NPB101: Neurophysiology Part 6
1/84
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Touch
Pressure (skin)
Vision
Lightwaves
Hearing
Pressure waves traveling through air
Vestibular System
Central Balance
detect where body is relative to space/gravity
Transducing/Transduction
changing the energy of the stimulus (chemical) into an electrical signal to basically a bunch of AP
General Somatic Sensory Afferent
Touch sensitive neurons that are innervating the skin
Innervating
supply (the body/skin) with nerves
General Somatic Senses: Touch Receptor
Embedded in the skin
What is the name for these Touch Receptors
Mechanosensitive Neurons
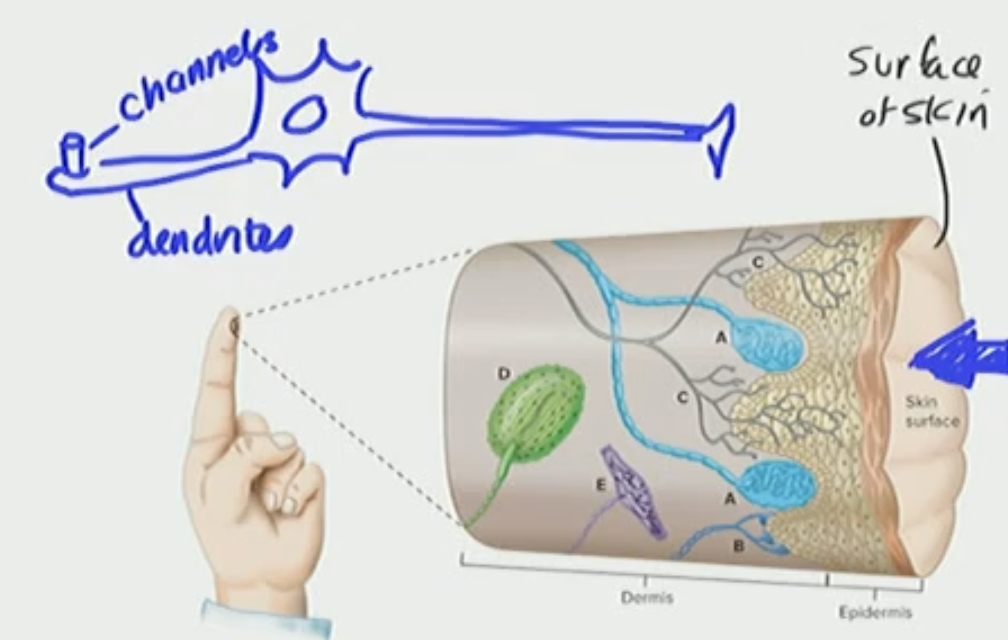
What happens when you apply a stimulus to the dendrite
It deforms the dendrite/channel
the mechanical pressure pushes on the dendrite to open the ion channel with a depolarizing current of Na+ influxing into the cell
The influx is from touching the finger
When we get this depolarizing influx we create a graded potential, but the depolarizing influx creating graded potential is a “Receptor Potential”
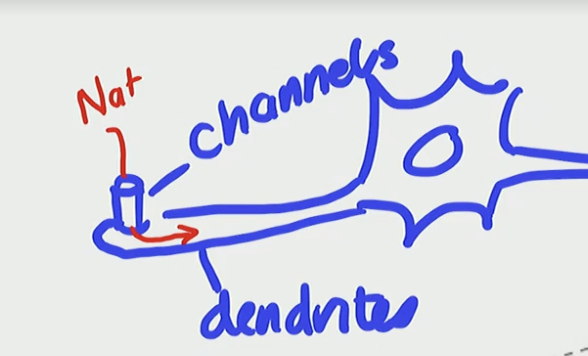
