exam 4 flash cards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/255
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:02 AM on 12/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
256 Terms
1
New cards
gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs
What does the digestive system consist of
2
New cards
Blastula
Stage of development where digestive system is made
- many cells fold in on itself
- fold gets bigger until it goes through it
- the hole is called an endoderm
- hole is surrounded by mesoderm
- many cells fold in on itself
- fold gets bigger until it goes through it
- the hole is called an endoderm
- hole is surrounded by mesoderm
3
New cards
Protosome
Mouth is made first
4
New cards
Deuterostomes
Anus is made first
- humans
-Mouth made second
- humans
-Mouth made second
5
New cards
Peritoneum
Serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity
- largest serous membrane in body
- simple squamous
- contains folds = mesenteries
- largest serous membrane in body
- simple squamous
- contains folds = mesenteries
6
New cards
Parietal peritoneum
Outer layer lining that touches wall
7
New cards
visceral peritoneum
Inner lining that covers organs
8
New cards
Mesentery
a fused double sheets of the peritoneal membrane
- stabilize position of organs & BV's
- provide attachment for BV's
- stabilize position of organs & BV's
- provide attachment for BV's
9
New cards
Mesentery proper
binds jejunum and ileum to posterior abdominal wall
- holds small intestine to body wall
- holds small intestine to body wall
10
New cards
Mesocolon
binds transverse colon and sigmoid colon to posterior abdominal wall
- holds large intestine to body cavity
- holds large intestine to body cavity
11
New cards
Greater Omentum
Drapes over transverse colon & small intestine
Largest mesentery
Fatty apron
Largest mesentery
Fatty apron
12
New cards
lesser omentum
Connects the stomach and duodenum to the liver
- contains major blood vessels, bile & lymph structure
- hepatic portal vein
- contains major blood vessels, bile & lymph structure
- hepatic portal vein
13
New cards
intraperitoneal
Digestive organs are completely surrounded by visceral peritoneum
14
New cards
Retroperitoneal
Organs lie against the posterior abdominal wall
- kidney
- kidney
15
New cards
Mucosa
inner lining of digestive tract
- epithelium
- Lamina propria - only place inbody where this CT is found
- makes mucus
- epithelium
- Lamina propria - only place inbody where this CT is found
- makes mucus
16
New cards
Submucosa
dense irregular connective tissue
Glands that secrete acid, BV & nerve plexus
Glands that secrete acid, BV & nerve plexus
17
New cards
Muscularis
smooth muscle that helps more food
