cardio embryology and gross anatomy
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What does the primary heart field develop from?
Splanchnic layer of the lateral plate mesoderm (horseshoe-shaped)
The secondary heart field forms?
Part of the right ventricle and the outflow tract (consists of conus cordis and truncus arteriosus)
Overall result of heart tube folds?
atria on top and ventricles below
truncus arteriosus gives rise to
Ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
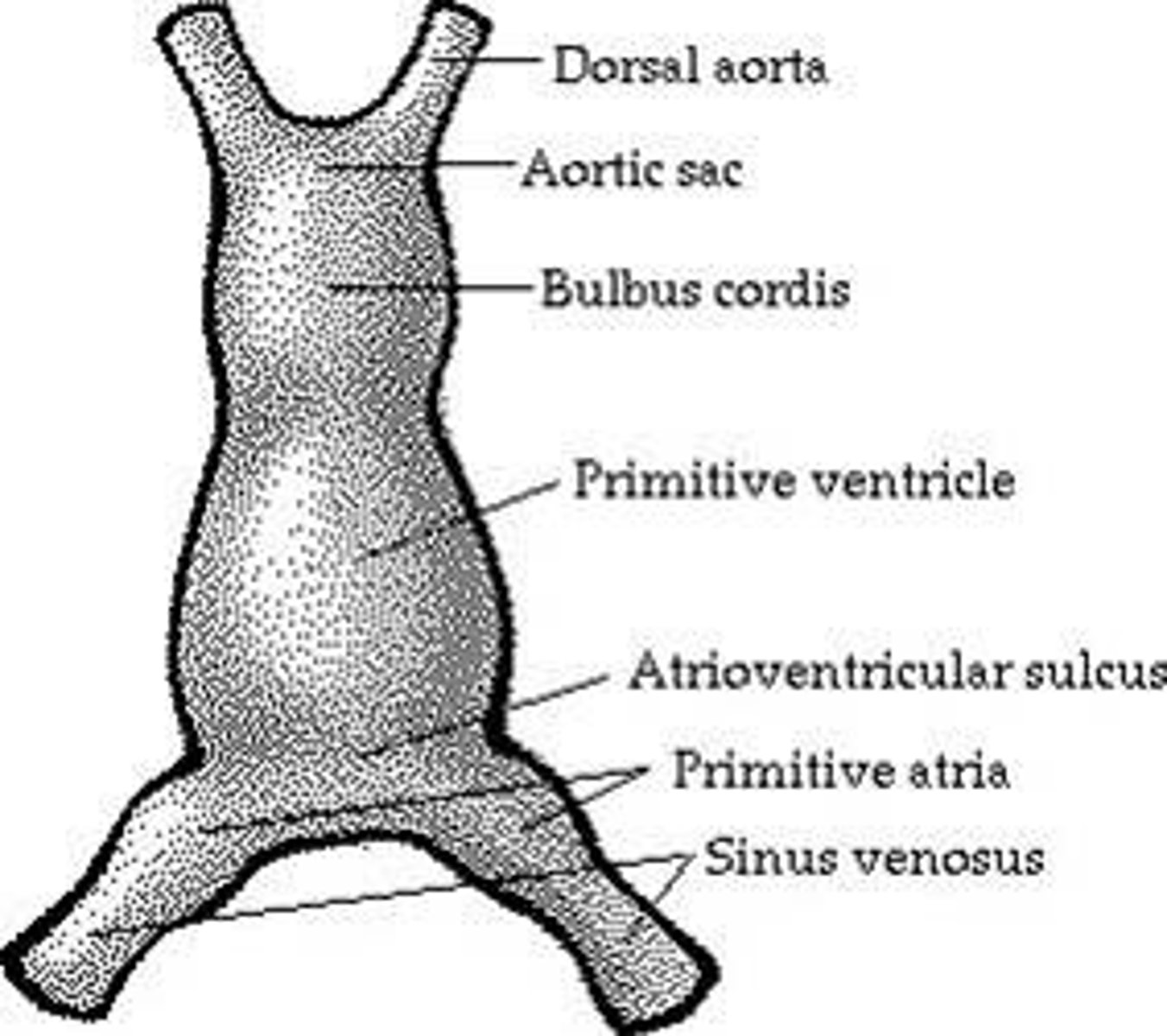
bulbus cordis gives rise to
Smooth parts (outflow tract) of left and right ventricles
primitive ventricle gives rise to
Trabeculated left ventricles
primitive atrium gives rise to
trabeculated L and R atria
Sinus venosus gives rise to
- right horn --> smooth RA (sinus venarum)
- left horn: cornary sinus, oblique vein of LA
Atrial septa development
• First wall: septum primum grows down → leaves a hole (ostium primum).
