Periodic Table
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are properties of elements?
Functions of their group/family
Why are elements put in the same group?
They have similar properties and they have the same number of valence electrons
What is group one of the periodic table?
Alkali metals
What is group two of the periodic table?
Alkaline metals
What is group 17 of the periodic table?
Halogens
What is group 18 of the periodic table?
Noble gases
Elements that are not in groups 1, 2, 17, or 18 are in _____.
families
This is because not all of them behave the same way.
What are periods/rows?
Elements in rows (1-7) have the same number of electron shells.
Describe group one of the periodic table.
You never find them free in nature. They are very reactive.
Describe group two of the periodic table.
You don’t see them that much, but sometimes in a lab setting. They are less reactive.
Describe group seventeen of the periodic table.
Just as reactive as group one. One and Seventeen want to be perfect, which is why they are so unstable. All three phases of matter are in group seventeen. They are not seen much in nature.
What are the liquids of the periodic table?
Hg (mercury, liquid metal)
Br (in group 17)
What are the gases of the periodic table? (monoatomic/noble gases)
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
What are the gases of the periodic table? (diatomic)
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2
F2 and Cl2 are in group 17.
What are the metalloids of the periodic table?
B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te
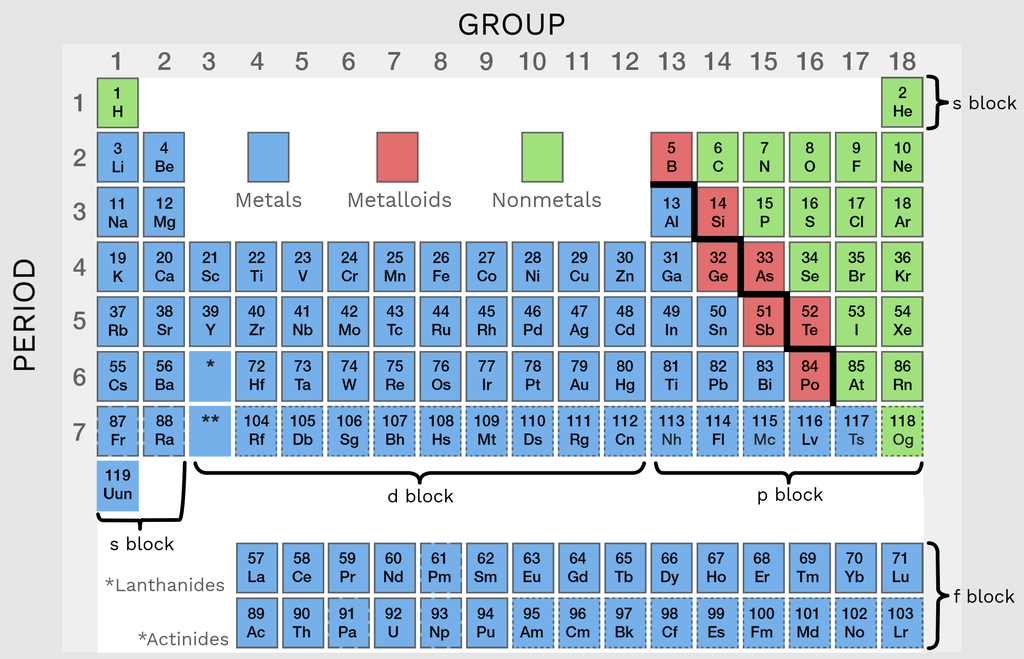
What are the elements on the metalloid staircase that aren’t considered metalloids?
