The Chemistry of Life ch. 2
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary from the Chemistry of Life chapter, focusing on atoms, molecules, chemical bonds, water, acids, bases, organic compounds, and energy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
Biochemistry
The study of the molecules that compose living organisms. Carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids. Useful for understanding cellular structures, basic physiology, nutrition and health.
Chemical element
Simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties. Each identifies by an atomic number.
Atomic number
Number of protons in the nucleus. Periodic table arranges elements (1-2 letter symbols) by atomic number.
How many naturally occurring elements are there
91
How many naturally occurring elements play roles in humans?
24
Which 6 naturally occurring elements are most abundant in humans? (98.5% body weight)
Carbon, calcium, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus. (CCHNOP)
Minerals
Inorganic elements extracted from soil by plant, passed up food chain to humans
What percentage of body weight do humans have in our body weight, and which elements are the most?
4%, calcium and phosphorus
What body structures do minerals make up in the human body
Bones, teeth, enzyme function, nerve and muscle cell functions
Atom
Smallest unit of matter
Nucleus
Center of atom, composed of protons and neutrons
Proposed planetary model of atomic structure in 1913, useful as schematic but not an accurate structure.
Neils Bohr
Protons
Single (+) charge. Mass = 1 atomic mass unit (amu)
Neutrons
No charge. Mass = 1 amu
Atomic mass is…
Approximately equal to total number of protons and neutrons
Electrons
In concentric clouds surrounding nucleus. Have a single (-) charge, very low mass
An atom is electronically _____, as number of electrons equals number of ____.
Neutral, protons
Valence electrons
In the outermost shell and determine chemical bonding properties of an atom.
Isotopes
Varieties of an element that differ only in the number of neutrons and therefore in atomic mass. Extra neutrons increase atomic weight. Isotopes of an element are chemically similar because they have the same number of valence electrons.
Atomic weight (relative atomic mass)
Accounts for the fact that an element is a mixture of isotopes.
Radioisotopes
Unstable isotopes that decay and give off radiation in a process called radioactivity
The difference between an atom and an ion
Atom has an equal amount of protons and electrons so it is neutral
Ion has gained or lost electrons so it’s either pos or neg
Every element has at least one…
Radioisotope.
Ionizing radiation
Ejects electrons, destroys molecules, creates free radicals—and can cause genetic mutations and cancer
Examples of ionizing radiation
UV radiation, x-rays, alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays
Physical half-life of radioisotopes
Time required for 50% to decay to a stable state
Biological half-life of radioisotopes
Time required for 50% to disappear from the body
Standard acceptable exposure of radiation per year
50 mSv
Fatal amount of Sv
5 Sv or more
The feature that contrasts a lipid from a carb is that a lipid
Has a lower ratio of oxygen to hydrogen
Amphipathic lipids of cell membranes are called
Phospholipids
Chemical that is derived from ATP and is a second messenger
CAM (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
When oxygen is limited to meet ATP demand a cell employs
Anaerobic fermentation
All the synthesis reactions in the body form a division of metabolism called
Anabolism
Suffix that denotes sugar and suffix that denotes an enzyme
-ose and -ase
Any substance that increases the rate of a reaction is _______. In the body _____ serve this function
Catalyst, enzymes
Background radiation
Natural sources such as radon gas and cosmic rays
What function of carbs is more likely to be than proteins
Energy storage
Average background radiation Per year
2.4 mSv
Artificial sources of radiation
X-rays, color tvs
Average mSV of artificial sources of radiation per year
0.6
What was madame Curie known for
-first woman to receive Nobel prize
-first woman in the world to receive a PhD
-discovered and coined the term radioactivity
-trained the physicians on use of X-rays and pioneered radiation therapy as cancer treatment
Ion
Charged particle (atom or molecule) with unequal number of protons and electrons
Ionization
Transfer of electrons from one atom to another
Anion
Particle that has a net negative charge due to gain of electrons
Cation
Particle that has a net positive charge due to loss of electrons
Ions with opposite charges are
Attracted to each other
Electrically neutral compounds of cations and anions, dissociate in water ions and act as electrolytes
Salts
Sodium chloride, calcium chloride
Examples of salts
Electrolytes
Substances that ionize in water and form solutions capable of conducting electric current
Functions of electrolytes
Chemical reactivity, osmotic effects, electrical excitability of nerve and muscle
Electrolyte balance is one of the most important considerations in patient care because…
Imbalances can lead to coma or cardiac arrest
Free radicals
Unstable, highly reactive particles with an unusual number of electrons
What type of ions are produced by normal metabolic reactions, radiations and certain chemicals?
