Human Sexuality Ch. 5 - Sex Hormones, Sexual Differentiation, and the Menstrual Cycle
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Note about how I make these: words in BOLD in the definitions are the type of word it's defining (i.e. "hormone" for the term "testosterone"). Words that are UNDERLINED are details that are the most important to remember, or that will simply help you figure out the answer. IMPORTANT: For those that don't know, you do NOT have to remember the exact spelling or the full name of an abbreviated term, even if Knowt counts it as wrong. This only works during the typing portion, but if you get an answer "wrong" that you generally got correct (like putting the abbreviation instead of the full name), you can click "Override: I got it right." This should work on both mobile and desktop. **Also note that a lot of these questions are about specific numbers/times - I will remove these if Dr. Mollie says they won't be on the exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
hormones
powerful chemical substances manufactured by the endocrine glands and secreted directly into the bloodstream
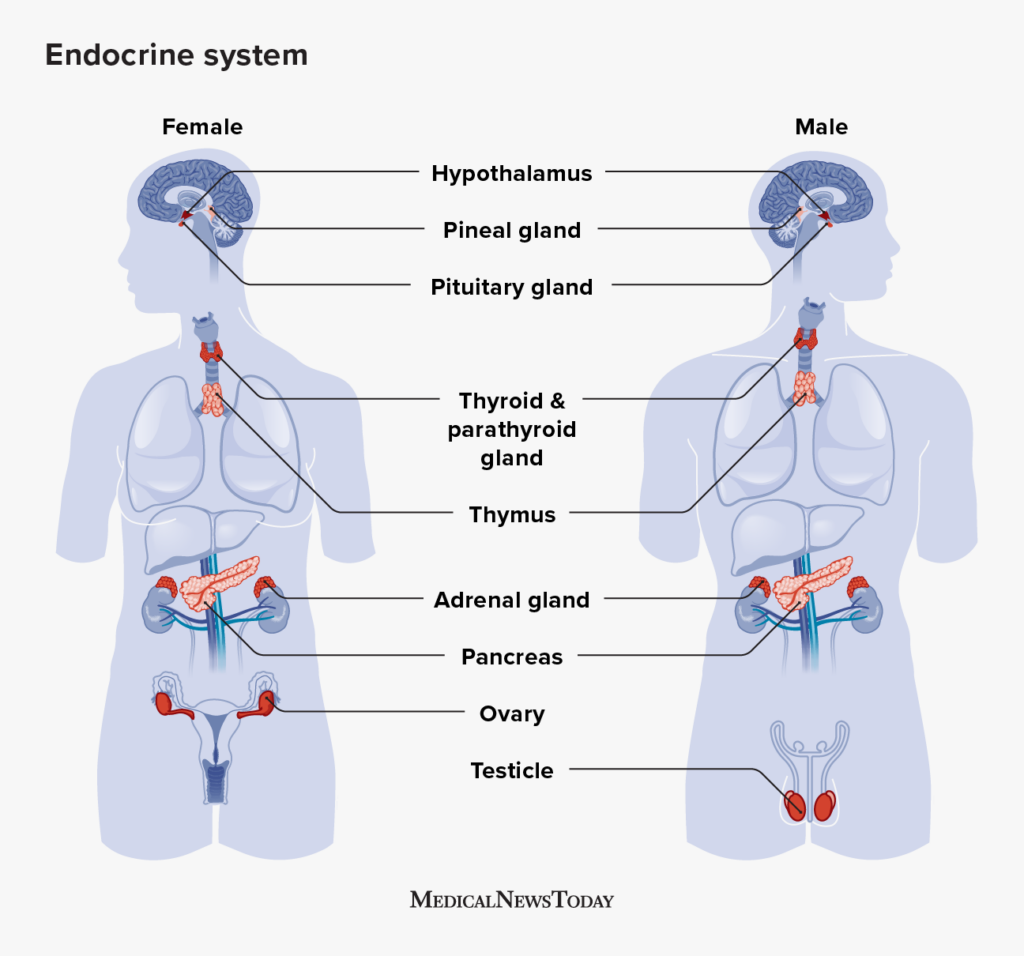
endocrine glands
tissues, glands, or organs that produce and regulate hormones in the body by secreting hormones directly into the bloodstream; includes the thyroid, the adrenals, the pituitary, the gonads, and others
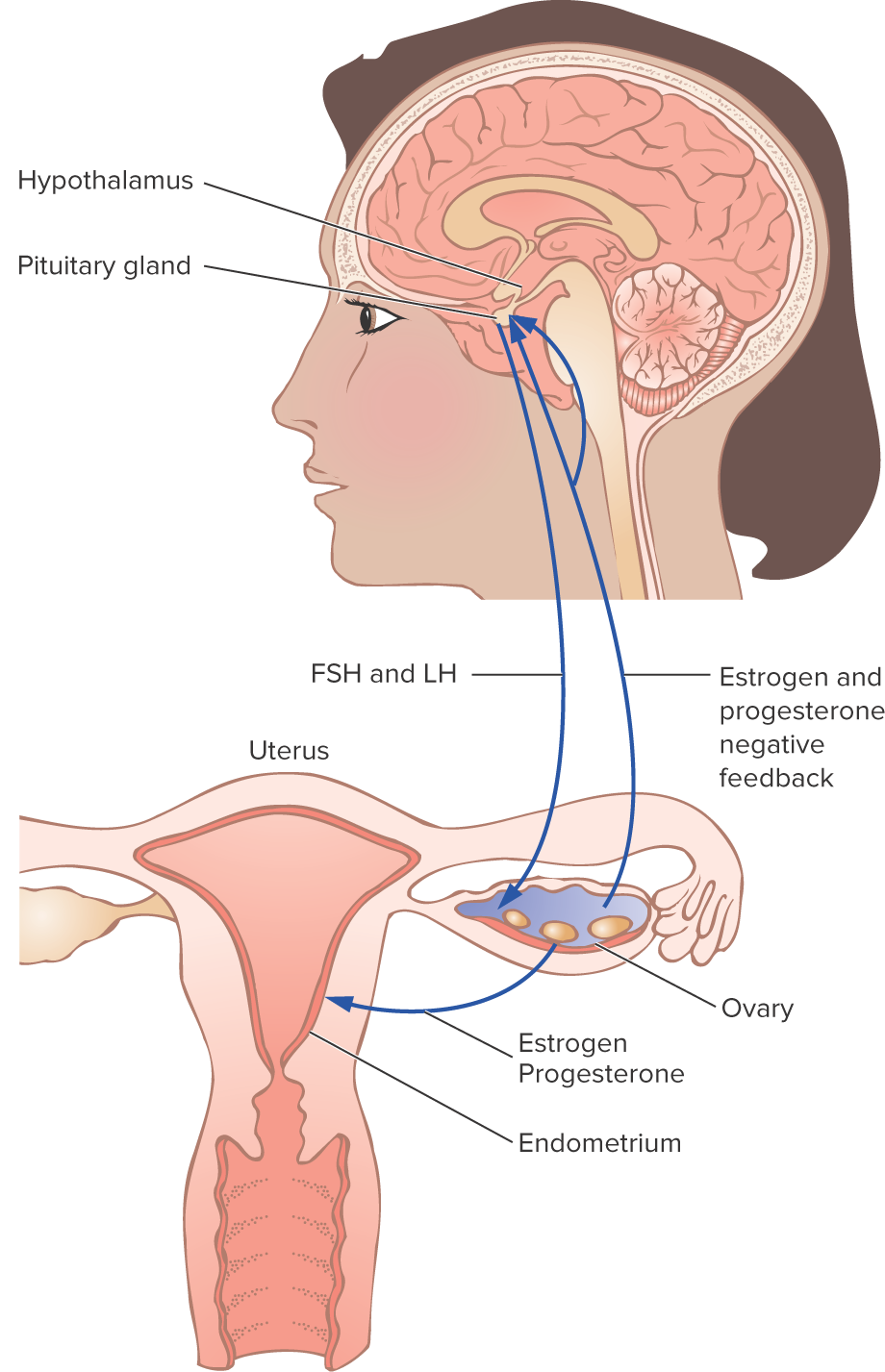
HPG (hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad) axis
a negative feedback loop that regulates sex-hormone production, as well as the development of the reproductive system; controls the uterine and ovarian cycles
negative
The hypothalamus, pituitary, and testes operate in a _________ feedback loop.
