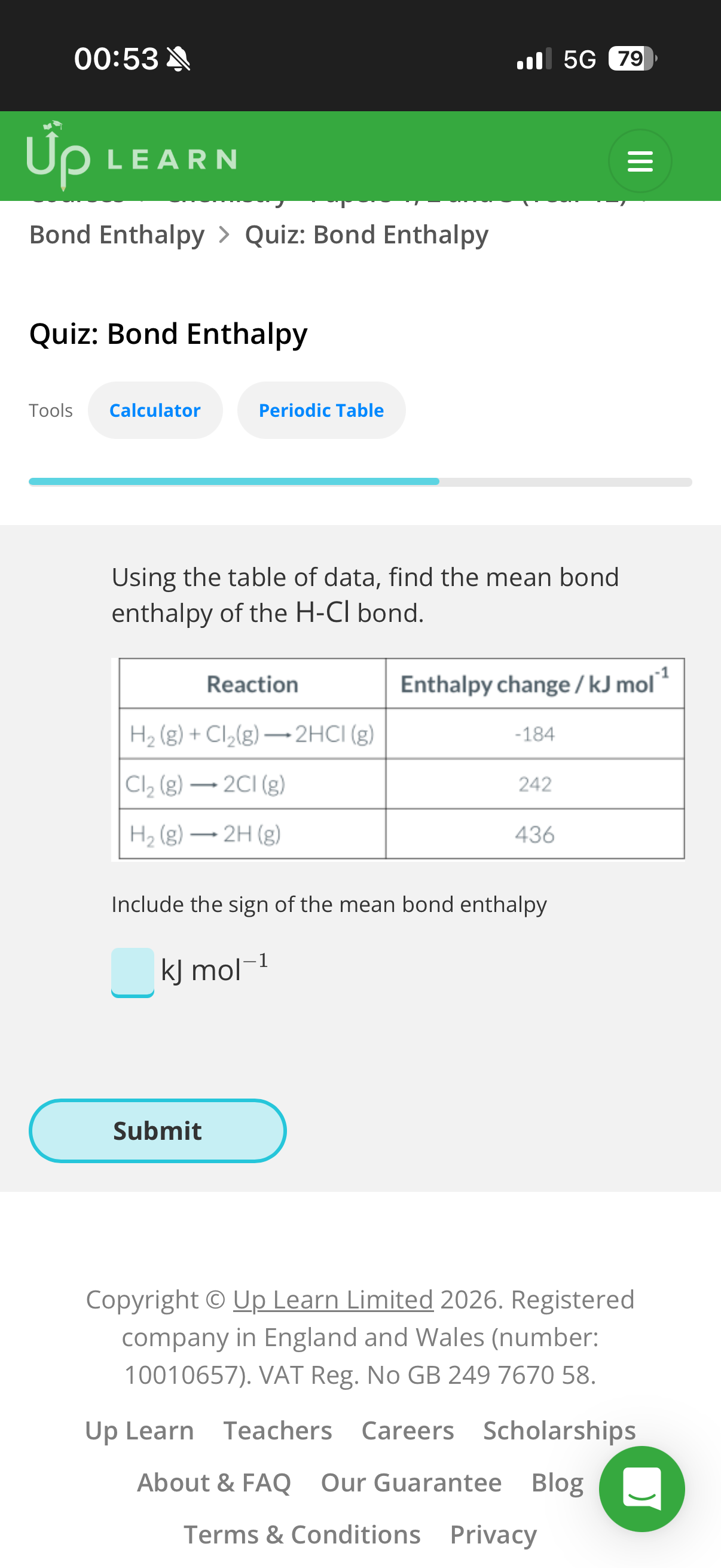
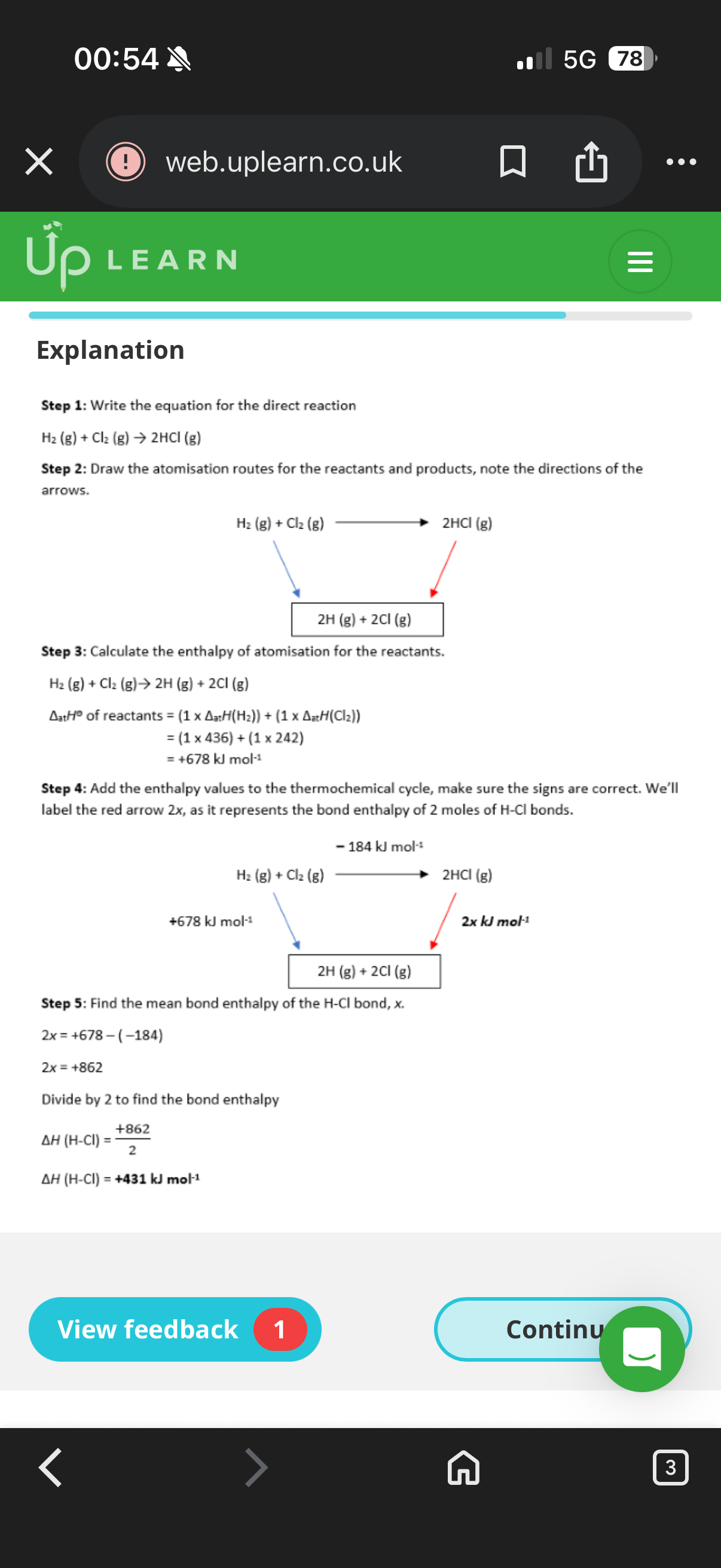
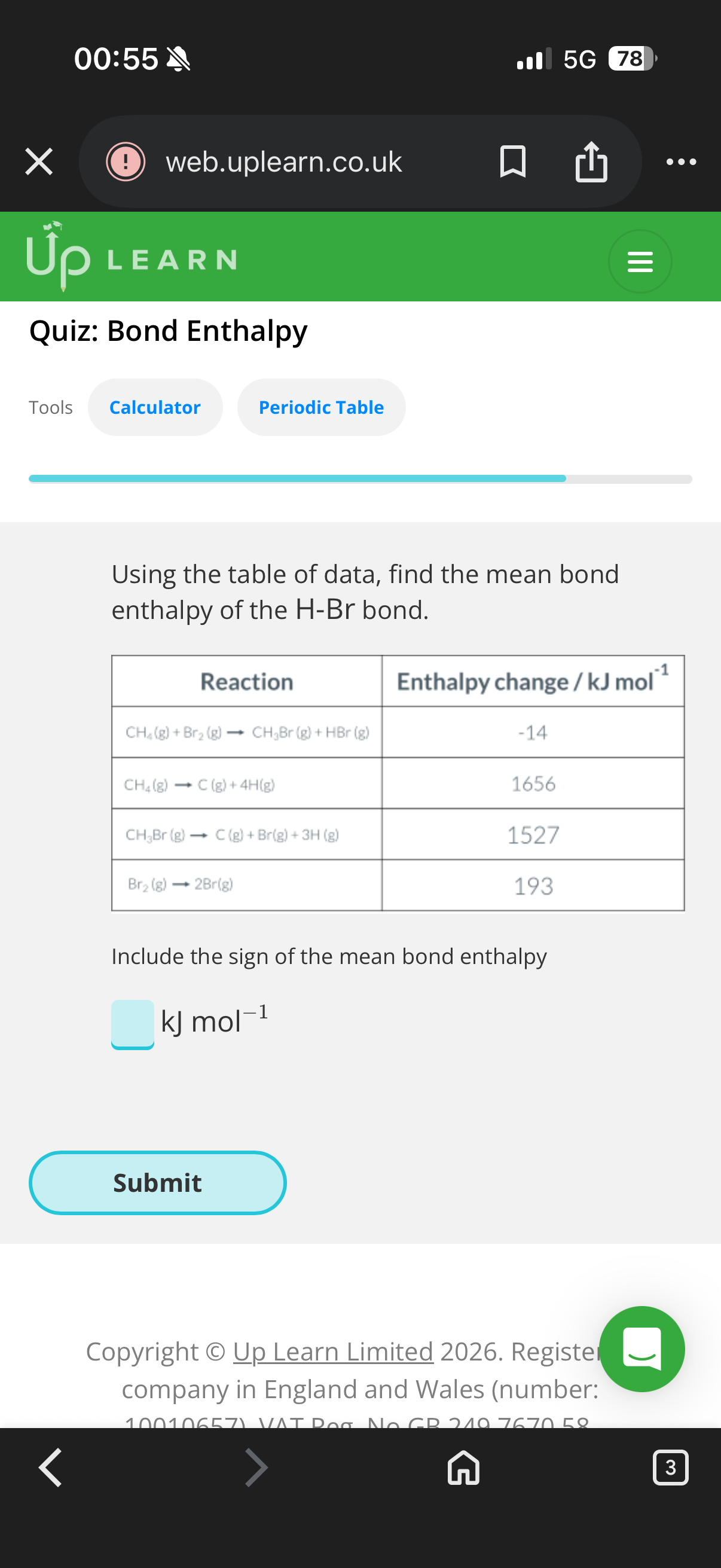
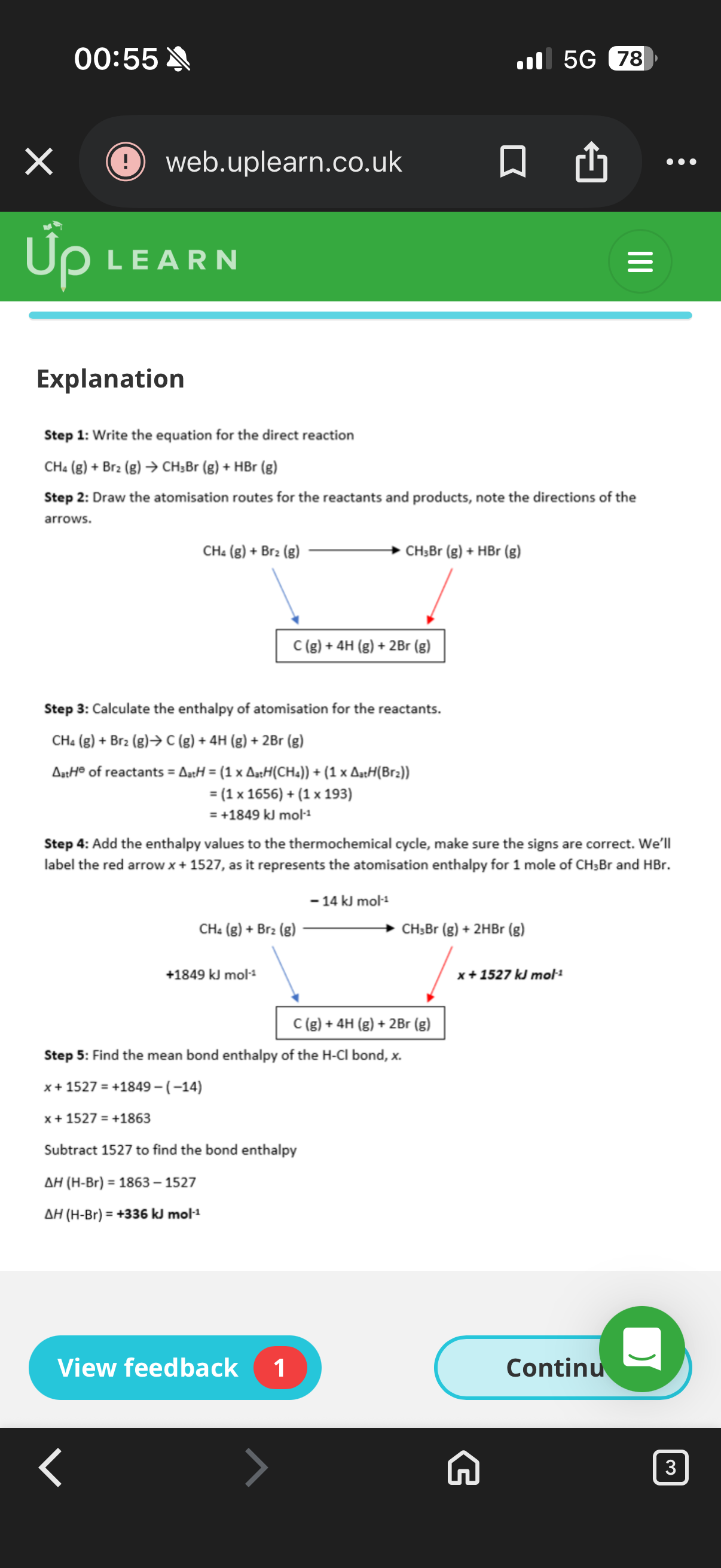