• That hole closes, but new hole (ostium secundum) opens higher.
• Second wall: septum secundum grows, leaves an opening called foramen ovale
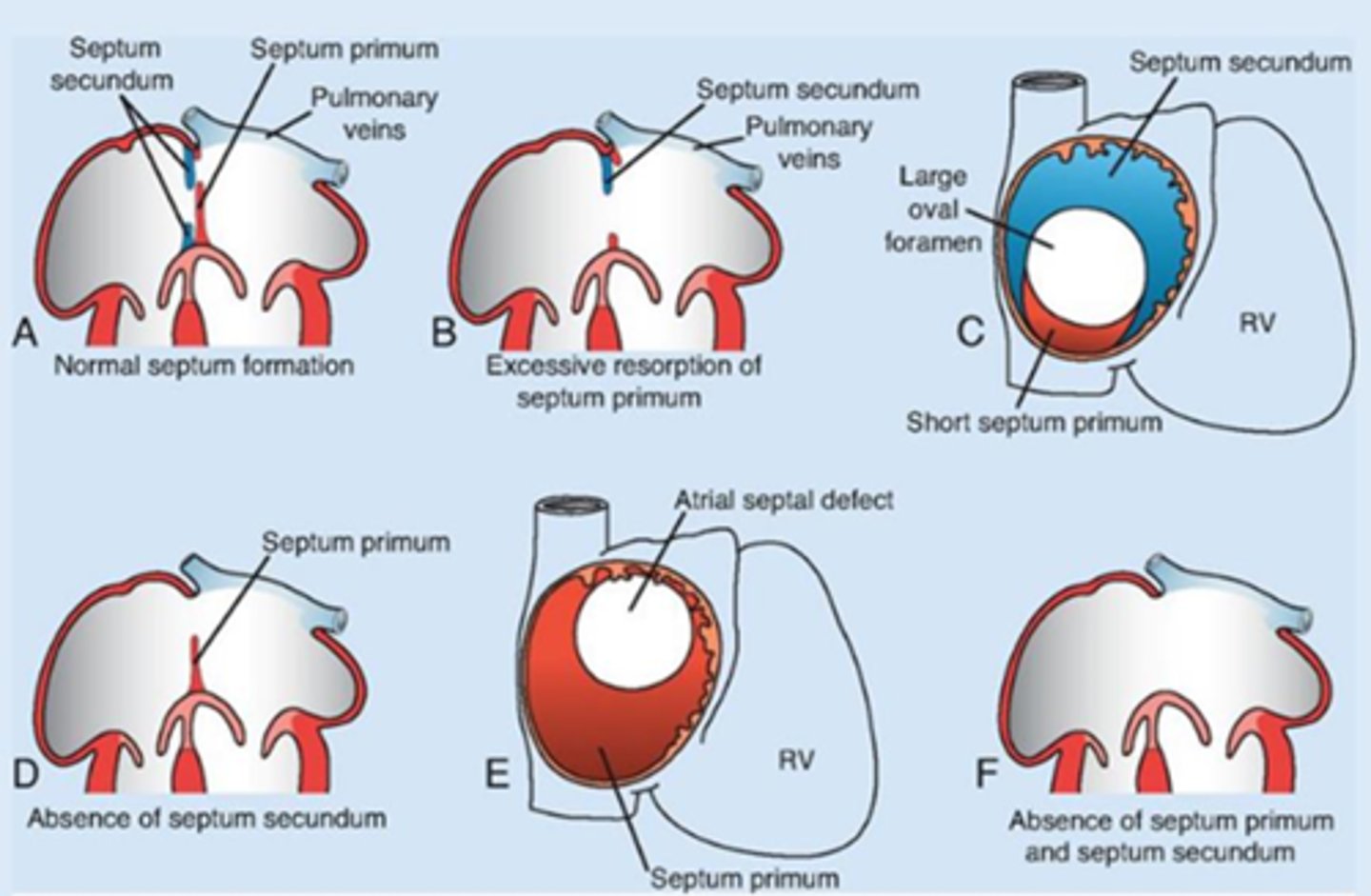
Atrial depta development (before birth)
blood can flow from R to L atrium through the foramen ovale
Atrial septa development (After birth)
pressure changed causing it to close and become the fossa ovalis
interventricular septum (vent. seperation)
• Muscular septum: grows upward from apex
• Membranous septum: forms from endocardial cushions + conotruncal ridges + muscular septum
• Fusion: complete interventricular septum
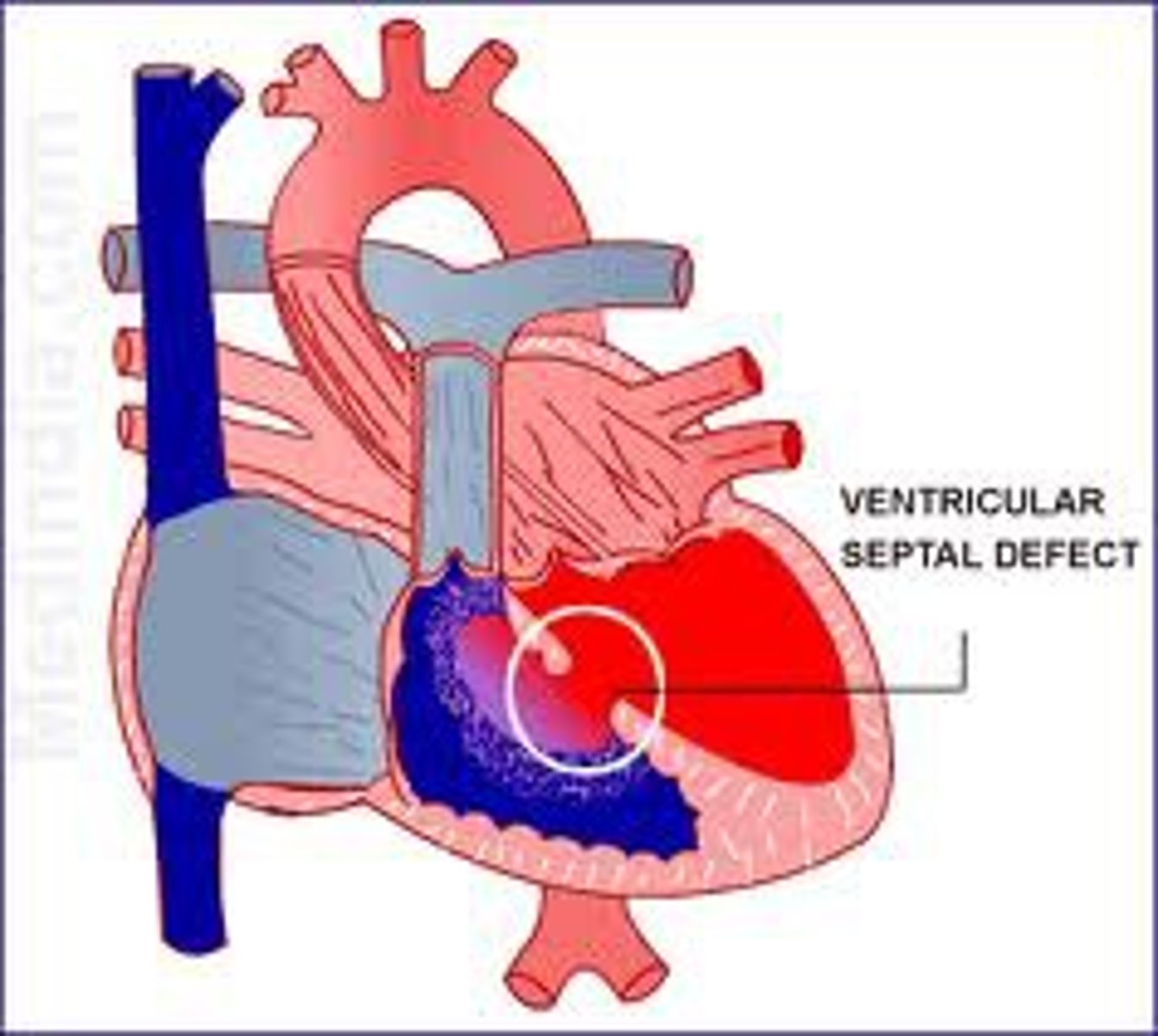
ventricle seperation clinical correlation
VSD ( ventricular septal defect)
neural crest cells migration through pharyngealarches 3, 4, and 6 to the outflow tract of the heart contribute to ?
septation of the conus cordis and truncus arteriosus.