-Inner circular layer & outer longitudinal layer
-Inner circular layer & outer longitudinal layer
18
New cards
Serosa
visceral peritoneum - layer of serous membrane attached to organ.
- NOT FOUND IN: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, OR rectum
- NOT FOUND IN: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, OR rectum
19
New cards
Inner circular
Pushing food along
20
New cards
outer longitudinal
Smooshing
21
New cards
processing food
Food → macros
Food → macros
What is the primary function of the digestive system
22
New cards
1. Ingestion - swallowing food
2. Digesting-Chem (enzymes cut food smaller) vs mech (teeth )
3. Absorption - large & small intestine absorbing nutrients
4. Elimination- waste leaving body
2. Digesting-Chem (enzymes cut food smaller) vs mech (teeth )
3. Absorption - large & small intestine absorbing nutrients
4. Elimination- waste leaving body
What are the steps of food processing
23
New cards
oral cavity
mouth
Cheeks form the lateral walls
- lined by stratified squamous epic
- lips - muscles
Cheeks form the lateral walls
- lined by stratified squamous epic
- lips - muscles
24
New cards
Start of mech & chem digestion
bolus forms when we swallow good
Bonus = food & saliva
bolus forms when we swallow good
Bonus = food & saliva
Oral cavity primary function
25
New cards
soft and hard palate
uvula
tongue
mouth
cheeks
teeth
lips
muscles
uvula
tongue
mouth
cheeks
teeth
lips
muscles
What does the oral cavity consist of
26
New cards
Palate
roof of the mouth
Hard & soft
Hard & soft
27
New cards
Uvula
CT from soft palate
- closes off nasopharynx while swallowing
- gag reflex
- closes off nasopharynx while swallowing
- gag reflex
28
New cards
Tongue
Skeletal muscle, held down by the lingual frenulum
29
New cards
Chewing, gestation, and speech
Tongue primary function
30
New cards
Teeth
20 deciduous (baby) & 32 adult
31
New cards
Periodontal ligament
Anchors tooth to the bone
32
New cards
Incisors - scraping
Cuspids (canines)- hold food in place
Bicuspids (premolars) - transitional teeth both canines and molars
Molars- grinding of food
Cuspids (canines)- hold food in place
Bicuspids (premolars) - transitional teeth both canines and molars
Molars- grinding of food
What are the types of teeth and function
33
New cards
Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks down starches
34
New cards
parotid
Biggest gland over the masseter muscle
35
New cards
Submandibular
salivary gland under mandible
36
New cards
Sublingual
salivary gland under the tongue
37
New cards
Deglutition (swallowing)
Passing something from mouth the pharynx & into esophagus
Bonus moves through esophagus via peristalsis
Bonus moves through esophagus via peristalsis