When you have a depolarizing influx you create a graded potential, this ____ potential is called a _____ potential
graded, Receptor
Receptor Potential
travels through the dendrite and cell of body of neuron and then finally to axon
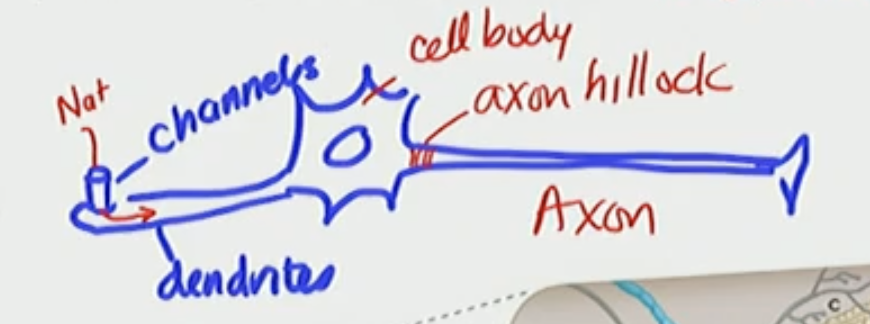
Axon Hillock Facts
front of the axon
depolarize the neuron —→ AP—→ localized current
Touch Receptors
Uncapsulated, free nerve endings —→ Free Neuron Ending
Encapsulated nerve endings —→ special channel in the dendrite and then opens channel and depolarizes
Meissner’s corpuscle
Merkel’s corpuscle
Pacinian corpuscle
Free Neuron Ending
slowly adapting
free nerve endings
no special structure at the end
itch receptor
thermoreceptors
uncapsulated
Meissner’s Corpuscle
touch and pressure, rapidly adapting
Merkel’s Corpuscle
touch and pressure, slowly adapting
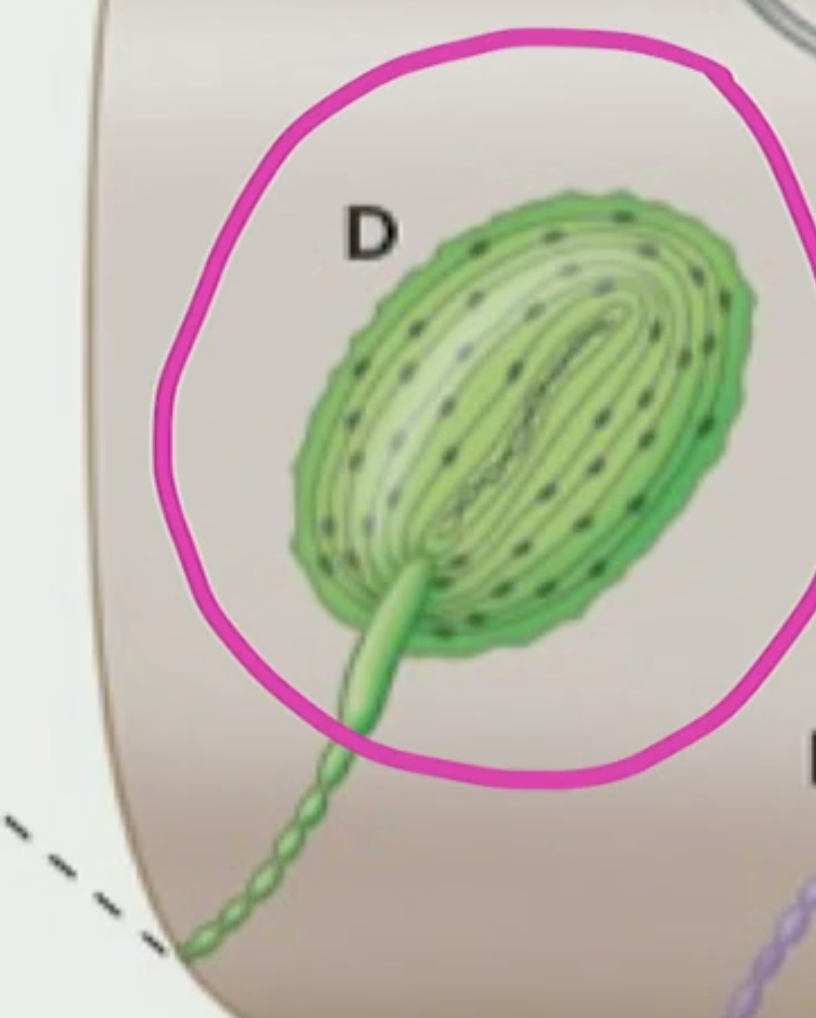
Pacinian Corpuscle
Dendrite with cells wrapped around it, rapidly adapting
Afferent Process
Like a dendrite, senses
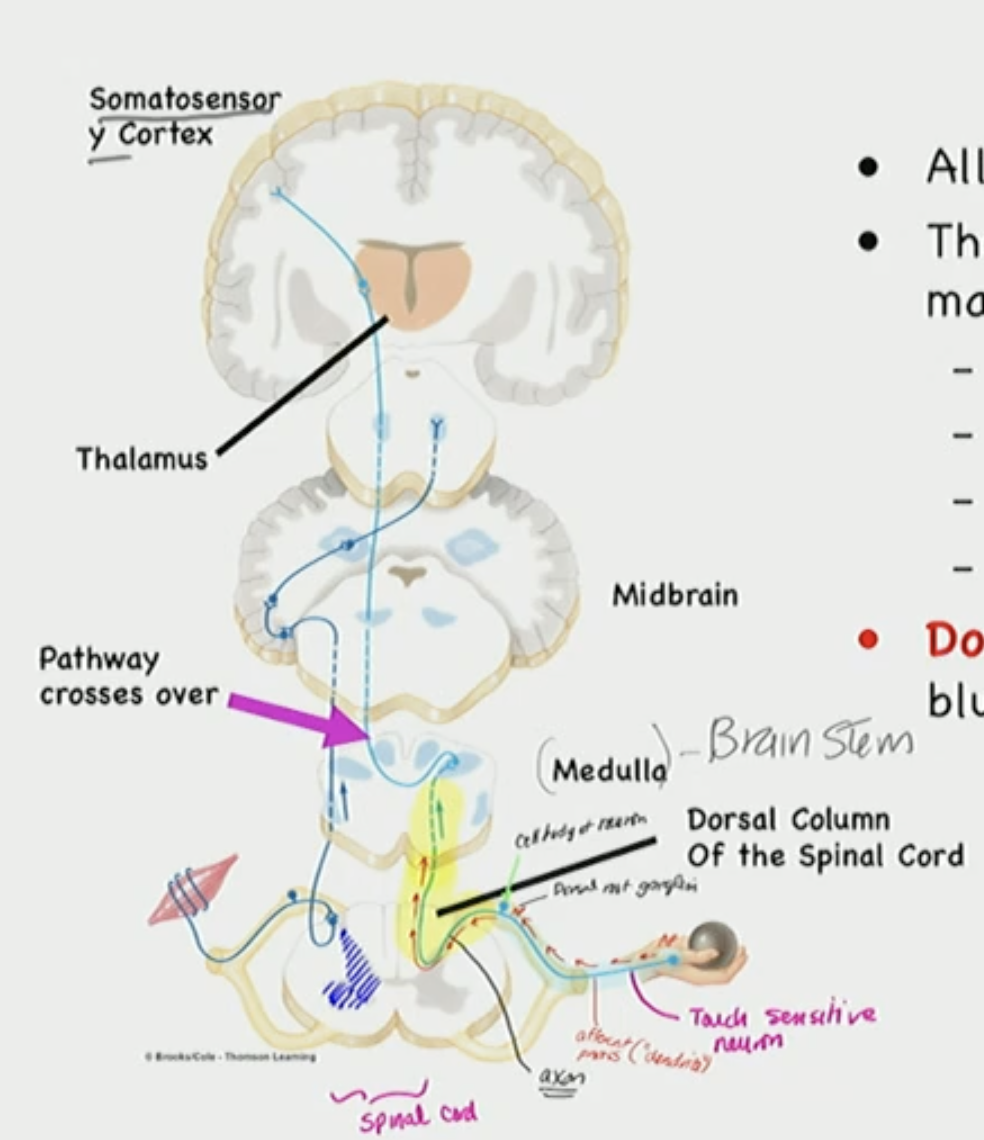
Afferent moves through
Spinal Cord, Medulla (brainstem), Thalamus, Cortex
Touch info is sent to the ___, with the Dorsal ____ pathway
