6-The Great Depression/New Deal
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Causes of the Great Depression
-Stock Market Crash
-Speculation
-Buying on Margin
-Unequal distribution of income
-Overproduction
-Foreclosure of Farms
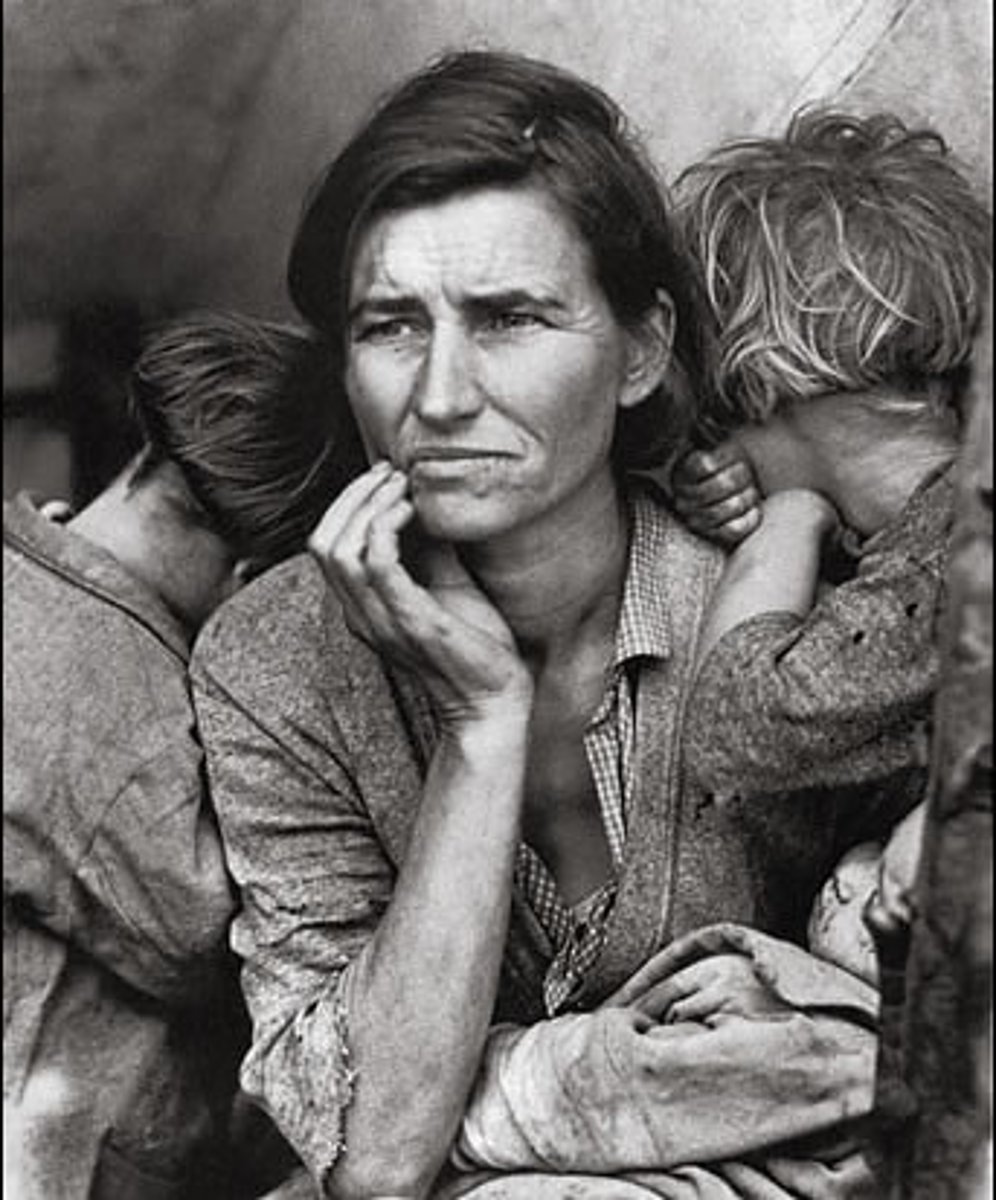

Effects of the Great Depression
- Many banks fail.
- Many businesses and factories fail.
- Unemployment

