Chapter 22 Prokaryotes
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Who created the first microscope to see bacteria?
Leeuwenhoek
What does a culture medium contain?
contains all the nutrients needed by the target microorganism, can be liquid (broth) or solid
What does a pure culture medium contain?
a laboratory culture containing a single species of microorganism
Cocci
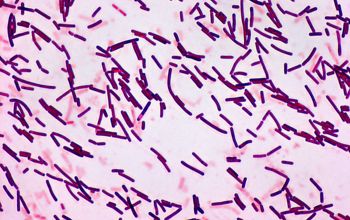
Bacilli
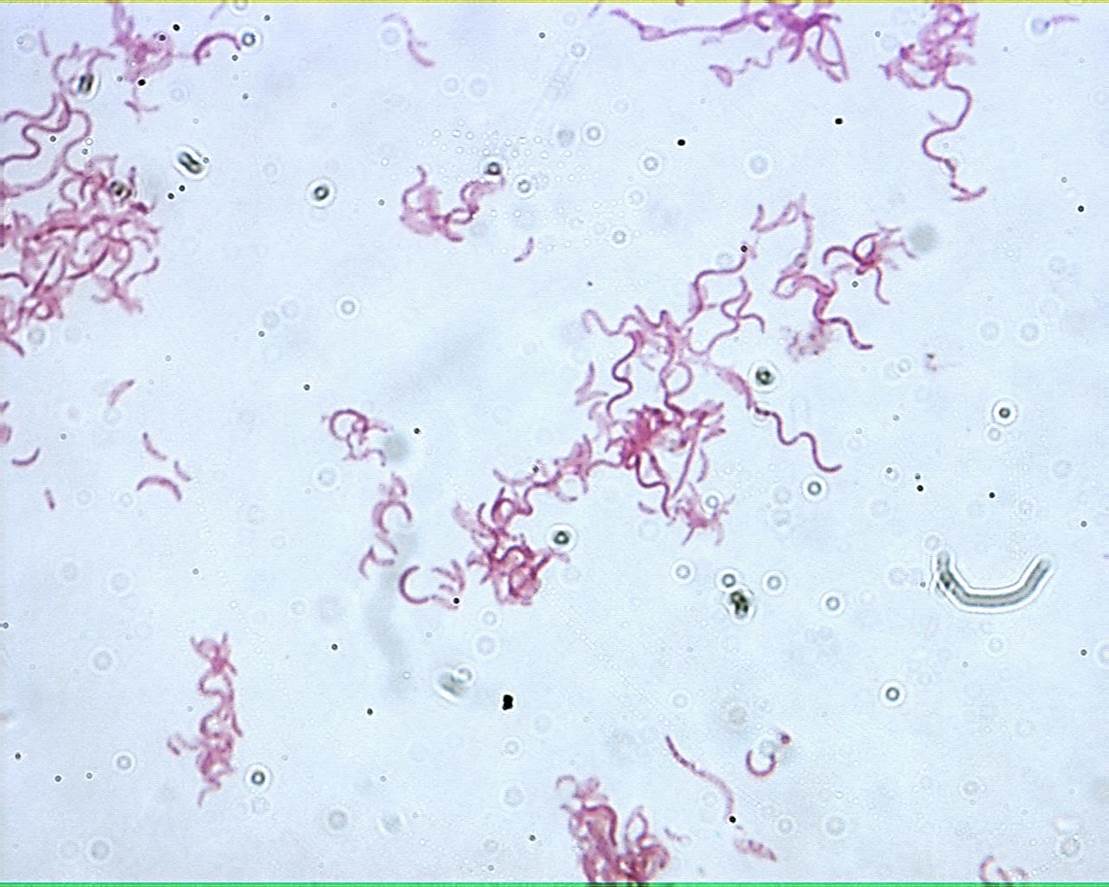
Spirili
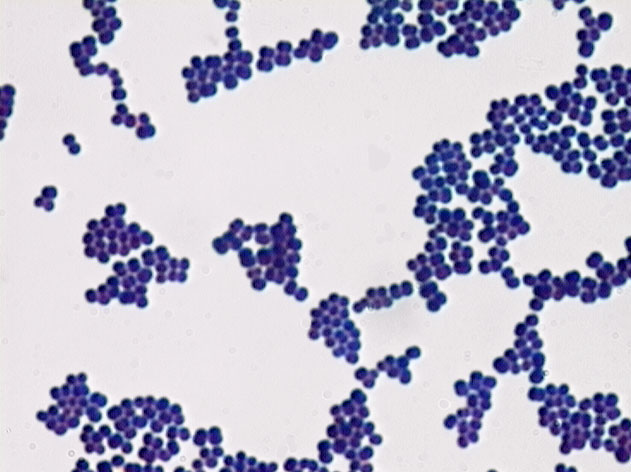
Staphylococci
cocci in groups/clusters
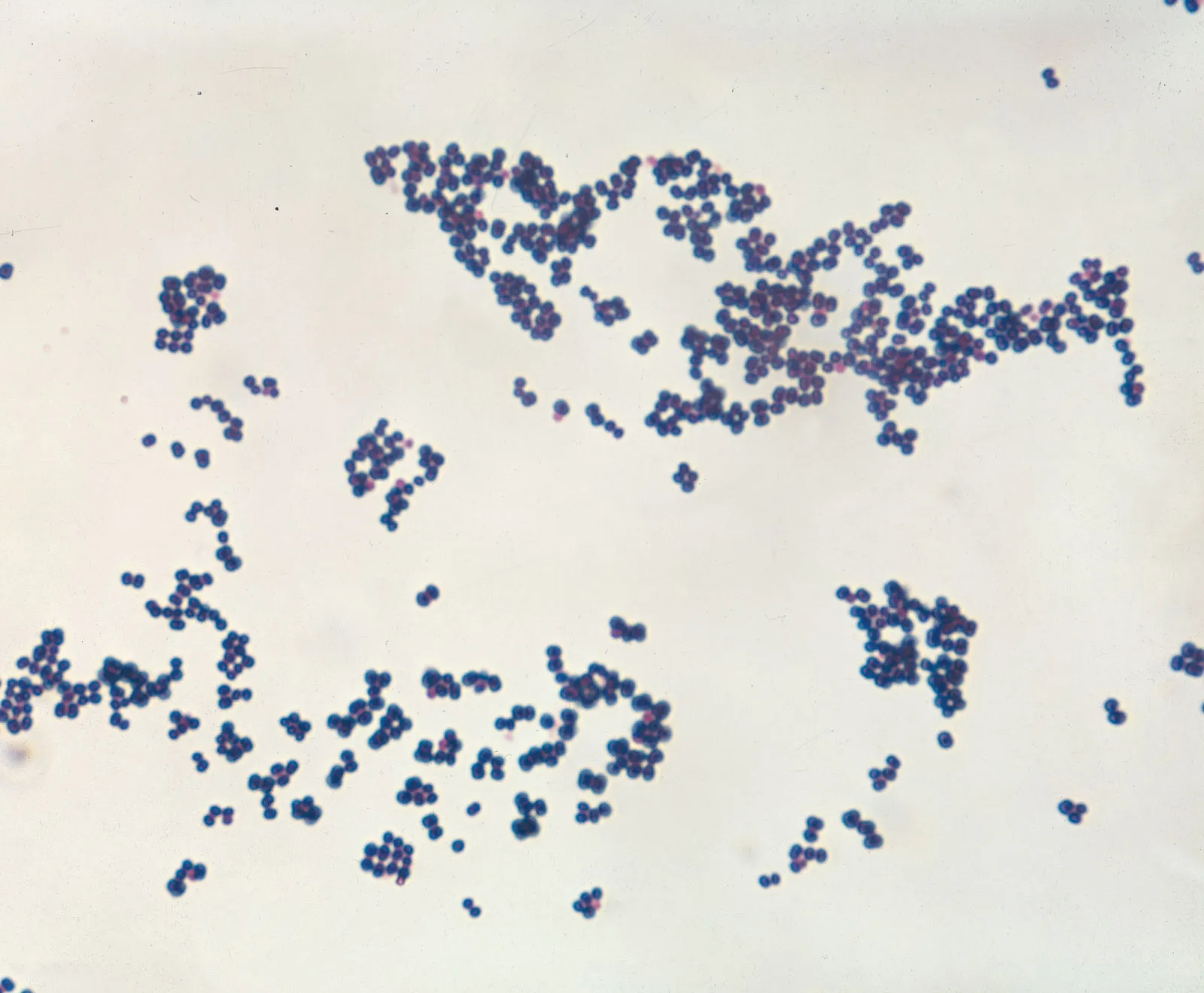
Streptococci
overlaps but is the round shape
Prokaryote structure
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, double stranded DNA genome, ribosomes
What do prokaryotes not contain
No membrane bound organelles, no nucleus, no microtubules, ribosome “free”
Do bacteria contain peptidoglycan in the cell wall
Yes
Do Archaea contain peptidoglycan in the cell wall?
No
Where do the cells walls in prokaryotes lie?
the cell wall lies outside the plasma membrane and prevents lysis
What stain color does Gram positive bacteria give?
Purple
What stain color does Gram negative bacteria give?
Pink
How many periplasmic spaces are in gram positive bacteria?
One gap between cell wall and cell membrane
How many periplasmic spaces are in gram negative bacteria?
two gaps between cell membrane and cell wall(first gap) and a gap between cell wall and outer membrane(second gap)
What is the cell membrane in bacteria made up of?
Phospholipids
What is the outer membrane of gram negative bacteria made of?
Lipopolysaccharide
What is the function of the Lipopolysaccharide layer(outer membrane)?
Is a toxic layer that resists drugs and the immune system
What is the slime layer on bacteria called?
Glycocalyx
What is the function of Glycocalyx?
Sticky carbs and proteins secreted from the cell wall that glues to surfaces and resists attacks from the immune system. It holds in moisture.
What are hair-like protein called?
