Cybersecurity Notes
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
complexity, computational power, and security measures
Success of brute force attack depends on..
accounta
brute force process
start→generate possible combination→check if successful→ access granted→ end
types of brute forcing
simple
dictionary
hybrid
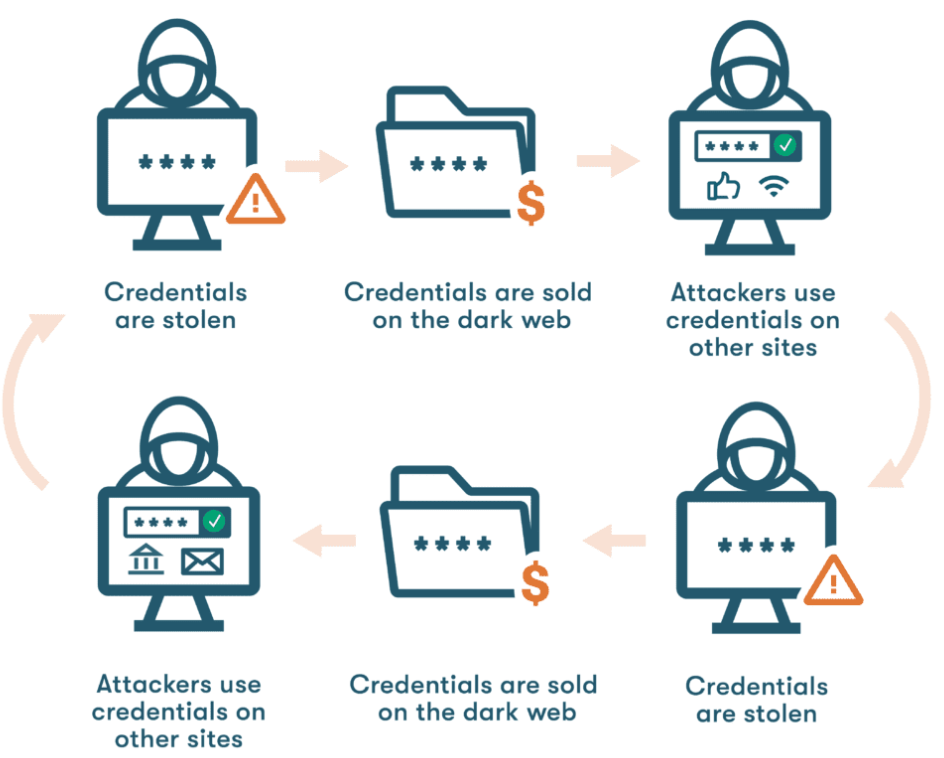
credential stuffing
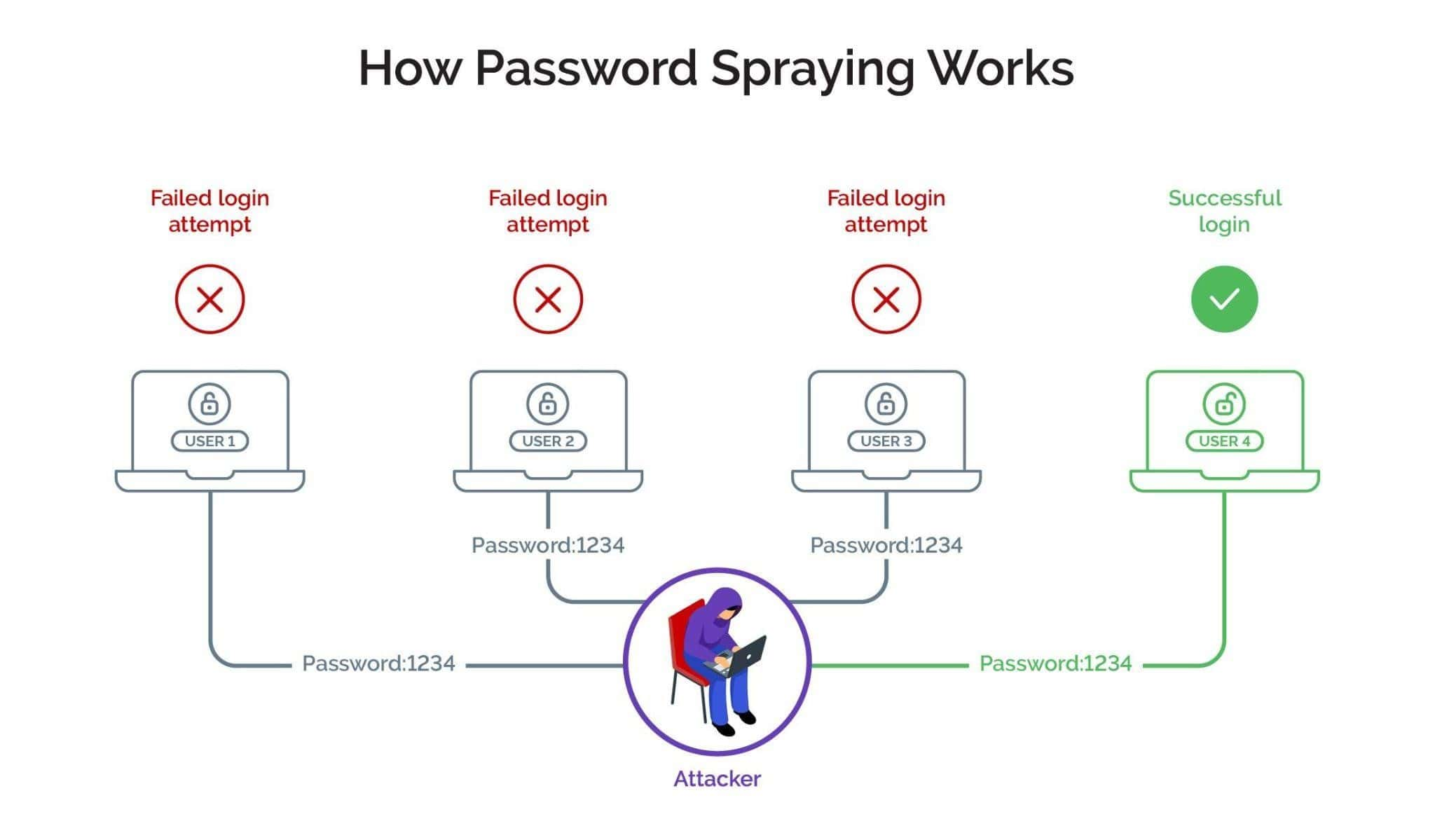
password spraying
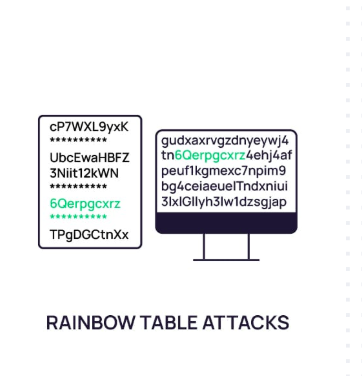
rainbow table
reverse
distributed
simple bf attack
definition: systematically trying all possible combinations of characters within defined character set and length range
best when used when: no prior information is available and comp resources are abundant
dictionary attack
definition: use pre-compiled list of common words, phrases, and passwords
best when used when: target likely uses weak or easily guessable password based on common patterns
which brute force attack method is equivalent to using wordlists in john the ripper?
dictionary
hybrid attack
def: combines elements of simple bf attacks and dictionary attacks, often appending or prepending characters to dictionary words…….
best usage: the target might use a slightly modified version of a common password
delete
delete
password spraying
def: attempts a small set of commonly used passwords against large number of usernames
best usage: you could be locked out, so you spread attempts across multiple accounts; if one door closes, another one is still open
reverse brute force
def: using a leaked password from one service to try logging into multiple accounts with different usernames
best usage case: A strong suspicion exists that a particular password is being reused across multiple accounts
rainbow table
def: uses pre-computed tables of password hashes to reverse hashes and recover plaintext passwords quickly
best to use when: a large number of password hashes need to be cracked, and storage space for rainbow tables is available
which is the best to use when a large number of password hashes need to be cracked, and storage space for this method is available?
