IB Physics HL A1, A2, A3, and C1 Review
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
The _____ force acts perpendicular to the surface that counteracts the body
Normal
Elastic restoring force follows _____ law
Hooke’s
_____ Force opposes the motion of a body through a fluid
Drag
_____ is a product of the mass and the velocity of the body
Momentum
In inelastic collisions, _____ is conserved but _____ is not conserved
momentum; kinetic energy
A block of mass 2.0 kg accelerates from a speed of 15 m/s to a speed of 20 m/s without changing its direction. What impulse acts on the block
10 N s
A Body is held in translational equilibrium by 3 coplanar forces of magnitude 3N, 4N, and 5N. 3 statements about these forces are 1. All forces are perpendicular to each other. 2. The forces cannot act in the same direction. 3. The vector sum of the forces is equal to 0. Which statements are true?
2 and 3
An object is suspended from. A spring balance. When the object is in the air the spring balance read 900 N. When the object is completely submerged in water the spring balance reads 400 N. The density of water is 1000 kg / m³. What is the volume of the object?
0.05m³
A child stands on a horizontal rotating platform that is moving at constant angular speed. The centripetal force on the child is provided by
The friction of the child’s feet
A block is mass 45 kg is placed on a horizontal table. There is no friction between the block and the table. An object of mass 15kg is placed on top of the block. A force F acts on the block so that it accelerates. The acceleration of the object and the acceleration of the block are the same so that they do not move relative to each other. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the object is 0.60. State the nature and direction of the force that accelerates the 15kg object.
friction to the right
A block is mass 45 kg is placed on a horizontal table. There is no friction between the block and the table. An object of mass 15kg is placed on top of the block. A force F acts on the block so that it accelerates. The acceleration of the object and the acceleration of the block are the same so that they do not move relative to each other. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the object is 0.60. Determine the largest magnitude of F for which the block and the object do not move relative to each other.
360 N
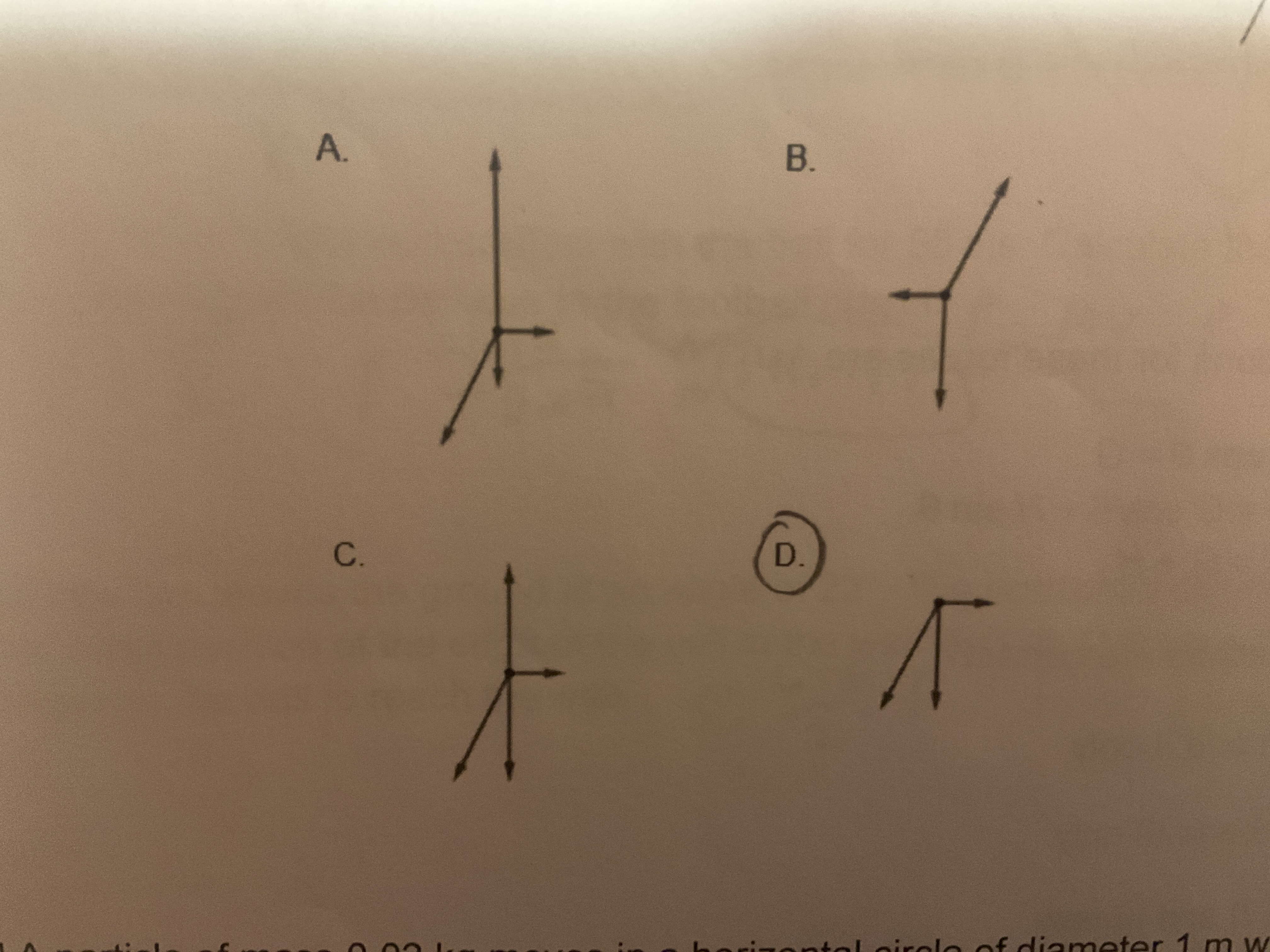
A toy balloon floats at the end of a string. A wind blows to the right. The balloon is in translational equilibrium. What is the Free Body Diagram of the forces acting on the Balloon?