brain, Columnar
Dorsal Columnar Pathway: TOUCH SENSITIVE PATHWAY
3 Neuron pathway
info crosses at the brain stem (medulla)
If there is pain is crosses over to the ____ ____ & this is ____ order neuron
spinal cord, second
If you touch something it crosses over to the ______ & this is ____ order neuron
brainstem, second
NOCICEPTIVE NEURONS
Pain info is carried by this
Detects painfully strong stimuli
T/F: Nociceptive neurons cross over at the spinal cord
True, nociceptive neurons detects painful strong stimuli and carries pain info to the Anterolateral Pathway(Spinothalamic pathway), pain sense from the general somatic sense of cutaneous pain cross overs at the spinal cord with second order neuron
Anterolateral Pathway (Spinothalamic pathway),
Pain
T/F: Mechanosensor neurons cross over at the brainstem (medulla)
True, Mechanosensor neurons that detect normal touch with General Somatic Sensor cross over at the brainstem (medula) via the Dorsal Columnar Pathway with second order neuron in spinal cord trasmitting info to third order where it crosses at brainstem
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Homunculus
First part of Cerebral Cortes involved in conscious perception of general somatic senses (touch, pain, temperature)
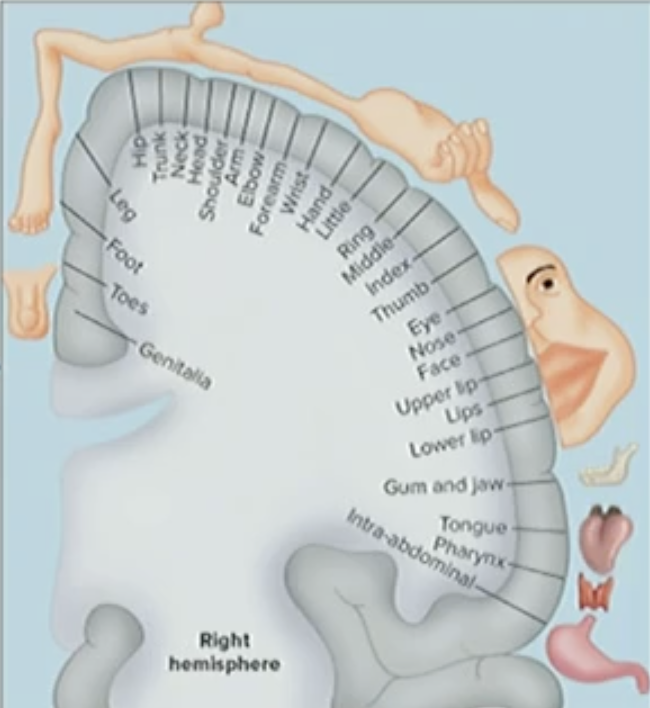
Homunculus
Body Representation
Homunculus is part of the ____ somatosensory cortex that is involved in the ___ somatic sensory (touch,____, temperature)
Primary, General, pain
Central Sulcus
Process Somatic Afferent information (touch)
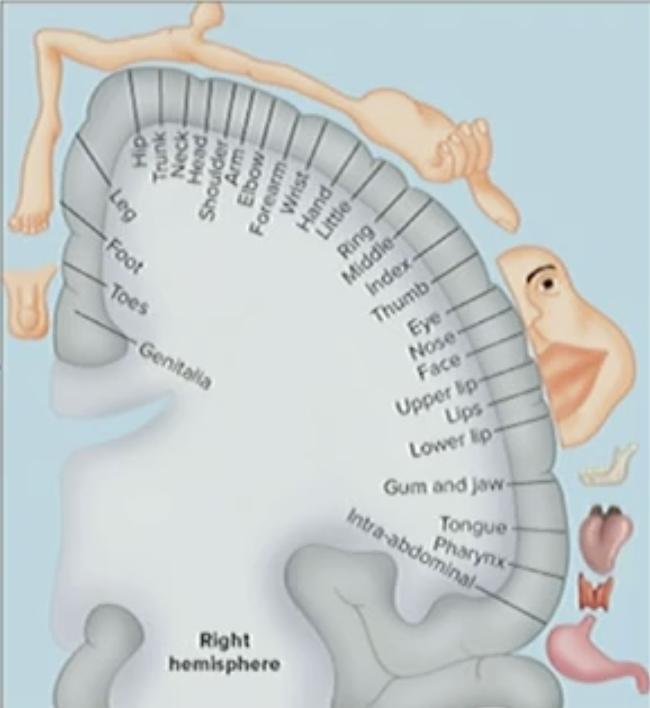
Conscious Perception of Touch
Greater in thumb, lips
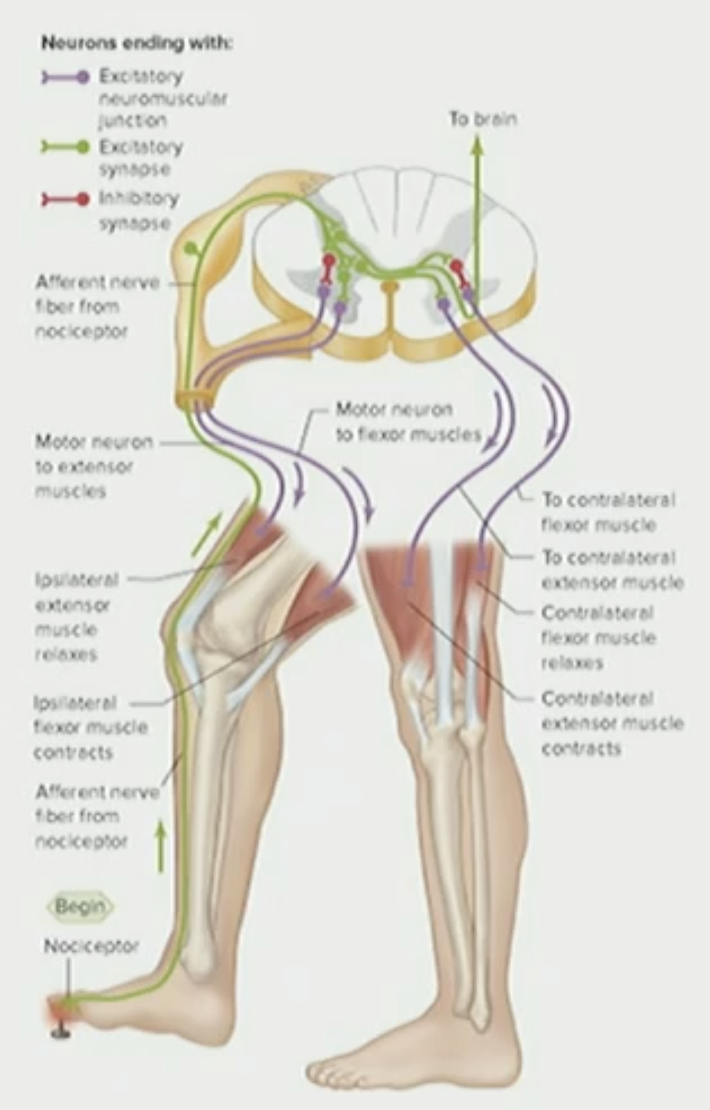
Pain Withdrawal Reflex
cause activation of certain muscles so we can pull away the organ (limb) while shutting off action of a given muscle
Pain Withdrawal Reflex Example
Want to contract hamstring to pull away limb (leg) that is experiencing the pain on the foot when you step on a tack and then contract muscle in the quads on the other leg or else you’ll fall
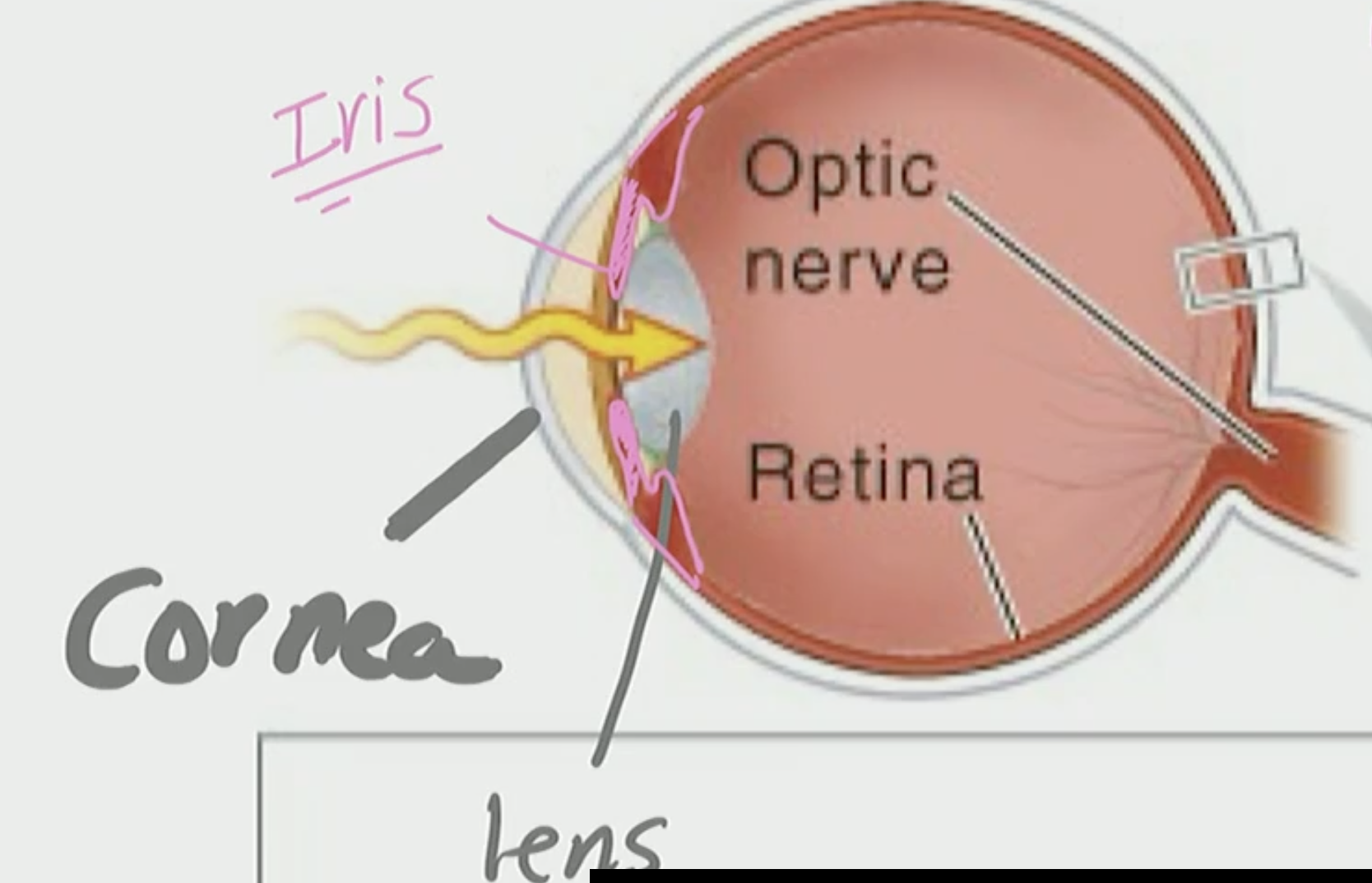
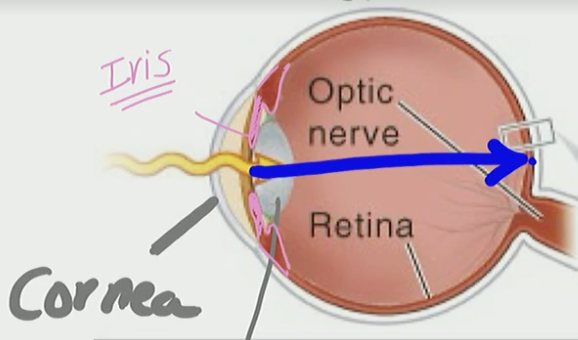
Retina
detects photoreceptor
sees fine detail
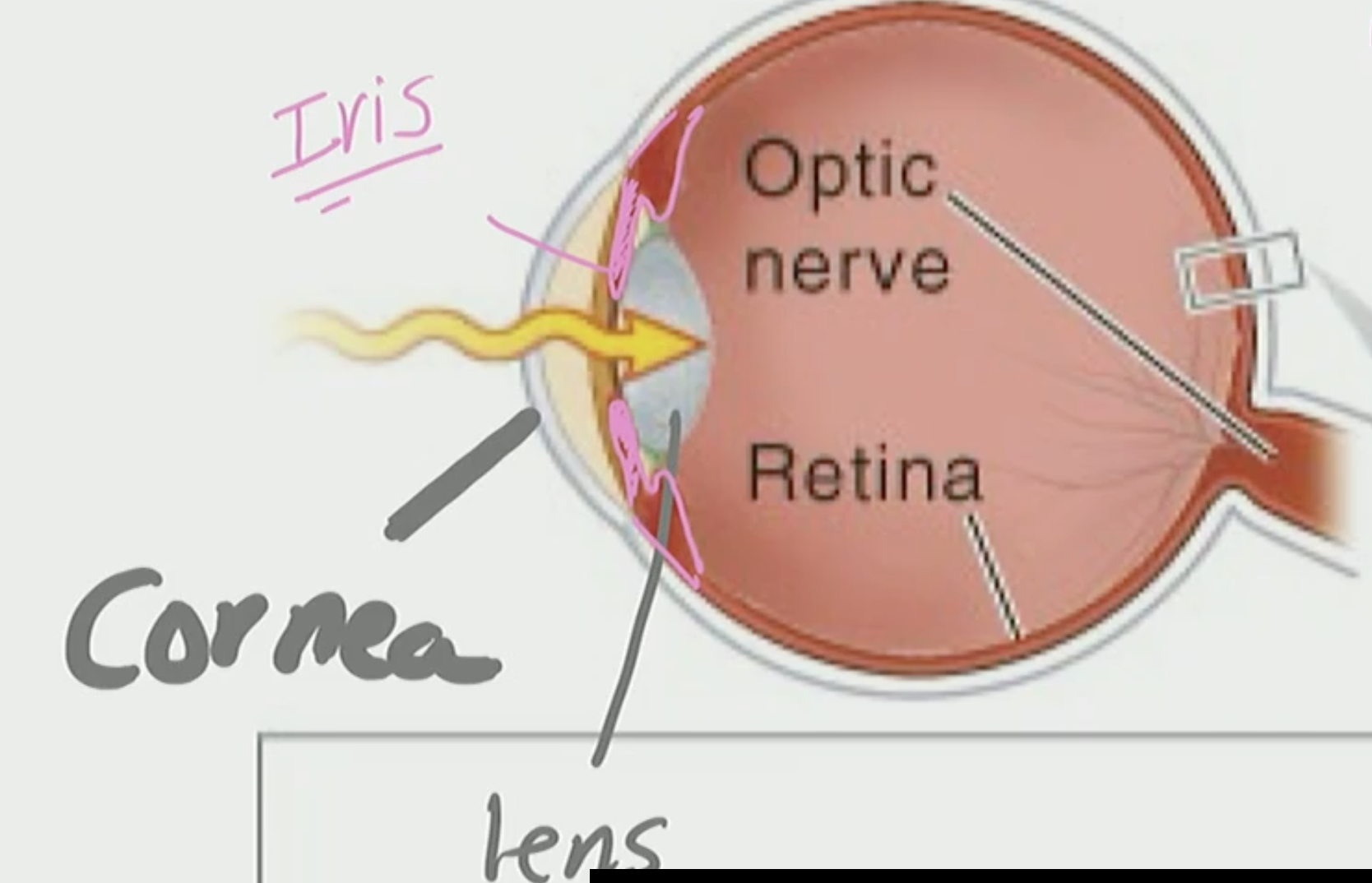
Cornea & Lens
Help focus image onto Retina
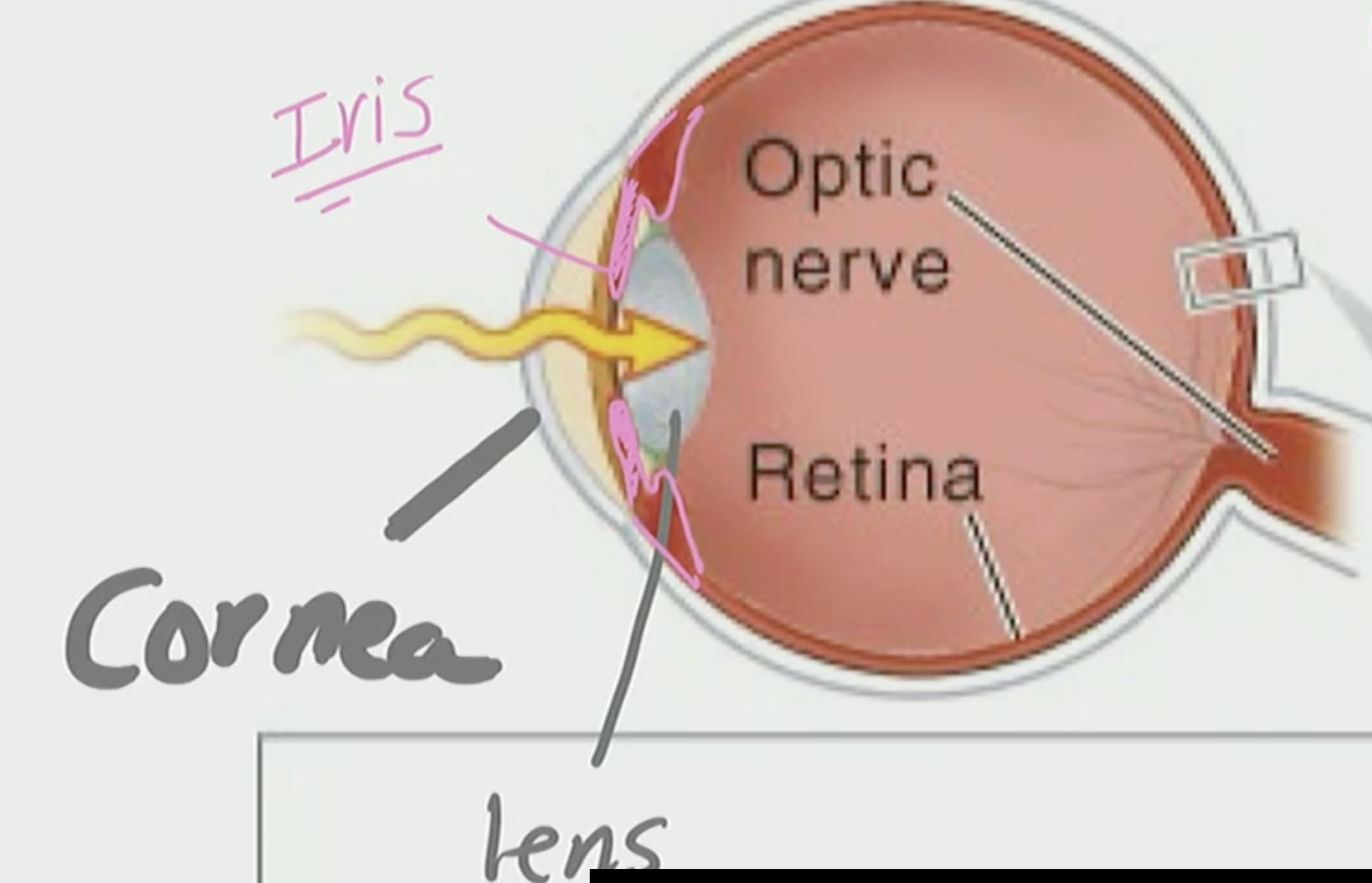
Iris