rainbow tables
distributed brute force
def: distributes brute forcing workload across multiple computers or devices to accelerate process
best usage: target password or key is highly complex and a single machine lacks comp power to crack it
password problems
when orgs created easy default usernames and passwords; makes people who are too lazy to change them perfect targets
what tools are used is determined by how complex passwords are perceived to be (to optimize resources)
increasing the number of passwords by just two characters has the potential to
a. double the combinations
b. triple the combinations
c. 10x the combinations
c
-p-
scans all ports
-sV
performs service detection on specified ports
-v
adds more detail to scan
arp
stands for address resolution protocol; t’s a way for computers to find out where to send their messages
—disable-arp-ping
disables arp ping
makes scan more stealthy
arp ping
when a device sends an ARP request instead of using regular ICMP ping
benefits:
(1) Hides users from basic network scans
(2) Limits what methods are used during discovery and scanning
-Pn
disables ICMP Echo requests
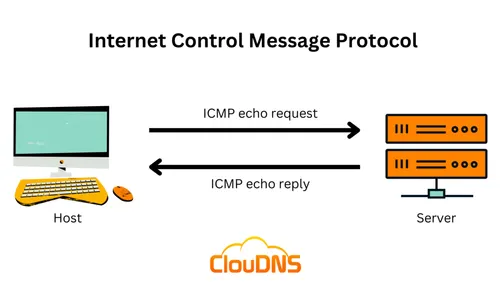
ICMP
Stands for internet Control Message protocol: used by computers to send helpful messages to eachother about network information
auth
determines authentication credentials
broadcast
scripts which are used for host discovery by boradcasting and the discovered hosts, can be added to remaining scans brute
brute
executes scripts that try to log in to service by brute forcing with creedentials
default
default scripts executed by the -sC option
discovery
evaluation of accessible services
dos
scripts used to check services for denial of service vulnerabilities and are used less as it harms the services experience
exploit
category of scripts that try to exploit known vulnerabilities for the scanned port
external
scripts that use external services for further processing
intrusive
nmap scripts that could negatively affect the target system
malware
an nmap script category that checks if some malware infects target systems
safe
defensive scripts that do not harm the target
version
an extension for service detection
-O
nmap scanning option for OS detection
-A
nmap command for an aggressive scan approach
type the command needed to call a specific script category
sudo nmap (ip) —script (category)
TCP
transmission control protocol; enables applications and computing to send messages over a network; designed to send packets
—packet-trace
nmap scripting text that when used, shows all packets sent and received
—reason
nmap script that shows why port is in specific state
-sV
scan for version
how to create alias
determine what you want to shortcut
write:
alias alias_name='nmap -n -Pn—open
this shows only open ports
icmp echo request
a tool for network diagnostics that sends a message via the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to check if a device on an IP network is reachable
packet
A formatted unit of data carried by computer networks, consisting of control information (headers) and user data (payload). They enable the breaking down of large messages into smaller chunks for efficient transmission across networks, with each packet containing addressing information to ensure proper routing.
how many different states are there for a scanned port?
6
unfiltered
This state of a port only occurs during the TCP-ACK scan and means that the port is accessible, but it cannot be determined whether it is open or closed.
-D RND:5
Rotates ports
Cntrl+C
how to get nmap to stop running
ls /usr/share/nmap/scripts/*category*
how to view all scripts in an nmap category
http-auth
nmap script categories & contents
auth
http-auth: Tests HTTP authentication
ssh-auth-methods: Lists SSH authentication methods
ftp-anon: Checks for anonymous FTP login
mysql-auth-bypass: Tests MySQL authentication bypass vulnerabilities
rdp-ntlm-info: Extracts information from RDP NTLM authentication
smtp-auth-methods: Enumerates SMTP authentication methods
broadcast
broadcast-dhcp-discover: DHCP service discovery
broadcast-dns-service-discovery: DNS service discovery
broadcast-dropbox-listener: Listens for Dropbox broadcasts
broadcast-netbios-master-browser: Discovers NetBIOS master browsers
broadcast-ping: Sends broadcast ping packets
broadcast-upnp-info: Discovers UPnP devices
brute
ftp-brute: Brute-forces FTP credentials
http-brute: Brute-forces HTTP basic authentication
mysql-brute: Brute-forces MySQL credentials
smb-brute: Brute-forces SMB accounts
ssh-brute: Brute-forces SSH credentials
rdp-brute: Brute-forces RDP credentials
default
ssl-cert: Retrieves SSL certificates
http-title: Shows HTTP title
ssh-hostkey: Retrieves SSH host keys
smb-os-discovery: Attempts OS discovery via SMB
dns-recursion: Checks for DNS recursion
banner: Grabs banners from network services
discovery
http-methods: Finds supported HTTP methods
dns-service-discovery: Discovers services using DNS
smb-enum-shares: Enumerates SMB shares
snmp-interfaces: Lists network interfaces via SNMP
http-sitemap-generator: Spiders websites to create sitemaps
ssh-hostkey: Retrieves target SSH host keys
dos
http-slowloris: Tests Slowloris DoS vulnerability
smb-flood: Floods SMB with requests
dns-flood: Performs DNS amplification attack tests
ipv6-ra-flood: Floods IPv6 router advertisements
smb2-vuln-uptime: Tests SMB2 DoS vulnerability
http-apache-server-status: Attempts to retrieve server status
exploit
smb-vuln-ms17-010: Tests for EternalBlue vulnerability
http-shellshock: Checks for Shellshock vulnerability
ftp-vsftpd-backdoor: Tests for vsftpd backdoor
smtp-vuln-cve2010-4344: Checks for Exim SMTP vulnerability
mysql-vuln-cve2012-2122: Tests MySQL authentication bypass
ssl-heartbleed: Checks for Heartbleed vulnerability
external
shodan-api: Uses Shodan API for additional information
whois-ip: Performs WHOIS lookups
dns-blacklist: Checks IP addresses against DNS blacklists