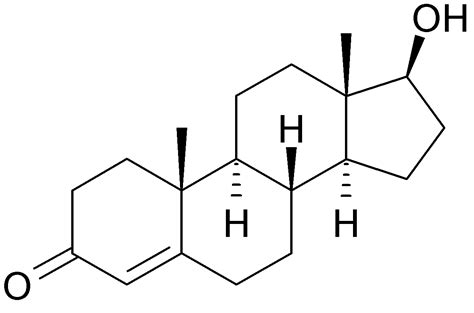
testosterone
a masculinizing hormone secreted by the testes in males (also present at lower levels in females) that:
stimulates and maintains male secondary sex characteristics
maintains the genitals and their sperm-producing capability
stimulates the growth of bone and muscle
androgens
a group of sex hormones produced in the testes, one of which is testosterone, that control the development and maintenance of male sex characteristics; stimulate growth of pubic and axillary hair in females, and related to the female sex drive
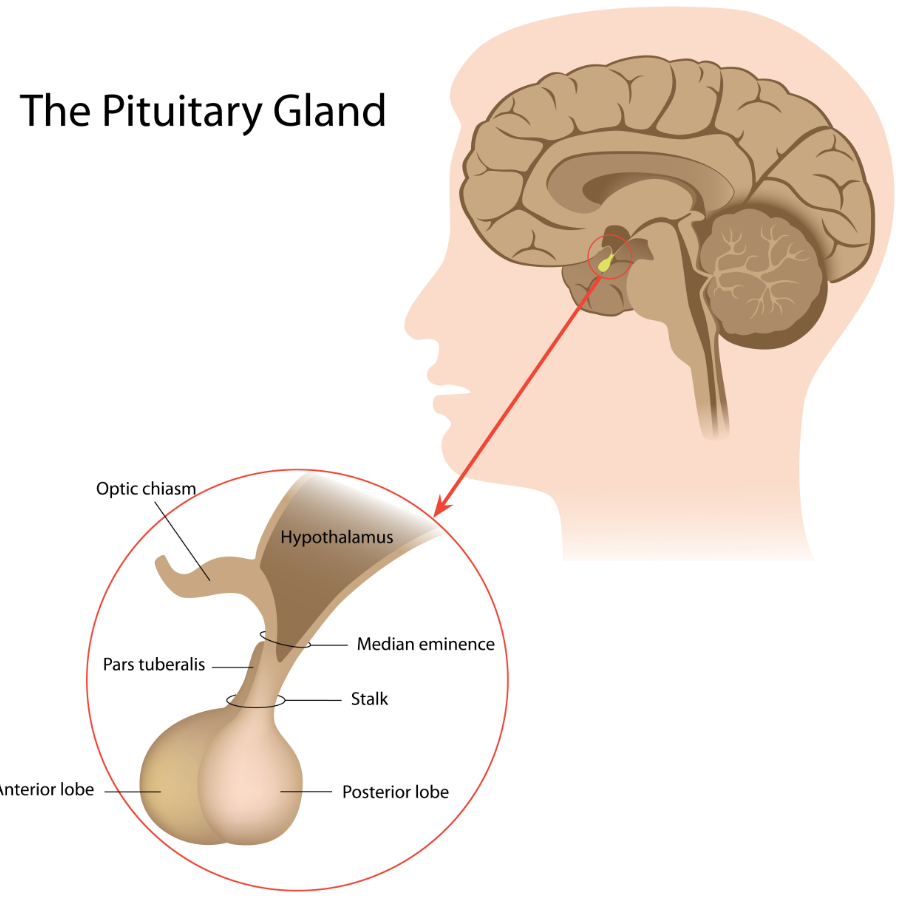
pituitary gland
a small endocrine gland located on the lower side of the brain below the hypothalamus; also called the “master gland” of the endocrine system; responds to GnRH by secreting LH and FSH
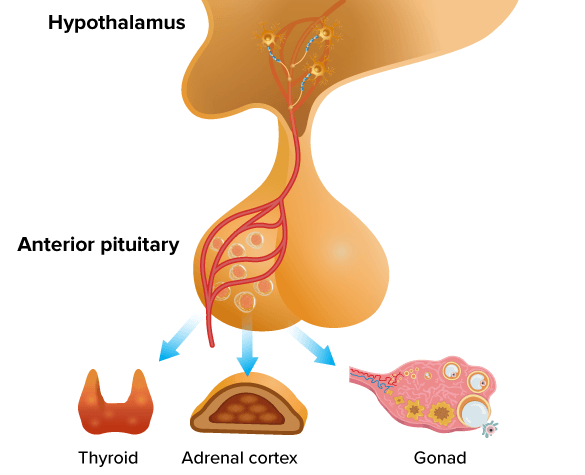
anterior lobe
the part of the pituitary gland that interacts with the gonads
hypothalamus
a small region of the brain that is important for many reasons, but for this class, the most important part is the regulation of the sex hormones/the pituitary gland; monitors the levels of testosterone present
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland in response to GnRH that:
regulates the levels of estrogen and progesterone in females
stimulates LH production
acts on the ovaries to promote the formation of follicles and eggs
acts on the testes to promote the production of sperm
luteinizing hormone (LH)
a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland in response to GnRH that:
stimulates estrogen/progesterone secretion and ovum development in females
is responsible for ovulation (makes the follicles release their eggs)
plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle
stimulates testosterone production in the testes
production is decreased when testosterone levels get high and the hypothalamus reduces production of GnRH, causing the pituitary to reduce production of this hormone
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
a hormone secreted by the hypothalamus that stimulates the pituitary’s secretion of gonad-stimulating hormones (LH and FSH); output is influenced by testosterone in males
inhibin
a hormone secreted by the testes and ovaries that regulates FSH levels in a negative feedback loop (suppresses FSH production)
GnIH (gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone)
a hormone produced by the hypothalamus that inhibits FSH and LH secretion from the anterior pituitary gland, therefore inhibiting reproduction/reproductive behavior and gonadal development; lowers the levels of LH, FSH, and testosterone
estrogens
a group of sex hormones produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands that promote the development and maintenance of female sex characteristics (though males produce it too, just in lower levels) have the following functions:
inhibits FSH and stimulates GnRH production
stimulate the growth of the uterus, vagina, and breasts