Limits the amount of light that enters via pupil
is the color we see in peoples eyes
Light
comes in through the cornea, pass the iris, through the lens, and it shoots across to the retina
Ganglia Cell (in Retina)
neuron that takes sensory info to the brain (thalamus)
Photoreceptors
Cones
Rods
Cones
Allow iris to detect color of wavelength
Rods
hardly any stimuli in dark so its used in low light situations & bright situations
Photopigments
Rhodopsin
Cone opsins
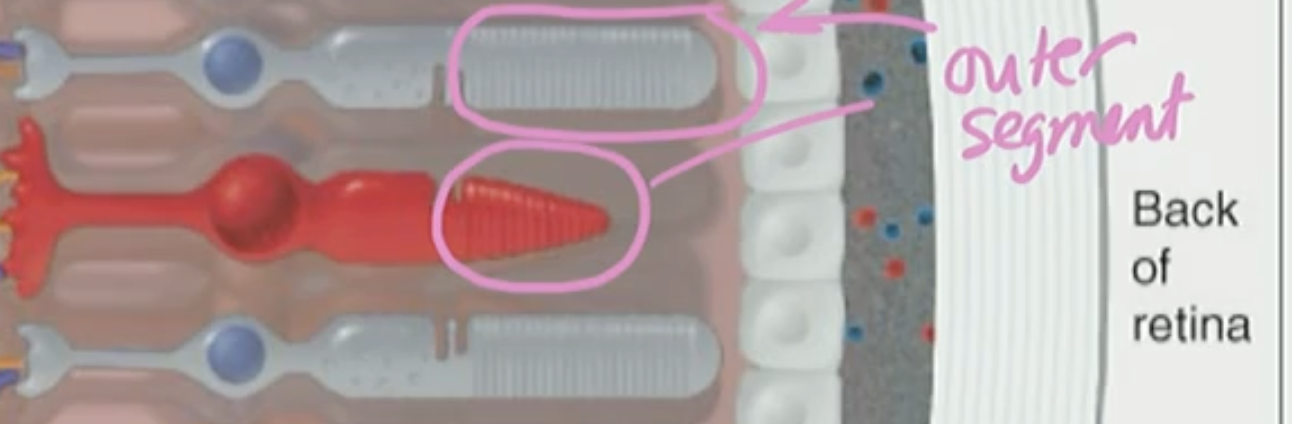
In outer segment of photoreceptors(cones & rods)
change shape when light waves are absorbed
Rhodopsin
Rods photopigment that detects visible wavelength
Cone opsin
Cone photopigment
The ___ segment of cones and rods have layers of ____
outer, photopigment

11-cis
Before exposure to a light wave

All trans
After exposure to a light wave
Dark Current
in the dark where cGMP opens/activates a channel where a depolarizing current occurs

cGMP
open Na+ channels within the outer segment of photoreceptors
T/F: Even if you don’t have lightwaves on stimulus it depolarizes
