LECTURE 15 - THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what are the 2 subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system? what direction does the information travel? what type of information does each subdivision carry?
-afferent division
carries sensory information towards the central nervous system
-efferent division
carries motor information from the central nervous system to peripheral tissue (like muscles, glands, etc.)
what are the 2 subdivisions of the efferent division? how do they differ? what structures does each innervate?
-somatic nervous system
serves skeletal muscle
under our conscious control
-autonomic nervous system
serves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and various glands
involuntary
what type of information does the dorsal root carry? the ventral root? what is the dorsal root ganglion? Be able to identify these 3 structures on a diagram.
-dorsal root
sensory nerve entry point
-dorsal root ganglion
collection of sensory neuron cell bodies
-ventral root
motor nerve exit point
what are mixed nerves? what two structures form mixed nerves?
mixed nerves: contain both somatic sensory & somatic motor fibers.
formed by the union of the dorsal and ventral roots.
what is the general spinal nerve structure?
-individual axons/nerve fibers are surrounded by endoneurium
endoneurium = loose areolar connective tissue
-bundles of axons/nerve fibers form fascicles
perineurium = layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds an individual fascicle
-fascicles are “bundled” together forming a nerve trunk
epineurium = layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the entire nerve trunk
continuous with dura mater
provides strength & support
Be able to identify the following terms/structures on a diagram and know their histology when necessary:
nerve fibers
endoneurium
fascicles
perineurium
nerve trunk
epineurium
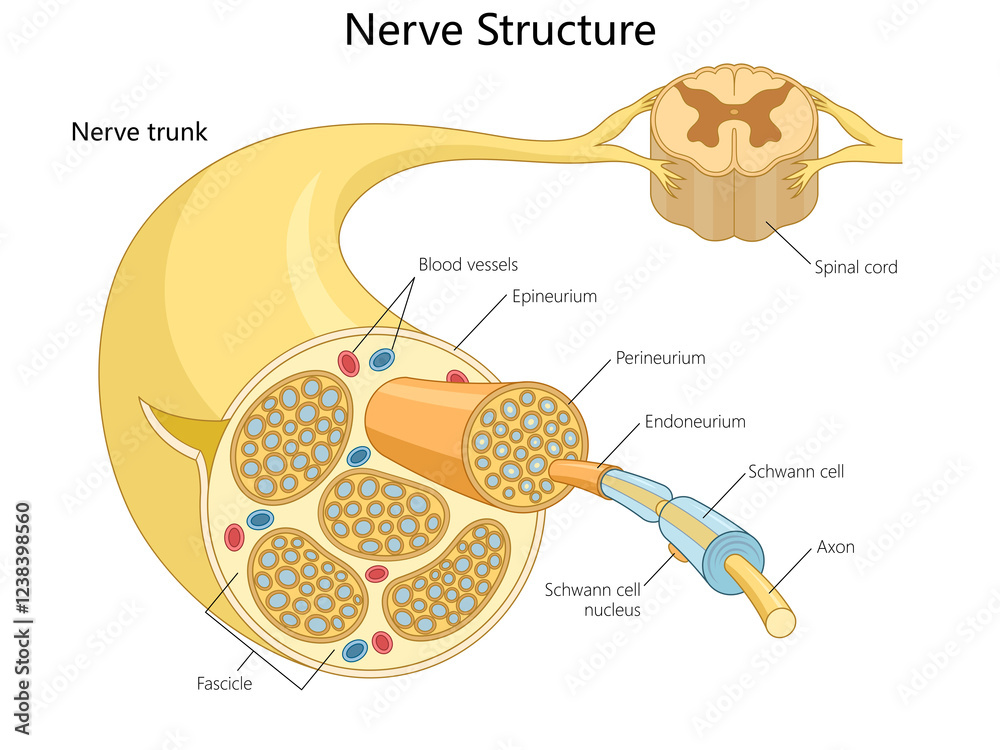
histology:
endoneurium = loose areolar connective tissue
perineurium = layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds an individual fascicle
epineurium = layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the entire nerve trunk
what is a nerve plexus? what are the 4 nerve plexuses discussed in class? what structures does each innervate?
nerve plexus: merging network of spinal nerve trunks leading to and from specific body regions.
includes:
cervical plexus
brachial plexus
lumbar plexus
sacral plexus
what structures does each innervate?
cervical plexus
brachial plexus
lumbar plexus
sacral plexus
-cervical plexus
innervates the neck, jaw, upper back, & diaphragm
-brachial plexus
innervates the shoulder, arm, & hand
-lumbar plexus
innervates the lower back, lower abdominal wall, thigh, and genitalia
-sacral plexus
innervates the hip region, posterior thigh, calf, & foot
what are reflexes?
reflexes: rapid, automatic, involuntary, reactions of muscles/glands to a stimulus
what are the components of a reflex arc?
components of a reflex arc:
begins at a sensory receptor within the peripheral nervous system —→
signal travels towards the spinal cord (central nervous system) —→
integration —→
signal carried to effector —→
motor response produced —→
be able to diagram a basic reflex arc
?
know the functions of the cranial nerves given in class. is each nerve motor, sensory, or mixed?
I. olfactory (special sensory)
II. optic (special sensory)
III. oculomotor
IV. trochlear (motor)
V. trigeminal (mixed)
I. olfactory (special sensory)
SENSORY
function: smell
II. optic (special sensory)
SENSORY
function: vision
III. oculomotor
MOTOR
function: eye movements, eyelid and iris movement
IV. trochlear (motor)
MOTOR
function: eye movement
V. trigeminal (mixed)
MIXED
ophthalmic (SENSORY): orbital structures, nasal cavity, skin of forehead, superior eyelid, eyebrows, part of nose
maxillary (SENSORY): inferior eyelid, upper lip, gums, teeth, cheek, nose, palate, part of pharynx
mandibular (MIXED):
SENSORY: lower gums, teeth, lips, palate, tongue.
MOTOR: muscles of mastication
know the functions of the cranial nerves given in class. is each nerve motor, sensory, or mixed?
VI. abducens
VII. facial
VIII. vestibulocochlear (special sensory)
IX. glossopharyngeal (mixed)
X. Vagus (mixed)
XI. accessory (motor)
XII. hypoglossal (motor)
VI. abducens
MOTOR
function: eye movements
VII. facial
MIXED
functions: SENSORY from taste receptors on the anterior 2/3 of the tongue. MOTOR: muscles involved in facial expressions, lacrimal and salivary glands
VIII. vestibulocochlear (special sensory)
SENSORY
functions:
vestibular branch: balance and equilibrium
cochlear branch: hearing
IX. glossopharyngeal (mixed)
MIXED
functions:
SENSORY: taste of posterior 1/3 of tongue and pressure within the throat
MOTOR: swallowing and salivation
XI. accessory (motor)
MOTOR
runs to/from the muscles of the upper back
XII. hypoglossal (motor)
MOTOR
function: tongue movements
what is the vagus nerve? is it sensory or motor? what important structure does it innervate?
X. Vagus (mixed)
X. Vagus (mixed)
MIXED
runs to/from the chest and abdomen
functions:
SENSORY: visceral pain
MOTOR: controls heart, lungs, and G.I. tract