SSEH1104
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
What is a leader?
Leaders produce change by supporting members, monitoring progress, addressing group issues & providing direction & motivation towards a specific goal.
What is a manager?
Managers produce stability by facilitating groups' actions, organising specific roles & assisting rather than directing.
What is the purpose of leadership communication?
Influence & inspiration (supporting individual needs).
What is the purpose of management communication?
Planning & executing tasks (organisation).
Warmth & competence dimensions account for __% of variance in perceptions of social behaviour.
82
What terms are associated with the warmth dimension?
Friendliness, trustworthiness, empathy & kindness.
What type of behaviours does the warmth dimension predict?
Active
What strategies can be used to improve the warmth dimension?
Duchenne smile (smiling with your eyes), immediacy cues (leaning forward, nodding, being relaxed) & mirroring.
What terms are associated with the competence dimension?
Intelligence, power, efficacy & skill.
What type of behaviours does the competence dimension predict?
Passive
What strategies can be used to improve the competence dimension?
Expansive & open postures.
Which dimension (warmth & competence) is easier to undermine?
Warmth
Which dimension (warmth & competence) is harder to establish?
Competence
What is the halo effect?
The tendency to perceive a warm person as competent.
What is the hydraulic effect?
The tendency to perceive a warm person as less competent.
What level of warmth & competence does admiration exhibit?
High warmth & high competence
What level of warmth & competence does contempt exhibit?
Low warmth & low competence
What level of warmth & competence does envy exhibit?
Low warmth & high competence
What level of warmth & competence does pity exhibit?
High warmth & low competence
What are the three aspects of personality according to Daniel McAdams?
Characteristics adaptation (e.g. coping strategies), narrative identity (life story) & personality traits.
What are personality traits?
Enduring behavioural tendencies over time.
What is the Big Five or OCEAN model?
Openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness & neuroticism (Peabody & Goldberg, 1989).
What does high openness indicate?
Desire to work creatively, unorthodox working environments & liberal political views.
What does low openness indicate?
Resist novel ideas, conservative & right-wing political preferences & aversion to new experiences.
What does conscientiousness mean?
An ability to conform to socially prescribed impulse control which aids goal & task-oriented behaviour.
What does high conscientiousness indicate?
Organised, productive, tend to have higher GPAs, work better according to job requirements & conservative.
What does low conscientiousness indicate?
Impulsive, poor health behaviour & bad at planning/organisation.
What does high extraversion indicate?
Engaged with social & material world, assertive, enthusiastic & tend to occupy leadership positions.
What does low extraversion indicate?
Less organised by social organisation & often have fewer friends.
What are the two facets of agreeableness?
Compassion & politeness.
What is the link between someones political stance & their levels of compassion & politeness?
Politically progressive people tend to be high on compassion while politically conservative people to be high on politeness.
What does high neuroticism indicate?
Less emotional stability & a tendency to ruminate on things.
What does low neuroticism indicate?
More emotional stability, satisfaction with their working organisation, tendency to have better relationship satisfaction & emotional wellbeing.
What effect do personality traits have on leadership?
OCEA positively relate to leadership (E most) while N negatively related & Big Five account for 50% variance in leadership ratings.
If personality helps it does so through a tendency to behave in ways aligning with what good leadership looks like.
What effect do personality traits have on relationships?
OCEA conducive to more successful relationships & within coach-athlete relationships, a perceived dissimilarity on O & E leads to reduced commitment & relatedness.
What effect do personality traits have on team functioning?
Smart, conscientious teams with low neuroticism & no disagreeable or introverted members perform better while teams with highly variant levels of conscientiousness perform poorly.
Task & team performance requires a minimum level of conscientiousness & agreeableness.
High team extraversion & emotional stability contribute to social cohesion.
What is the link between resilience & how stressful a leader's job is?
There is a direct relationship between how stressful a leader's job is & their ability to maintain resilience when experiencing prolonged exposure with adversity.
What does being anti-fragile mean?
