Unit 4 - AP Biology
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Cell communication purpose (3)
Autoimmunity
Reproduction
Homeostasis
Types of cell communication (3)
Direct - cell to cell via shared cytoplasm (channels/junction) or surface receptors
Local regulators - short distance chemical messages to nearby cells
keywords: surrounding, nearby
Long distance signaling - using hormones, can travel to multiple areas
Types of local regulators (2)
Paracrine signal - using regulatory molecules that as a signal to neighbor cells
Synaptic signal - using neurotransmitters thru axons/nerves to signal other neurons
Types of long distance signaling (2)
Chemical signaling - plant based hormones thru xylem/phloem to tissues
Endocrine signaling - animal based hormones thru blood to gain a response from specific cells
Stages of cellular communication (3)
Reception
Transduction
Response
Reception
When a stimulus/signal is received by the cell via it binding to the receptor protein
Ligand
Signaling molecule that can bind + changes a receptor proteins shape to be a intercellular signal
(what’s going on outside?)
Types of ligands (2)
Hydrophilic - molecules that bind to a MEMBRANE RECEPTOR
Hydrophobic - molecules that bind to a receptor INSIDE THE CELL by passing the membrane
transcription factors, steroid (lipid) hormones
Types of hydrophilic ligands (3)
G-protein coupled receptors - activates g proteins that initiate a cellular signal
Receptor tyrosine kinases - activates phosphorylation for cell division, targets proteins
Ligand gated ion channels - channels that allow in ions after a ligand binds onto receptor
Transduction
regulatory pathways that cause cellular responses
extracellular → intracellular signals
Phosphorylation cascade
When addition of phosphates triggers chain reaction of activating protein intermediates till the protein for a response is activated
Kinase
enzymes that add phosphate to activate signals to intermediates
Phosphatase
enzymes that REMOVE phosphate to deactivate signals to intermediates
Second messengers
NONPROTEINS that amplify responses from transduction- can assist activating kinases
cyclic AMP
Response (3)
regulation of cell processes.. including
activating proteins/enzymes
gene expression
membrane permeability
cell growth
cell division
cell differentiation → specialization of genes
apoptosis
Process of cellular communication (4)
Ligand binds with receptor to create signal
Phosphorylation cascade is triggered; kinases activate proper proteins needed until
Kinase enters the nucleus activating transcription factors for the gene required for response
Genes will synthesize the REQUIRED PROTEIN for the FINAL response of the cell (outside)
Feedback (2)
communication between cells/organs for a response
Negative - inhibition
Positive - enhances
Stimulus, receptor, effector, response (what is all of these?)
Stimulus - causes response
Receptor - detects stimulus
Effector - increase/decrease stimulus effect
Response - handles stimulus
Interphase (3)
LONGEST phase of a cell cycle
G0 (default) → G1 (intending to divide, replenish organelles)
S - DNA synthesis
G2 - prep for mitosis, duplicate centrosomes
M Phase
Mitosis + cytokinesis occurs (PPMAT)
Chromatin vs chromosomes
Chromatin - DNA w histones, default form of DNA in nucleus = interphase
Chromosomes - condensed units, 1-2 sets of chromosomes = M phase
Haploid vs diploid
Haploid - one set of chromosomes (2 total) - in GAMETES/sex cells/meiosis
Diploid - two sets of chromosomes (4 total) in SOMATIC/body cells/mitosis
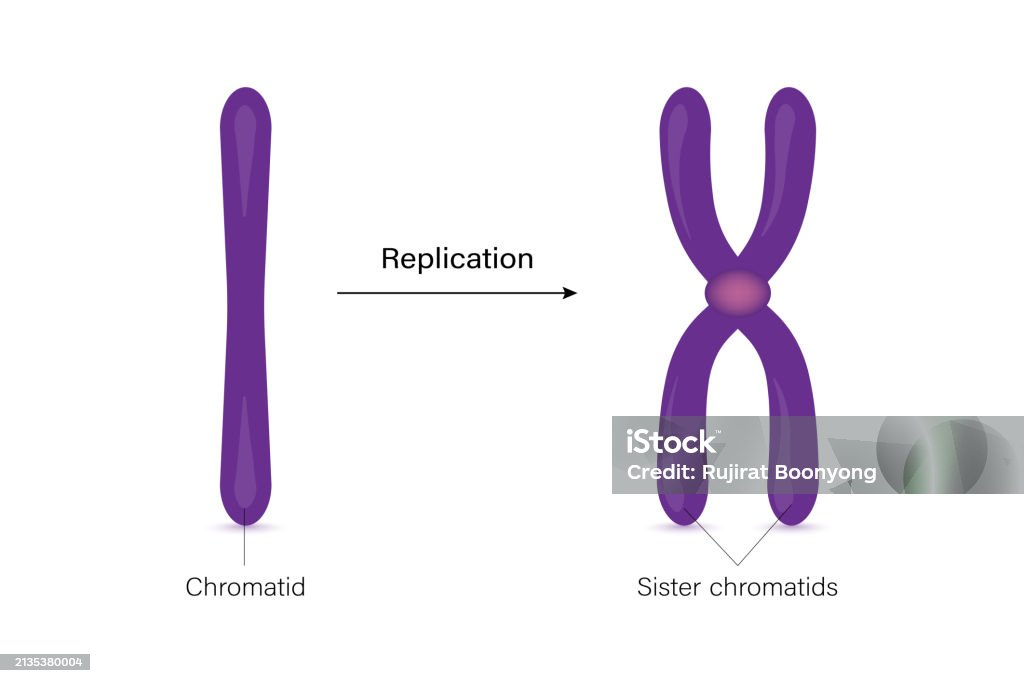
Sister chromatid
Duplicated chromosomes (2)
Centromere vs kinetochore
Centromere - center of chromosome that keeps chromatids together
Kinetochore - protein that allows spindles to attach to the centromere to pull the chromosome apart
Stages of cell division/M phase (6)
Prophase
Prometophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Prophase (3)
Nucleus dissolves
Chromosomes condense
Centrosomes seperate to make spindles
Prometophase
Spindles dome over chromatids
Metaphase
Centrosomes align on polar ends of the cell, aligning chromatids to the MIDDLE
Anaphase
Spindles pull apart the chromatids from the centromere to the ends of the cell
Telophase (2)
New nucleuses form on each side, taking the chromatids to uncondense into chromatin
Removes spindles
Cytokinesis (2)
Animals - form cleavage furrow to split into two new cells
Plants - form cell plate to merge the cells to form a grid
What regulates the cell cycle? (3)
Cyclins - signals cell division
Cyclin dependent kinase - activate proteins w cyclin
Growth factor - proteins to make other cells do mitosis
Only will if enough space or cells are anchored
Checks between phases (interphase → m phase)
is it G1? is there no mutations in S? is chromatids aligned and attached in M?
Positional inhibition (2)
Ability of cell cycle regulation in growth factors.. will work if
Density dependent - is there enough space
Anchorage - are the cells locked on a area
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell division that act w/o or make their own growth factors, routing blood vessels for nutrients (angiogenesis)
Benign vs malignant
Benign - mass of cells with no effects
Malignant - mass of cells that can spread by moving in the circulatory system (metastasizing)
Proto-oncogenes vs tumor suppressor genes
Proto-oncogenes are made up of mutated Ras proteins that overproduce cyclin
Tumor suppressor genes are p53 mutated to not inhibit mitosis
Causes of cancer (4)
Genetics
Viruses - damage regulatory genes
HPV
DNA damage (UV, radiation)
Mutations
Cancer treatments (3)
Chemo
Radiation
Surgery