5.1- Introduction to Health Psychology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Health Psychology
The subfield of psychology concerned with ways psychological factors influence the causes and treatment of physical illness and the maintenance of health
Stress
The process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors, that we appraise as threatening or challenging
Hypertension
High blood pressure
Immune Suppression
A weakening of the body's ability to fight disease
Stressor
Anything that causes stress
Eustress
Positive stress
Distress
Negative stress
Adverse Childhood Experiences
Traumatic events occurring before age 18 that can have negative, lasting effects on health and well-being
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
A three-stage physiological response that appears regardless of the stressor that is encountered
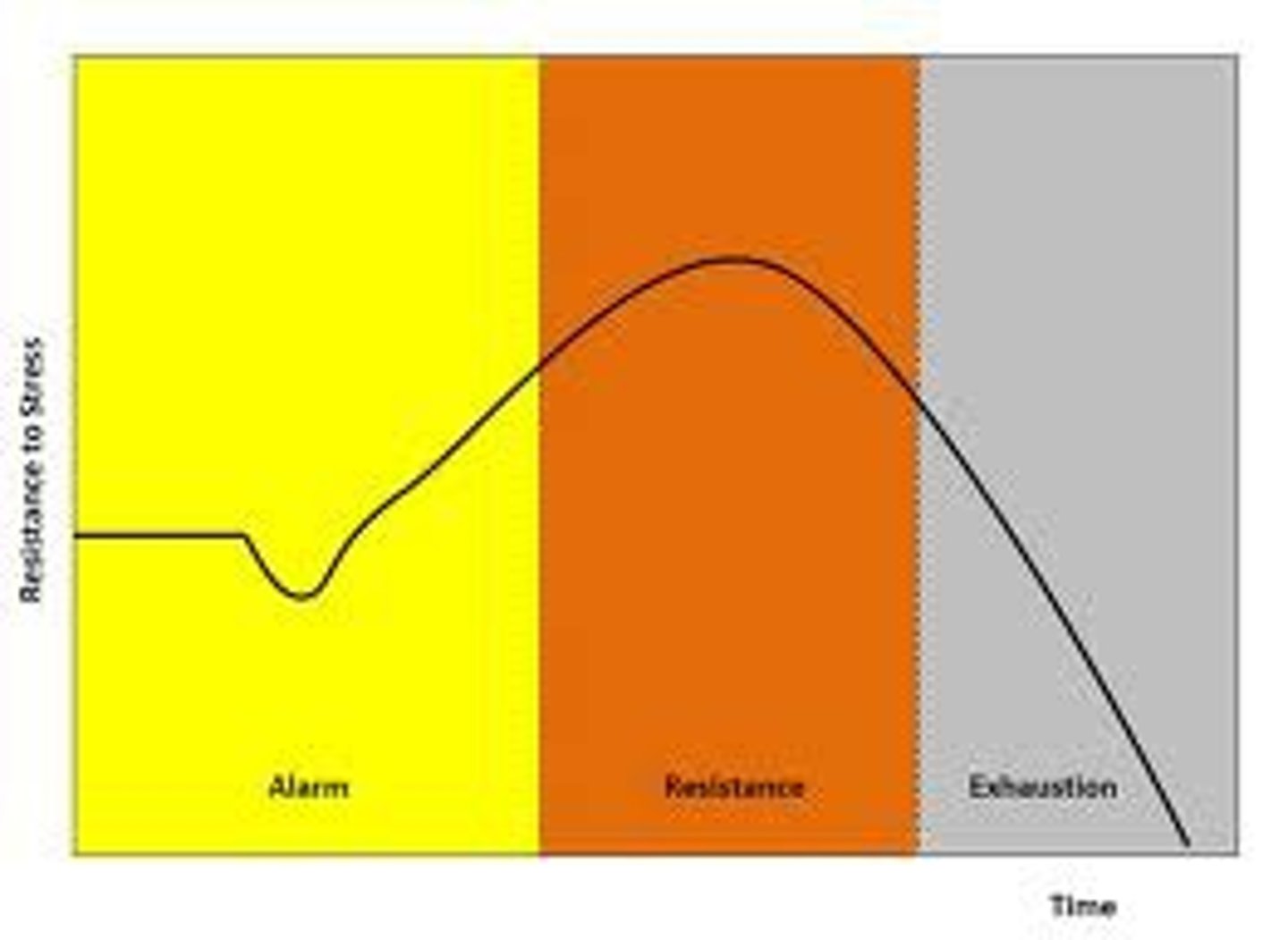
Alarm Reaction Phase
The first step in GAS, where your sympathetic nervous system is suddenly activated
Resistance Phase
Second phase of the GAS, during which the body adapts to and maintains resources to cope with the stressor.
Fight-Flight-Freeze Response
An involuntary, physical response to a sudden and immediate threat (or stressor) in readiness for fight (confront), flight (escape) or freeze (avoid detection)
Exhaustion Phase
The third stage of GAS in which stress continues beyond the body's ability to adapt, leading to potential physiological and structural breakdown
Tend-and-Befriend Theory
A theory that suggests people seek social support and tend to others in times of stress (especially women)
Problem-Focused Coping
Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor
Emotion-Focused Coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction