CS 2810 Exam 2 Weber State Universtiy
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CS 2810 Exam 2 Weber State Universtiy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
When using floating point numbers, underflow occurs when:
a negative exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
a positive exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
a number becomes too small to fit in the mantissa field.
a negative exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
When printing a floating point number in MIPS, in which register do you put the number that is to be output?
$a0
$v0
$f12
$f0
$f12
What code is used to call a macro with a parameter?
the name of the macro is macro_name
the value to be sent is at the label value_label
.macro_name(#value_label)
.macro_name(%value_label)
macro_name(value_label)
macro_name(%value_label)
macro_name(#value_label)
.macro_name(value_label)
macro_name(value_label)
When getting input that is a floating point number in MIPS, in which register will the number be stored?
$a0
$v0
$f12
$f0
$f0
What mask is needed to isolate the mantissa?
mantissa_mask: .word 24
mantissa_mask: .word 0x007FFFFF
mantissa_mask: .word 23
mantissa_mask: .word 0x008FFFFF
mantissa_mask: .word 0x007FFFFF
What code is used to begin a macro with a parameter?
the name of the macro is macro_name
the name of the parameter is parameter
.macro macro_name(%parameter)
.macro macro_name(parameter)
.macro macro_name(#parameter)
.macro macro_name(%parameter)
When using floating point numbers, overflow occurs when
a negative exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
the number of digits becomes too large to fit in the mantissa field.
a positive exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
a positive exponent becomes too large to fit in the exponent field.
Given the following mask, what series of instructions are needed to extract the exponent?
exp_mask: .word 0x7F800000
The binary representation of the number is in $t0.
lw $t1, exp_mask
or $t2, $t0, $t1
srl $t2, $t2, 23
lw $t1, exp_mask
and $t2, $t0, $t1
srl $t2, $t2, 23
and $t2, $t0, exp_mask
srl $t2, $t2, 23
or $t2, $t0, exp_mask
srl $t2, $t2, 23
lw $t1, exp_mask
and $t2, $t0, $t1
srl $t2, $t2, 23
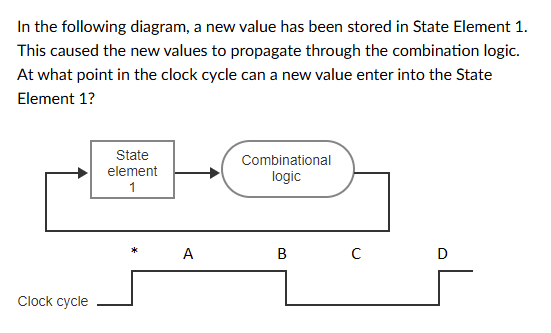
D: The rise of the Asserted signal
B: the start of the Deasserted signal
C: The middle of the Deasserted signal
A: Immediately, it doesn't need to wait for a clock cycle
D: The rise of the Asserted signal
Consider the first five steps for a typical MIPS instruction in a pipeline. What is the correct order that it goes through the pipeline?
Read Registers, Use ALU, Fetch instruction from Memory, Memory Access, Write Back
Fetch instruction from memory, Read Registers, Use ALU, Memory Access, Write Back
Fetch instruction from memory, Write Back, Read Registers, Use ALU, Memory Access
Read Registers, Fetch instruction from memory, Write Back, Memory Access, Use ALU
Fetch instruction from memory, Read Registers, Use ALU, Memory Access, Write Back
What is the purpose of the sign-extend unit?
To improve memory efficiency
To ensure positive offsets in memory access
To decrease the size of the offset for speed
Increases the size of the original data and preserves the sign
Increases the size of the original data and preserves the sign
What is pipelining?
The process of breaking down complex instructions into simpler microinstructions
The synchronization of clock cycles in a computer system
The execution of multiple instructions in a sequential manner to ensure accuracy
A technique in computer architecture that allows multiple instructions to be overlapped in execution
A technique in computer architecture that allows multiple instructions to be overlapped in execution
What is a structural hazard in a processor?
Prediction error in branch instructions
Conflict for the use of a resource
Delay due to pipeline stalls
Dependency between instructions
Conflict for the use of a resource
What type of hazard is caused by a conflict in accessing a particular hardware resource, such as a memory unit or an ALU, in a pipelined processor?