Benefitting from shock & growing from adversity (Nicholas Nassim Taleb). For example, humans.
What are dynamic state systems models?
Shows that the points where people "tip" into a mentally disordered state have different heights and slopes. (Kallisch & colleagues, 2019)
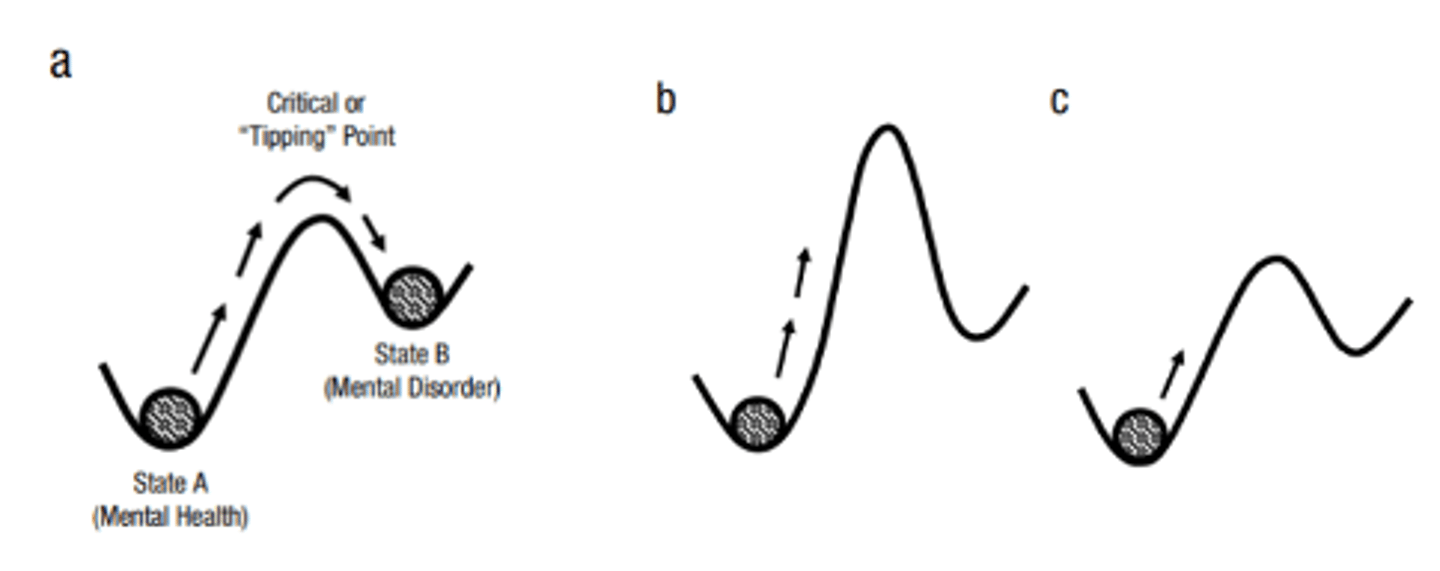
What do dynamic state systems models indicate about symptoms?
That different symptoms feed into themselves & can create a feedback loop.
What is self-compassion?
An adaptive form of self-to-self relating that involves being caring & compassionate to yourself during hardship (Kristen Neff & colleagues, 2007).
What are emotions?
Relatively short-lived states involving a trigger & a subjective, physiological & behavioural response.
Why are emotions useful?
They help organisms reproduce, protect offspring, maintain cooperative alliances & avoid physical threats.
What are the characteristics of emotional intelligence?
Self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, social skill.
What is emotional intelligence ability?
Perceiving emotions → understanding emotions → using emotions → managing emotions (Mayer & Salovey, 1997)
What is the TEIQue (trait emotional intelligence questionnaire)?
Measures wellbeing, self-control, emotionality & sociability & some aspects map onto the Big Five model, particularly N & E. (Petrides, 2009)
According to George (2000) what does effective leadership involve?