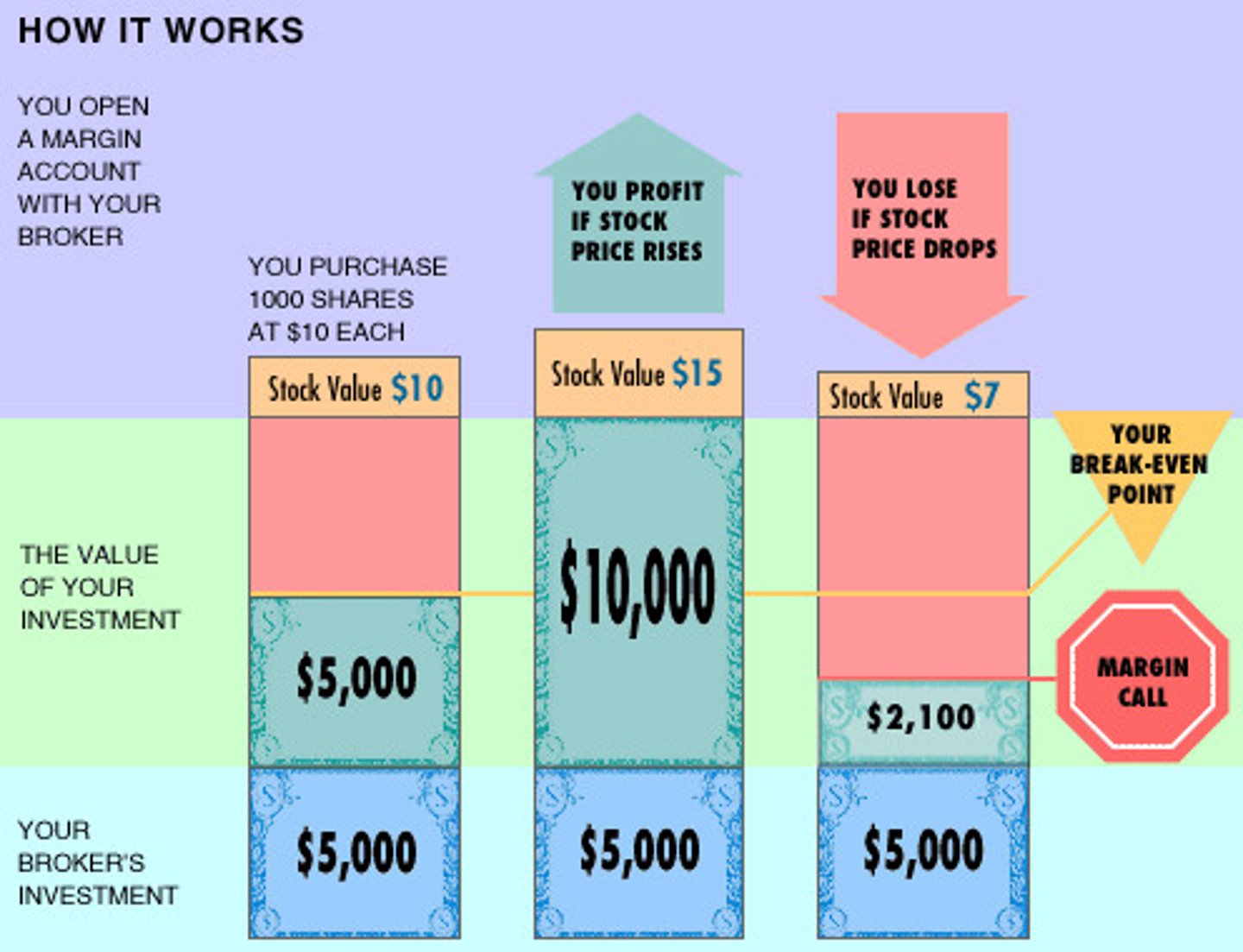
Buying on Margin
Borrowing money to buy stocks
Black Tuesday
October 29, 1929- the day the stock market crashed, signaling the start of the Great Depression

Great Depression
Worst period of economic decline in United States history, beginning in 1929 lasted throughout the 1930's decade. Unemployment reached record 25%.

22nd Amendment
Created after FDR's presidency, it limits the President to two terms in office.