Control hazard
Branch prediction hazard
Data hazard
Structural hazard
Structural hazard
What is the primary motivation for using branch prediction in a pipelined processor?
To improve efficiency and avoid pipeline stalls
To optimize arithmetic operations
To accelerate memory access
To eliminate data hazards
To improve efficiency and avoid pipeline stalls
What is Edge Triggered Clocking?
A clocking scheme in which all state changes occur on a clock edge
A clocking scheme with slow transitions from low to high or vice versa
A clocking scheme with a continuous clock signal
A clocking scheme where state changes occur continuously
A clocking scheme in which all state changes occur on a clock edge
What is a clocking methodology?
The approach used to determine when data is valid and stable relative to the clock
The logic complexity of digital circuits
The speed at which a processor operates
The technique for reducing power consumption
The approach used to determine when data is valid and stable relative to the clock
Which of the following is an example of a combinational element?
ALU
Control Signal
Register
Memory
ALU
What is the program counter?
A memory unit for storing program instructions
A control signal for datapath elements
A register containing the address of the next instruction in the program to be executed
A combinational adder in the ALU
A register containing the address of the next instruction in the program to be executed
What does a control hazard refer to?
Incorrect branch prediction
Conflict for resources
Dependency between instructions
Introduction of pipeline stalls
Incorrect branch prediction
What type of hazard is caused by a conflict in accessing a particular hardware resource, such as a memory unit or an ALU, in a pipelined processor?
Structural hazard
Control hazard
Branch prediction hazard
Data hazard
Structural hazard
Why might a programmer or compiler choose to insert a NOP (No Operation) instruction in a code sequence in the context of processor hazards?
To introduce a structural hazard
To create a pipeline stall (bubble)
To align memory addresses for better performance.
To fill instructions slots for increased efficiency
To create a pipeline stall (bubble)
What is the primary motivation for using branch prediction in a pipelined processor?
To accelerate memory access
To improve efficiency and avoid pipeline stalls
To optimize arithmetic operations
To eliminate data hazards
To improve efficiency and avoid pipeline stalls
What is the primary difference between State Elements and Combinational Elements?
Internal Storage
Logical complexity
Clock Speed
Operating Voltage
Internal Storage
What is a datapath element whose output values depend only on the present input value.
State Element
Combinational element
Clocking element
Edge-Triggered element
Combinational element
What is a register file?
A state element that consists of a set of registers that can be read and written by supplying a register number to be accessed.
A combinational element that consists of a set of registers that calculate the outcome of multiple inputs.
A combinational element containing the calculating the next instruction in the program to be executed.
A state element containing the address of the next instruction in the program to be executed.
A state element that consists of a set of registers that can be read and written by supplying a register number to be accessed.
What does it mean to "flush" instructions in the context of a pipeline?
Group of answer choices
To optimize instruction execution
To minimize data hazards
To discard instructions due to an unexpected event
To introduce a delay in the pipeline
To discard instructions due to an unexpected event
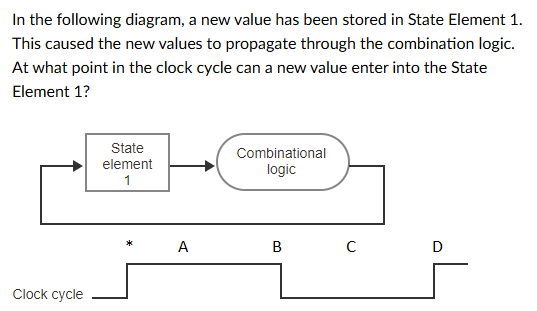
D: The rise of the Asserted signal
A: Immediately, it doesn't need to wait for a clock cycle
B: the start of the Deasserted signal
C: The middle of the Deasserted signal
D: The rise of the Asserted signal
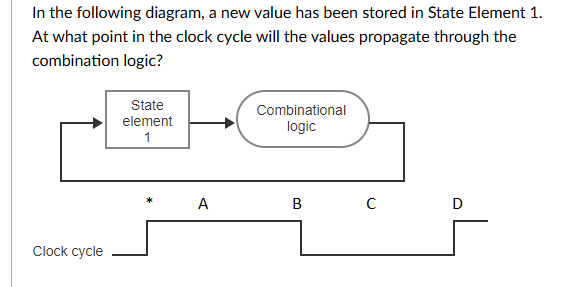
A: Immediately, it doesn't need to wait for a clock cycle
D: The rise of the Asserted signal
C: The middle of the Deasserted signal
B: the start of the Deasserted signal
A: Immediately, it doesn't need to wait for a clock cycle
Temporal locality is related to how close in _____ a memory access is.