help stimulate growth of the egg follicle
maintain the thickness of the vaginal wall
regulates the flow and thickness of uterine mucus secretions
stops the growth of bone and muscle (hence females typically being shorter than males on average)
progesterone
a pituitary hormone secreted by the ovaries as well as the testes; prepares the uterus for pregnancy by preparing the endometrium for a fertilized egg to implant and grow; also does the following:
raises body temperature
inhibits LH secretion
high levels correlate to less sexual desire
decrease causes endometrium to shed
prolactin
a pituitary hormone that promotes the development of mammary glands within breast tissues and stimulates secretion of milk by the mammary glands after childbirth
oxytocin
a pituitary hormone produced in both males and females that:
stimulates contractions of the uterus during childbirth
stimulates ejection of milk from the nipples
promotes affection bonding (“snuggle chemical”)
sex chromosomes
chromosomes that transmit information to various organs on how to differentiate in the course of development
epigenetics
the study of heritable traits caused by the activation and deactivation of genes that do not alter the genetic code itself; these changes often involve methylation
Y chromosome
This is the smaller of the two sex chromosomes, therefore having fewer genes and carrying less information than the other. Only has about 80 genes compared to 1,090 genes on the other chromosome.
Klinefelter’s syndrome
a genetic condition caused by a chromosome anomaly where a male has an extra X chromosome (XXY), resulting in small testes, no sperm production, and low testosterone levels
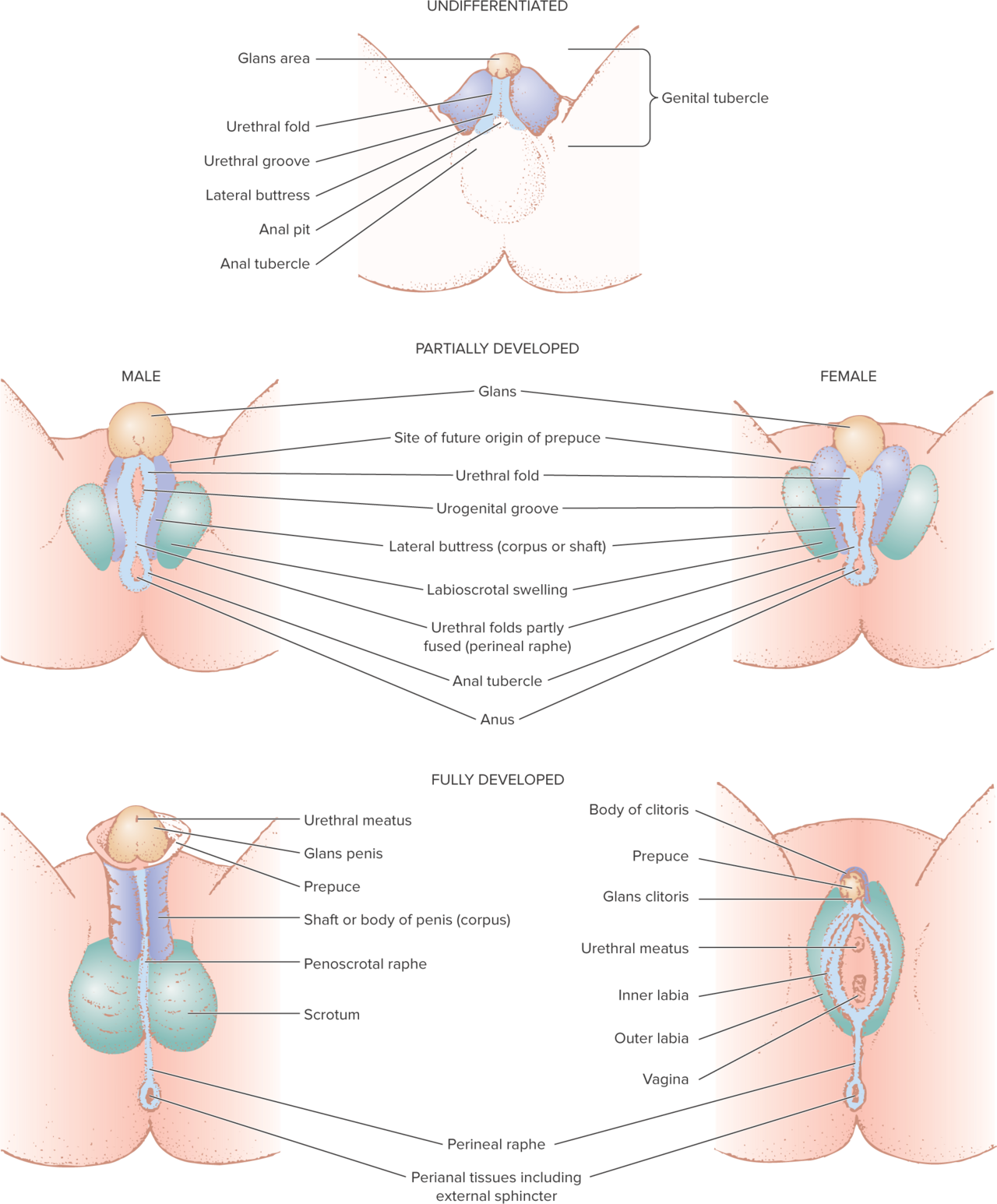
tubercle
a body of tissue present in the development of the reproductive system that’s separated into several parts parts (including the glans area, urethral fold, urethral groove); during sexual differentiation, they develop into the external genitalia
in females: the glans area becomes the clitoris, the folds become the inner lips, and the swelling becomes the outer lips
in males: the glans area becomes the glans penis, the folds form the shaft of the penis, and the swelling develops into the scrotum
Müllerian ducts
ducts found in both male and female fetuses
in males, they degenerate
in females, they develop into the fallopian tubes, the uterus, and the upper part of the vagina
AMH (anti-Müllerian hormone)
a hormone secreted by the testes that causes one of the 2 ducts to degenerate
Wolffian ducts
ducts found in both male and female fetuses
in females, they degenerate
in males (supported by testosterone), they develop into the epididymus, the vas deferens, and the ejaculatory duct
SRY (sex-determining region, Y-chromosome)
an important gene located on the Y chromosome that directs the differentiation of the gonads; causes the manufacture of testis-determining factor
TDF (testis-determining factor)
a substance that makes the gonads differentiate into testes; manufacture is caused by the SRY gene
