Chpt 5 - Electricity in the home
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
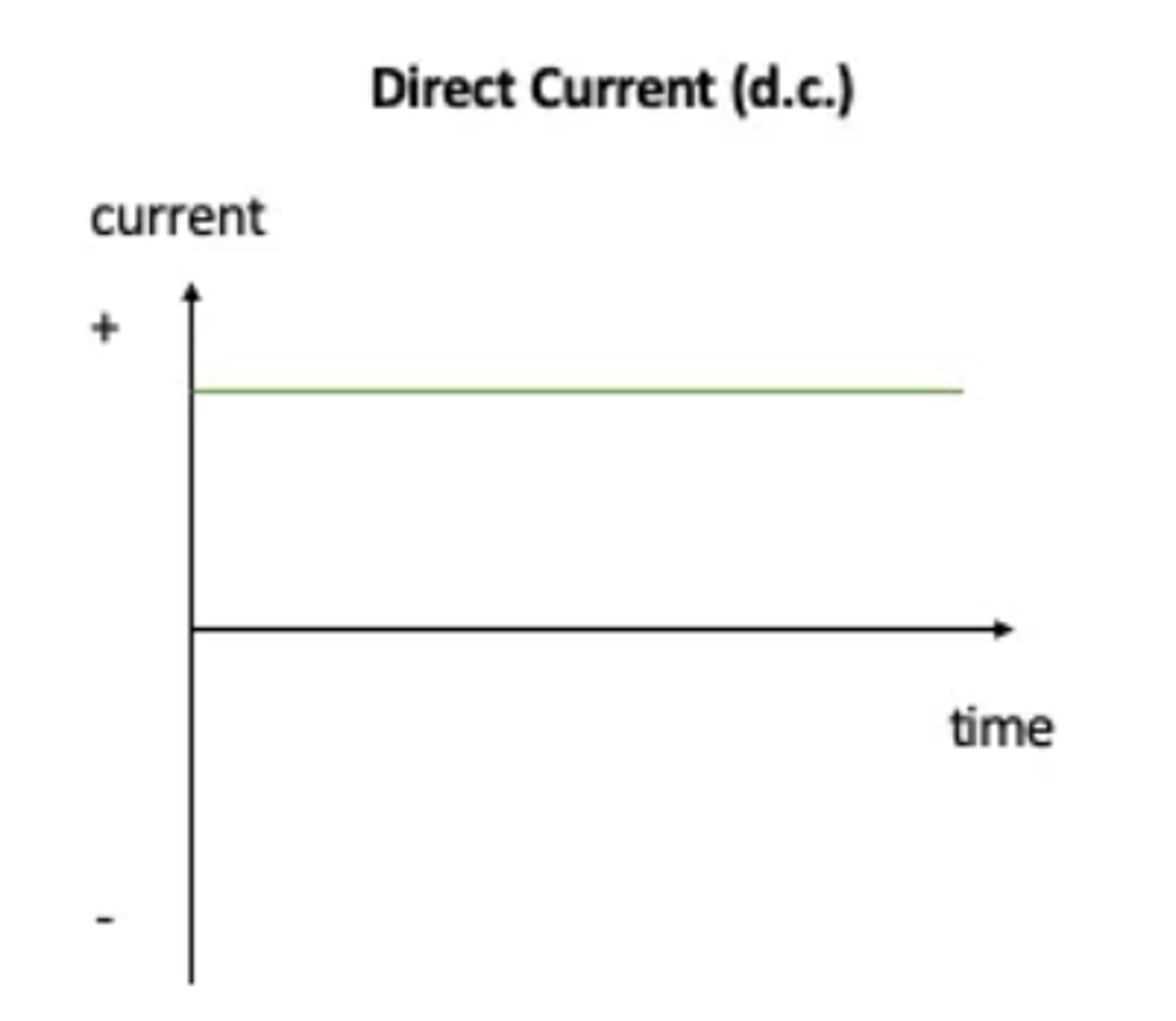
What is direct current (d.c.)?
A current that always flows in one direction. It is the current found in circuits powered by a cell or battery.