Soup kitchens
Place where food is provided to the needy at little or no charge

Public works
Projects built by the government to help the public

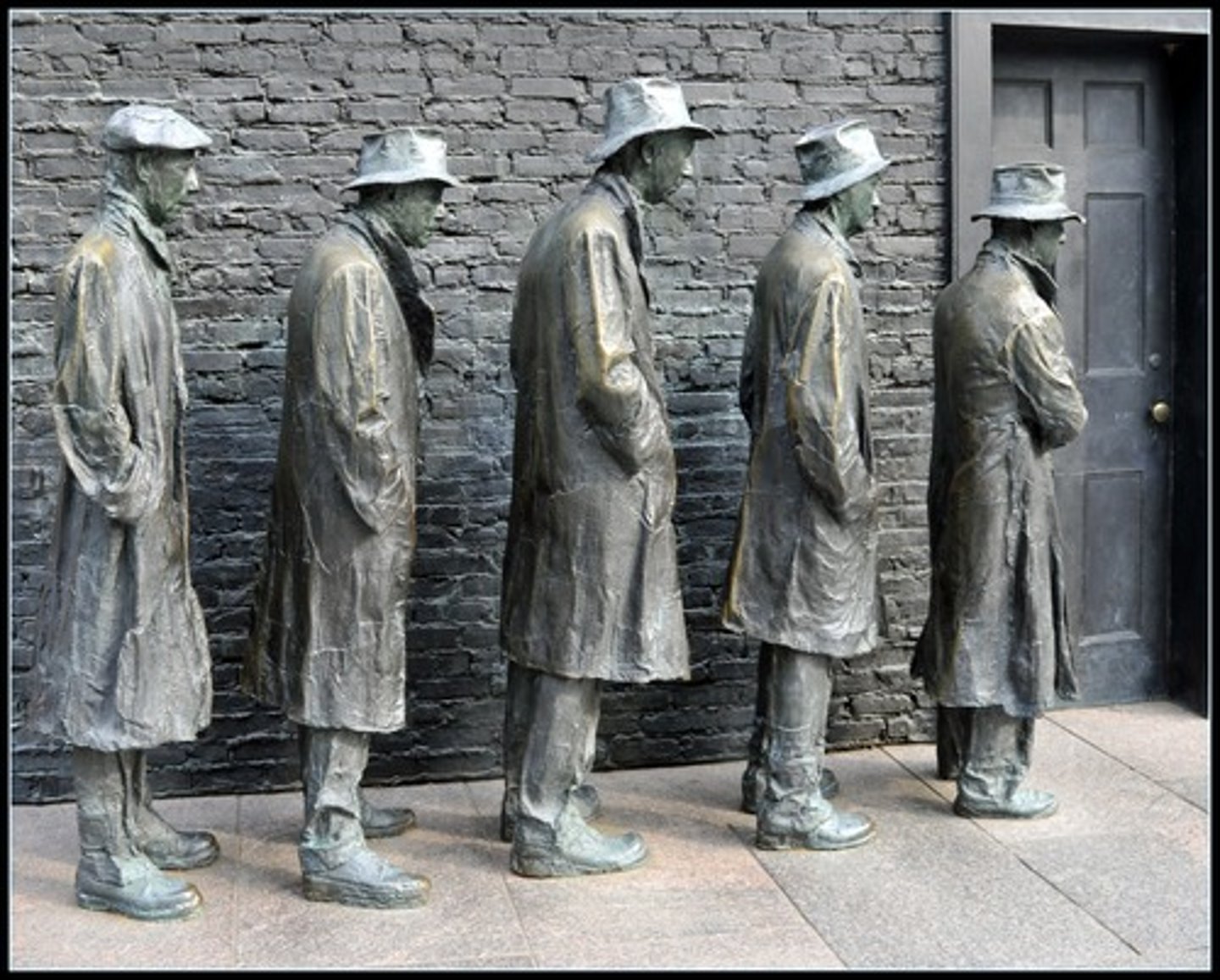
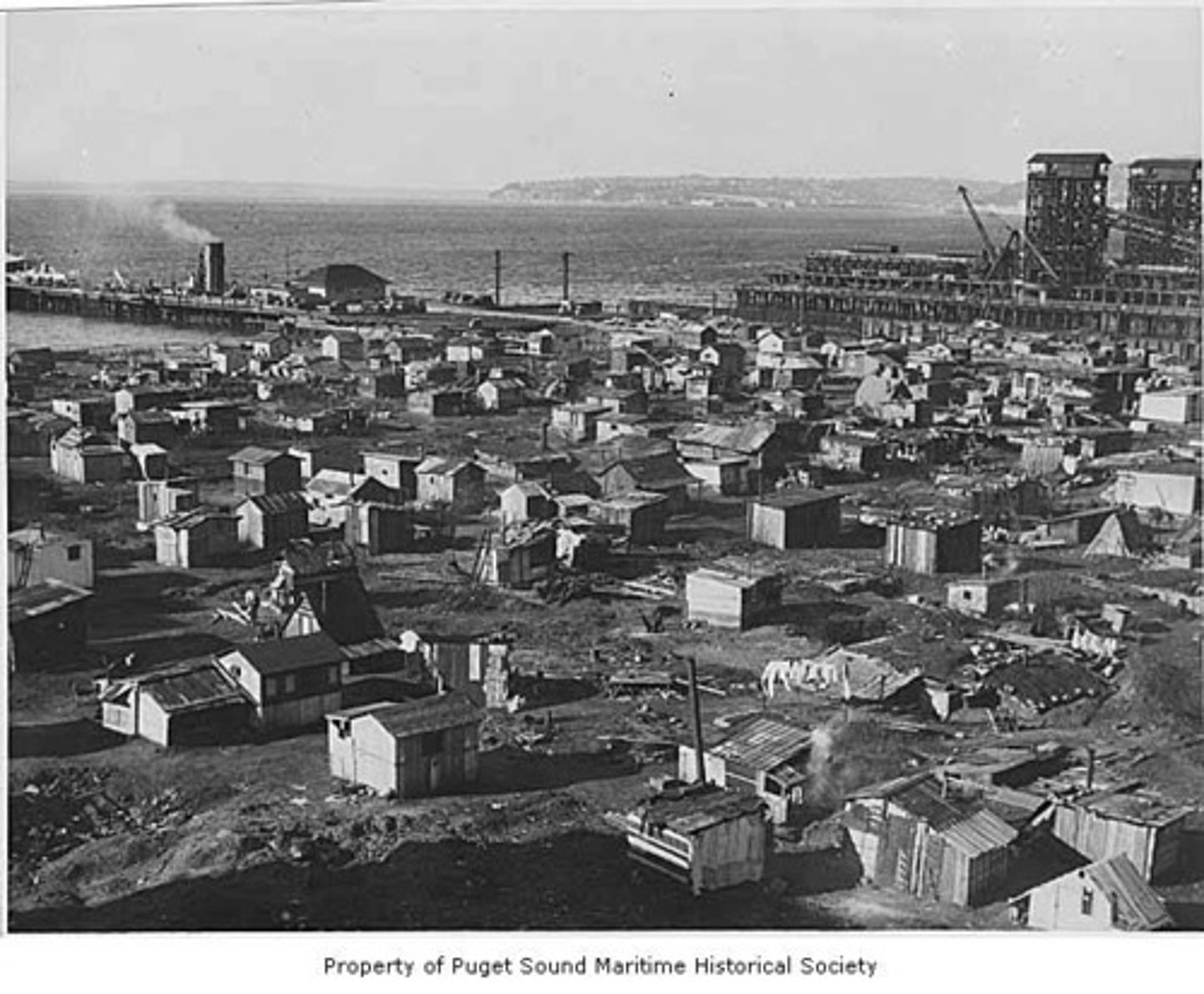
Hoovervilles
Group of shacks in which homeless lived during the Great Depression

Works Progress Administration (WPA)
Provided employment assistance directly to the poor. Hired jobless people to build public buildings and parks.