38
New cards
Peristalsis
Rhythmic contract/relax of GI tract muscle
- moves food
- smooth muscle
- happens in esophagus, stomach, large/small intestine
-Slowly
- I secs from esophagus to stomach
- moves food
- smooth muscle
- happens in esophagus, stomach, large/small intestine
-Slowly
- I secs from esophagus to stomach
39
New cards
Esophagus
Collapsible, muscular
Connects oral cavity to stomach
posterior to trachea
Start of peristalsis
Connects oral cavity to stomach
posterior to trachea
Start of peristalsis
40
New cards
gastroesophageal sphincter
Stomach & esophagus sphincter
- regulate and control the rate of food going into stomach
- regulate and control the rate of food going into stomach
41
New cards
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
long term condition in which stomach acid goes into esophagus
● Acid in the back of the mouth, heartburn, bad breath, chest pain, regurgitation, breathing problems, and wearing away of the teeth
● Risk Factors: obesity, smoking, pregnancy, LES isn't functioning
● Acid in the back of the mouth, heartburn, bad breath, chest pain, regurgitation, breathing problems, and wearing away of the teeth
● Risk Factors: obesity, smoking, pregnancy, LES isn't functioning
42
New cards
stomach
Primary function - chem (cut protein) & mech digest
Secondary function- food storage, protein digestion (starts in mouth), hormone production that signals how full we are and for acid to be made
Tertiary function
Absorption
SOME H2O
SOME meds ex aspirin
Alcohol
Caffeine
mucosal layer has goblet cells
Secondary function- food storage, protein digestion (starts in mouth), hormone production that signals how full we are and for acid to be made
Tertiary function
Absorption
SOME H2O
SOME meds ex aspirin
Alcohol
Caffeine
mucosal layer has goblet cells
43
New cards
Chyme
Food (bolus) mixed with acid
44
New cards
Oblique
Innermost layer
- churns food inside stomach
- churns food inside stomach
45
New cards
cardia
Transition from esophagus to stomach
46
New cards
Fundus
most superior part of the stomach
Helps with expansion
Helps with expansion
47
New cards
Body
largest region of the stomach
Churning happens
Churning happens
48
New cards
Pylorus
Most inferior region of stomach
49
New cards
gastroesophageal sphincter
Controls rate of food entering body
50
New cards
Greater curvature
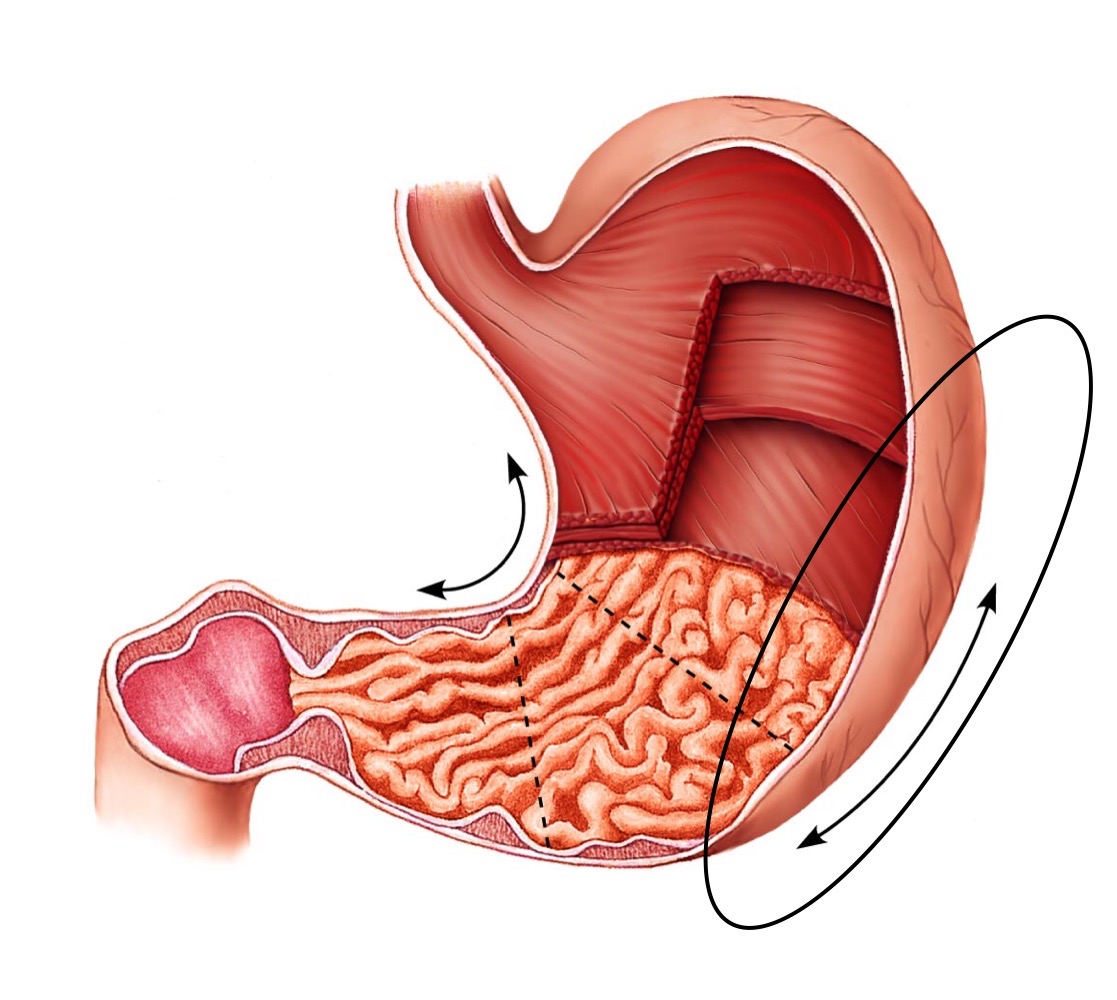
51
New cards
rugae of stomach
Expansion
52
New cards
pyloric sphincter
Between stomach and small intestine
53
New cards
slow and controlled
I tsp at a time
Empties in 2-6hrs
I tsp at a time
Empties in 2-6hrs
How fast does the stomach empty slow an
54
New cards
Acid + digestive juice, gastric glands
Stomach structures?