location
content
time
time
Data is requested by the processor. 85 out of 100 requests find the data in the upper level and returns the data in 0.3 ns. The remaining requests require 0.9 ns to return the data.
Determine the corresponding values for the upper level memory.
Hit rate
?
Miss rate
?
Hit time
?
Miss penalty
?
Hit rate
.85
Miss rate
.15
Hit time
.3
Miss penalty
.9
The minimum unit of information that can be either present or not present in the memory hierarchy is a
word
block
bit
byte
block
Consider a memory hierarchy. The memory that is closest to the processor is the ____________.
slowest and smallest
fastest and smallest
slowest and biggest
fastest and biggest
fastest and smallest
Match the principle to its corresponding description.
Temporal Locality:
Spatial Locality:
A memory location recently accessed is likely to be accessed again.
A memory location never previously accessed is likely to accessed soon.
A memory location in close proximity to a recently accessed location is likely to be accessed as well.
Temporal Locality | A memory location recently accessed is likely to be accessed again. |
Spatial Locality | A memory location in close proximity to a recently accessed location is likely to be accessed as well. |
Which TWO of the following is true about SRAM?
SRAM requires a periodic refresh rate
SRAM uses fewer transistors per bit of memory than DRAM
SRAM used as the memory closest to the processor
SRAM is faster than DRAM
SRAM used as the memory closest to the processor
SRAM is faster than DRAM
What are the primary differences between magnetic disks and semiconductor memory technologies?
Semiconductor memory has slower access times but higher storage capacity
Magnetic disks are mechanical devices, while semiconductor memory is electronic
Magnetic disks have faster access times but higher costs per bit
Semiconductor memory is more volatile, while magnetic disks are nonvolatile
Magnetic disks are mechanical devices, while semiconductor memory is electronic
Which TWO of the following is true about DRAM?
DRAM has fewer transistors than SRAM
DRAM Requires a periodic refresh
DRAM is used as the memory closest to the processor
DRAM is Faster than SRAM
DRAM has fewer transistors than SRAM
DRAM Requires a periodic refresh
What is virtual memory?
An event that occurs when an accessed page is not present in main memory
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address mapping to a physical address when memory is accessed.
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
An address in main memory
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
What is a page fault?
The process by which a virtual address is mapped to an address used to access memory.
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
An event that occurs when an accessed page is not present in main memory
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address mapping to a physical address when memory is accessed.
An event that occurs when an accessed page is not present in main memory
What is a virtual address?
An event that occurs when an accessed page is not present in main memory
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address mapping to a physical address when memory is accessed.
An address in main memory
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address mapping to a physical address when memory is accessed.
Which RAID configuration does not have any redundancy of data?
RAID 1
RAID 5
RAID 6
RAID 0
RAID 0
Which RAID level resolves the parity-write bottleneck by distributing parity information across all disks?
RAID 1
RAID 5
RAID 4
RAID 3
RAID 5
What is the primary advantage of P + Q redundancy in RAID 6 over RAID 5?
RAID 6 distributes parity information more efficiently.
RAID 6 requires fewer disks for redundancy.
RAID 6 allows recovery from two simultaneous failures.
RAID 6 provides faster read speeds.
RAID 6 allows recovery from two simultaneous failures.
What was the original motivation of using disk arrays.
To increase the reliability of storage devices
To reduce the cost of storage systems
To improve computational efficiency
To accelerate I/O performance
To accelerate I/O performance
Which of the following best describes rotational latency?