Developing a collective sense of goals & objectives
Instilling knowledge & appreciation of important work activities
Maintaining excitement, enthusiasm, confidence, optimism & trust
Encouraging flexible decision making
Establishing & maintaining a meaningful organisation identity
Is there a correlation between trait EI & transformational leadership?
Yes, it is large if self-assessed & small if multi-sourced (Harms & Crede, 2010).
How can emotional intelligence & self-awareness of emotions be developed?
Tracking emotions, soliciting feedback from others, engaging in extraverted social behaviour & practicing in everyday situations
What is self-efficacy?
A domain-specific belief in one's ability to perform behaviours required to achieve a given outcome (Bandura, 1977)
What does self-efficacy differ in term of?
Level (of task complexity), strength (of certainty that they can perform at a given level) & generality (degree of transfer of efficacy belief from one context or skill to another)
What are the sources of self-confidence?
Past performance, vicarious modelling, verbal/non-verbal persuasion & physiological states/affect.
What are the pitfalls of self-confidence?
Efficacy beliefs are not universally adaptive, self-doubt can stimulate effort & protect against complacency & self-efficacy negatively affects performance if conditions are ambiguous.
What are groups?
Categories according to shared characteristics.
What are the characteristics of an effective group?
Appropriate size, adequate level of complementary skills, truly meaningful over-all goal, clear approach to work, specific goals & sense of mutual accountability (Katzenbach & Smith, 1993).
What are teams?
Groups with a common, shared goal.
What are the stages of Tuckman's model of group development?
Forming, storming, norming, performing, adjourning.
What is the forming stage of group development?
Determines the extent to which group members are properly oriented to group task & involves establishing ground rules
What is the storming stage of group development?
Ambiguous group structure lacking unity
Uncertainty about positions on key-interpersonal issues
Resisting discussion of groups 'unknown' aspects
Opting for safe or secure subject positions
Expressing hostility towards leaders as a means of expressing individuality & resisting group structure
Responding emotionally to task demands
What is the norming stage of group development?
Task & social cohesion developing
Beginning to accept members' idiosyncrasies & expressing personal opinions
Establishing roles & norms
Figuring out how to best work with each other
Becoming a real entity
Psychological processes beginning to take effect (e.g. in group feeling)
Often try to maintain harmony by neglecting task-related conflicts
What is the performing stage of group development?
When inter-personal structure supports task performance
Functional role relatedness developing
Becoming a problem-solving instrument
Little energy required to maintain social cohesion when task cohesion becomes salient
What is the adjourning stage of group development?
Group separation is important for the life of future groups.
What is the social cure?
Social identities have profound impacts on mental & physical health.
What is the Optimal Distinctiveness Theory?
Opposing needs of assimilation & differentiation govern relationship between self-concept & group membership (Brewer, 1991). Reviewed by Leonardelli & Pickett in 2010.