Free radicals
Which ion can trigger reactions that destroy molecules, cause cancer, death of heart tissue and aging?
Free radicals
Antioxidants
Chemicals that neutralize free radicals
Examples of antioxidants obtained through the diet
Selenium, vitamin E, vitamin C, carotenoids
Molecule
Particle composed of two or more atoms united by a chemical bond
Compound
Molecule composed of two or more different elements
What can be represented by a molecular formula which identifies constituent elements and how many atoms are present?
Compounds
Isomers
Molecules with identical molecular formulae but different arrangements of their atoms
Molecular weight (MW)
Sum of the atomic weights of its atoms
Ionic bonds
Attraction of a cation to an anion, relatively easily broken by something more attractive such as water
Chemical bonds
Hold atoms together within a molecule, or attract one molecule to another.
Covalent bonds
Atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
What is a single covalent bond
Nuclei share 1 pair of electrons
Double covalent bond
Nuclei shares 2 pairs of electrons
If electrons are shared equally it is a…
Nonpolar covalent bond ex. Carbon atoms bonding together
If electrons are shared unequally, its a…
Polar covalent bond. Ex. Hydrogen bonding with oxygen, electrons spend more time by oxygen
Nonpolar covalent bond
If electrons are shared equally
Polar covalent bond
If electrons shared unequally
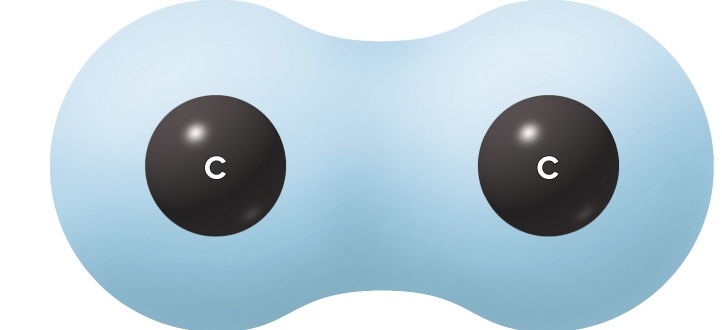
What is this called
Nonpolar covalent
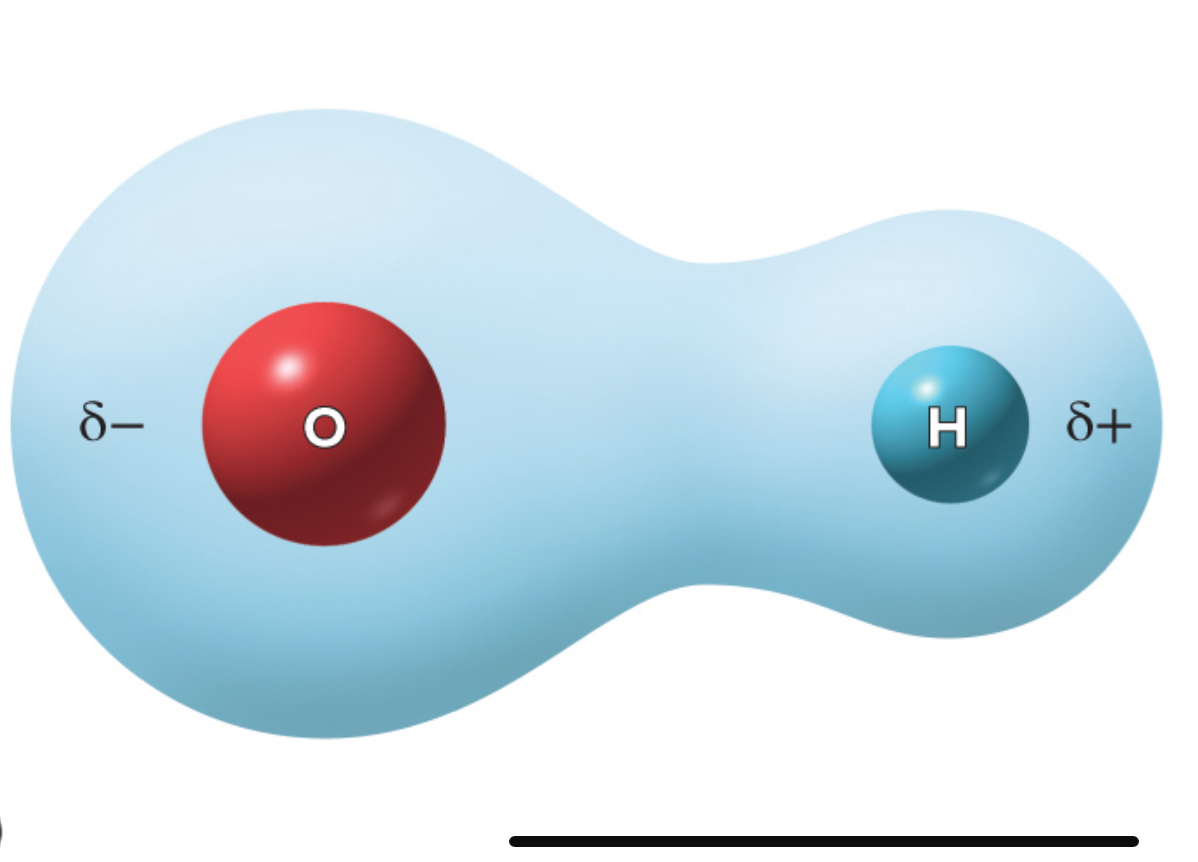
What is this called
Polar covalent bond
Hydrogen bond
Weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one molecule and a slightly negative oxygen or nitrogen atom in another atom
Why are hydrogen bonds important to physiology
Water molecules are attracted to eachother by hydrogen bonds. Large molecules (DNA and proteins) are shaped in part by the formation of hydrogen bonds within them
Van der Waals forces
Weak, brief attractions between neutral atoms, only 1% as strong as a covalent bond but are important in physiology (protein folding)
Mixtures
Consist of substances that are physically blended but not chemically combined, each substance retains its own chemical properties
What percentage of our body weight is water?
50-70%
The difference between a mixture and a compound
