Introduction to the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine – Vocabulary Flashcards
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This vocabulary set covers thoracic and lumbar spine anatomy, joints, ligaments, landmarks, neural and autonomic anatomy, disc disease, and somatic dysfunction principles discussed in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
True ribs
Ribs 1–7 that attach directly to the sternum via costal cartilage.
False ribs
Ribs 8–10 that attach indirectly to the sternum via costal cartilage of the rib above.
Floating ribs
Ribs 11–12 that do not attach to the sternum.
Costal cartilage
Cartilage that connects ribs to the sternum or to the cartilage of the rib above.
Costal facets
Articular surfaces on vertebral bodies and transverse processes for rib articulation.
Inferior border of scapula landmark
T7 spinous process and T8 transverse process
Costotransverse joint
Joint where the tubercle of a rib articulates with the transverse process of a vertebra.
Zygapophyseal (facet) joints
Joints between the superior and inferior articular facets of adjacent vertebrae.
Facet orientation mnemonic
Cervical: Backwards, Upwards, Medial; BUM
Thoracic: Backwards, Upwards, Lateral; BUL
Lumbar: Backwards, Upwards, Medial; BUM
Facet arthropathy
Degenerative changes of the facet joints causing pain and reduced motion.
Pars interarticularis
The bony segment between the superior and inferior articular facets; a common site of stress fracture (spondylolysis).
Mammillary process
Posterior-lateral projection on lumbar vertebrae for muscle attachment.
Vertebral canal
The space within the vertebral column that houses the spinal cord and its protective membranes.
cervical nerve exits
The cervical spinal nerves emerge from the neural foramen above their corresponding vertebral segments
C8 nerve exits between C7 and T1; there are 8 cervical nerves but only 7 cervical vertebrae.
Spinal nerves (rami) and branches
Spinal nerves divide into posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) rami; dorsal/posterior ramus supplies the back; rami communicantes connect to sympathetic trunk.
Sympathetic nervous system (general mapping)
Thoracolumbar outflow from T1–L2; includes stellate ganglion (inferior cervical + T1) and sympathetic trunk.
Stellate ganglion
A fusion of the inferior cervical ganglion with the upper thoracic (T1) sympathetic ganglion.
Thoracic diaphragm anatomical hiatuses
Vena caval foramen (T8) for the inferior vena cava;
esophageal hiatus (T10) for the esophagus and vagus;
aortic hiatus (T12) for the aorta.
(I Ate Ten Eggs At Noon)
Psoas
Innervated primarily by L1–L3 nerve roots.
Hypertonicity may cause flexion, rotation, and sidebending towards the ipsilateral side
Thomas test
Clinical test used to evaluate iliopsoas muscle tightness. The patient lies supine, and the examiner flexes one hip while observing the other leg's movement to assess for tightness.
Iliolumbar ligament
Ligament connecting L4–L5 to the iliac crest; restricts motion at the lumbosacral junction and is often tender in dysfunction.
Iliolumbar region ligaments
Includes the iliolumbar ligament and related sacroiliac ligaments that stabilize the SI joint.
Sacroiliac ligaments
Key ligaments (sacrospinous, sacrotuberous) stabilizing the SI joint.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
Interventional treatment for facet arthropathy that ablates nerve fibers to reduce pain but does not decrease joint motion.
Facet joint capsule and innervation
Facet joints have a capsule innervated by posterior rami from two spinal levels.
Facet joint degeneration signs
Pain worse with extension/rotation, improves with flexion; may involve osteophytes and capsule inflammation.
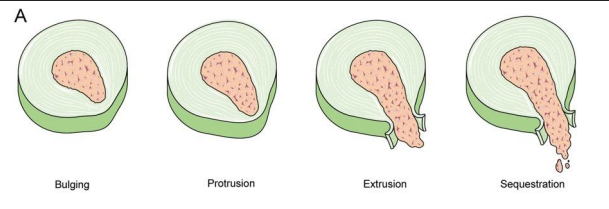
Bulging vs protrusion vs extrusion vs sequestration
Terminology describing disc pathology by extent and direction of disc material displacement.