Fimbriae (short pili)
What structure allows movement on prokaryotes
flagellum
What is taxis?
movement directed toward or
away from (+ or -) stimulus
What is Chemotaxis
Stimulus toward chemicals
Phototaxis
Stimulus toward light
Geotaxis(magneto taxis)
magnetic
Do prokaryotes have plasmids
Yes
Do plasmids add diversity?
Yes
Do Archaea contain a nucleus(nuclear envelope)
No
Do Archaea contain membrane bound organelles?
No
Archaea and Eukarya starting codons are methionine(AUG)
True
Do bacteria contain histones
No
Are histones present in archaea?
In some species
Are histones present in Eukarya
Yes
Bacteria and Archaea have circular chromosome
True
What are Archaea membranes formed by?
Glycerol skeleton with ether linkages
What are Extremophiles
Bacteria and archaea that are adapted to grow under extreme
conditions (e.g. deep see vent, heat, dry, cold, radiation, etc.)
Acidophiles
Live in conditions with a pH of 3 or below
Alkaliphiles
Live in conditions with a pH of 9 or above(basic solutions)
Thermophiles
Live in conditions with temperatures of 60–80 °C (140–176 °F)(extremely hot)
Psychrophiles
Live in extremely cold environments of temperatures of -15-10 °C (5-50 °F) or lower
Halophiles
Salt concentration of at least 0.2 M(high salt concentration)
Osmophiles
High sugar concentration
What are photoautotrophs energy source?
use energy from sunlight, and carbon from carbon dioxide.(plants)
What are photoheterotrophs energy source?
obtain their energy from light, but their carbon from organic compounds.
What are Chemoheterotrophs energy source?
obtain both energy and carbon from chemical sources.(humans and animals)
What are Chemolithoautotrophs energy source?
obtain their energy from inorganic compounds, and they build their complex molecules from carbon dioxide.
What is symbiosis?
two species living in close relationship
What is Parasitism?
– smaller parasite benefits at
expense of other species (host)
• incl. pathogens (cause disease)
What is commensalism?
one species benefits without any impact (good or bad) on other species
• Ex: most bacteria on our skin
What is mutualism?
– both species benefit from each other
• Ex: Rhizobium in legume roots get sugar & water; provide fixed N for plant
Why are chemoheterotrophic bacteria important?
are the most important decomposers on earth
Secreted enzymes hydrolyze dead material or wastes
What bacteria caused the Oxygen revolution?
Cyanobacterial photosynthesis and are a major producer of oxygen to this day!
What does carbon fixation produce?
Sugar
In prokaryotes do they produce sexually or asexually?
Asexually
What type of asexual reproduction do prokaryotes do?
Through Binary fission: does not provide genetic diversity.
Where does genetic diversity come from in prokaryotes?
Horizontal gene transfer
Prokaryotes have a higher cell division rate and short generation times
True
What are the 3 types of horizontal gene transfer?
Conjugation, Transduction, Transformation
What is transformation?
From the environment, it is when the cell takes up prokaryotic DNA directly from the environment.
The DNA may remain separate as plasmid DNA or be incorporated into the host genome.
What is transduction?
a bacteriophage injects DNA into the cell that contains a small
fragment of DNA from a different prokaryote.
By Bacteriophages.
What is conjugation?
cell-to-cell contact: DNA is transferred from one cell to another via a pilus that connects the two cells.
What do endospores do?
survive heat, drought for years. They are indestructible(Ex: Tetanus and anthrax)
Domain Archaea
Includes extremophiles and methanogens. Do not cause disease in humans
Domain Bacteria: Proteobacteria
Gram negative(stain pink): includes nitrogen fixing bacteria. Includes gastrointestinal pathogens
Examples of Proteobacteria
Cholera, salmonella, and Escherichia coli
Domain Bacteria: Chlamydia
Gram negative(pink): are all endoparasites (live within animal cells). Example: Chlamydia in humans causes STD
Domain bacteria: Spirochetes
Spiral shape, free-living but include disease causing pathogens. Examples: Syphilis and Lyme disease
Domain Bacteria: Cyanobacteria
Oxygen generating photosynthesis. Some are nitrogen fixing. Cyanobacteria blooms are toxic
Domain Bacteria: Gram Positive Bacteria
include many decomposers in soils. Includes many pathogens.
Examples of Gram positive bacteria
Anthrax, tetanus, Staph(MRSA), strep
What do pathogenic bacteria cause?
Infections produce bacterial poisons
What is Produced by both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria
Exotoxins(excreted)
What are Endotoxins?
are toxic outer membranes of some gram negative bacteria Ex: salmonella
Antibiotics
kill bacteria cells but not eukaryotic cells
Example of antibiotics
Penicillin: affects peptidoglycan cell wall
What causes bacteria to resist more and more drugs?
Horizontal gene transfer
What is Microbial bioremediation?
is the use of prokaryotes (or microbial
metabolism) to remove pollutants
• Some bacteria can remove toxic metals
• Some can transform toxic mercury into nontoxic forms