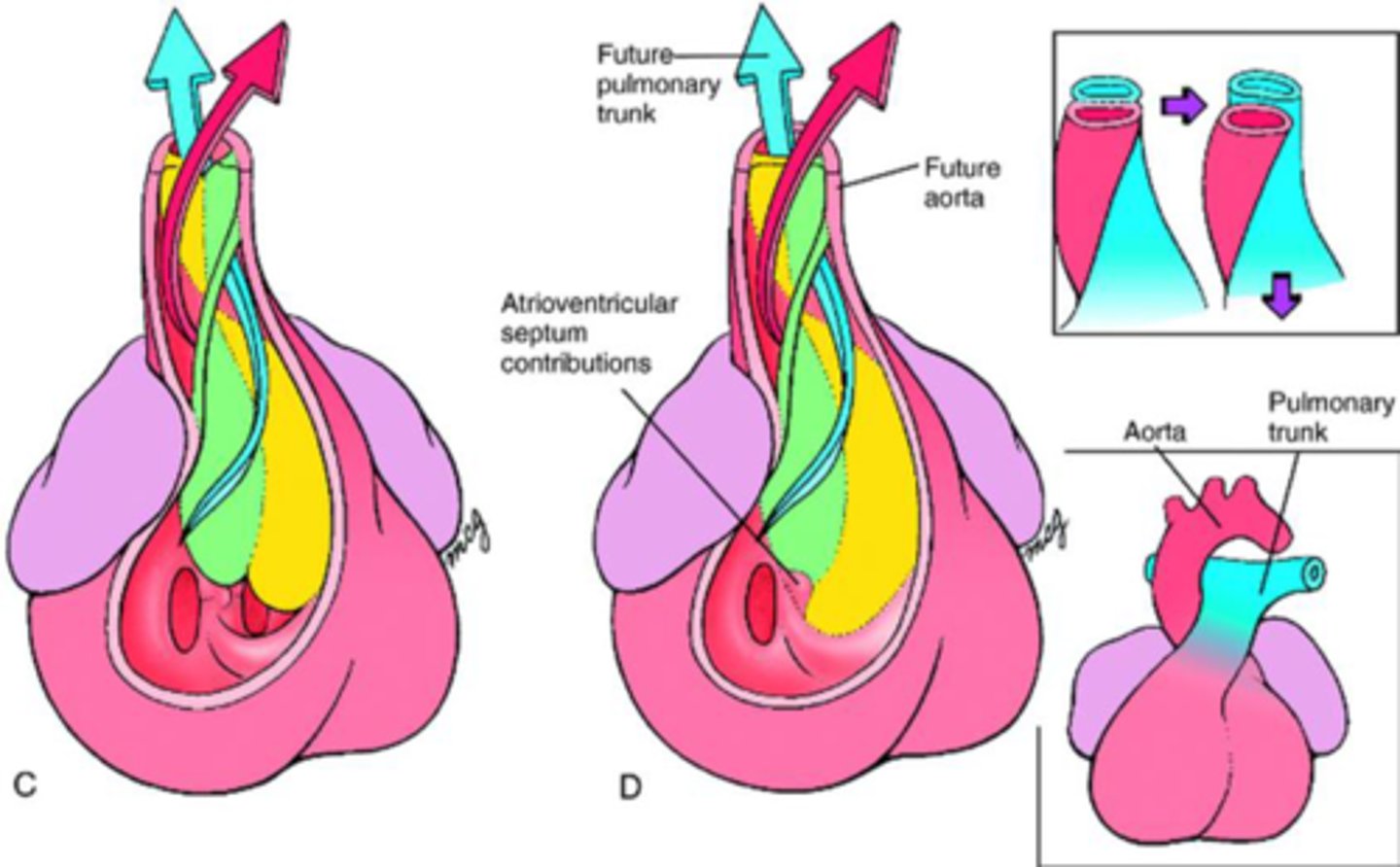
outflow tract septation
• Conotruncal ridges: form with the truncus arteriosus and thebulbus cordis
• Spiral and fuse: aorticopulmonary septum
• Separates outflow into