Issues and Techniques - Interviewing Children
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Developmental Issues - Childhood Amnesia
64% adults agree we can remember memories from early childhood
Evidence of absolute and relative amnesia
Amnesia for non-emotional events
No children ages 2 remembered
50% children aged 3 remembered
Most children aged 5+ remembered
Freud saw this as repression of memories
Developmental explanations
neurogenesis
sense of self
Memories sparse and sporadic for first 4-6 years of life
From 7 years on show adult levels of remembering
Language Development - Syntax issues
construction of sentences
Telegraphic speech
Compressed speech
‘Go park’
Use of negatives
Because it a word they have they might just use it ‘no’
Over generalisation of grammatical rules
Refinement of grammar
Language Development - Semantics issues
Basic understanding
Over and under extension of word meanings
‘orange’ could be used to describe any fruit
Have their own words for certain things
Conceptual development
Language Development - Language Issues
Young children are very literal
Example

Change from asking if the child ‘did’ something

Changed to did someone ‘do’ thins to them
Literally take the question
Developmental Issues - Cognitive Development
Priorities
‘central’ details best remembered for emotionally tagged events
children tend to think description information is irrelevant
Interviews need to carefully explain importance of such information
Specific knowledge
Measurement (height weight
Time (too abstract)
Example
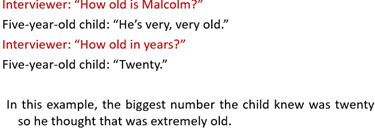
Feeling ‘touch’ vs feeling ‘emotion’
Associate a memory with emotion rather than the actual physical feeling of it
Cognitive Interview - Children
Option posing/leading
Suggestive
Information provided by the interviewer not child
Implying a desired response
Open prompts
Invitations
Cued invitations/time segmentation
Earlier you mentioned
Free recall
Get more detailed responses
most accurate
Non-suggestive
Difficult for defence to criticise
Wh..? specific questions
Children use words before they understand them
Children try to answer question they don’t understand
cued-recall memory
Children have difficulty with some concepts
Times/dates/ages
Size/height/weight
Same/different
Neither/either
Easy to answer
Names
Hard to answer
back of 50p’
Confusion
‘what colour was car’ (inside or outside)
Not remembered
‘when was this’
Research
Obarch & Lamb (2001) – Open prompts vs closed question
Analysis of interviews with abused 5 year old
90% of contradictory details were gained by closed questions
No contradictory details to open prompts
Research on interviewing England and Wales
Sample 119 children who had allegations of abuse
Results
Only 7% were interviewed with open prompt
33% was option posing
Found similar results in USA, Israel and Sweden
Worrying
trained and aware of practise they believed they were doing it right
NICHD Overview
Introduction
Ground rules
Truth and lies
Transfers of control – don’t know, don’t guess, correct interviewer
Rapport – what do you like to do?
Practice interview
Transition
Why they are there and what’s going to happen
Investigative incidents
Open ended prompts
Separation of incidents
Break
Focused questions about information not mentioned
Disclosure information
Who did they tell
Closure – anything else
Neutral topic – what are you going to do
NICHD - Importance of ground rules
Make children aware that they
Are in control
Not pressured to answer questions
Shouldn’t guess
Important as it removes the pressure to give answers but aren’t sure about
NICHD - Importance of practice interview
Practice at remembering events
helps level of detail
Practice open prompts
build rapport
Child can feel in control/successful
Practice for interviewer
Useful in cases of multiple incidents
Fewer questions needed in substantive phase
understand cognitive abilities
Research
Two practice interviewing techniques compare
Results
Response to first open prompt was twice as long and detailed when practice interview had taken place
NICHD - Reported reasons for not conducting practice interview
Takes to much time
5-7 minutes of practice produces benefits
Fatigues – tire child out
illogical to say to leads to fatigue as children give more info
Get to the point
Sometimes children what to get started
BUT
Children don’t know how much detail to give
If preparation isn’t adequate they may never get to the point
Advantages of NICHD protocol
all children given equal opportunity to disclose to not disclose alleged abuse
underestimating child capabilities are minimized
standardised format helps maintain desirable interview standards
Validated world wide
NICHD protocol did increase the use of open prompts question interviewing (Lamb et al)
NICHD - Research
Benia et al 2015
Had more invitations, fewer option posing and suggestive prompts
Children provided more central details in response to invitations than controls
Pipe et al 2012
more likely to result in charges being filed against a suspect
higher conviction rate
Current: Revised NICHD protocol
RP empathised intensive rapport building and provision of emotional support
appeared to enhance children’s willingness to make credible allegations
Issues in interviewing seriously abused/ maltreated children
Little research
Chae 2011
Abused status was not associated with memory deficit
Maltreated child were more likely to display trauma related psychopathologies (PTSD symptoms, higher dissociative tendency)
Importance of individual difference
Malloy 2007 – disclosure and recantation
Examined 257 case files
Recantation rate of 23%
Consistent with Filial Dependency model: children who were more vulnerable to influence from assault family were mostly likely to recant
Interviewing vulnerable witnesses and victims
Cognitive/social/developmental defects
Both permanent and time limited (children, elderly, intoxicated)
ABE guidelines – Policy for England and Wales
Interviewing Intellectual disability
Increased risk of sexual abuse, physical maltreatment and criminal victimization
Not a homogeneous group
Even when same or similar diagnosis in place
Ability to recall is based on the individual
Henry & Gudjonsson 2003
Children with mild intellectual disability performance as well a mental age matched typically developing children
Children with moderate disabilities performed worse
Use of NICHD protocol, appears to assist children with intellectual disability
Interviewing Autistic Spectrum Disorder
Increases risk factors for becoming victims/witness
Cognitive deficits and interpersonal nature of the interview may be challenging
Not a homogenous group – individual need to be assessed
Care needed with interviewing technique
Mara & Bowler 2012 notes that elements of CI were problematic for this group – context and reinstatement