A mixture is a combo of substances that are physically blended and can be separated
A compound is a substance formed by a chemical bond and can’t be separated.
Properties that account for waters ability to support life
Adhesion, chemical reactivity, cohesion, solvency, thermal stability
Solvency (of water)
Ability to dissolve other chemicals. Water is the universal solvent because it dissolves more substances than any other solvent
Hydrophilic substances
Dissolve in water, are polarized or charged
Hydrophobic substances
Do not dissolve in water, are Nonpolar or neutral
Adhesion (of water)
Tendency of one substance to cling to another
Cohesion (of water)
Tendency of molecules of the same substance to cling to each other
Water is very cohesive due to its…
Hydrogen bonds
Surface film is due to
Molecules being held together by surface tension
Chemical reactivity
Ability to participate in chemical reactions
Thermal stability due to high Heat capacity
Amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°C
Calorie (cal)
The base unit of heat, 1 cal is the amount of heat to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1 degree C
Solution
Consists of particles called the solute mixed with a more abundant substance (usually water) called the solvent. Can be gas, solid or liquid
Action of buffers and function in the body
Help keep pH steady by soaking up extra acid or base
They keep things like blood from getting too acidic or too basic which helps the overall function of the body.
Solute particles are defined by
Are under 1 nm
Do not scatter light
Will pass through most membranes
Will not separate on standing
Water stabilizes
Internal temperature
Colloids
Often mixtures of protein and water and Can change from liquid to gel state within and between cells
Colloids are defined by
Range from 1-100 nm in size
Scatter light and usually cloudy
Too large to pass though semipermeable membrane
Remain permanently mixed with the solvent when mixture stands
Suspension (mixtures) are defined by
Particles exceed 100 nm, Too large to penetrate selectively permeable membranes, Cloudy or opaque in appearance, and Separates on standing
Ex. Blood cells in blood plasma
Emulsion
Suspension of one liquid in another. Ex. Oil and vinegar, fat in breast milk
Acid
Proton donor; releases H+ ions in water
Base
Proton acceptor; accepts H+ ions in water