Week 12 - UEA Anatomy & Duplex Exam
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
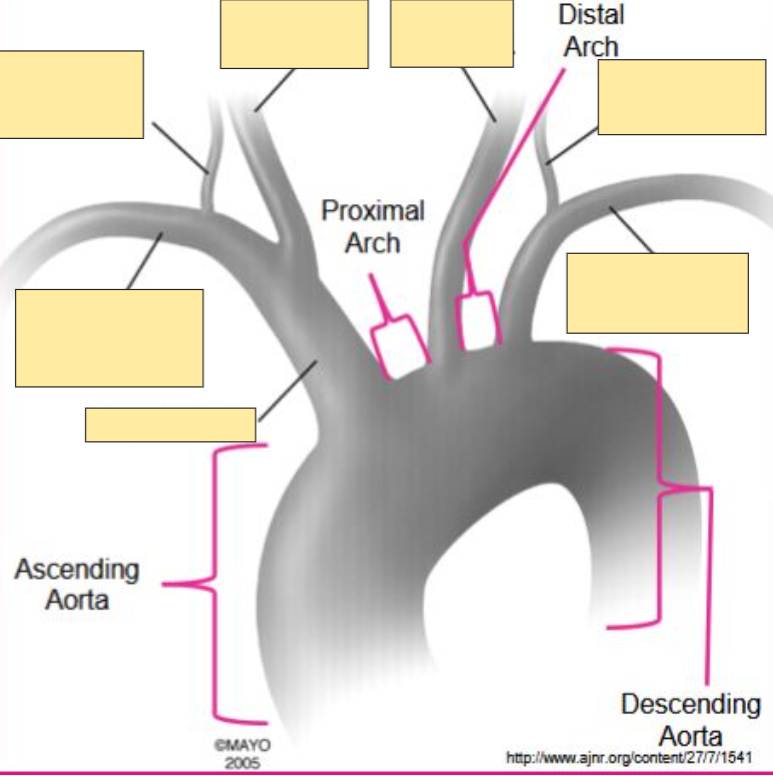
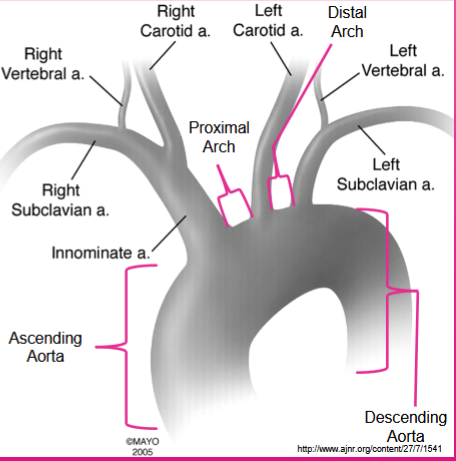
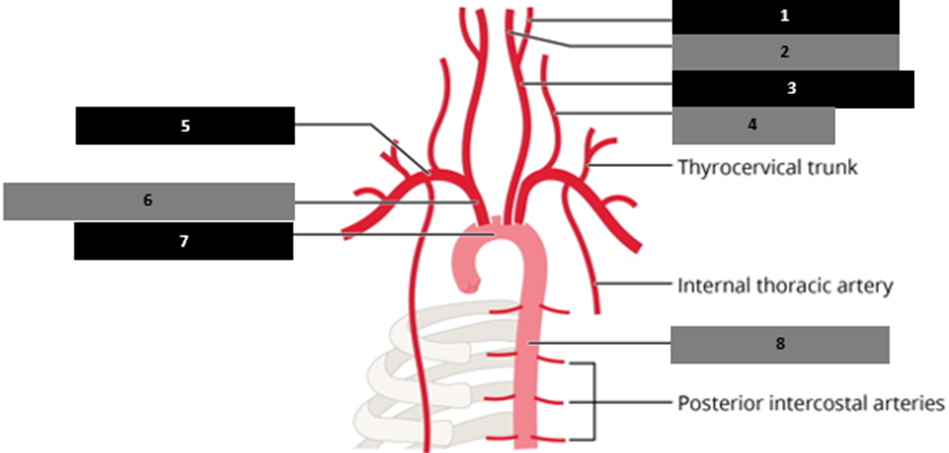
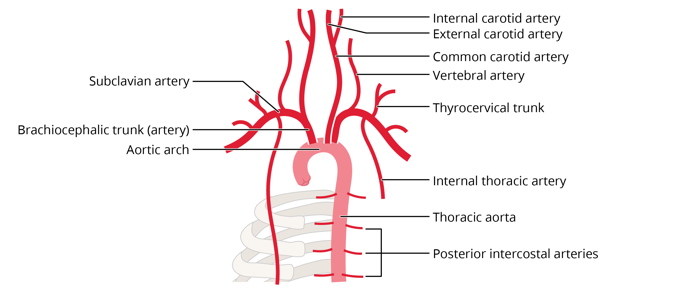
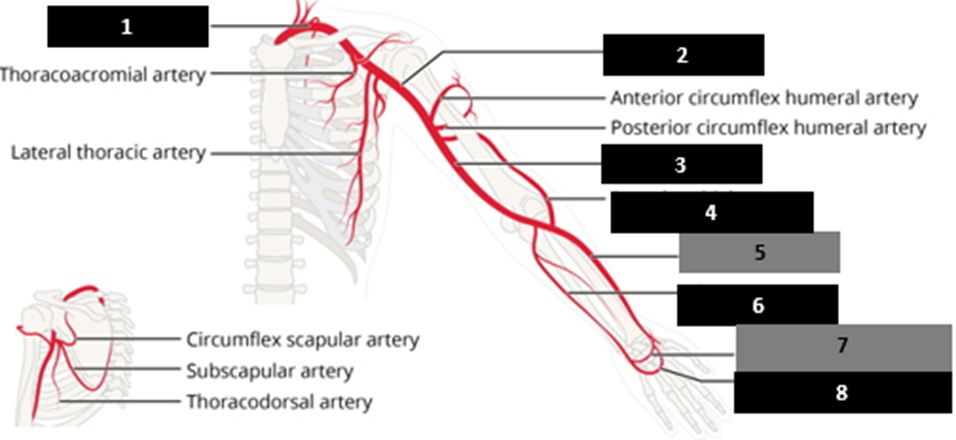
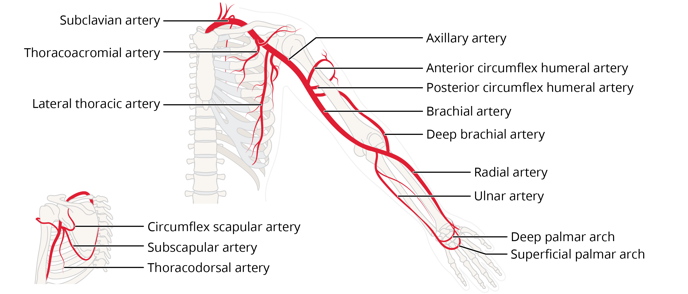
What differentiates the axillary from the subclavian artery?