55
New cards
Gastric glands
Inside of mucosa gastric pits
Make mucus or acid
Secretory cells
Make mucus or acid
Secretory cells
56
New cards
Vomiting
involuntary & forceful expulsion of the contents of the stomach
● Mouth or nose :(
burns bc or acid
● Risk factors: Motion sickness, head trauma, food poisoning, overeating, gastritis, drugs, stress
● Treatment: Medication, waiting it out, staying hydrated
● Mouth or nose :(
burns bc or acid
● Risk factors: Motion sickness, head trauma, food poisoning, overeating, gastritis, drugs, stress
● Treatment: Medication, waiting it out, staying hydrated
57
New cards
Small intestine
Between stomach & large intestine
18-20 ft
- 1.5 - 2.5in diameter
- feeds with villi that contain microvilli
- nutrients absorbed by touching
18-20 ft
- 1.5 - 2.5in diameter
- feeds with villi that contain microvilli
- nutrients absorbed by touching
58
New cards
Digestion & absorption of nutrients
Primary function of small intestine
59
New cards
SI absorption
BVs for sugars & amino acids
- lacteals for large macros
- eventually back general circulation
- lacteals for large macros
- eventually back general circulation
60
New cards
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
What are the 3 parts of the small intestine
61
New cards
Duodenum
first 10-13in segment of small intestine
● Chyme from stomach + digestive secretions
● Common bile & pancreatic duct open into duodenum○ Hepatopancreatic ampulla sphincter
-breaking down
● Chyme from stomach + digestive secretions
● Common bile & pancreatic duct open into duodenum○ Hepatopancreatic ampulla sphincter
-breaking down
62
New cards
Receive chyme from stomach
Neutralize acids
HCO3 - +H+ → H2O + CO2
Neutralize acids
HCO3 - +H+ → H2O + CO2
Duodenum functions
63
New cards
jejunum
Middle segment of small intestine
Approx. 8ft
Chem digestion
Nutrient absorption
Approx. 8ft
Chem digestion
Nutrient absorption
64
New cards
Ileum
The final segment of the small intestine
Approx. 12ft
ileocecal valve
cleaning
Approx. 12ft
ileocecal valve
cleaning
65
New cards
Segmentation
si digestion
si digestion
Mixing of food stuffs+ digestive secretions
No net movement
-Pushes back and forth to mix then pushes → with peristalisis
No net movement
-Pushes back and forth to mix then pushes → with peristalisis
66
New cards
Liver
largest organ of the body
Located under diaphragm
Can regenerate
Primary function: detox
Located under diaphragm
Can regenerate
Primary function: detox
67
New cards
Falciform ligament
Attaches liver to anterior abdominal wall & diaphragm
68
New cards
hepatic portal system
connects the digestive tract and liver
- specialized venous blood pathway
- from GI tract → liver → heart
- nutrient rich / O2 poor
- stomach, small intestine, pancreas, and spleen blood get together to form hepatic portal vein to dump blood into liver
- specialized venous blood pathway
- from GI tract → liver → heart
- nutrient rich / O2 poor
- stomach, small intestine, pancreas, and spleen blood get together to form hepatic portal vein to dump blood into liver
69
New cards
Lobules
functional units of the liver
70
New cards
hepatocytes
liver cells