The time required for _____________________
the read/write head to complete a full rotation
the disk to reach its maximum rotational speed
the desired sector to rotate under the read/write head
the disk to rotate to the next track
the desired sector to rotate under the read/write head
What technology is primarily used for levels closer to the processor, such as caches?
Flash memory
DRAM
SRAM
Magnetic disk
SRAM
What determines the transfer time in a disk access?
The seek time, disk size and rotational latency
The number of sectors, operating system and the track position
The size of the cache, file system type, and the rotation time
The rotational speed, recording density, and sector size
The rotational speed, recording density, and sector size
What is the primary purpose of virtual memory?
To allow efficient and safe sharing of memory among multiple programs and remove the programming burdens of limited main memory
To provide faster access to recently-used portions of a program's code and data
To act as a cache for the processor
To allocate additional storage space for secondary storage devices
To allow efficient and safe sharing of memory among multiple programs and remove the programming burdens of limited main memory
What is address translation?
An event that occurs when an accessed page is not present in main memory
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
The process by which a virtual address is mapped to an address used to access memory.
An address in main memory
The process by which a virtual address is mapped to an address used to access memory.
What is virtual memory?
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address mapping to a physical address when memory is accessed.
An address in main memory
An event that occurs when an accessed page is not present in main memory
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
What is the primary function of RAID 0?
To distribute parity information across multiple disks
To improve performance by spreading data across disks
To encrypt data for secure storage
To provide redundancy for data storage
To improve performance by spreading data across disks
What was the original motivation of using disk arrays.
To improve computational efficiency
To increase the reliability of storage devices
To reduce the cost of storage systems
To accelerate I/O performance
To accelerate I/O performance
What is the term used to describe the process of spreading data over multiple disks in RAID?
Mirroring
Interleaving
Striping
Parity calculation
Striping
Why is DRAM less costly per bit compared to SRAM?
DRAMs use fewer transistors per bit
DRAMs require periodic refreshing
DRAMs use more transistors per bit
DRAMs have slower access times
DRAMs use fewer transistors per bit
How are modern DRAMs organized to improve performance?
By increasing the number of transistors per bit
By using a single transistor per bit
By incorporating rotating access through address interleaving
By adding clocks and employing synchronous operation
By incorporating rotating access through address interleaving
What is the role of sectors on a magnetic disk?
To store the rotational latency of the disk
To divide the disk surface into concentric circles
To position the disk heads over the proper track
To contain the smallest amount of information read or written on a disk
To contain the smallest amount of information read or written on a disk
What is the key characteristic of mirroring (RAID 1)?
It uses error detecting and correcting code
It spreads data across multiple disks
It increases data availability through bit-interleaved parity
It duplicates data on redundant disks
It duplicates data on redundant disks
What is the purpose of standby spares in RAID systems?
To reduce repair time for disk failures
To increase system performance
To immediately replace failed components
To provide additional redundancy
To immediately replace failed components
What is a track in the context of magnetic disks?
One of thousands of concentric circles on the disk surface
A division of information containing error correction code
A segment that makes up a sector on a disk
A component used in the seek process of accessing data
One of thousands of concentric circles on the disk surface
What technology is primarily used for levels closer to the processor, such as caches?
Magnetic disk
SRAM
DRAM
Flash memory
SRAM
What is the process of positioning a read/write head over the proper track on a disk called?
Cache
Seek
Rotation
Transfer
Seek
In RAID 3, what is the purpose of the protection group?
To store redundant copies of data
To distribute parity information across disks
To restore lost information in case of disk failure
To provide error detection and correction for memory hierarchies
To restore lost information in case of disk failure
What technique is commonly used in flash memory to prolong its lifespan by spreading writes evenly across memory blocks?
Address interleaving
Synchronization
Wear leveling
Refreshing
Wear leveling
What is a physical address?
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address
A technique that uses main memory as a "cache" for secondary storage
An address that corresponds to a location in virtual space and is translated by address mapping to a physical address when memory is accessed.
An address in main memory
An address in main memory
What does "hot-swapping" refer to in the context of RAID systems?
Replacing disks while the system is running
Allocating spare disks for immediate use
Shutting down the system to replace disks
Replicating data across multiple disks
Replacing disks while the system is running