True, you don’t have to have a stimulus (light) in order to depolarize in the eye, so the photoreceptor depolarizes to darkness and it continually releases neurotransmitters
Absorbing Light Waves
when exposed to light the photopigment absorbs it and changes shape because it changes from the 11-cis(bent) to all-trans (straight)
Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
an enzyme that when activated it decreases cGMP (closes dark current channel)
T/F: When there is lightwaves neurotransmitters stop from getting released
True, This is because in the eye neurotransmitter release it opposite as when you have a stimulus=no neurotransmitter release & when there is no stimulus=neurotransmitter released
Cones have a 1:1:1 connection with?
Rods: bipolar cells: afferent neurons(single ganglion cell)
Afferent Neuron (Single Ganglion Cell)
have a big receptive field with all the bipolar cells and it goes to the photoreceptors
so many bipolar cells this is a big receptive field where it cannot detect fine detail
Macula Densa
this is where rods are
Part of retina where this is all rods
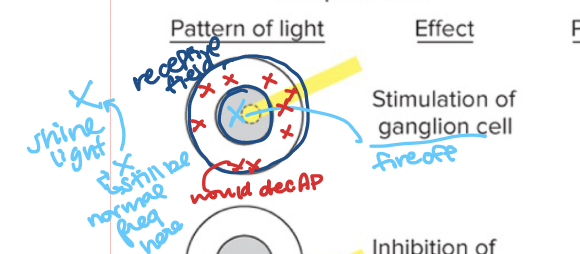
ON center/OFF surround
Ganglion Cell fires off AP at center, but decrease AP in the surround
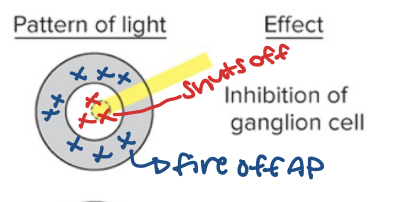
OFF center/ON surround
Ganglion cells fire off in surround (periphery) but when in center it dec AP
T/F: The left visual field is processed by the left visual cortex
False, the left visual field is processed by the right visual cortex
Right Visual Cortex is processed by the ____ brain
Contralateral
The left Visual Cortex is processed by the ____ brain
bilateral
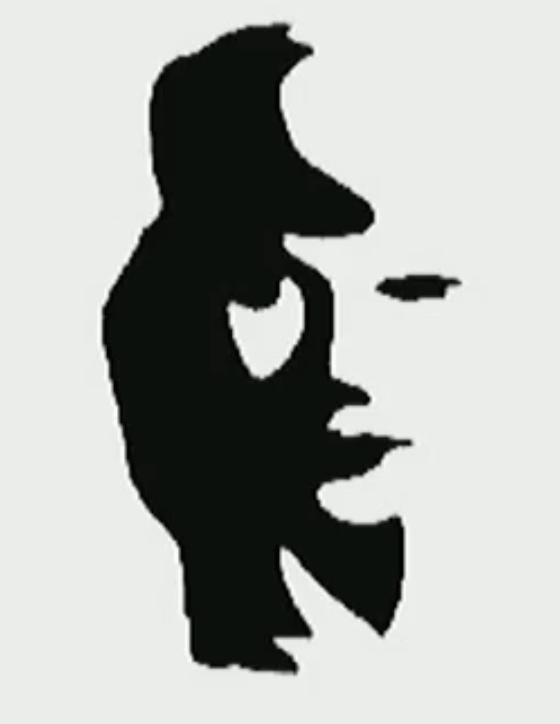

The guy playing saxophone
signal (dark color) is where our attention goes
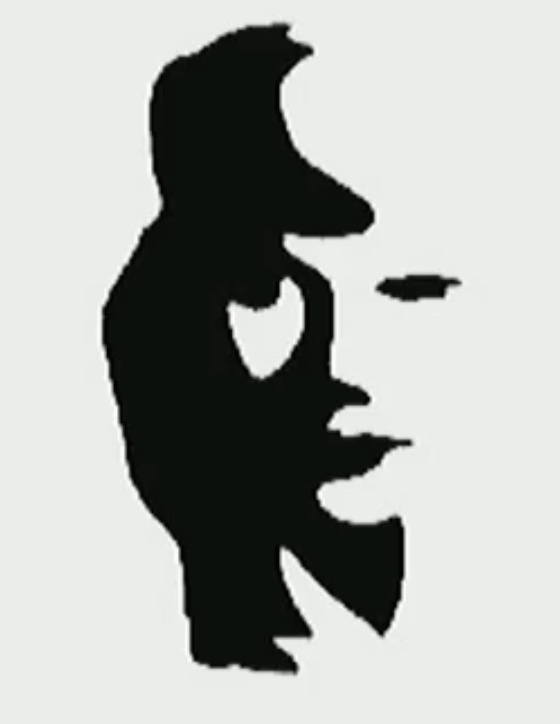

Women’s face
noise (white color) is something we tend to ignore
The brain loves to perceive where its supposed to signal
As if something is supposed to be there the “dark dots” this is the blind spot (fill in blind spot)
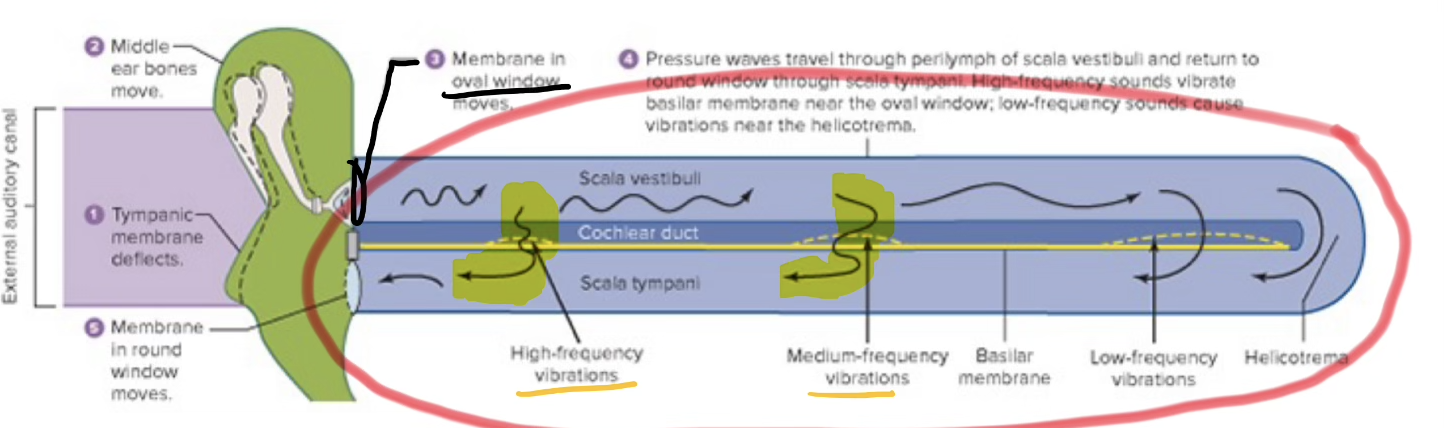
Sound Waves
Pressure Wave (air or solid)
Auditory Canal
receives sound waves
Tympanic Membrane
Vibrates
Inner Ear Bone
concentrate sound wave energy to one spot (Cochlea)
Where is the soundwaves concentrated to, what area of the ear?
Cochlea
Chambers
Scala Media
Scala Tympani
Scala Vestibuli
M.T.V.