Break down parasites
A lot of rough/smooth ER and ribosomes
Break down parasites
A lot of rough/smooth ER and ribosomes
71
New cards
Kupffer cells
Immune system cells
72
New cards
hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, small bile duct
What makes up the portal triad
73
New cards
Hepatic sinusoid
Holds kupffer cells
74
New cards
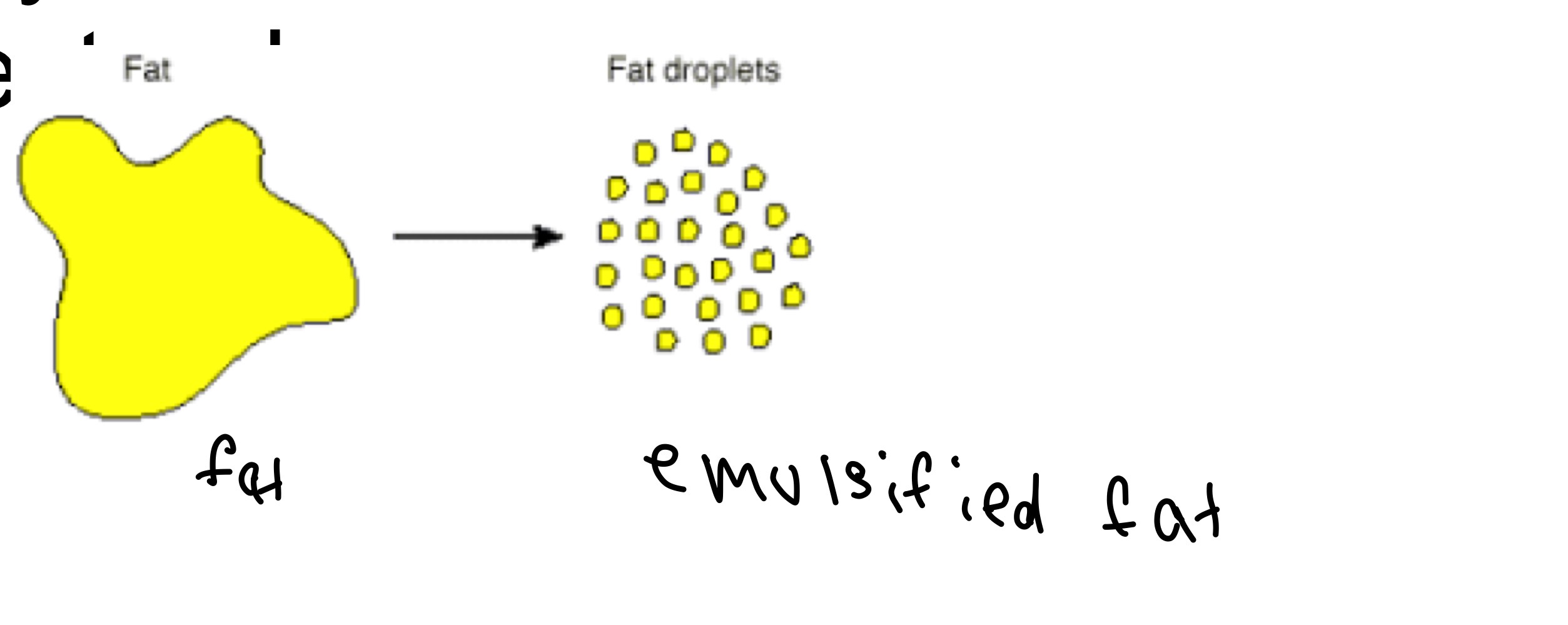
Storage of Fe, vit: A, D, E, K, & BI2
Production of glycerol & amino acids→ glucose when hangry
Cholesterol
Bile - cuts down fat increases sa
Production of glycerol & amino acids→ glucose when hangry
Cholesterol
Bile - cuts down fat increases sa
Liver secondary function
75
New cards
Gallbladder
Primary function: store bile
Located under liver
Located under liver
76
New cards
gall stones
a stone formed within the gallbladder/bile duct
● Cholesterol / ↓ bile salts = stone
● Crampy pain in the right upper part of the abdomen, fever, yellowish skin, vomiting, or tea-colored urine
● Other acc. organs to become inflamed
● Risk Factors: estrogen + 40 years, weight, and diet hormonal birth control too
● Treatment: Diet change, Surgery or shock waves
● Cholesterol / ↓ bile salts = stone
● Crampy pain in the right upper part of the abdomen, fever, yellowish skin, vomiting, or tea-colored urine
● Other acc. organs to become inflamed
● Risk Factors: estrogen + 40 years, weight, and diet hormonal birth control too
● Treatment: Diet change, Surgery or shock waves
77
New cards
Pancreas
Primary functions
endo: make insulin and glucagon
exo=pancreatic juices
Located behind stomach
endo: make insulin and glucagon
exo=pancreatic juices
Located behind stomach
78
New cards
Lipase- lipids /fats
Pancreatic amylase-starch
Pancreatic trypsin -protein
Pancreatic amylase-starch
Pancreatic trypsin -protein
What are the enzymes for all macros
79
New cards
Pancreatic juices
Contains sodium bicarb
Bicarb protect small intestine from stomach acid b/c no mucus
Bicarb protect small intestine from stomach acid b/c no mucus
80
New cards
Large intestine
Primary function:
Last chance absorption & storage
Located around the small intestine
4-5 ft long
Approx 3in in diameter
Absorb H2O and vitamins made by proks (B complex and K)
K- help with blood clots I made by our E. coli
Last chance absorption & storage
Located around the small intestine
4-5 ft long
Approx 3in in diameter
Absorb H2O and vitamins made by proks (B complex and K)
K- help with blood clots I made by our E. coli
81
New cards
Feces
When it enter iliocecal value it becomes feces for 1st time
3/4 h20 & 1/4 undigested solids+ coliforms
bilirubin processing+ oxidized iron = brown poop
3/4 h20 & 1/4 undigested solids+ coliforms
bilirubin processing+ oxidized iron = brown poop
82
New cards
Cecum
transitionary pouch that connects small to large intestine
83
New cards
Appendix
Lymph tissue
84
New cards
appendicitis
inflammation of the appendix
●Caused by blockage
● Right/lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, & decreased appetite
● Sepsis- infection could happen by fecal matter getting stuck
● Treatment: Removal
●Caused by blockage
