Renal system
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
purpose
rid body of nitrogenous waste
protein breakdown
water and acid/base balance
toxin/drug elimination
breakdown product elimination
produces hormones
types of nitrogenous waste
ammonia
uric acid
urea
ammonia
ammonotelic = aquatic animals
fish, aquatic invertebrates
water can reduce toxicity of ammonia
fish produce ammonia
tanks
nitrifying bacteria introduced to nitrogen cycle
very toxic
water soluble
uric acid
uricotelic animals
birds, reptiles
renal portal system
formed in the liver, concentrates, becomes precipitant
semi-solid
acidic
requires little water, lots of energy
urea
ureotelic animals
mammals, amphibians, sharks
allows water balance
amount excreted dependent on conditions
low toxicity
build of of ura can cause problems
kidneys basics
retroperitoneal
separated in the abdominal cavity
have their own peritoneum
smooth in most species
lobulated in cattle and dolphins
birds have elongated lobulated kidneys
heart shape in horses
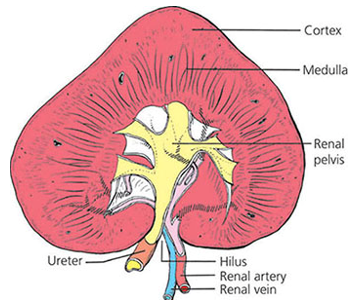
kidneys anat
hilus
indentation where renal artery enters, renal vein and ureter leave
cortex
outer, darker, rough
medulla
inner, lighter, striated
pyramids/peaks
within medulla
pelvis
near hilus, space for urine collection/storage
ureter
brings out urine
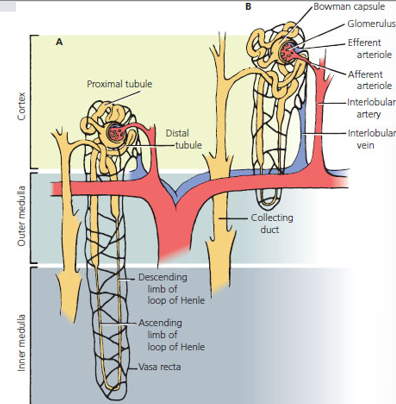
nepheron
kidney cell
functional unit
Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Loop of Henle
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
collecting tube or duct
vasa recta
starts in cortex
extends down to medulla via descending loop
back up to nepheron via ascending loop
back down to medulla and exits via collecting duct
Glomerulus
Capillary tuft
Afferent arteriole: brings blood in
Efferent arteriole: drains blood out
This is the filter
Bowman’s capsule
Podocytes = visceral layer
Parietal layer = simple squamous epithelium
Both podocytes and simple squamous epithelium necessary for filtration
Sits above capillaries
Receives filtrate
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Simple cuboidal epithelium
increases surface area
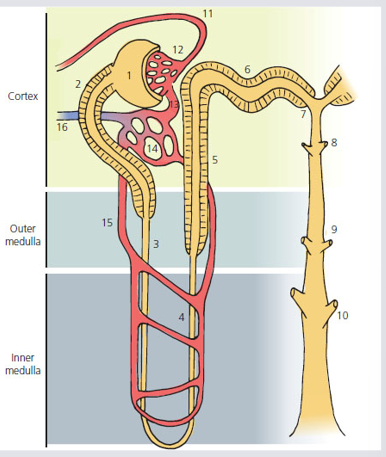
Loop of Henle
descending limb
most simple squamous
does down into medulla
ascending limb
thin = simple squamous epithelium
thick = simple cuboidal for strength
coes up to cortex
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
simple cuboidal
increases surface area
convoluted
collecting tube or duct
simple cuboidal
no brush border
vasa recta
capillary network in the medulla
around loop of henle
essential for flow of filtrate
ureters
tubes from renal replica of the kidney to neck of urinary bladder
angle prevents backflow
trigone
area at neck of bladder where ureters enter and urethra leaves
smooth muscle and loose connective tissue in walls
lines with transitional epithelium
ureterovesicular junction
oblique entrance of ureter into the urinary bladder
Urine is conveyed to the urinary bladder from the renal pelvis by peristalsis and enters at the ureterovesicular junction.
During micturition (emptying of the urinary bladder), urine is directed through the neck of the bladder to the urethra.