National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA)
Develops rules for doing business

Polio
Franklin D. Roosevelt was stricken with this disease leaving him paralyzed from the waist down.
Bank Holiday
Presidential closing of banks four days during the Great Depression to help recover

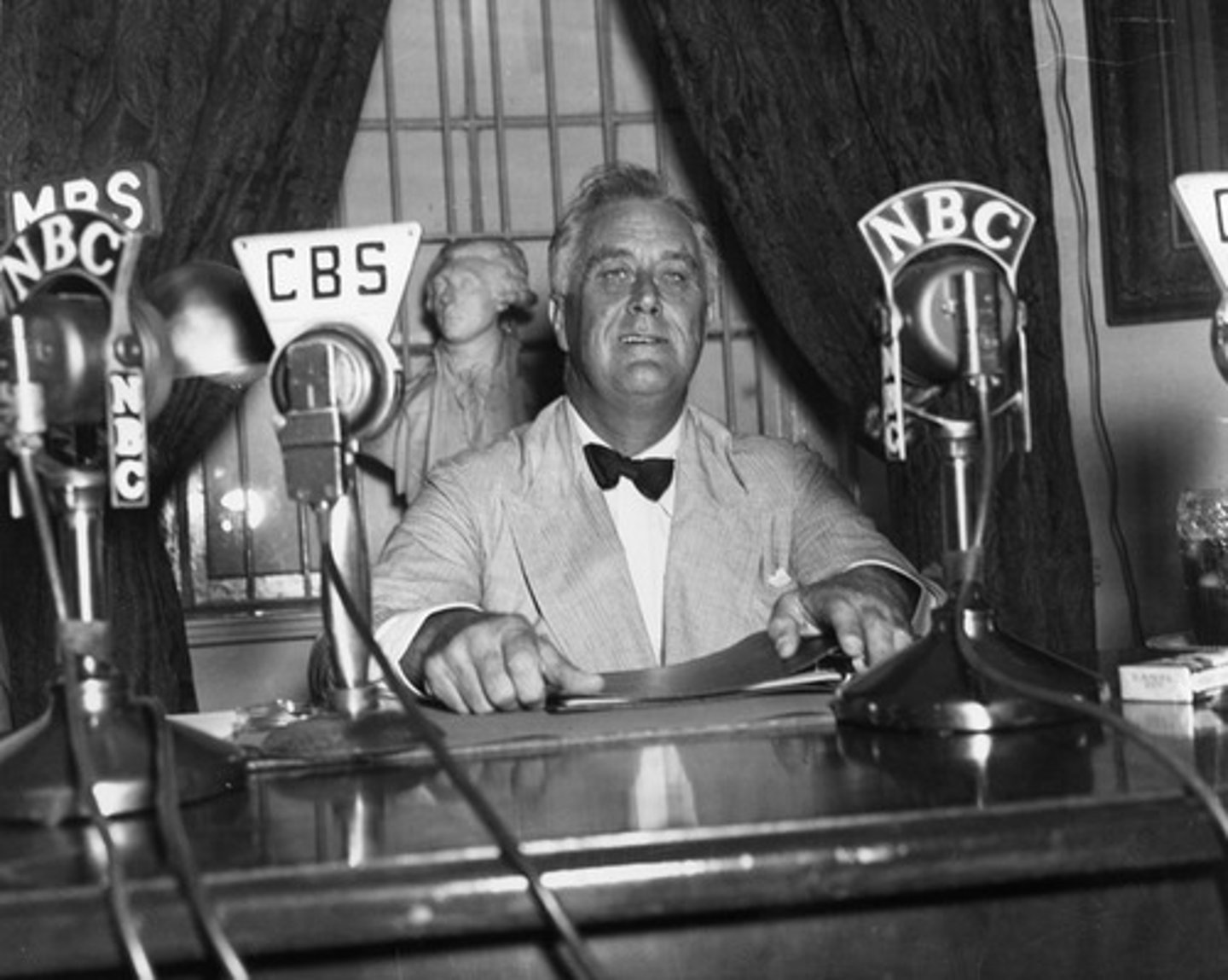
Fireside chats
Radio speeches given by Franklin D. Roosevelt describing the New Deal

Hundred Days
Period of time when the New Deal was implemented.

New Deal
Program of President Franklin D. Roosevelt to combat the Great Depression