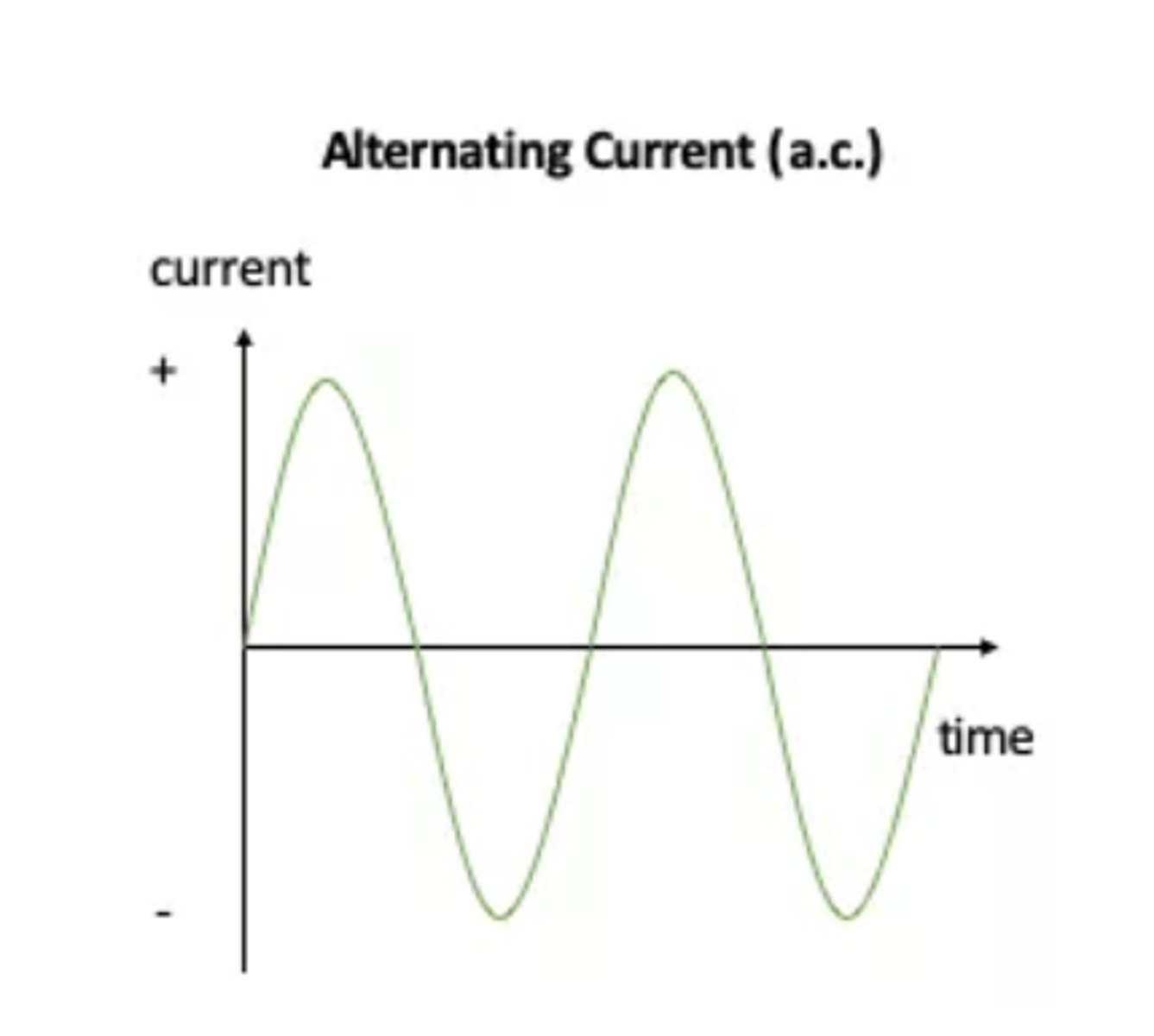
What is alternating current (a.c.)?