first rib
muscular border
pectoralis minor
teres major
When does the brachial artery bifurcate into the radial and ulnar arteries?
at the cubital (antecubital) fossa
What area does the radial artery perfuse?
posterolateral aspect of the forearm
What area does the ulnar artery perfuse?
anteromedial aspect of the forearm
Describe the course of the radial artery
passes into the flexor muscles of rhe forearm
becomes more superficial at the wrist & bifurcates
superficial branch: anterior to the thumb
feeds the superficial palmar arch
main deep branch: posterior to the thumb
feeds the deep palmar arch
Describe the course of the ulnar artery
courses deep to the hook of the hamete (carpal bone where the wrist meets the hand)
terminates into the superficial palmar arch
gives rise to the interosseous arteries: supply deep forearm structures
anterior
posterior
rarely, continues to the wrist as the median artery
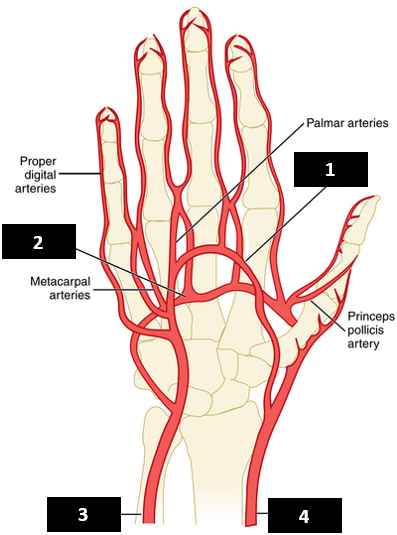
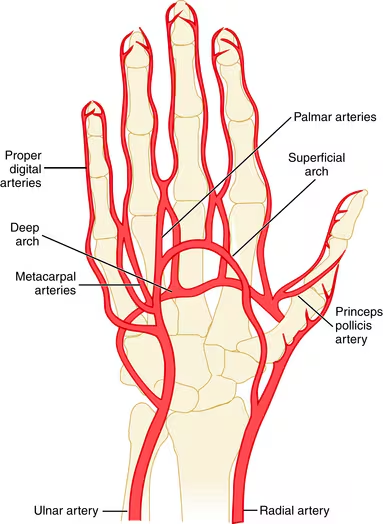
The superficial palmar arch is mainly supplied by the ________ artery.
ulnar
The deep palmar arch is mainly supplied by the ________ artery.
radial
Anatomical positioning of the hand
palm forward, back of hand facing towards me
UEA Duplex Indications
absent peripheral pulses
abnormal arterial arm pressures
BP Difference >20 mmHg
TOS symptoms
cold sensitivity
digital cyanosis
raynaud’s syndrome
bruit
claudication
rest pain
extremity ulcer
gangrene
trauma to an artery (iatrogenic or incidental)
arterial aneurysm
known hx of PAD
BPG
preprocedural assessment
postoperative assessment
pulsatile mass
rubor
palpable thrill
marked temperature difference between the hands/fingers
Where do arterial ulcers typically occur at in the upper extremity?
at the fingertips
If a patient is experiencing UE claudication, what are the typical associated activities?
exercise
typing
writing
6 P’s of acute limb ischemia
pain
pulselessness
pallor
paresthesia
paralysis
perishingly cold
Abnormal PSV ratio
>/= 2.1 indicates a >50% (hemodynmically significant) stenosis
diagnostic criteria for UEA stenosis
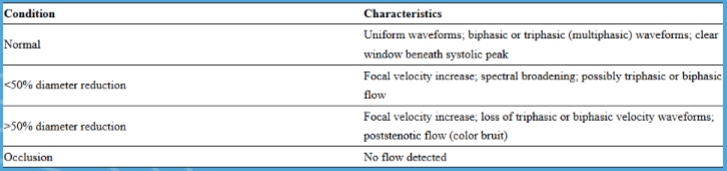
How to calculate the PSV ratio
PSV @ stenosis / PSV pre-stenosis