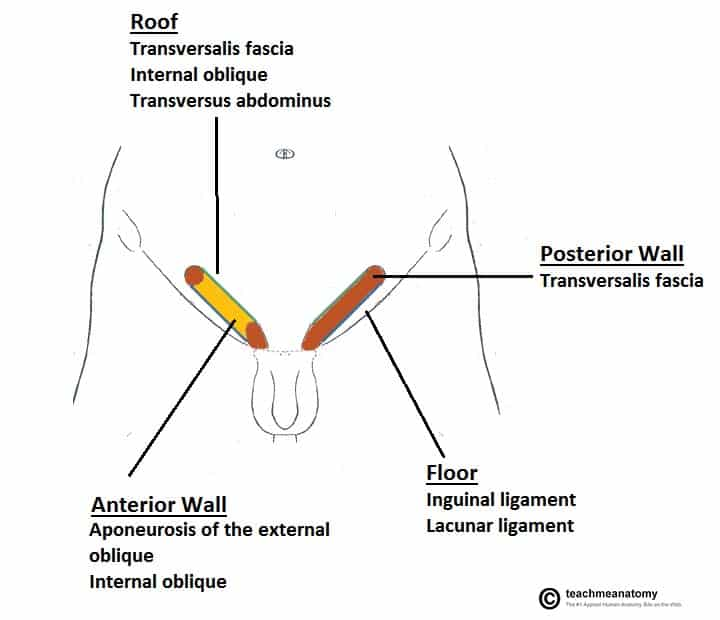
inguinal canal
a tubular structure in the lower anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body in which the testes travel from near the top of the abdominal cavity and down into the scrotum through this passageway around the 7th month after conception; closes off after the testes descend
cryptorchidism
a condition that occurs in 2-3% of males in which one or both (typically just one) of the testes fail to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum; is usually corrected by surgery if the testes don’t descend spontaneously, but if not done soon after the first birthday, can later cause problems with fertility if both testes fail to descend; cancer is also more likely to develop in undescended testes
inguinal hernia
a condition that occurs when the inguinal canal does not close off completely and reopens later in life, creating a passageway through which loops of the intestine can enter the scrotum; can be remedied by simple surgery
preoptic area
a region of the hypothalamus with a sexually dimorphic nucleus (at least in animals, not so much in humans); mostly known for it’s pivotal role in the central regulation of body temperature, but important here because it regulates sexual behavior in animals
estrogen receptors
a group of proteins found inside cells in the hypothalamus that:
become insensitive to estrogen if testosterone is present during fetal development
become highly sensitive to levels of estrogen in the blood stream if estrogen is present during fetal development
plasticity of the brain
the brain’s constant change in response to experiences a person has (as opposed to something behind inherent from birth)
homologous
a word describing when an organ in males and an organ in females develop from the same embryonic tissue (having similar origins)
analogous
a word describing when an organ in males and an organ in females have similar functions
chromosomal gender
one of the eight variables of gender (#1) that refers to females having XX chromosomes and males having XY chromosomes; this is a biological variable
gonadal gender
one of the eight variables of gender (#2) that refers to females having ovaries and males having testes; this is a biological variable
prenatal hormonal gender
a subcategory of one of the eight variables of gender (#3a) that refers to males having testosterone and AMH before birth, but not females; this is a biological variable
prenatal and neonatal brain differentiation
a subcategory of one of the eight variables of gender (#3b) that refers to the presence of testosterone for masculinization and the absence of it for feminization; this is a biological variable
internal organs
one of the eight variables of gender (#4) that refers to the fallopian tubes, uterus, and upper vagina in females and the prostate, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles in males; this is a biological variable
external genital appearance