Aims of the New Deal
Relief, Recovery, and Reform

Dust Bowl
Region of Great Plains that was hit by a severe drought during the Great Depression
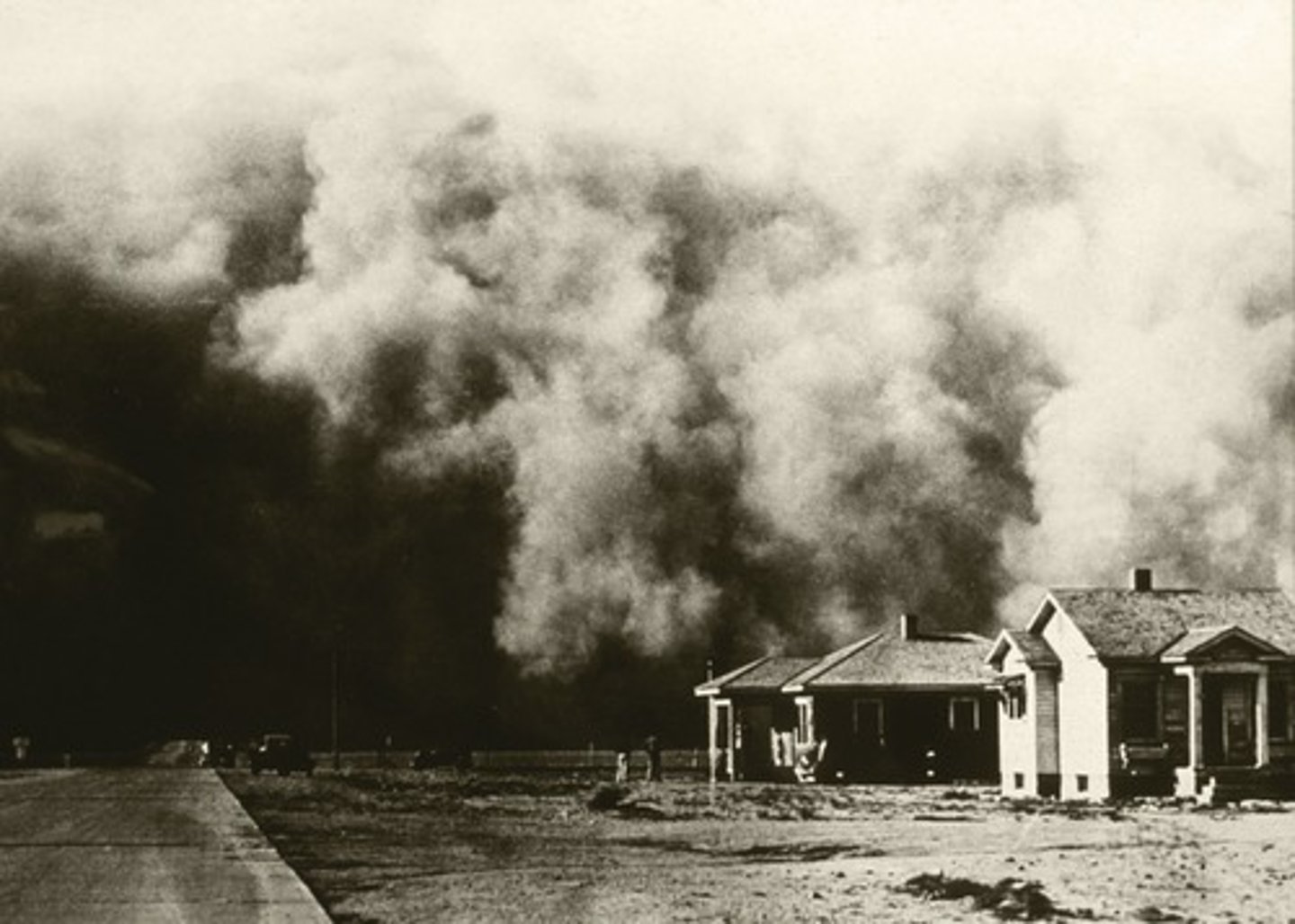

Franklin D. Roosevelt
32nd President of the United States, Roosevelt, the President of the United States during the Depression and WWII.

S.E.C
Independent federal agency that oversees the stock market to protect investors

Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
A federal guarantee of savings bank deposits initially of up to $250,000.

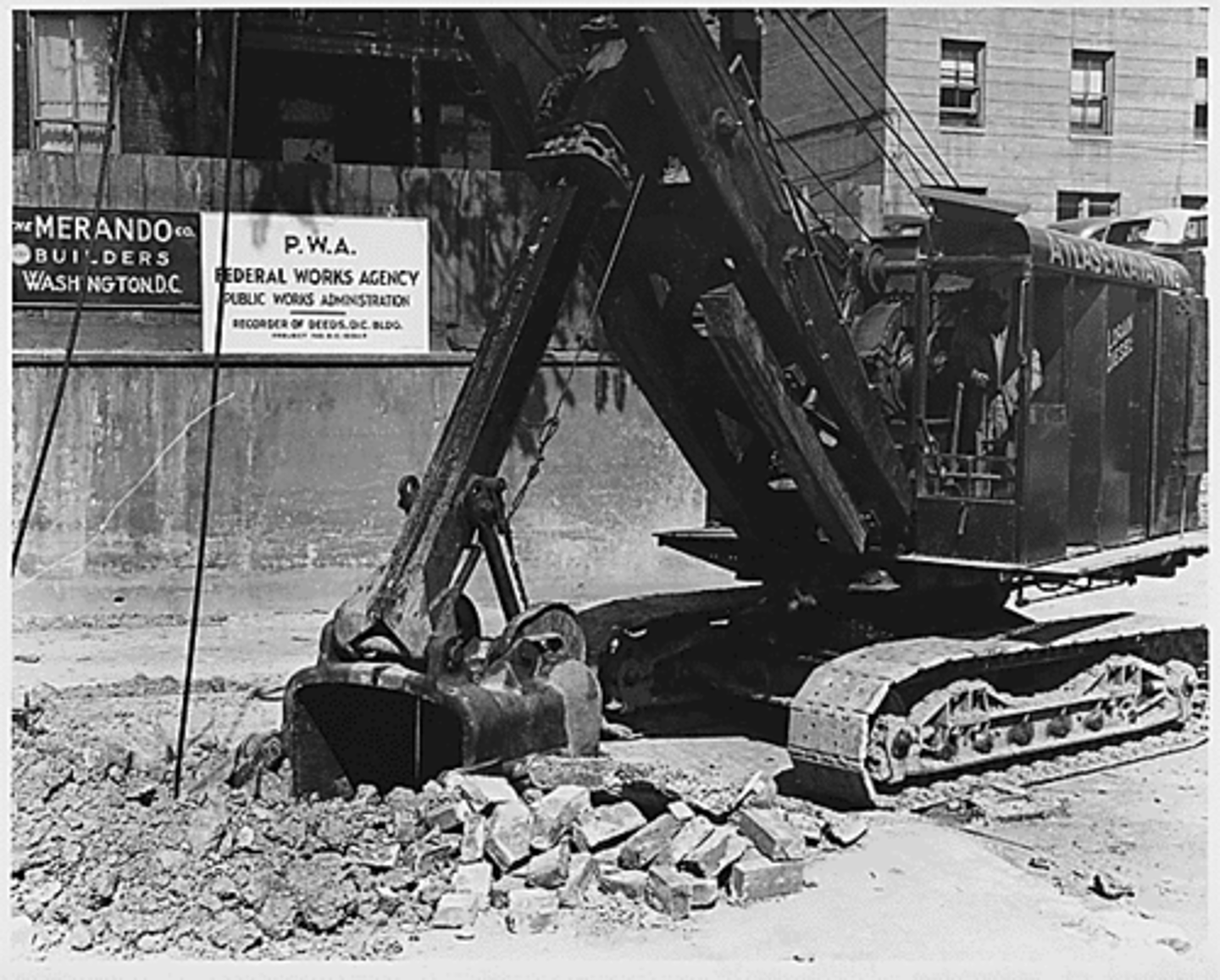
Public Works Administration (PWA)
Put people to work building or improving public buildings like schools, post offices, etc.