When electricity flows in alternate directions back and forth in a circuit due to an alternating potential difference. Found in mains electricity
Name the 3 wires in a plug
- Live
- Neutral
- Earth
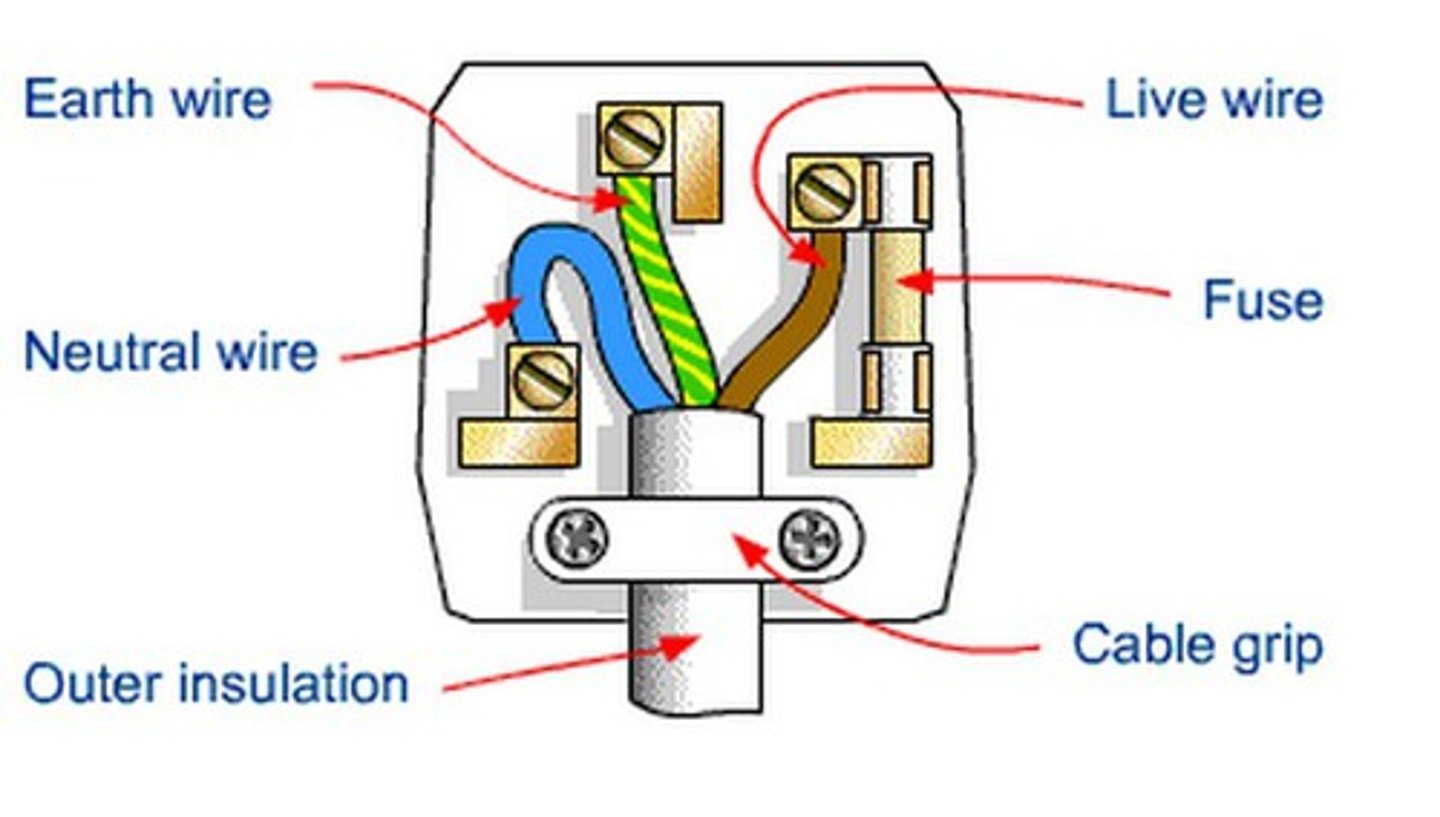
What is the live wire?