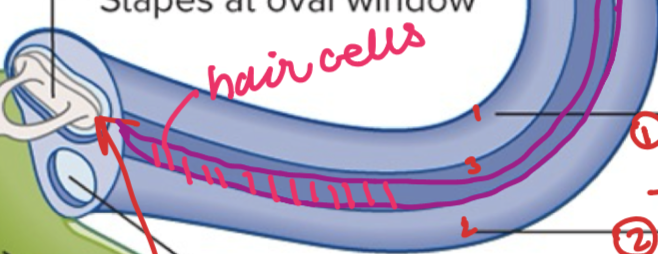
Sensory Cell- Hair cell
sensory receptor
pays attention to sound waves
Sound Waves are _____ by hair cells
transduced
Sound Waves Working
can zip all the way across/ cut across
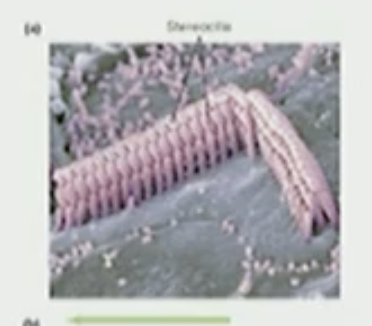
Stereocilia
Bend towards & away from the Kinocilium
Bends Towards—→Hair cell depolarize
Bends Away—→ Hair cell hyperpolarize
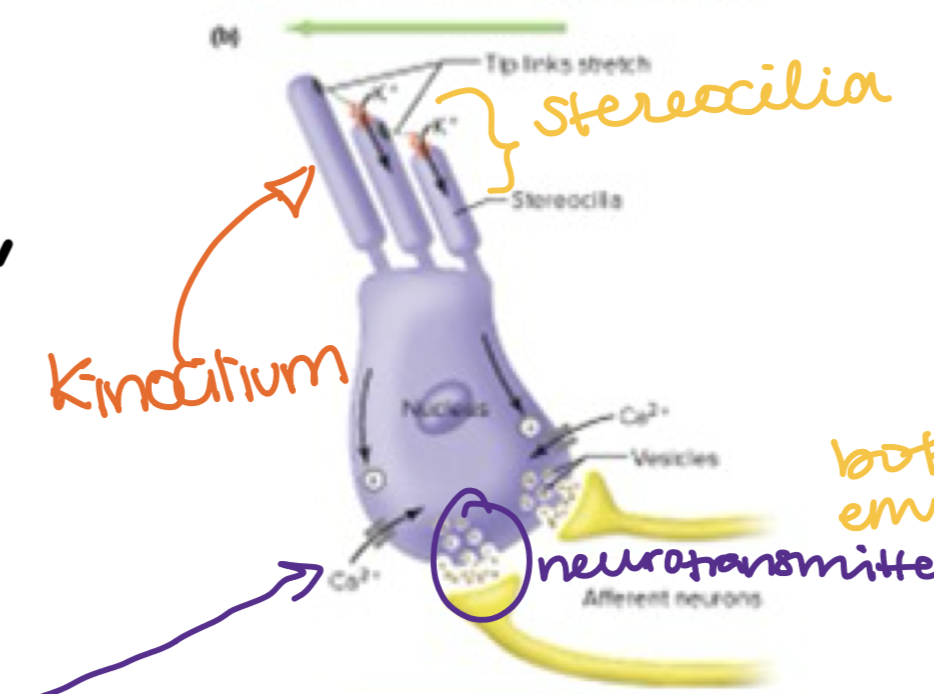
Hair cell Bend Towards Kinocilium
the hair cell depolarizes
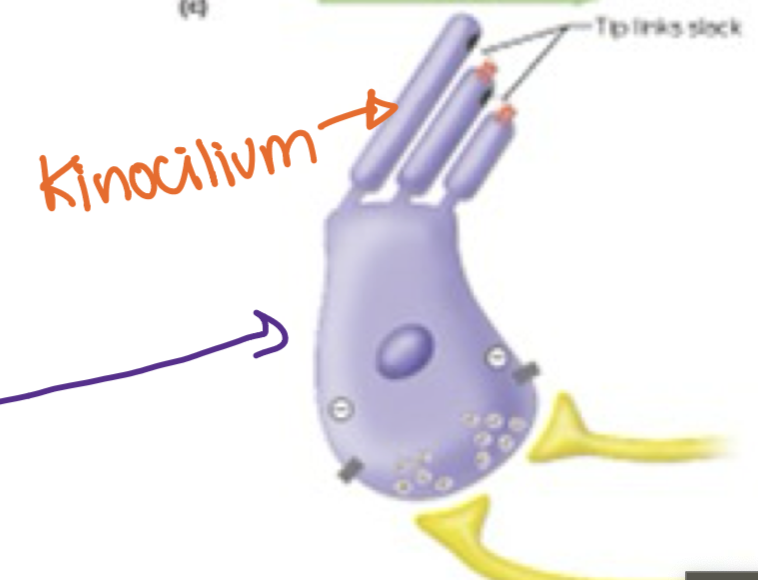
Hair bends away from the Kinocilium
the hair cell hyperpolarizes
Basilar Membrane
a flexible membrane that vibrates in response to sound and varies in stiffness along its length to distinguish different frequencies
High Pitch
High Frequency
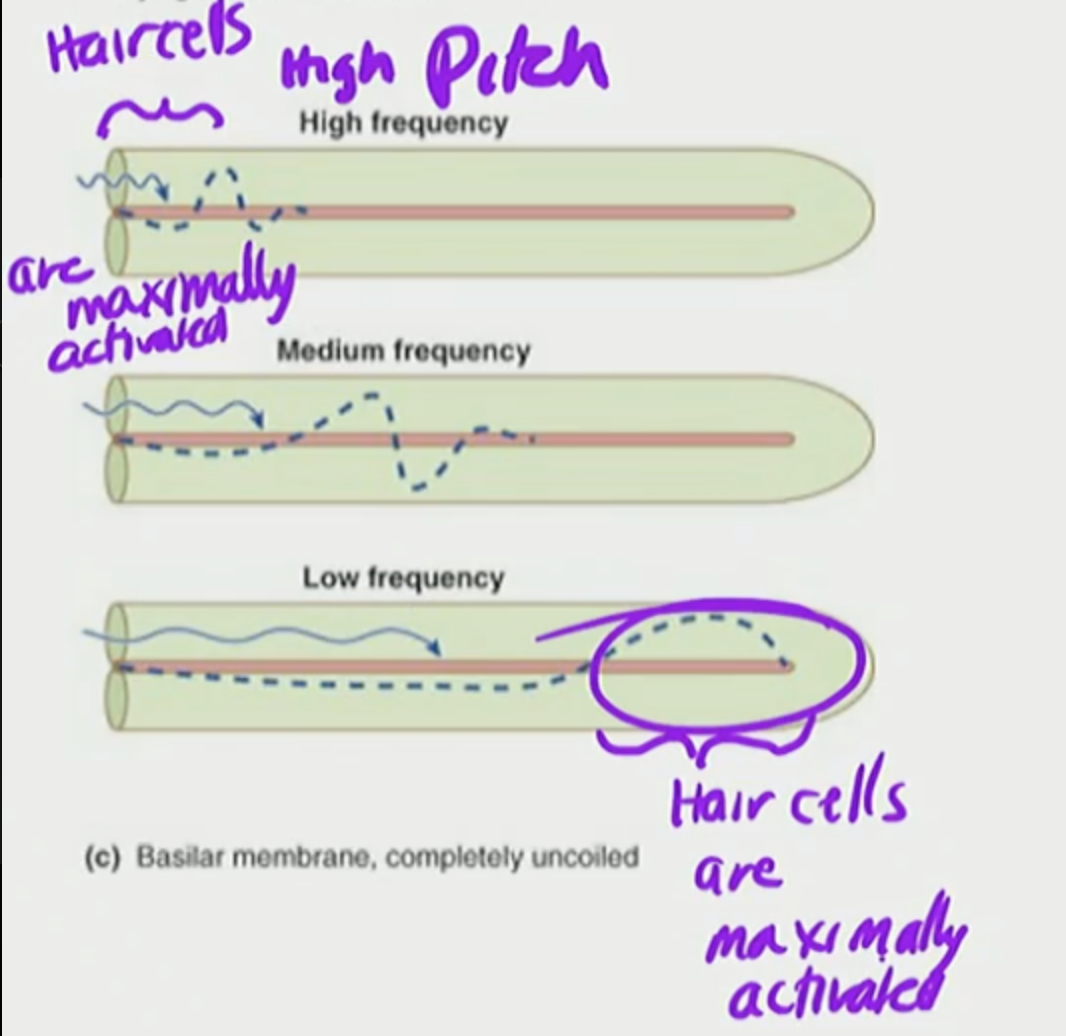
Hair cells in cochlea are maximally activated a specific locations along the basilar membranes based on pitch frequency
maximally activated
highest possible level of activity or response
T/F: Stereocilia grows back
False stereocilia cannot grow back once destroyed
High Pitch
base of membrane
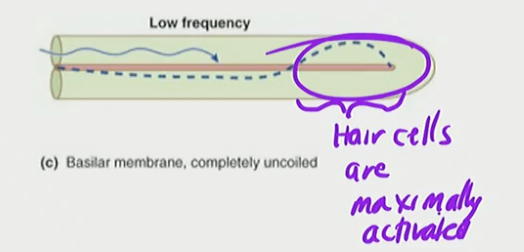
Low Pitch
Tip of membrane