National Recovery Administration (NRA)
Set production limits, prescribed wages and working conditions, and forbade price-cutting and unfair competitive practices. Ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 1935

Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA)
Attempted to regulate agricultural production through farm subsidies to decrease the amount of crops produced; ruled unconstitutional.

Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA)
Provided navigation, flood control, electricity generation, fertilizer manufacturing, and improved farming in the South

Eleanor Roosevelt
First lady of the United States from 1933-1945. The legs and eyes of FDR

Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC)
Agency set up under the Hoover administration to make loans to banks and other lending institutions.

Midwest farming
Effected most by the "Dust Bowls"

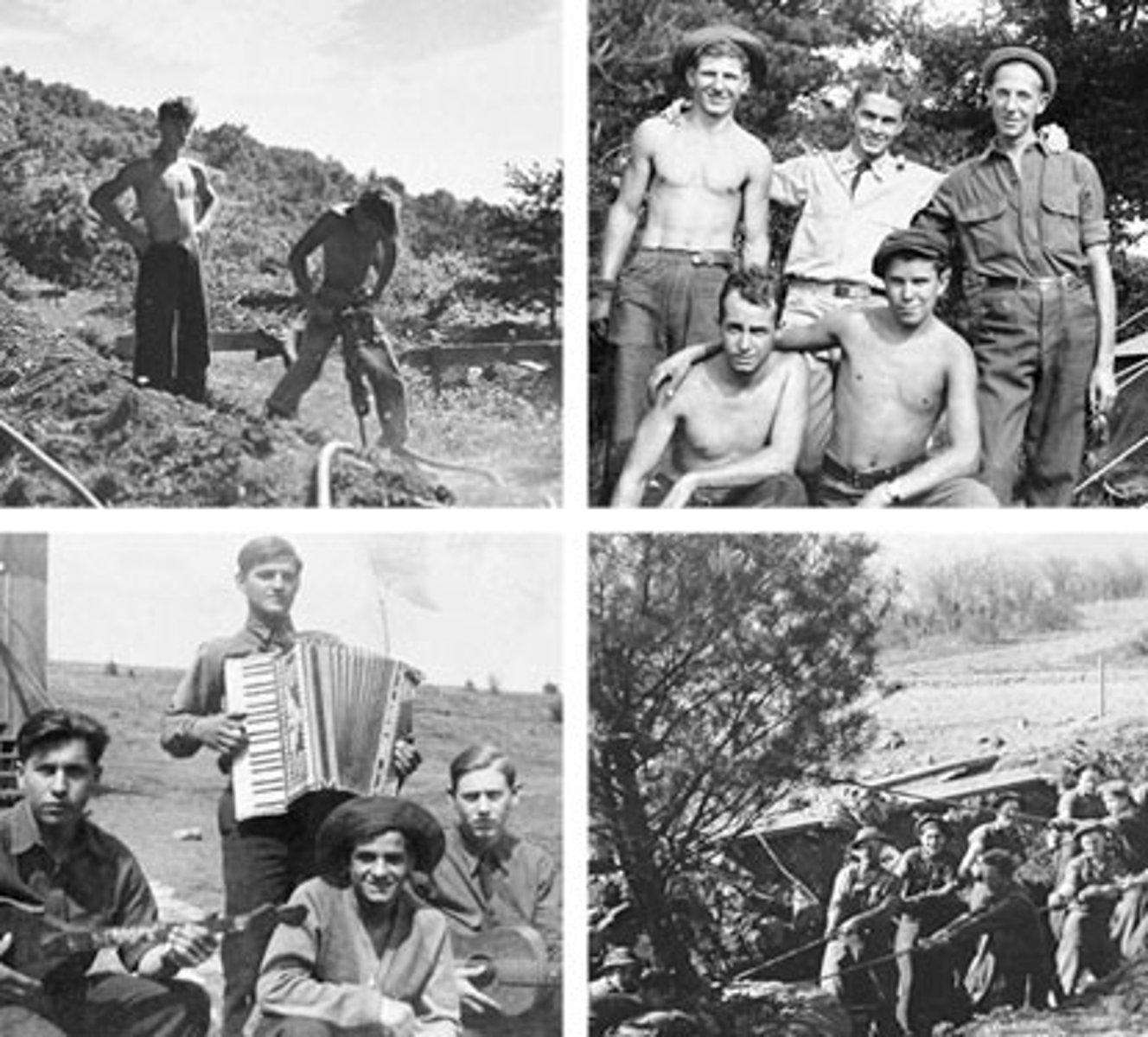
Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC)
Relief program that employed jobless youths in such government projects as reforestation, park maintenance, and erosion control.

