TEST 2 CLASS REVIEW FLUORO
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
what is the formula for magnification?
input screen diameter / diameter of input screen used
what is total brightness gain?
measure of the increased image intensity/brightness done by image intensifier tube (II Tube)
minification gain - total brightness gain
compacting the same number of electrons from a large input screen on a small output screen
flux gain - total brightness gain
measurement of the increase in light photons due to the conversion efficiency of the output phosphor
never use fluoro to ….
positioning guide/preview
position anatomy
the cones of eyes control what type of visual activity?
PHOTOPIC acuity (daylight)
image intensifiers amplify the brighter of fluoro images to activate photopic acuity
increases image brightness 500-8000 times
what lies between the input screen and photocathode? What it’s purpose?
thin protective coating
prevents any chemical interactions between the two
What is the function of the photocathode?
it absorbs LIGHT PHOTONS and emits ELECTRONS
what does the output screen do? (output phosphor)
converts/absorbs ELECTRONS to LIGHT PHOTONS that exit the tube
- coated with zinc-cadmium sulfide phosphor
a single incident photon can potentially produce how many light photons at the input screen?
over 1,500
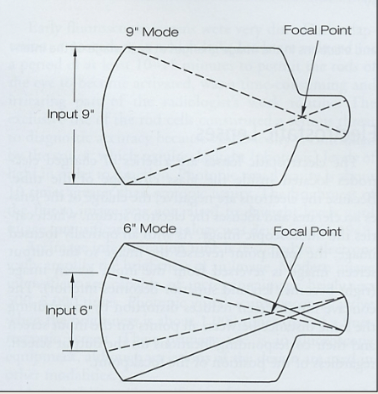
what happens when greater voltage is applied to the electrostatic lenses?
increased voltage accelerates the electrons and moves the focal point closer to the input screen
what degree from the patient/primary beam produces the highest energy scatter?
90 degrees
what does photoemissive materials do?
absorb light photons and emit electrons
photocathode material is photoemissive metals
what is the name of edge distortion in image intensification tubes?
vignetting - dark fuzzy cloudy
TGT technology for fluoro allows for what type of contrast detectability?
low contrast detectability = optimizes fine detail
what is the math formula for minification gain?
input screen diameter2 / output screen diameter2
steps in processing an image in an intensifying tube?
xray to light
light to electrons
electrons to light
what does the final light go through and what it’s changed into?
video camera then converts to electronic signal for viewing on our monitors
define vignetting
edge distortion
diminished resolution and contrast at the image periphery due to decreased exposure rate and periphery. affects 8-10% of image edge distortion
why is fluoro the domain of the rads?
they’re actively diagnosing - called dynamic imaging
what invention enabled the brightness to be enhanced
the image intensifier
includes II tube, video camera and monitor system
the rad tech responsibilities during fluoro
post fluoro xrays
assist radiologist/PA
static exams
what does flux gain do to image quality
decreases image quality
what does flux gain deal with
gain accomplished by electron to light conversion at the output screen.
what are the mA ranges for fluoro
0.5 - 5 mA
what are the mA ranges for diagnostic?
50-1200 mA
cumulative timers sound after how long in fluoro?
5 min
what is the minimum skin distances for mobile fluoro?
12 inches
what is the minimum skin distances for stationary fluoro equipment?
15 inches
what does CSI (phosphors) stand for?
what % of the incident beam do they absorb?
Cesium Iodide Phosphors
66%
what are the components of the image intensification tube (tube II)?
input screen
photocathode
electrostatic lenses
anode
output screen
the fluoro skirt has ___ mm pb/eq
0.25
how do you reduce patient dose when utilizing the mag factor?
collimation
digital fluoro resolution cannot be as high as radiography because the fluoro pixels are ___ lp/mm
2-3 lp/mm
digital fluoro resolution cannot be as high as radiography because the radiography is ___ lp/mm.
10-12
digital fluoro reduces patient exposures up to __%
90
after the x-ray photon leaves the patient, what does it strike next?
input screen
what is the purpose of electrostatic lens?
accelerates and focus electrons
intensifies the image
what is ABC? How does it function?
Automatic Brightness Control
Automatically adjusts the exposure
what is the output screen made of?
zinc cadmium sulfide phosphor (silver activated zinc cadium)
the photocathode is comprised of what material?
photoemissive iodine / CSI
what reduces quantum mottle?
increase mA
list some dynamic studies
BE
UGI
VCUG
Esophogram
Arthrogram
What are the types of c-arm arrangements / fluoro machines
under-table unit
over-table unit
T/F: In fluoro the focal point reverses the image so that output screen is reversed from the input screen?
TRUE, the focal spot DOES reverse image
what is the purpose of the concaved shape of the input screen?
to maintain an equal distance to the output screen
Over-table units operate with a minimum tabletop exposure rate not to exceed ___ R/min.
10 R/min
Most units exposure range operate around __ R/min
1-3
what is the formula of Total Brightness Gain?
minification gain x flux gain
what is the formula of flux gain?
output / input
order of fluoro
tube - patient - light - electron - light
what is image intensifiers
they amplify brightness to activate photopic activity
what are electrostatic lenses order?
reverses
Right to Left - Inferior to Superior on output screen
what do electrostatic lenses do?
accelerate and focus the electron steam
greater voltage causes what in electrostatic lenses?
accelerate more - moves focal point closer to input screen = increase magnification
define ABC
intensity flowing from cathode and anode, and maintains fluoroscopic density and contrast.
SLOW
Varying kvp / mas / pulse time
digital fluoro contrast?
good low contrast resolution
what do CSI phosphors do in TFT flat pannels?
the absorb xray photons and emit light from TFT
what does removing the grid do in dose while in fluoro?
reduces dose from 30-50%
lead apron and gloves
0.5 pb/eq
last image hold does what to exposure?
it reduces additional pt dose
name 4 digital flat panel benefits
ensures best image brightness
best spatial resolution
low contrast
lowest patient dose
benefits in digital flat panel Magnification mode
no vignetting
no increase in patient dose