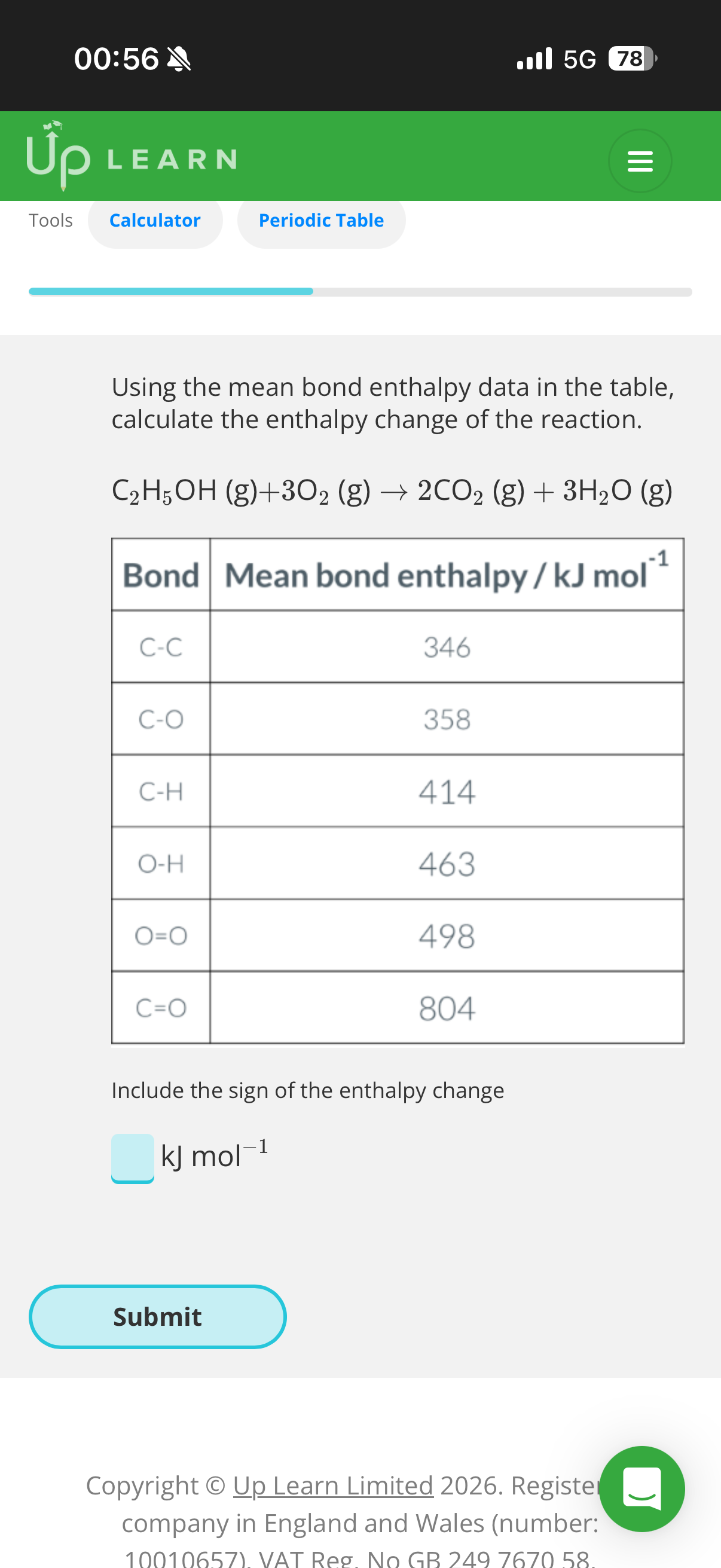
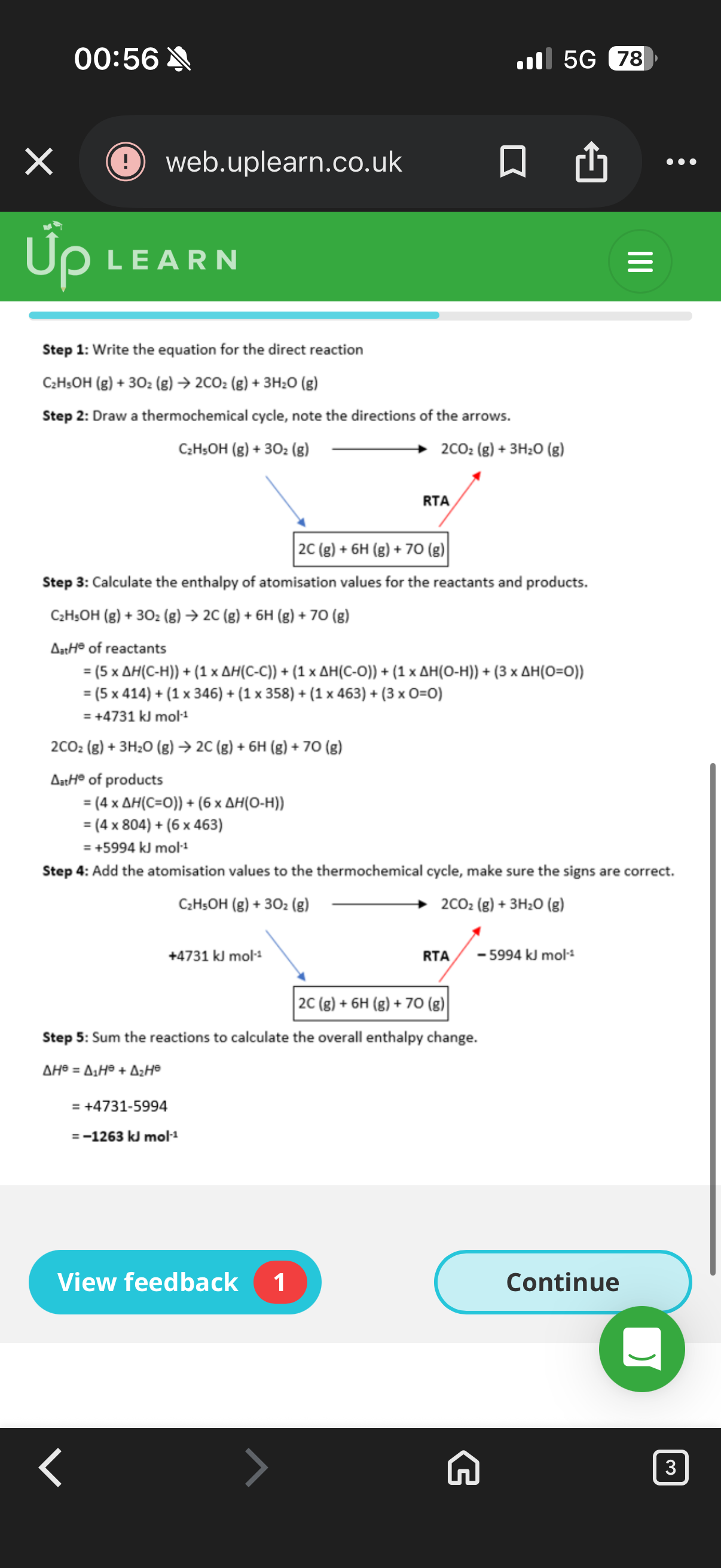
Limitations of bond enthalpies:
1.Why is there a difference between the enthalpy change Emma calculated using a bomb calorimeter and the enthalpy change we calculated?
2.Mean bond enthalpies will never give a totally accurate result for the enthalpy change of a direct route reaction because the values are taken from a…
1.We used mean bond enthalpies to calculate our answer, which are calculated from a range of different compounds. On the other hand, when Emma combusted methane in a bomb calorimeter she was only breaking the CH bonds in methane. So, the values are different.
2.range of different compounds