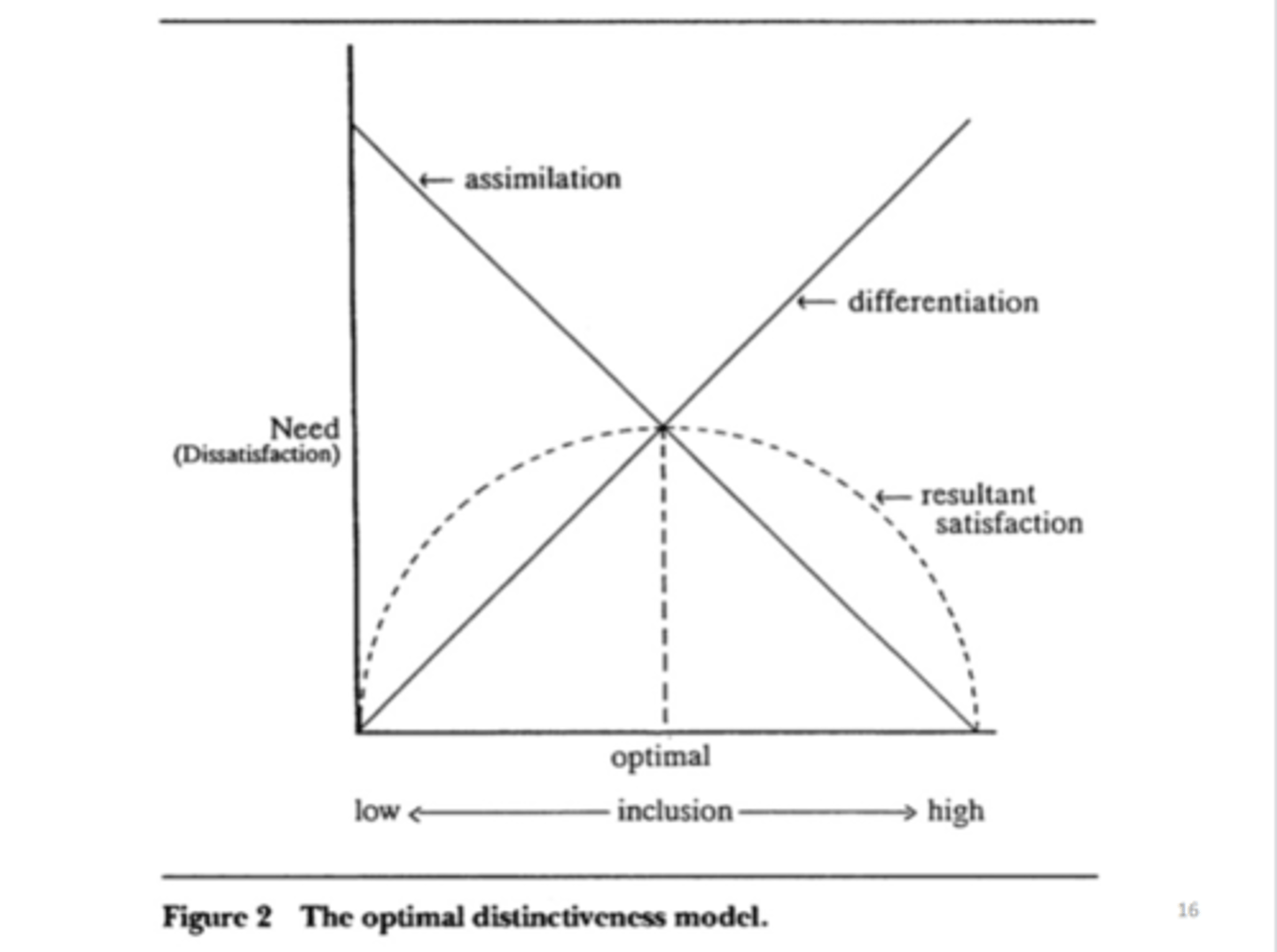
What is the Optimal Distinctiveness Theory an extension of & why?
Social Identity Theory (Tajfel) & Self-Categorisation Theory (Turner) which only explained why we want to maintain positive in-group impressions.
What is the evolutionary hypothesis underpinning the Optimal Distinctiveness Theory?
If defining groups (by differentiating them & drawing boundaries) is functional for social cooperation then psychological mechanisms must exist at a psychological level to motivate & sustain in-group identification.
What are some qualifications of the Optimal Distinctiveness Theory?
Identities have context specific natures & their motives may vary across situations, cultures & individuals
Optimal distinctiveness is a dynamic equilibrium
Groups' satisfactions of both needs may be related
What is the definition of cohesion?
Total field of forces which act on members to remain in a group (Festinger & colleagues, 1950).
What is the effect of increasing group cohesion?
Increases influence over group members.
What is social cohesion?
Extent to which group members feel connected to their group as a whole.
What is task cohesion?
Extent to which group members share group goals & work together to achieve them.
What are the characteristics of cohesion?
Multidimensionality: several factors cause a group to remain united which vary between groups
Dynamic
Instrumental: reflect reason(s) group formed & remains together
Affective: associated with positive affect
What is Group Integration (GI)?
Perceptions held by individual members regarding group's closeness, similarity & bonding as a whole & degree of unification.
What is Group Attraction (ATG)?
Perceptions held by individual members reflecting their feelings about & personal motivations to remain in the group.
How can you facilitate cohesion?
Group goal setting (most effective approach)
Create opportunities for 'unscripted' group interaction & communication
Foster a sense of group identity
What are the methods of group decision making?
Brainstorming
Dialectical enquiry (group debates possible advantages & disadvantages of prosed decision)
Nominal group technique (each write ideas list & present one for team to rank)
What are the types of conflict?
Task (conflict over the goals of the group)
Social/relationships
Process (''hows') (particularly damaging in long term)
How can conflict be energising?
Can experience positive & negative emotions at same time.
Mild, frequent task conflict leads to more information acquisition
Information gains lead workers to experience more interest, excitement, energy & activity which increases job satisfaction
How can you manage conflict?
Focus on info not delivery.
Focus on problem not people.
Avoid process-related conflict in early team development.
Embrace some conflict since since it's a sign that group isn't over overemphasising social harmony over task performance.
What does collective efficacy?
A belief in the capabilities of the group as a collective to do what's required to achieve an outcome.
What is relation-inferred self-efficacy?
A metaperception about what we believe someone else believes about our capabilities to achieve certain outcomes.
What are sources of team confidence?
Bandura's sources of past performance, vicarious modelling, social persuasion & physiological states.
Confident leadership
Practice performance
Perceptions of cohesion
Team conflict undermines confidence in team's abilities
What is a mastery climate?
An environment where positive reinforcement is provided for hard work, improvement & good teamwork - improves team confidence.
What are roles?
A defined set of behaviours expected from a person (within a team).
What does role definition do & what should it be driven by?
Minimise conflict, maximise efficiency & should be driven by group cohesion.
What are the role receptions?
Role ambiguity
Role conflict
Role acceptance
Role efficacy
What are the dimensions of role ambiguity?
Scope of role responsibilities
Behaviours required to fulfil responsibilities
How performance is evaluated
Consequences of not meeting responsibilities
What are the types of role conflict?
Intra-sender (one person provides multiple conflicting expectations)
Intra-sender (2+ people provide conflicting expectations)
Person-role (role expectations conflict with person's values or motivations)
What is Steiner's model of group productivity?
As groups increase in size, individual productivity decreases
Actual productivity = potential productivity - losses due to faulty group processes
Optimal group size is 3-6
What is the Ringelmann effect?
Individual performance decreases as the number of people in the group increases.
What is social loafing?
Individuals within a group or team put forth less than 100% due to losses in motivation.
What is the Kohler effect?
When an inferior team member performs a difficult task better in a team or coaction situation than one would except (based on knowledge of their individual performance) due to upward social comparison & indispensability of group members' efforts.
What is group polarisation?
Group moving towards extreme positions in either caution or risk shift.
What are causes of group polarisation?
Diffusion of responsibility, leadership, social comparison & persuasive arguments.
What is group think?
Groups going along with bad ideas because member's don't feel comfortable disagreeing.
What causes group think?
High group cohesion, structural faults & situational elements.
How can you avoid group think?
Leadership should avoid expressing opinions when assigning tasks
Ensure groups actively explore alternative strategies
Member play devil's advocate
What are Bandura's eight types of moral disengagement?
Moral justification
Euphemistic language (obscures meaning)
Advantageous comparison
Downplay consequences of behaviour
Displacement of responsibility
Diffusion of responsibility
Attribution of blame
Dehumanisation
What is social facilitation?
Presence of others makes us perform simple tasks faster & more accurately but complex tasks slower & less accurately.
What are the individual differences in the effects of social facilitation?
High self-esteem & extraversion = improved performance under social pressure
Low self-esteem & high neuroticism = impaired performance under social pressure