Carries alternating potential difference from the supply. It is brown
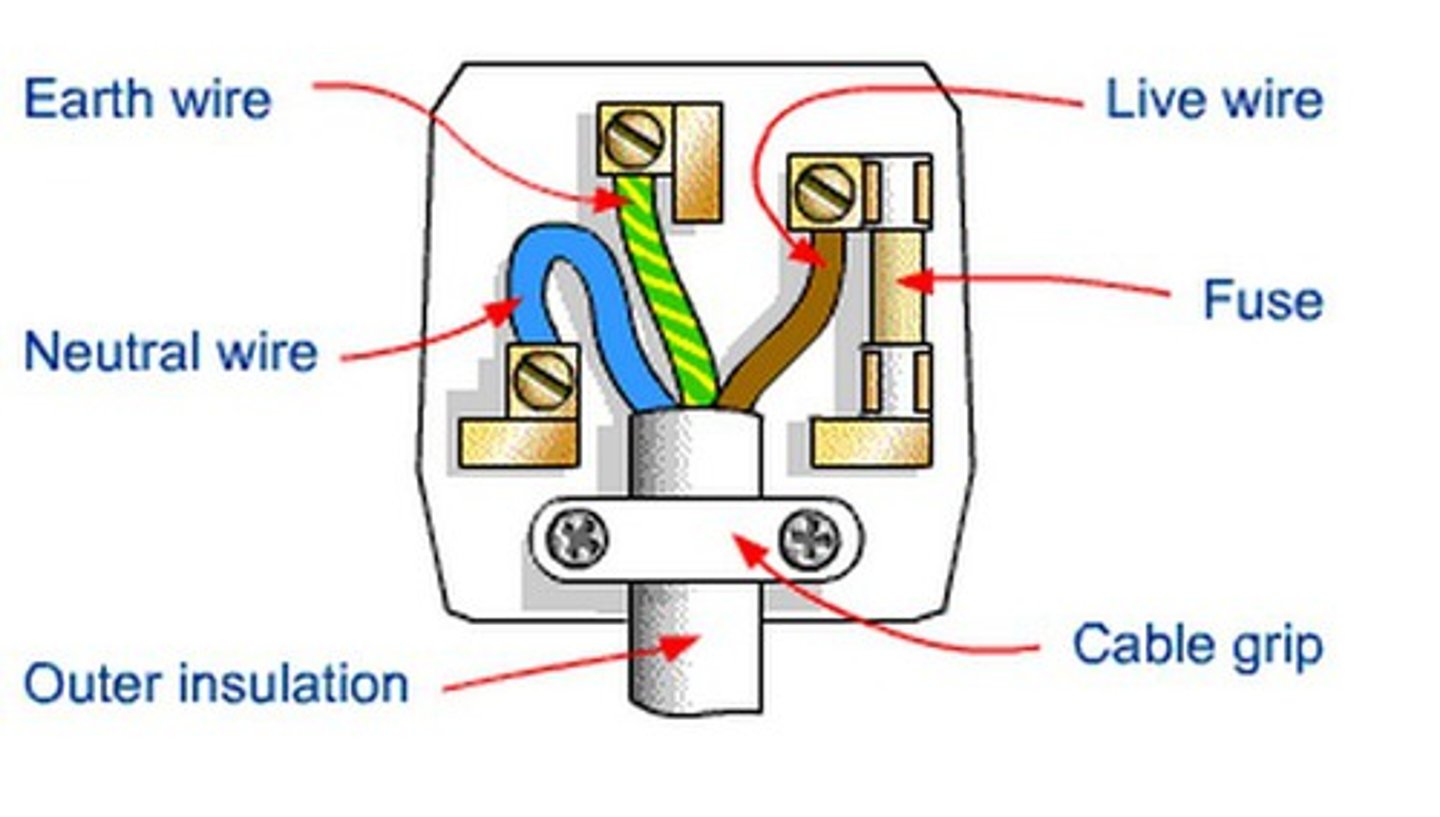
What is the neutral wire?
Completes the circuit and carries current away from the appliance (0v). It is blue
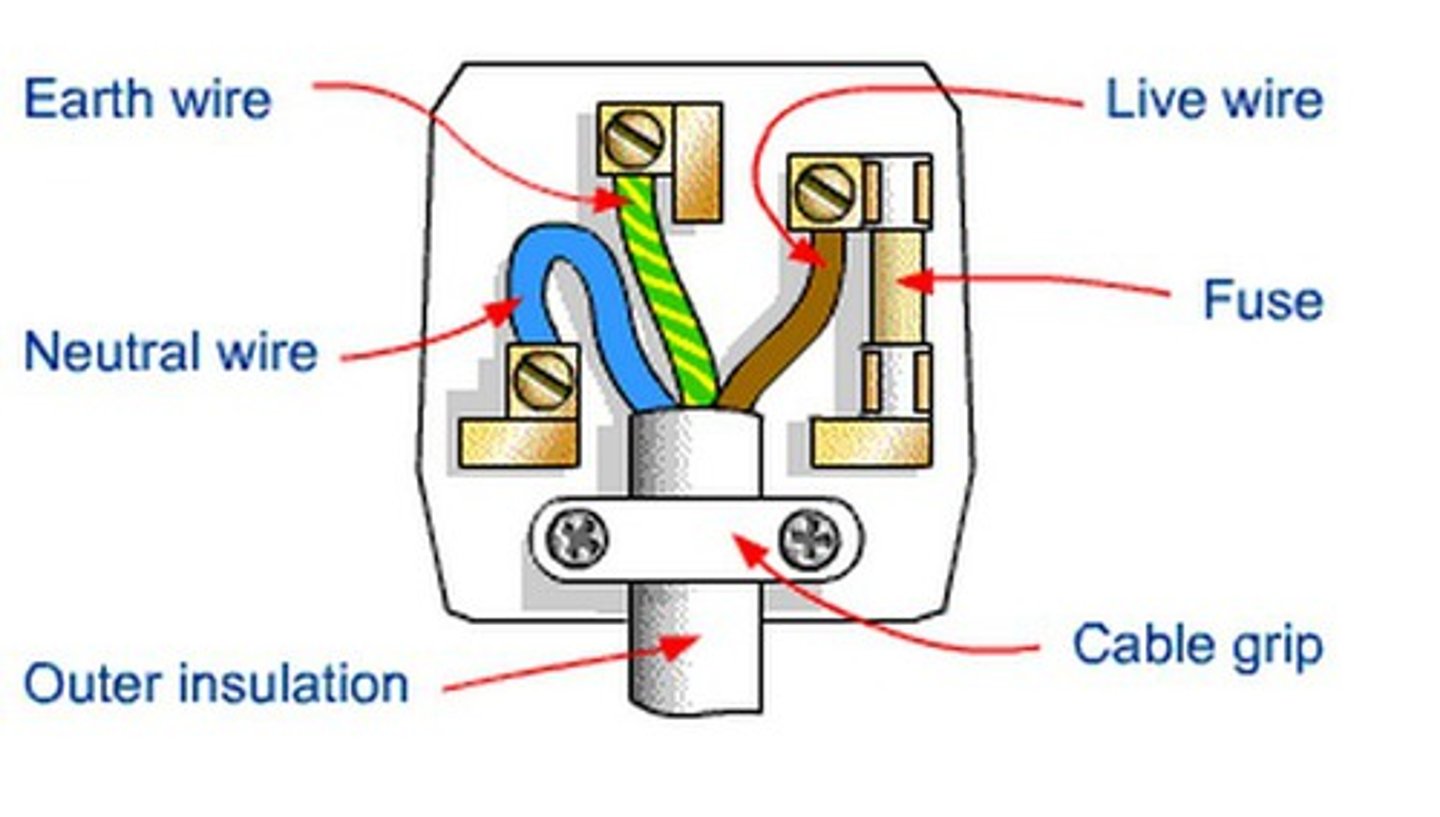
What is the earth wire?