Schechter Poultry Corporation v. United States
Supreme Court case that found parts of the New Deal Unconstitutional

Free enterprise system
Opposition of the New Deal believe it went against

Social Security Act
Launched a federal-state program of workers' pensions, unemployment insurance, and other welfare benefits.

Court Packing
This plan made Congress fear that FDR was disrupting the system of Checks and Balances.

Relief
Provide aid for the needy
Recovery
Support for business, banking and farms so that they can return to normal
Reform
Try to prevent another great depression from occurring through legislation
Bonus Army
WWI veterans marched on Washington D.C to pressure Congress to pay them their retirement bonuses early.

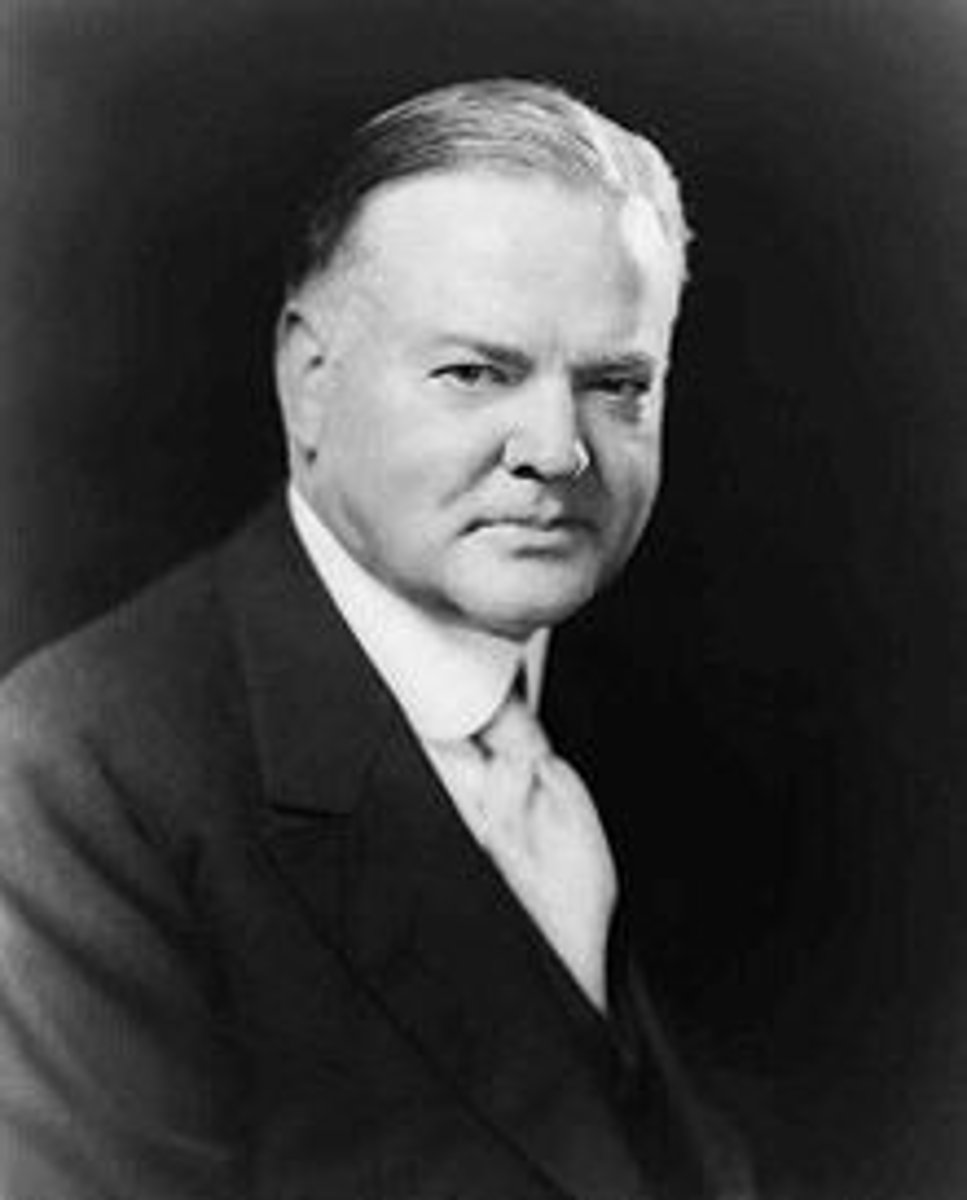
"Rugged Individualism"
Hoover's belief of how society would get itself out of the Depression

Hobos
Homeless wanderers during the depression, often traveled in boxcars on the railroad

Mexican Repatriation Act
A law sending Mexican-American immigrants back to Mexico

Deficit Spending
Used by FDR to finance the New Deal, it was the government spending more money than it received in revenue.