one of the eight variables of gender (#5) that refers to the clitoris, labia (both minora and majora), and vaginal opening in females, and the penis and scrotum in males; this is a biological variable
pubertal hormonal gender
one of the eight variables of gender (#6) that refers to estrogen and progesterone in females during puberty and testosterone in males during puberty; this is a biological variable
gender assigned at birth
one of the eight variables of gender (#7) referring to the announcement at birth based on the appearance of the external genitals and/or the gender the parents and the rest of society believe the child to be; this is a psychological variable
gender identity
one of the eight variables of gender (#8) referring to a person’s private, internal sense of maleness, femaleness, or something else, such as nonbinary; this is a psychological variable
intersex
a condition in which the individual has a mixture of male and female reproductive structures, so that it is not clear at birth whether the individual is a male or female; gender is biologically ambiguous; approx. 2% of births have this condition
congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
a condition in which the normally-developed ovaries of a fetus begin to function abnormally as a result of a recessive genetic condition (unconnected with the sex chromosomes), causing them to produce an excess amount of androgens and therefore resulting in the person having male-appearing genitals (whether partly or completely) at birth
androgen-insensitivity syndrome (AIS)
a genetic condition in which the body tissues are unresponsive to androgens, causing prenatal development to be feminized so that a genetic male, who produces typical levels of testosterone, may be born with a female-appearing body (small vagina but no uterus, undescended testes)
5-alpha reductase deficiency syndrome
a genetic-endocrine condition causing genetic males to have a vaginal pouch instead of a scrotum and a clitoris-sized penis at birth, but develop a penis at puberty due to a spontaneous biological change; studied in a small community in the Dominican Republic - children were raised as females until penis developed at puberty, and are called “Geuvodoces” within their culture (a third gender)
puberty
the time during which there is sudden enlargement and maturation of the gonads, other genitalia, and secondary sex characteristics, so that the individual becomes capable of reproduction
adolescence
a socially defined period of development that represents a psychological transition from the behavior and attitudes of a child to the behavior, attitudes, and responsibilities of an adult (around ages 10-20 in the U.S., which is unusually long compared to in the past); some cultures don’t have this at all
breast development
The first sign of puberty in females is the beginning of ______ ___________.
menarche
first menstruation
2
Females are not capable of becoming pregnant until ovulation begins, typically about ____ years after menarche.