- green and yellow
- works with fuse to prevent fires and shocks
- used for safety
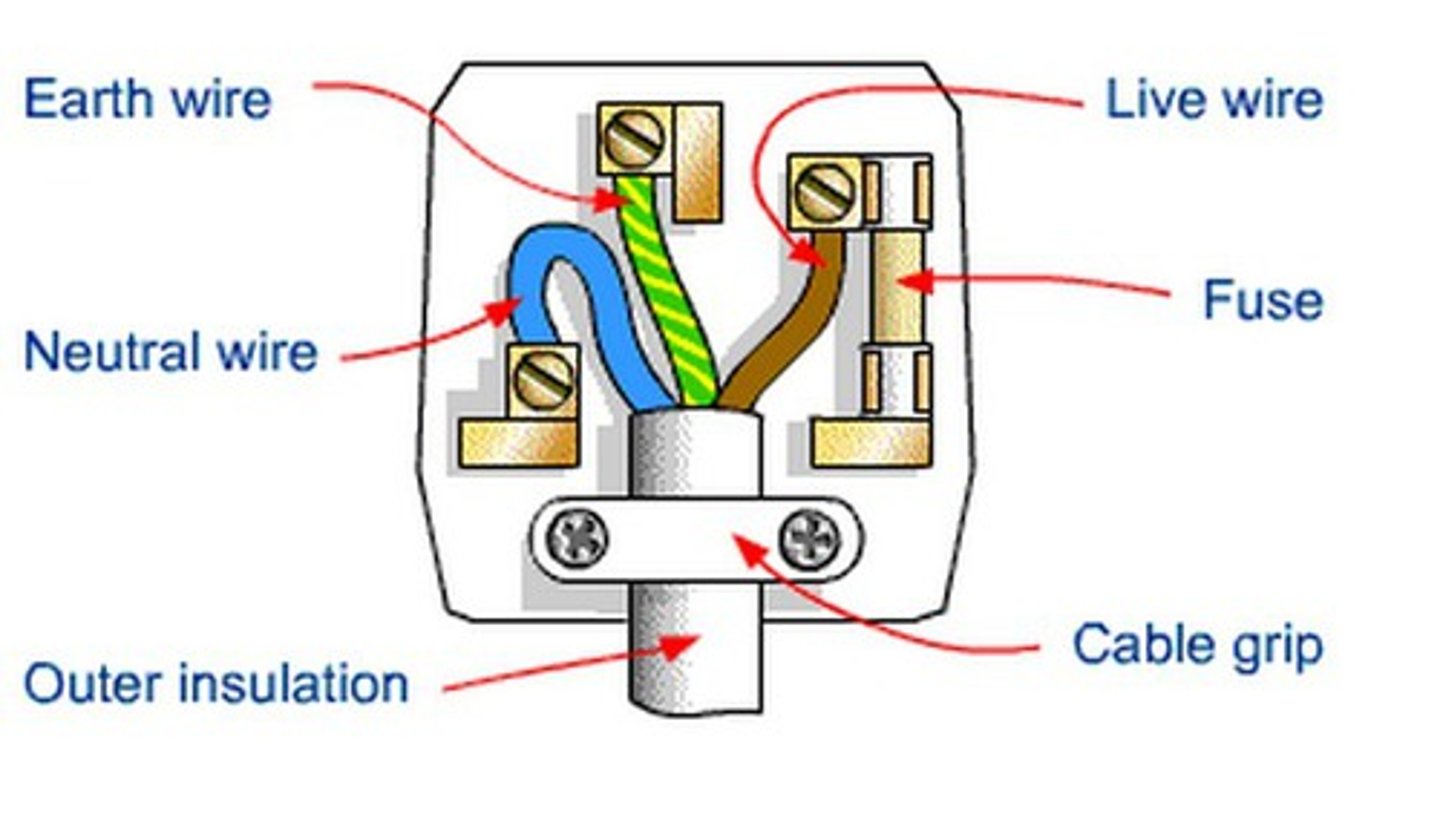
What is a short circuit?