Al, Po, At (Po and At are sometimes considered metalloids, but in this class we will say that they aren’t)
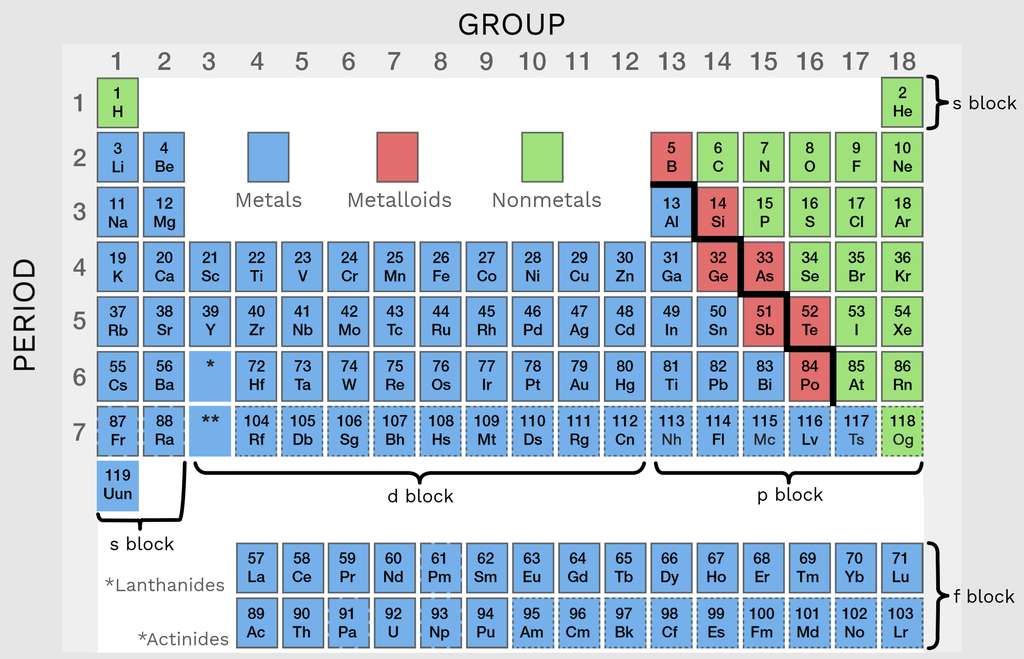
Metalloids have properties of…
Both metals and nonmetals
What is the only radioactive noble gas? Why aren’t the other noble gases reactive?
Rn (radon)
The rest aren’t reactive because they already have a full outer shell (except for helium), they do not need to gain/lose an electron.
What is the most reactive nonmetal?
F (fluorine)
What is the most reactive metal?
Fr (francium)
Metals and nonmetals are…
direct opposites.
As you move down any group of metals, they…
get more reactive because they want to get rid of their last valence electrons
The farther away a valence electron is…
the easier it is to remove.
What are the transition metals?
Groups 3-12
Electron shells fill up to more than 8
Many have more than one oxidation state
They give you colored solutions.
What are radioactive elements?
Elements 43, 84 and above
They are elements with no stable isotope
What does it mean if an element has a 0 ion?
It isn’t reactive.
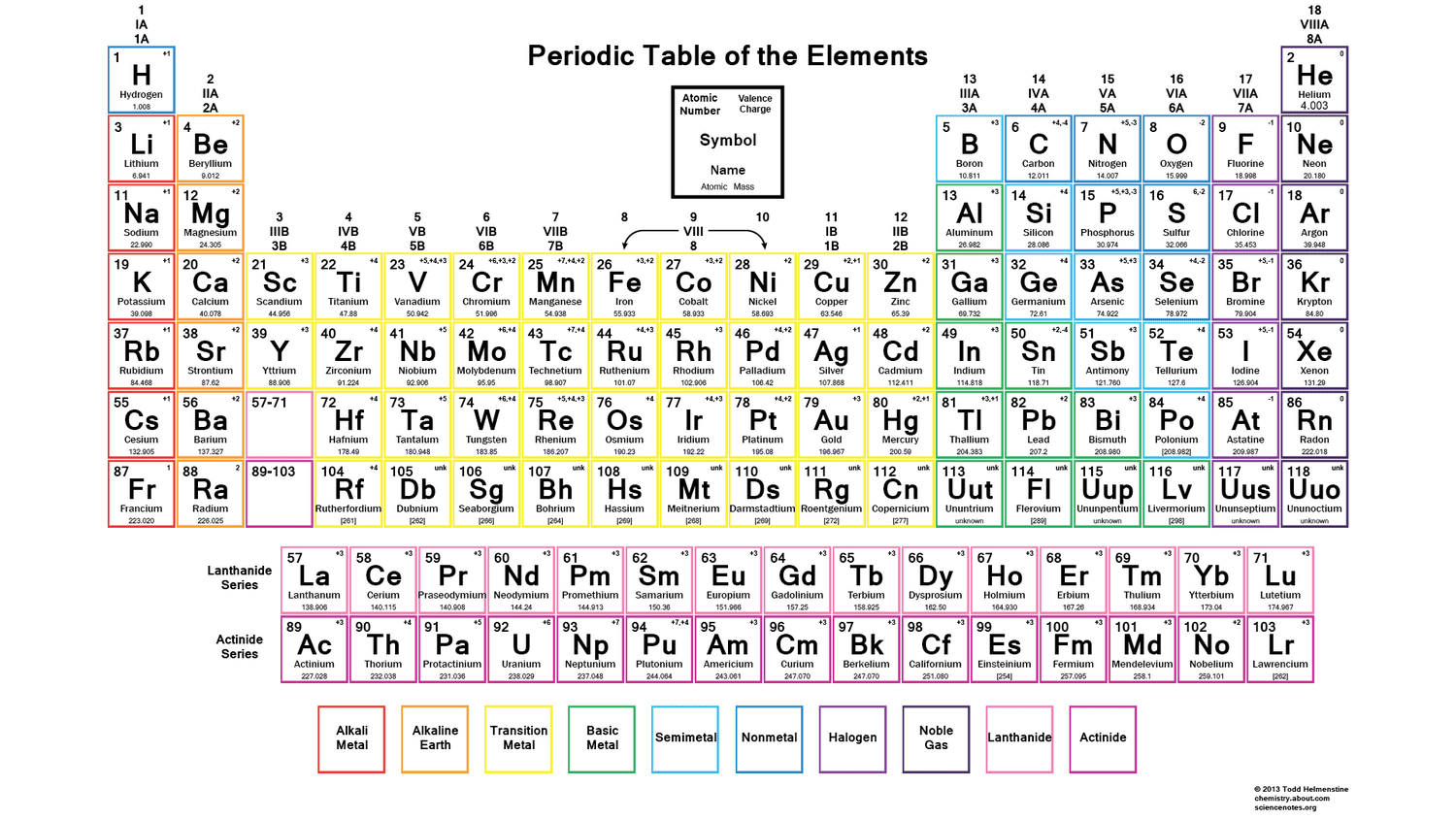
Some elements have multiple ions written in their box. Which ion do you write down?