Pars interarticularis fracture (spondylolysis)
Stress fracture through the pars between the superior and inferior facets, common in the lumbar spine.
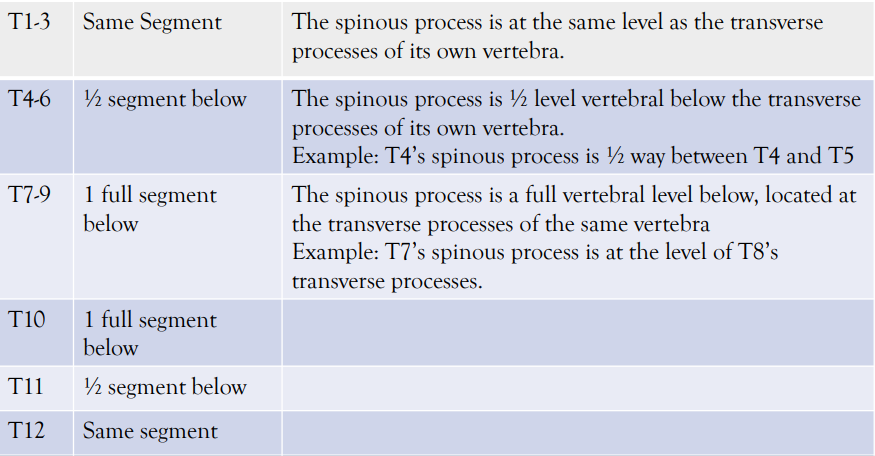
Rule of 3's (thoracic palpation mnemonic)
Fryette's Laws: 1
In a neutral position, sidebending and rotation occur in opposite directions. The vertebrae will first sidebend and then rotate in neutral dysfunctions
Type I dysfunction
Neutral pattern: multiple vertebrae rotate and sidebend in opposite directions; primary plane is sidebending. larger muscle groups involved, less common than Type II.
Written as: (Vert locations) (N) (S) (R opposite)
Type II dysfunction
Non-neutral pattern: one vertebra rotates and sidebends in the same direction; primary plane is rotation. Smallest muscle groups involved.
Written as: (Vertebra location) (E or F) (R)(S)(sameThis pattern indicates that the vertebrae involved are not in a neutral position and primarily demonstrate rotation along with sidebending occurring in the same direction, often involving smaller muscle groups in the process. )
Naming somatic dysfunction (order)
For Type I: vertebral level; Neutral; Sidebending; Rotation. For Type II: vertebral level; Flexed/Extended; Rotation; Sidebending.
Vertebral motion planes
Sagittal (flexion/extension), coronal (sidebending), transverse (rotation).
thoracic/lumbar nerve exits
The Spinal nerves emerge from the neural foramen below their corresponding vertebral segments.
12 thoracic, 5 lumbar
Shingles
• Painful, vesicular (fluid filled/blistering) rash that is caused by reactivation of a dormant herpes zoster viral infection (chicken pox reactivation)
• This reactivation inflames the sensory nerve root ganglia, and can result in crippling pain
• It SPECIFICALLY follows a dermatomal pattern; does not cross midline, unilateral
Somatic dysfunction detection
• The patient may experience pain or another symptom
• On an osteopathic structural exam, we have many ways to palpate a somatic dysfunction, such as:
• Redness, heat, sweatiness (vasodilation)
• Try using the back of the hand, as this is very temperature sensitive
• Clamminess, cold (vasoconstriction)
• Tenderness, tension
• Gentle percussion down the spine with your fingerpads
• Reduced range of motion
Fryette’s Laws: 2
In a non-neutral position (ie flexed/extended), rotation and sidebending occur in the same direction. The vertebra will first rotate and then sidebend in non-neutral dysfunctions
Fryette’s Laws: 3
Initiating motion in a vertebral segment will then affect (i.e. reduce) motion in the other two planes of motion Example: by flexing forward, the amount of sidebending and/or rotation that can then be achieved is reduced.