Urine does not reenter the ureter because the ureterovesicular junction is closed by the hydrostatic pressure of urine
urinary bladder
three layers
serosal epithelium
large layer of smooth muscle
detrusor muscle
transitional epithelium
lines lumen
cells slide apart and flatter to fewer layers as organ fills with urine
urethra
caudal continuation of the bladder
tube from neck of urinary bladder to outside
longer in males
goes through penis
less prone to UTIs
starts in transitional epithelium lining lumen
changes to moist stratified squamous
adds protection
urine is sterile until it exits the body
formation of urine
glomerular filtration
ultrafiltrate
tubular reabsorption
tubular secretion
PCT
loop of henle
DCT and CD
secretion
countercurrent mechanism
fluid flow through tubules
glomerular filtration
glomerulus
fenestrated capillaries
species between glomerular endothelial cells
substances from leaky capillaries goes to bowman’s capsule
most plasma leaves blood
dissolved nutrients, waste, electrolytes
large molecules stay inside
blood cells
most proteins
osmotic effect to keep some water
ultrafiltrate
product of filtration
not urine yet
tubular reabsorption
from glomerular filtrate ->
cells of tubules of nephron->
blood
tubular secretion
from blood ->
cells of tubules of nephron ->
fluid in tubules
rest of nephron needs to recover lost nutrients
most of water
fine tune water
acid/base balance
PCT
ultrafiltrate
glucose reabsorption by active transport
65% of water that enters gets sent back to eh blood via osmosis
amino acids coupled with sodium cotransport
needs energy
peritubular capillary reabsorption
NaCl and K
water will follow NaCl back into the blood
90% of bicarbonate is reabsorbed back into the blood
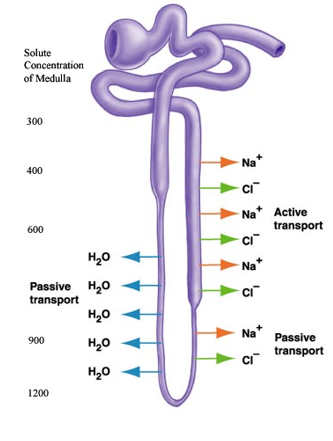
loop of henle
after PTC
filtrate goes from cortex to medulla
medulla has higher osmolarity than cortex and filtrate
descending
water permeable, solute impermeable
water follows by osmosis via channel
ascending
sodium and chloride reabsorbed by active transport
not followed by water
bottom of loop
most concentrated area
DCT and CD
sodium reabsorbed by active transport
influences by aldosterone
water reabsorbed by osmosis
influenced by antidiuretic hormone
hydrogen ion and some drugs secreted by active transport
acid/base balance
secretion
anything in the blood sent out to urine
toxins, bicarb, H, drugs, meds
countercurrent mechanism
flow of urine
opposite floes
creates concentration gradient
pass material from one table to another
medulla
hypertonic
sodium and ura in interstitial fluid
driving force of water going out is high, solute concentration on outside if high
cortex
isotonic to hypotonic
fluid flow through tubules
hypotonic
fluid in to loop of henle
becomes hypertonic
bottom of loop
loses water on the way down and becomes concentrated
hypotonic
during ascent
closed sodium/solutes and becomes dilute
hypertonic
in collecting duct
loses water
urine excreted
hypertonic to plasma
unless if excess water or osmotic effects draw water out
countercurrent flow in descending and ascending limbs but also in vasa recta
control of urine formation 3
blood pressure
autoregulation
thirst and osmolarity
blood pressure
increase BP yields increase glomerular filtration rate
forces more blood into the glomerulus
urine forms faster
lower BP slows urine formation
specifically changes afferent or efferent arteriole diameter
dilate afferent arteriole
more blood flows
increases GFR
constrict efferent arteriole
also increase GFR
autoregulation
juxtaglomerular apparatus JG
JG cells and macula densa cells of DCT
macula densa cells
chemoreceptors around DCT
sense increase NaCl in tubular fluid
slows GFR to increase sodium reabsorption
JG cells around afferent and efferent arterioles
acts as baroreceptors
secrete renin
causes Angiotensin I to form AII
causes efferent arteriole constriction
decrease GFR
also causes Aldosterone production
reabsorption of sodium and water
decrease urine output, increases blood pressure
thirst and osmolarity
cycle of events for the relief of hyperosmolality
increase thirst
predominant factor for the correction of hyperosmolality
regulated by ADH
diabetes insipidus
no ADH is produced
can’t send water to body
animal will keep drinking
increased urination
Atrial natriuretic hormone
ANH
causes sodium to be secreted into urine at the CD
water follows
increased urine volume
decreases urine concentration
control of urine formation
sympathetic nerve stimulation
vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole
decreased GFR