percent body fat hypothesis
a possible explanation for determining the age at which a female first menstruates stating that the percentage of body weight that is fat must rise to a certain level for menstruation to occur for the first time and for it to be maintained
leptin
a hormone related to the onset of puberty in both males and females that:
stimulates the growth of skeletal bone
stimulates the release of LH
stimulates the secretion of kisspeptin
kisspeptin
a hormone involved in the initiation of pubertal development; produced by the KISS1 gene and stimulates the hypothalamus to produce more GnRH in a pulsatile fashion, which initiates a cascade of secretion of hormones (including LH and FSH), which stimulates the ovaries to produce estrogen
adrenal glands
endocrine glands located just above the kidneys; major producer of androgens in females
adrenarche
the maturation of the adrenal glands resulting in the increased secretion of androgens, which stimulate the growth of pubic and axillary hair and are related to the female sex drive; generally begins slightly before age 8
acne
a skin condition that is stimulated by androgens (therefore affecting males more commonly than females) and caused by a clogging of the sebaceous (oil-producing) glands, resulting in pustules, blackheads, and redness on the face or other parts of the body
estrous cycle
the recurring reproductive cyclical pattern of ovarian activity that facilitates female mammals to go from a period of reproductive receptivity to non-receptivity; factors that differentiate this from the menstrual cycle include:
no menstruation
ovulation occurs when the animal is in “heat”
these animals only engage in sexual behavior when they’re in heat
follicular (or proliferative) phase
the first phase of the menstrual cycle, which begins with the pituitary secreting relatively high levels of FSH due to falling levels of estrogen (caused by the third phase), signalling a follicle to start bringing an egg to the final stage of maturity while the follicle simultaneously secretes estrogen; the high levels of estrogen stimulate the endometrium to grow, thicken, and form glands that will eventually secrete substances to nourish the embryo
ovulation
the second phase of the menstrual cycle, when the follicle ruptures open and releases a mature egg; put into motion by estrogen reaching a high level and causing a sudden surge in LH, which stimulates the follicle (high estrogen inhibits FSH and stimulates GnRH, which produces LH)
luteal (or secretory) phase
the third phase of the menstrual cycle in which the follicle, after releasing an egg and being stimulated by LH, turns into the corpus luteum and begins manufacturing progesterone; the higher levels of progesterone:
inhibit the pituitary’s secretion of LH, causing the corpus luteum to degenerate, which in turn causes a sharp decline in estrogen and progesterone levels at the end of this phase
stimulates the glands of the endometrium to start secreting the nourishing substances
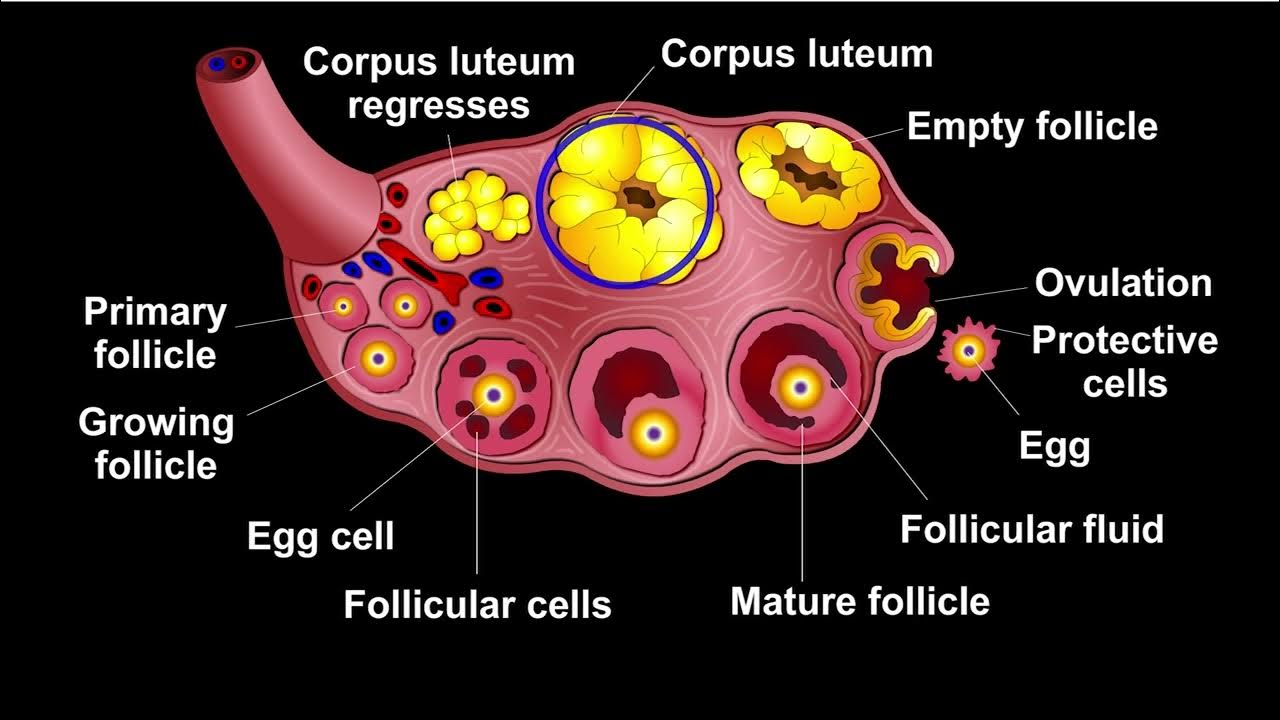
corpus luteum
the mass of cells of the follicle remaining after ovulation that secretes progesterone; high levels of progesterone inhibit LH production, causing this mass to degenerate as LH levels decline, causing a sharp decline in estrogen and progesterone levels; continues to produce estrogen and progesterone for about 10-12 days
menstruation
the fourth and final phase of the menstrual cycle in which the endometrium is shed and passed out through the cervix and the vagina; triggered by sharp decline in estrogen and progesterone levels at the end of the third phase; during this phase, estrogen and progesterone levels are still low, but FSH levels are rising
menstrual fluid
a substance that is a combination of:
blood from the endometrium
degenerated cells
mucus from the cervix and vagina
28
The average menstrual cycle lasts about ____ days.
