Art History 1001 Exam #1
5.0(1)Studied by 30 people
Card Sorting
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:49 AM on 10/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
Paleolithic
The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. It predates the Neolithic period.

2
New cards
Neolithic
The period of the Stone Age associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution. It follows the Paleolithic period.
3
New cards
Megalithic
A large stone used in some prehistoric architecture

4
New cards
radiocarbon dating
a chemical analysis used to determine the age of organic materials based on the amount of carbon-14 present
5
New cards
adobe
sun-dried mud brick

6
New cards
register
a horizontal band, often on top of another, that tells a narrative story
7
New cards
votive
an offering in accordance with a vow or prayer

8
New cards
hierarchy of scale
a system of representation that expresses a person's importance by the size of his or her representation in a work of art
9
New cards
Stele
A carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events.

10
New cards
Ziggurat
massive pyramidal stepped tower made of mudbricks. It is associated with religious complexes in ancient Mesopotamian cities, but its function is unknown.
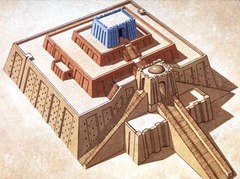
11
New cards
Heiroglyph
the Egyptian way of writing using symbols

12
New cards
Necropolis
A large ancient cemetery
13
New cards
Mastaba
An ancient Egyptian tomb with sloped sides and a flat roof. Has an underground burial chamber with rooms above it filled with offerings.

14
New cards
Ka
A statue of a human or gods spirit that survived with the soul

15
New cards
Serdab
An ancient Egyptian tomb that served as a chamber for the Ka statues.
16
New cards
Stepped pyramid
a pyramid consisting of several rectangular structures placed on top of one another

17
New cards
Sarcophagus
a stone coffin, typically adorned with a sculpture or inscription and associated with the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Rome, and Greece.
18
New cards
Obelisk
a stone pillar, typically having a square or rectangular cross section and a pyramidal top, set up as a monument or landmark.
19
New cards
Book of the Dead
Ancient Egyptian funerary text written on papyrus (new kingdom)
20
New cards
material culture
tangible, physical items produced and used by members of a specific culture group and reflective of their traditions, lifestyles, and technologies
21
New cards
Zoomorphic
having or representing animal forms or gods in animal form
22
New cards
Dogu
Small human figurines made in Japan during the Jomon period. Shaped from clay, the figures have exaggerated expressions and are in contorted poses. They were probably used in religious rituals.
23
New cards
Fang ding
a square or rectangular bronze vessel with four legs; used for ritual offerings in ancient China during the Shang dynasty
24
New cards
Taotie
a mask with a dragon or animal-like face common as a decorative motif in Chinese art
25
New cards
corbeled roof
a roof made of stone slabs that progressively overlap to create a door opening

26
New cards
Tholos
A temple with a circular plan. Also, the burial chamber of a tholos tomb.
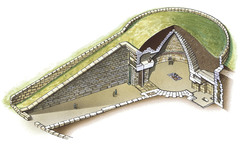
27
New cards
fresco
the technique of painting on dry plaster with pigments mixed in water.

28
New cards
incised
carving or engraving
29
New cards
relief
a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material to make it look raised
30
New cards
low relief
sculpted relief with figures that project only slightly from the background
31
New cards
high relief
a sculptural relief in which forms extend out from the background quite a bit
32
New cards
sanctuary
A place of protection
33
New cards
peristyle
a colonnade surrounding a building or enclosing a courtyard
34
New cards
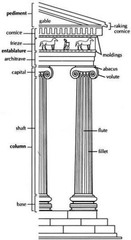
stylobate
a continuous base supporting a row of columns in classical Greek architecture.
35
New cards
Cella
the main room of a temple where the god is housed
36
New cards
Enstasis
the slight convex bulge given to a column to offset the optical illusion that it is thinner in the middle
37
New cards
metope
a square space between triglyphs in a Doric frieze.

38
New cards
Capital
top of a column
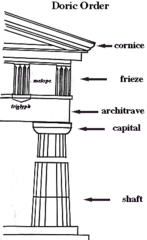
39
New cards
lost-wax casting
a method of casting metal by a process in which a wax mold covered with clay and fired, leaves a hollow form for metal molds to be made

40
New cards
Doric
Greek architectural order, simple and masculine. Metopes in frieze. Used on exterior of Parthenon
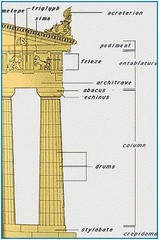
41
New cards
Ionic
Greek architectural order, More feminine and delicate. Scrolls on the capitals
Used on inner frieze of Parthenon
Used on inner frieze of Parthenon
42
New cards
Corinthian
Greek architectural order. Acanthus leaves on capitals. Used most often by the Romans.

43
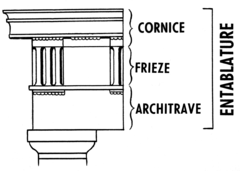
New cards
Frieze
ornamental band on a wall
44
New cards
Pediment
the triangular top of a temple that contains sculpture

45
New cards
Archaic smile
The smile that appears on all Archaic Greek statues from about 570 to 480 BCE. The smile is the Archaic sculptor's way of indicating that the person portrayed is alive.

