Medical Mycology: Diagnostic and Detection Methods
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Morphology
structure
Biochemistry
using certain elements of the fungus to find the fungus
Genetics
using specific genes of the fungus and comparing it to the infection to detect the fungus
Serology
Detecting the antibodies and antigen to find the fungus
Microscopy (positives)
First crucial, first line procedure to detect the fungal elements
Is rapid, useful, and effective
Gives preliminary info: yeast or mold
Microscopy (Negatives)
less sensitivity
false negatives
Limited info on extra morphological features
Culturing (Positives)
useful info on structures not seen on specimen (morphological keys)
Culturing (Negatives)
Time constraints (2-10 days)
Possible contaminations
False positives
Chance of non-sporulating cultures
Assimilation Tests
Use a small strips that has different substrates
The fungus will react to them producing products which give off color
The color combinations can identify the fungus
Antigen Test
Direct measurement of current disease activity
Latex Agglutination
Antigen test
Qualitative
Latex particles are coated with antibodies specific to that fungi
Take samples from the patient
When the fungus’ antigen interacts with the anti-bodies it causes clumping (agglutination)
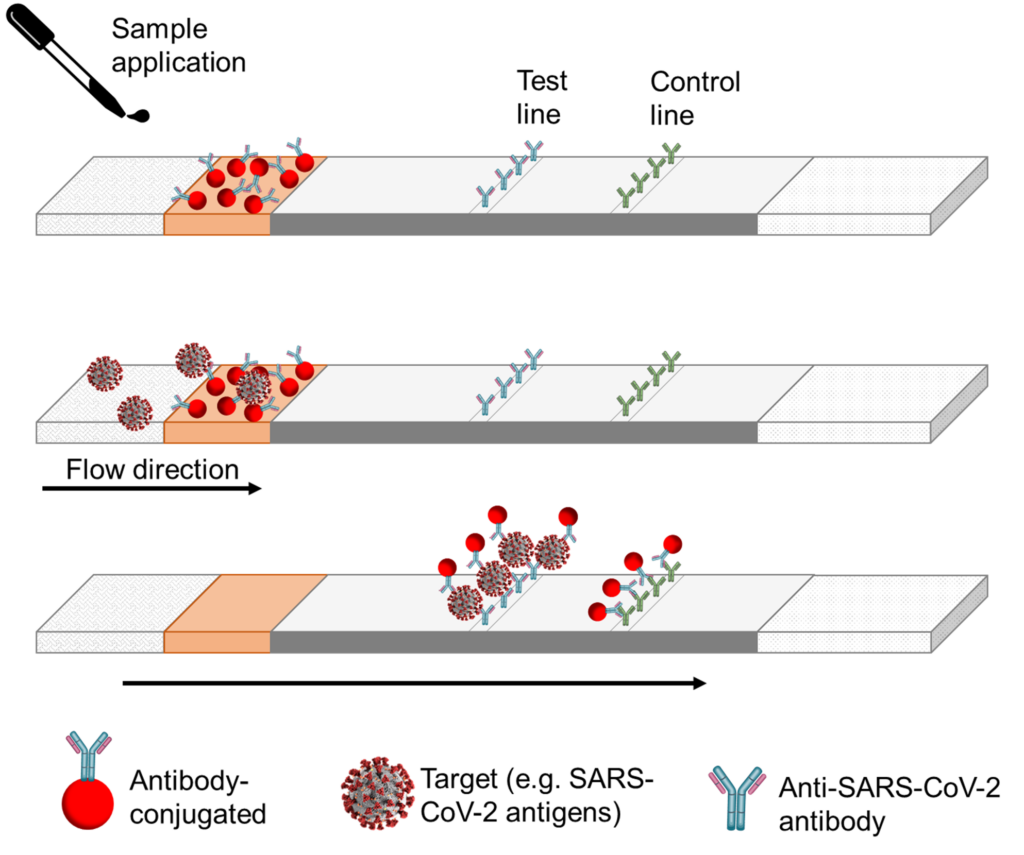
Lateral Flow Assay
Antigen test
Qualitative
Like a pregnancy test
Apply the patient sample to a strip and on that part of the strip are antibodies-conjugated
Then there is flow direction (capillary action)
As it flows, it will interact with a test line (anti-bodies), causing a color reaction if the antigen is present
Leftover antigen with interact with the test line causing it to light up too
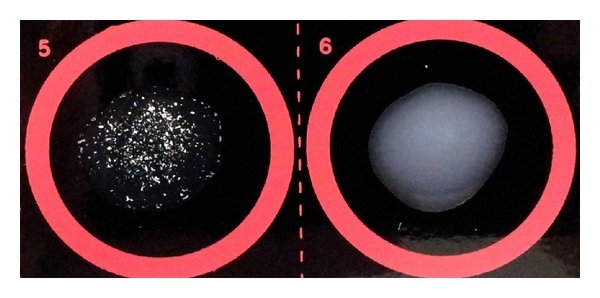
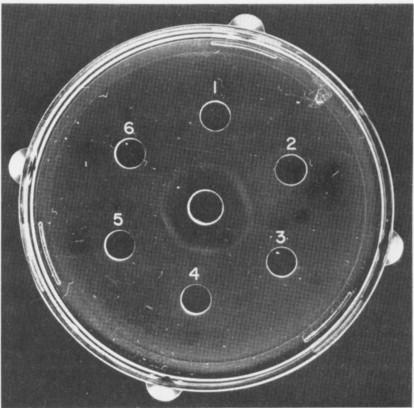
Immunodiffusion Assay
Antigen test
Quantative
Add patient serum to the hole
The serum will diffuse out
If it’s positive, it will cause rings to form
Thicker rings, mean higher concentration
Antibody Detection (titer)
A measure of how much a sample can be diluted before antibodies cannot be detected
A fourfold rise in the anti-body titer=positive
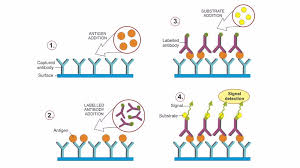
ELISA Test (Enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay
Antibody test
Quantitive and Qualitative
Antibodies are spread onto a micro titer plate, and antigen is added
Then a labeled antibody is added and will bind to the antigen if present
A substrate is added and will cause a color reaction if antigen is present
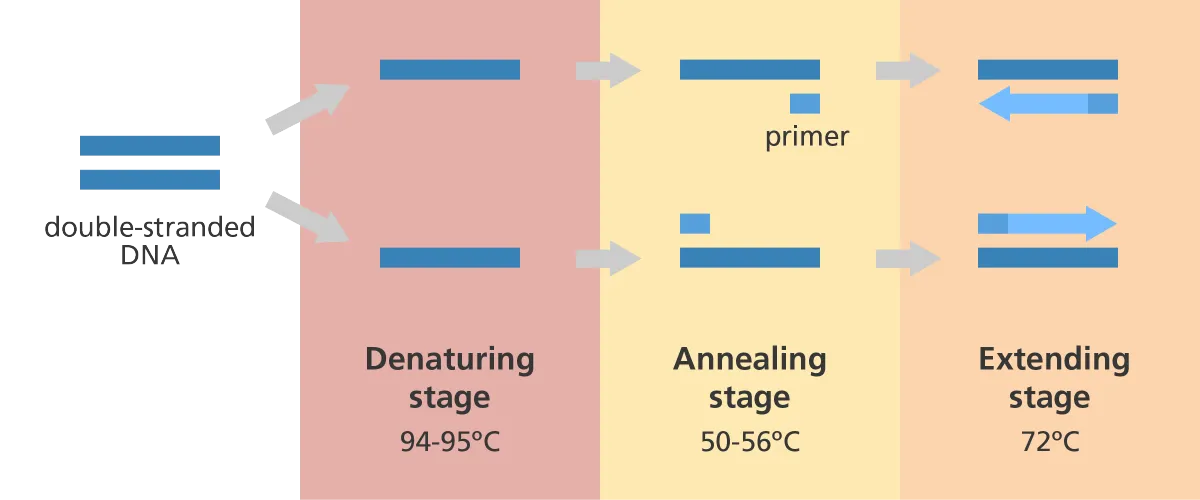
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Denaturing~occurs at 95 degrees, separating the strands
Annealing~occurs at 55 degrees causing primer to attach to separated strands
Extension~occurs at 72 degrees, synthesizing a new strand with the primers
Prevalence of Disease Formula
(Total Disease/total)*100
Sensitivity
Refers to a test’s ability to designate an individual with the disease as positive
High Sensitivity
Fewer false negatives, and less missed diseases
Specificity
The percentage of true negatives out of all subjects who do not have the disease
High Specificity
Less false positives
Sensitivity formula
(True positives)/(True positives+false positives)
Specificity Formula
(True negatives)/(True negatives+False positives)