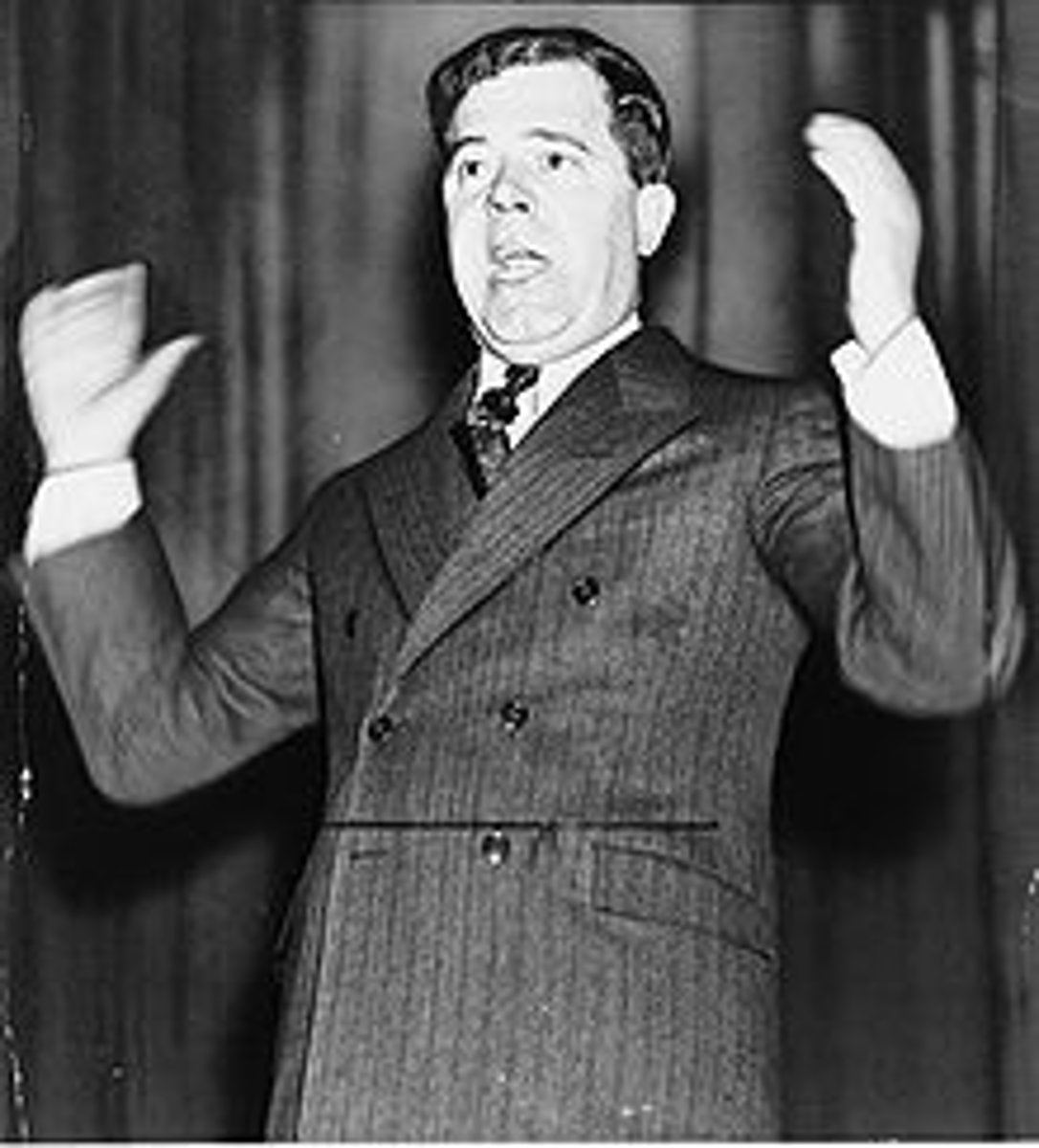
Huey Long
Pushed "Share Our Wealth" program a called for a massive redistribution of wealth.

WWI
This event led to overproduction during the 1920's

WWII
The start of this war would be the event that led the U.S out of the Great Depression.

Revenue Act of 1932
increased tax rates across the board in the United States to help balance the federal budget during the Great Depression.
Wagner Act
protected the rights of most workers in the private sector to organize labor unions, to engage in collective bargaining, and to take part in strikes and other forms of concerted activity in support of their demands.
Herbert Hoover (1929-1933)
Party: Republican
Major Events: Great Depression strikes; Promoted attitude of rugged individualism
Over speculation
buying stocks for more than what their worth
Over production and under consumption
Businesses produced too many goods due to early demand for products but products went unpurchased since there was a flood of products on the market.
Alphabet Agencies
In 1933 President Franklin D. Roosevelt launched his New Deal to deal with the Great Depression. The administrative style was to create new agencies. Some were set up by Congress (such as TVA) and others by Roosevelt's Executive Order (such as WPA). The agencies were also referred to as "alphabet soup".FIB,CIA,EPA,etc.
Hawley-Smoot Tariff (1930)
Passed under President Hoover, it raised tariffs up to sixty percent which became the nation's highest protective tariff during peacetime. Hoover & Republicans hoped it would help US economy, but instead it resulted in retaliatory tariff increases against the US by other countries. It deepened depression and increased international financial chaos.