46
New cards
Karyatid
sculpture of human figure used as architectural support

47
New cards
Krater
An ancient Greek wide-mouthed bowl for mixing wine and water.

48
New cards
Agora
the marketplace in ancient Greece
49
New cards
Contrapposto
A style of Greek sculpture where people are depicted standing and leaning so that the person's weight is being put on one side. People are depicted with their bodies curved like an "S"

50
New cards
Canon of Polykleitos
The renowned Greek sculptor Polykleitos designed a sculptural work as a demonstration of his written treatise, entitled the "Kanon" (or Canon, translated as "measure" or "rule"), exemplifying what he considered to be the perfectly harmonious and balanced proportions of the human body in the sculpted form.

51
New cards
wet drapery
sculpture carvings that appear to cling to the body as if it was wet.

52
New cards
Gigantomachy
In ancient Greek mythology, the battle between gods and giants.

53
New cards
Woman of Willendorf
- Austria, 24,000 BCE
- Made out of limestone
- Symbol of fertility
- Made out of limestone
- Symbol of fertility

54
New cards
Royal Standard of Ur
- A hollow wooden box with cuneiform writing
- Iraq, 2500 BCE
- Sumerian
- inlaid with a mosaic of shell, red limestone and lapis lazuli
- Iraq, 2500 BCE
- Sumerian
- inlaid with a mosaic of shell, red limestone and lapis lazuli

55
New cards
Palette of Narmer
- earliest surviving ancient Egyptian artwork
- shows the unification of Egypt after a great war
- Egypt, 3000 BCE
- shows the unification of Egypt after a great war
- Egypt, 3000 BCE

56
New cards
Law Stele of Hammurabi
- Babylon, 1760 BCE
- Babylonian
- Where all of the laws were written
- Babylonian
- Where all of the laws were written

57
New cards
Ishtar Gate
- The entrance gate into Babylon. It was built by Nebuchadnezzar.
- Babylon, 600 BCE
- lions, dragons, bulls
- Babylon, 600 BCE
- lions, dragons, bulls

58
New cards
Colossal Statue of Akhenaten
- Thebes, Egypt, 1350 BCE
- represents the 18th dynasty pharoah
- androgyny
- crook and flail
- resembles Osiris mummy statues
- represents the 18th dynasty pharoah
- androgyny
- crook and flail
- resembles Osiris mummy statues

59
New cards
Last Judgment before Osiris, Book of the Dead
- Egypt, 1275 BCE
- 19th dynasty new kingdom
- Drawings and painting on papyrus scroll
- 19th dynasty new kingdom
- Drawings and painting on papyrus scroll

60
New cards
Rack of Bells
- Marquis Yi, China, 450 BCE
- In the late Bronze Age
- rang different notes according to size
- ritual and sacred music/use
- In the late Bronze Age
- rang different notes according to size
- ritual and sacred music/use

61
New cards
Terra Cotta Army
- A group over 8000 clay soldiers with weapons, wagons, etc. built on Emperor Qin's order to guard his tomb in the afterlife.
- China, 210 BCE
- China, 210 BCE

62
New cards
Light Well in the Palace of Knossos
- Crete, 1600 BCE
- Minoan, 16th century
- open shafts that run the full height of a building, designed to bring light and fresh air into the interior of Minoan palaces and other large buildings
- Minoan, 16th century
- open shafts that run the full height of a building, designed to bring light and fresh air into the interior of Minoan palaces and other large buildings

63
New cards
La Venta Throne
- Olmec, 800 BCE
-high relief figure seated in a niche
-motifs
-likely to have expressed the idea of a cave to the underworld
-high relief figure seated in a niche
-motifs
-likely to have expressed the idea of a cave to the underworld

64
New cards
Iktinos and Kallikrates
- Architects of the Parthenon
- Parthenon, Athens, 440 BCE
- Athens, Greece
- Parthenon, Athens, 440 BCE
- Athens, Greece

65
New cards
Polykleitos, Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
- 450 BCE
- Classical period
- Artist/Architect: Polykleitos
- Pompeii, Italy
- depicts human movement; Imposes Polykleitan style: to perfect human movement, harmonic proportions, cross balance
- idealistic, detailed, perfect
- Classical period
- Artist/Architect: Polykleitos
- Pompeii, Italy
- depicts human movement; Imposes Polykleitan style: to perfect human movement, harmonic proportions, cross balance
- idealistic, detailed, perfect

66
New cards
Winged Victory (Nike)
- Samothrace, Greece, 200 BCE
- Hellenistic period, baroque art
- sculpted by Pythokritos of Rhodes
- Hellenistic period, baroque art
- sculpted by Pythokritos of Rhodes

67
New cards
Kouros
Greek word for "male youth." An Archaic Greek statue of a standing, nude youth.
68
New cards
Kore
an archaic Greek statue of a young woman, standing and clothed in long loose robes.