B
A particle of mass 0.2 kg moves in a horizontal circle of diameter 1 m with an angular velocity of 3 rad / sec. What is the magnitude and direction of the force responsible for this motion?
0.09π² towards center the circle
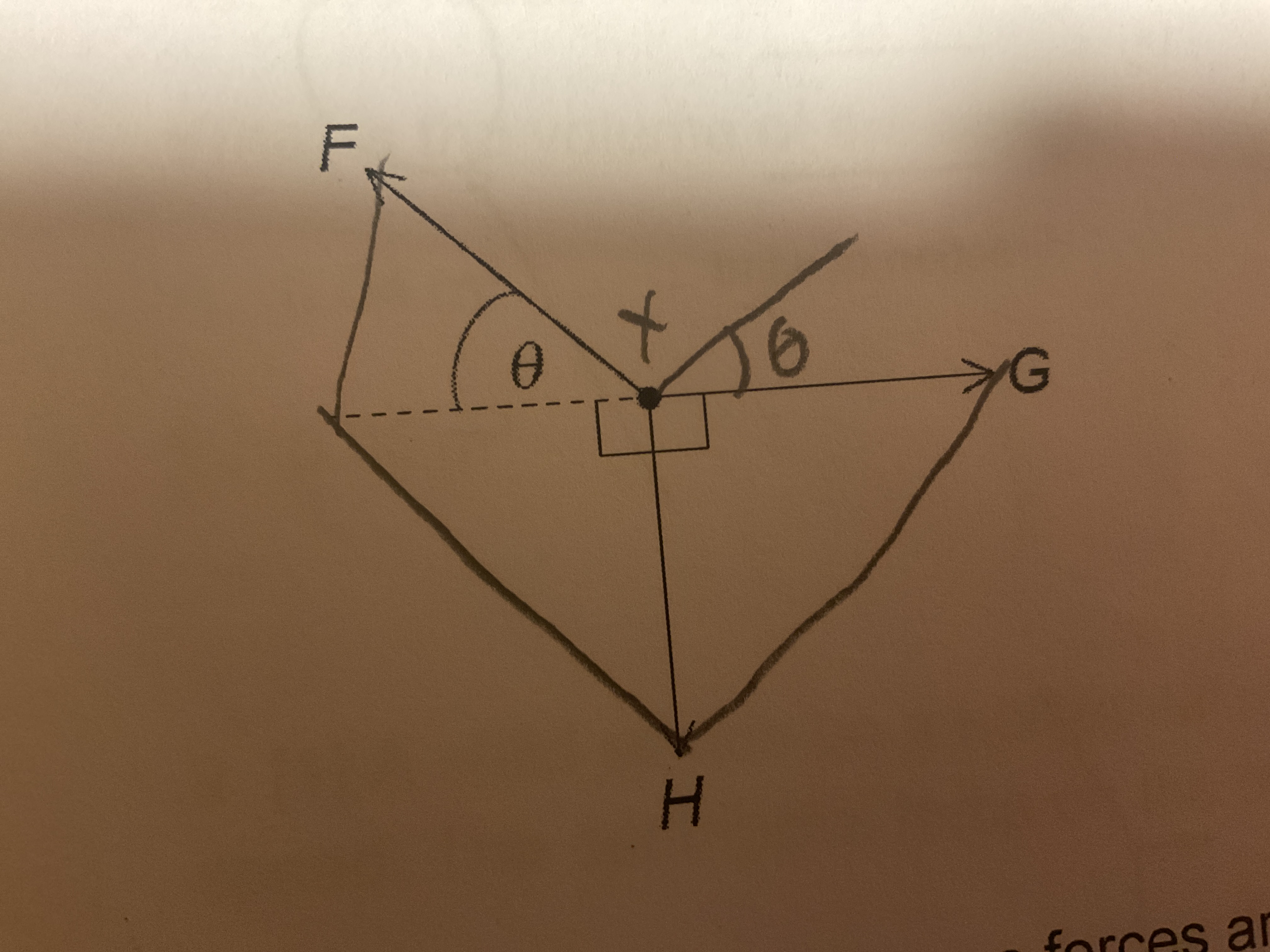
An object is held in equilibrium by 3 coplanar forces of magnitude F, G, and H that act at a point in the same plane as shown. 3 equations for these forces are 1. F cos (ø) = G. 2. F = G cos (ø) + H sin (ø). 3. F = G + H. Which equations are correct?