http-virustotal: Submits URLs to VirusTotal
ip-geolocation-*: Uses various services for geolocation
twitter-*: Scripts that interact with Twitter API
fuzzer
dns-fuzz: Fuzzes DNS service
http-form-fuzzer: Fuzzes HTTP forms
smtp-commands: Fuzzes SMTP commands
smb-enum-shares-fuzzer: Fuzzes SMB share names
http-method-fuzzer: Fuzzes HTTP methods
snmp-brute: Fuzzes SNMP community strings
intrusive
http-backup-finder: Searches for backup files
http-wordpress-users: Enumerates WordPress users
smb-enum-users: Enumerates SMB users
ftp-proftpd-backdoor: Tests for ProFTPD backdoor
mysql-empty-password: Checks for empty MySQL passwords
smtp-enum-users: Enumerates SMTP users
malware
smb-vuln-conficker: Detects Conficker infection
smtp-strangeport: Checks for malware on SMTP
dns-zeustracker: Checks against Zeus tracker
http-malware-host: Checks if web server hosts malware
ftp-libopie: Checks for OPIE backdoor in FTP
auth-spoof: Checks for authentication spoofing malware
safe
http-comments-displayer: Shows HTML comments
ssh-hostkey: Retrieves SSH host keys
ssl-cert: Retrieves SSL certificate information
banner: Retrieves service banners
dns-recursion: Checks for DNS recursion
http-headers: Shows HTTP headers
version
banner: Retrieves version from service banners
http-server-header: Retrieves HTTP server header
mysql-info: Retrieves MySQL server information
ssh2-enum-algos: Lists supported SSH algorithms
telnet-ntlm-info: Retrieves version from NTLM
tls-nextprotoneg: Determines supported protocols
vuln
http-vuln-cve*: Checks for various HTTP CVEs
smb-vuln-ms17-010: Checks for EternalBlue vulnerability
ssl-heartbleed: Checks for Heartbleed vulnerability
ftp-vsftpd-backdoor: Checks for vsftpd backdoor
smtp-vuln-cve*: Checks for SMTP vulnerabilities
mysql-vuln-cve*: Checks for MySQL vulnerabilities
tcpdump
a network packet analyzer that captures and analyzes network traffic. It allows users to capture packets transmitted over a network interface and provides a textual analysis of the captured packets. Tcpdump does not encrypt packets, but it can capture and analyze them for troubleshooting and security purpose
fuzzing
Sending random characters into a website to see how it reacts and find vulnerabilities. And, to see what pages **exist
union based
requires knowledge of table structure
combines results of injected SELECT with legitimate query; can be used to poison a query to return records from a different table
blind injection
type: sql injection
speed: slow
what happens: where the attacker does not receive an obvious response from attacked database and instead reconstructs the database structure step by step by observing behavior of database
time-based
External threats
threats that come from outside of an organization
security frameworks
Guidelines for building plans to help mitigate risks and threats to data and privacy
components include:
identify and document goals
setting guidelines to achieve goals
implementing strong security processes
communicating and monitoring the results
security controls
safeguards designed to reduce specific security risks. Used with security frameworks to establish strong security posture
Process of ensuring that assets stored in the _____ are properly configured, or setup correctly, and that access is limited to authorized users. It's a growing field that focuses on protection of data, applications, and infrastructure
processes in information security
risk assessment: identifies and evaluates potential threats and vulnerabilities determines potentail impact of security breaches help prioritize other security efforts
security planning: develops strategies to address identified risks creates policies and procedures to guide security efforts allocates resources for security initiatives
implementation of security controls: puts security plans into action; deploying technical solutions and enforcing policies; includes preventative and detective controls
monitoring and detection: continuously watches for security events and a using tools like SIEM systems and intrusion detection systems
disaster recovery: focuses on restoring systems and data after a major incident implementing backup and redundancy measures
continuous improvement: reviewing and learning from security incidents and near-misses; updates security measures based on new threats and technologies
asset security
security assessment and testing
security operations
CIA Triad
stands for confidentiality, integrity, and availability
logs
records of data
siem
stands for security information and event management tool
network protocol analyzer
tool designed to capture and analyze data within a network; examples of these tools include tcdump and netwire
linux
an open source operating system that relies on command line as primary user interface; not a programming language but can use text based commands
sql
stands for structured query language; used to create interact with and collect information from a database
risk mitigation
having the right procedures in place to reduce the impact of security breaches
compliance
method used to develop internal organization’s policies
continuance
the process of maintaining business operations with balancing security needs
asset security domain
the domain of security dedicated to securing physical and digital assets
shared responsibility
I&AM (identity and access management)
ensuring user access is limited to what people need and reducing overall risks to systems and data. components include
identification
authentication
authorization
accountability
identification
when someone identifies who they are
authentication
when someone proves their identity
authorization
gives level of access after authentication has been completed
accountability
recording attempts to ensure things are done properly
security assessment & testing
focused on conducting testing and audits
security operations
conducting and investigating and implementing preventative methods