4 to 5
In the average menstrual cycle, menstruation begins on day 1 and continues until about day ____ __ ____.
5 to 13
In the average menstrual cycle, the follicular phase (approximately) lasts from days ___ __ ___.
14
In the average menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs on day ___.
15
In the average menstrual cycle, the luteal phase lasts from day ____ until the end of the cycle (day 28).
Mittelschmerz
literally “middle pain”; the feeling some women report as ovulation; the sensation of cramping on one or both sides of the lower abdomen, lasting for about a day
anovulatory cycle
a menstrual cycle in which ovulation does not occur (egg doesn’t release from ovary); occurs once or twice a year in females in their 20s-30s and fairly common among females going through puberty and females in their 40s
cervical mucus cycle
a cycle involving glands in the cervix that secrete mucus throughout the menstrual cycle, which respond to changing levels of estrogen during the cycle; this mucus protects the entrance to the cervix from bacteria and becomes more alkaline, thin, and watery just before ovulation to make the environment for sperm passage most hospitable just at ovulation occurs
basal body temperature cycle
the cycle involving how a female’s internal body temperature at rest fluctuates with the phases of the menstrual cycle; temperature is low during the follicular phase and takes a dip on the day of ovulation, then rises noticeably the day after and continues at the higher level for the rest of the cycle
dysmenorrhea
painful menstrual cramps (possibly) caused by unusually high levels of prostaglandins, which cause intense uterine contractions and therefore choke off some of the supply of oxygen-carrying blood to the uterus — these things, plus heightened sensitivity of nerve endings caused by these prostaglandins, cause mentrual cramps
prostaglandins
hormone-like substances produced by many tissues of the body, including the lining of the uterus, which can:
cause smooth muscle to contract
affect the size of blood vessels
cause greater sensitivity in nerve endings
antiprostaglandins
drugs that interrupt the hormone-like substances that cause cramps; these are nonsteroidal anti-flammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen
pelvic edema
a buildup of fluid causing swelling in the soft tissues of the genital area that is one of the reasons for the discomfort of menstruation (specifically the pressure and bloating); increases during sexual arousal and orgasm, but dissipates after orgasm
endometriosis
a condition in which the endometrium grows abnormally outside the uterus (i.e. the ovaries, fallopian tubes, rectum, bladder, vagina, vulva, cervix, lymph glands); symptoms vary depending on where it’s growing, but typical symptoms are very painful periods that last an unusually long time
primary amenorrhea
the absence of menstruation in females who have not yet menstruated by age 18; caused by pregnancy, hormonal imbalance, cysts/tumors, disease, stress, strenuous exercise, anorexia, etc.
secondary amenorrhea
the absence of menstruation in females who have had at least one period; caused by pregnancy, hormonal imbalance, cysts/tumors, disease, stress, strenuous exercise, anorexia, etc.
premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
a combination of severe physical and psychological symptoms, such as depression, irritability, breast pain, and water retention, occurring just before menstruation; NOT a medical term, and there’s no scientific evidence of it (at least not for the majority of women)
premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
a diagnostic category in the DSM-5, characterized by symptoms such as sadness/hopelessness, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, tearfulness, changes in appetite, and irritability in the week before menstruation (last week of luteal phase)