1 and 2
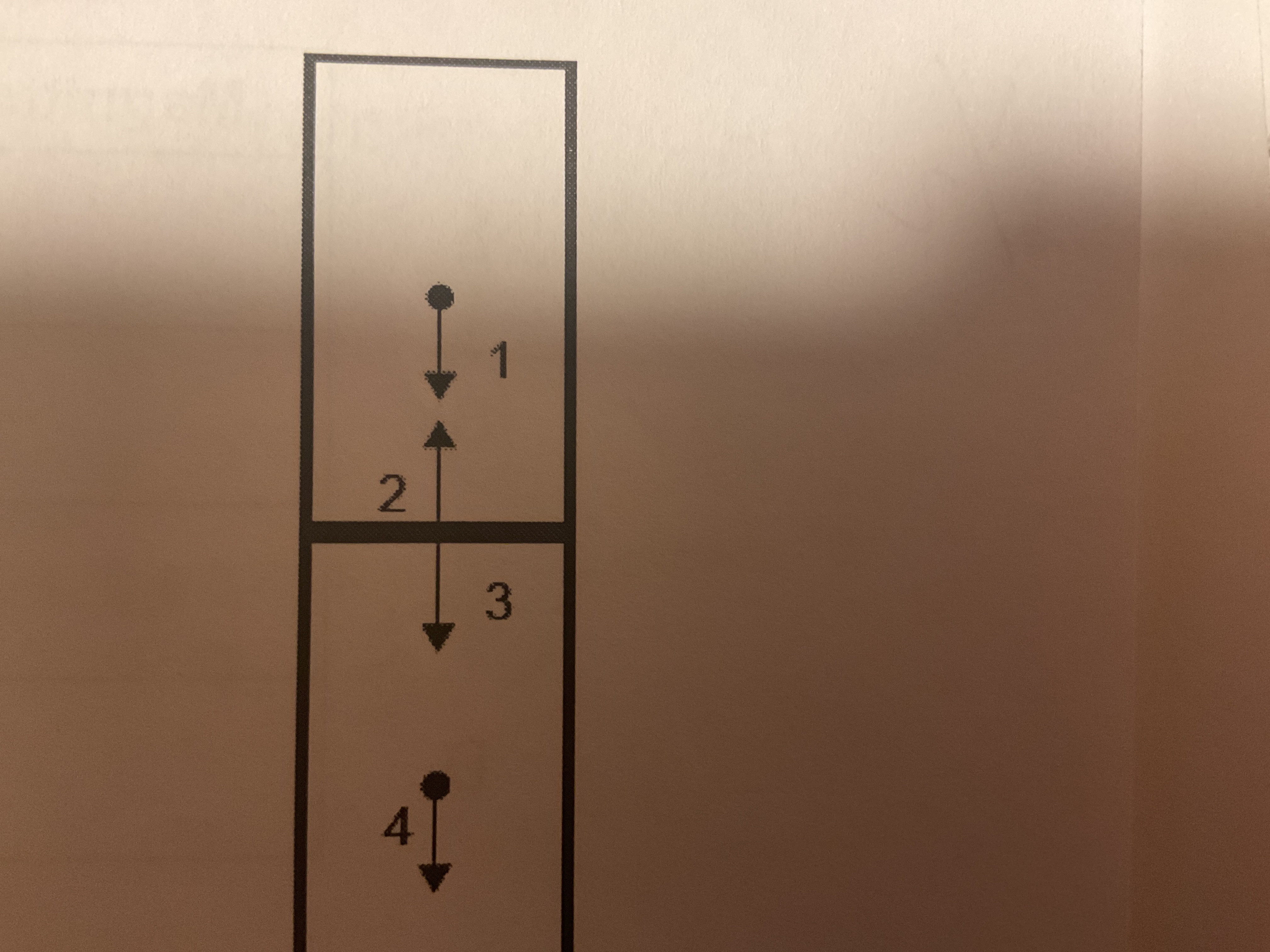
2 Identical boxes are stored in a warehouse as shown in the diagram. 2 Forces acting on the top box and 2 forces acting on the bottom box are shown. Which is a force pair according to Newton’s 3rd law?
2 and 3
A football (soccer) player kicks a stationary ball of mass 0.45 kg
W = F d \cos(\theta)
T = 2\pi \sqrt{m/k}
T = 2\pi \sqrt{L/g}
What is the horizontal acceleration of a projectile (neglecting air resistance)?
0
Formula for average velocity?
v_{avg} = \Delta x / \Delta t
Formula for the component of gravity acting parallel to (down) an inclined plane?
F_{g,x} = mg \sin(\theta)
Formula for the component of gravity acting perpendicular to an inclined plane?
F_{g,y} = mg \cos(\theta)
Formula for Gravitational Potential Energy (near Earth)?
U_g = mgh
Formula for Elastic (Spring) Potential Energy?
U_s = 1/2 k x^2