A connection that allows current to take the path of least resistance
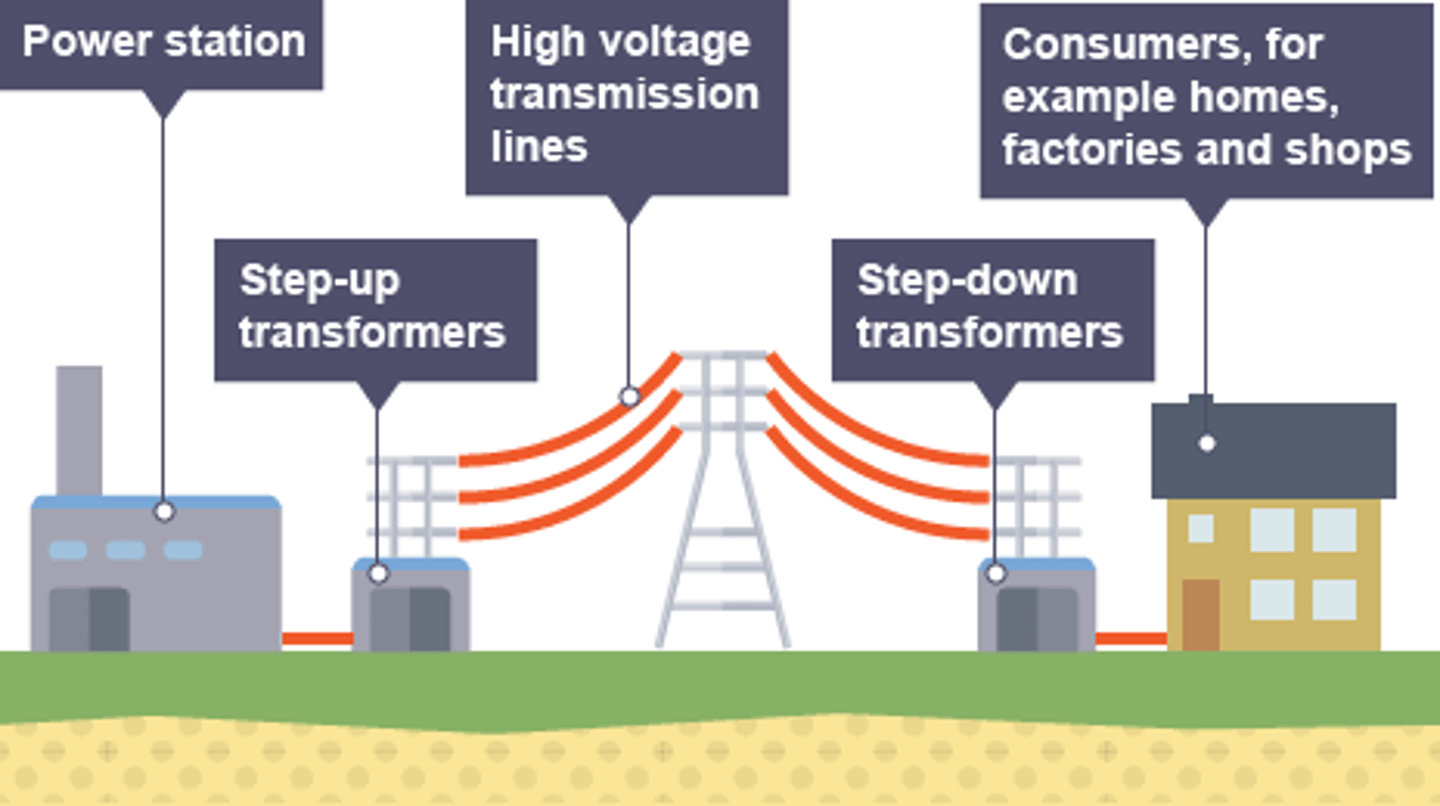
What is the National Grid?
A giant system of cables and transformers that covers the UK and connects power stations to consumers
What is the potential difference of the National Grid?
230V
What is the frequency of the National Grid?
50Hz
What is a transformer?
A device that increases or decreases the voltage of alternating current
Why is the potential difference stepped up to 40000V before it transfers through cables in the National Grid?
High potential difference means current is low. Due to low current, wires heat up less and less energy is wasted
Why is the potential difference stepped down back to 230V before it enters buildings?
So it can enter buildings at a safe potential difference. Plugs in the UK are only designed to transfer electricity at 230V and 50Hz. Anything higher than that, it would be very dangerous and could cause electrical fires.
Equations for power
power = current x potential difference
or
power = current² x resistance
Equation for charge flow
Charge flow = current x time
Equation for energy transferred to an electrical appliance
Energy transferred = charge flow x potential difference
Equation for energy transferred by an electrical appliance
Energy transferred = power x time