● Right/lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, & decreased appetite
● Sepsis- infection could happen by fecal matter getting stuck
● Treatment: Removal
85
New cards
Colon
Largest portion of LI
86
New cards
Ascend
Fecal matter goes up
87
New cards
Trans
Fecal matter goes on transverse plane
88
New cards
Descend
Fecal matter goes down
89
New cards
Sigmoid
S-shaped
Leads feces into rectum
Leads feces into rectum
90
New cards
Haustra
Pouches for expansion - helps with abs and storage
91
New cards
taeniae coli
longitudinal bands of smooth muscle
Helps with peristalsis of each pouch
Helps with peristalsis of each pouch
92
New cards
Rectum
Last 20 cm of LI
Storage area
Internal sphincter = involuntary
External sphincter = voluntary
Both control the rate of fecal exiting body
Storage area
Internal sphincter = involuntary
External sphincter = voluntary
Both control the rate of fecal exiting body
93
New cards
Anal canal
Site of defecation
Voluntary
Voluntary
94
New cards
lactose intolerance
- Only supposed to drink milk as babies
inability to digest milk sugars (lactose)
● If no lactase enzyme = can't digest lactose
● Bacteria breakdown lactose anaerobically, producing gas, bloating, diarrhea
● Cheese & yogurt OK, heavy cream & butter too! (more milk fat=less milk sugar)
● Risk Factors: being an adult
● Treatment: Diet & lactase supplement
inability to digest milk sugars (lactose)
● If no lactase enzyme = can't digest lactose
● Bacteria breakdown lactose anaerobically, producing gas, bloating, diarrhea
● Cheese & yogurt OK, heavy cream & butter too! (more milk fat=less milk sugar)
● Risk Factors: being an adult
● Treatment: Diet & lactase supplement
95
New cards
Excrete waste from proteins
Urea & ammonium from AAs
Urea & ammonium from AAs
Urinary system primary function
96
New cards
Water/salt (blood pressure) homeostasis
BP measured in salt
BP measured in salt
Urinary system secondary function
97
New cards
Aldosterone
regulates salt and stress homeostasis
increases blood vol and blood pressure
-stimulated by low sodium concentration (after exercise), blood loss (low blood volume), or low blood pressure
kidney reabsorption of Na+ & excretion of K+
NOT controlled by anterior pituitary
increases blood vol and blood pressure
-stimulated by low sodium concentration (after exercise), blood loss (low blood volume), or low blood pressure
kidney reabsorption of Na+ & excretion of K+
NOT controlled by anterior pituitary
98
New cards
RAAS
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
99
New cards
Renin -> RAAS hormone complex
Made from juxtaglomerular apparatus
kidneys: constrict bvs = increased blood pressure
Tells Adrenal glands to make: Aldo = increased salt retention
kidneys: constrict bvs = increased blood pressure
Tells Adrenal glands to make: Aldo = increased salt retention
100
New cards
Non urinary function: blood ph
If pH low/acidic = too many H ions & secretion of buffers (bicarb ion) increase
If pH high / too alkaline= increase excretions of buffers (bicarb ion) & secretion of H ion increase
If pH high / too alkaline= increase excretions of buffers (bicarb ion) & secretion of H ion increase