The first one.
What is an allotrope?
Different versions of the same element
What do multiple allotropes of the same element have in common?
The atomic number. Everything else about them is different
What are the allotropes we need to know about Oxygen?
O2 (what we breathe) and O3 (in the Ozone Layer)
What are the allotropes we need to know about Carbon?
Coal, graphite, and diamonds. All are made of pure carbon
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have high/low electronegativity.
low electronegativity.
They want to get rid of electrons, not gain one
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have high/low electronegativity.
high electronegativity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals only form positive/negative ions.
positive ions.
This is because they lose their valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals only form positive/negative ions. Why?
negative ions.
This is because they gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. They have a high number of valence electrons and a high electronegativity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have a high/low conduction of heat and electricity.
high conduction of heat and electricity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have a high/low conduction of heat and electricity.
low conduction of heat and electricity.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have high/low ionization energy.
low ionization energy.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have high/low ionization energy.
high ionization energy.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals are ductile and malleable/brittle.
ductile and malleable.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals are ductile and malleable/brittle.
brittle.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals have high/low densities, melting points, and boiling points.
high densities, melting points, and boiling points
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals have high/low densities, melting points, and boiling points.
low densities, melting points, and boiling points.
Metals vs nonmetals
All metals are solids but…
Mercury.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals are lustrous/not lustrous.
lustrous.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals are lustrous/not lustrous.
not lustrous.
Metals vs nonmetals
Metals will/will not react with acid to produce hydrogen
will react.
Metals vs nonmetals
Nonmetals will/will not react with acid to produce hydrogen.
will not react.
A trend going down is…
opposite of going across
Which one decreases across a period and increases down a group - metallic character or electronegativity?
Metallic character
Which one increases across a period and decreases down a group - metallic character or electronegativity?
Electronegativity
Which one decreases across a period and increases down a group - ionization energy or atomic radius?
Atomic radius
Which one increases across a period and decreases down a group - ionization energy or atomic radius?
Ionization energy
Reactivity increases down which group of metals: groups 1-2 or group 17?
Groups 1-2
Reactivity decreases down which group of metals: groups 1-2 or group 17?
Group 17
What is electronegativity?
It determines what kind of bond you get. Measures how much an element “wants” an electron. Measurement: .9 - 4.0 (low-high).
Which one has the highest electronegativity: 2-8-8-1 or 2-7-8?
2-7-8
The more reactive an element gets, the more/less electronegativity it gets.
Ex: F, the most reactive.
more
What is ionization energy?
The amount of energy needed to remove an element’s most loosely bound valence electron.
It decreases down a group because valence electrons are further away from the positive nucleus that they are attracted to, making them easier to remove. They are also shielded by the inner electrons.
It increases across a period because the number of valence electrons increases, resulting in greater attraction to the nucleus, so electrons are harder to remove.
What is atomic radius?
The size of an atom.
It increases when going down a group because there are more energy shells.
It decreases across a period because of increased nuclear charge. The nucleus pulls the electrons in.
Iron has a melting point of 1538oC and a boiling point of 2862oC. Its current temperature is 25oC. What is the property of matter of the iron?
Solid
Iron has a melting point of 1538oC and a boiling point of 2862oC. Its current temperature is 2000oC. What is the property of matter of the iron?
Liquid
Iron has a melting point of 1538oC and a boiling point of 2862oC. Its current temperature is 3000oC. What is the property of matter of the iron?
Gas