the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk
• Requires neural crest cells
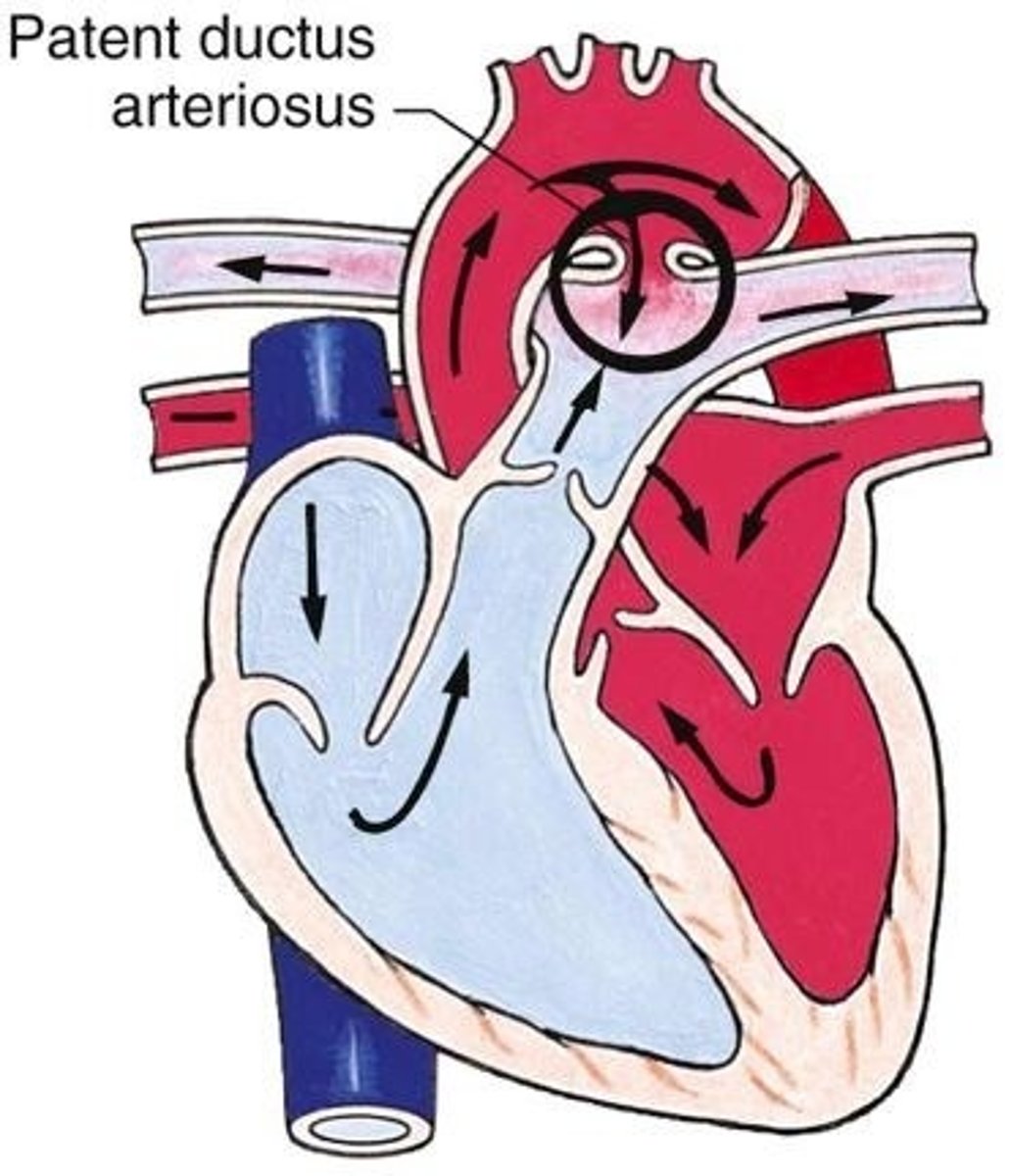
Transposition of the Great Vessels (defect)
the only access route to the lung is by patent ductus arteriosus
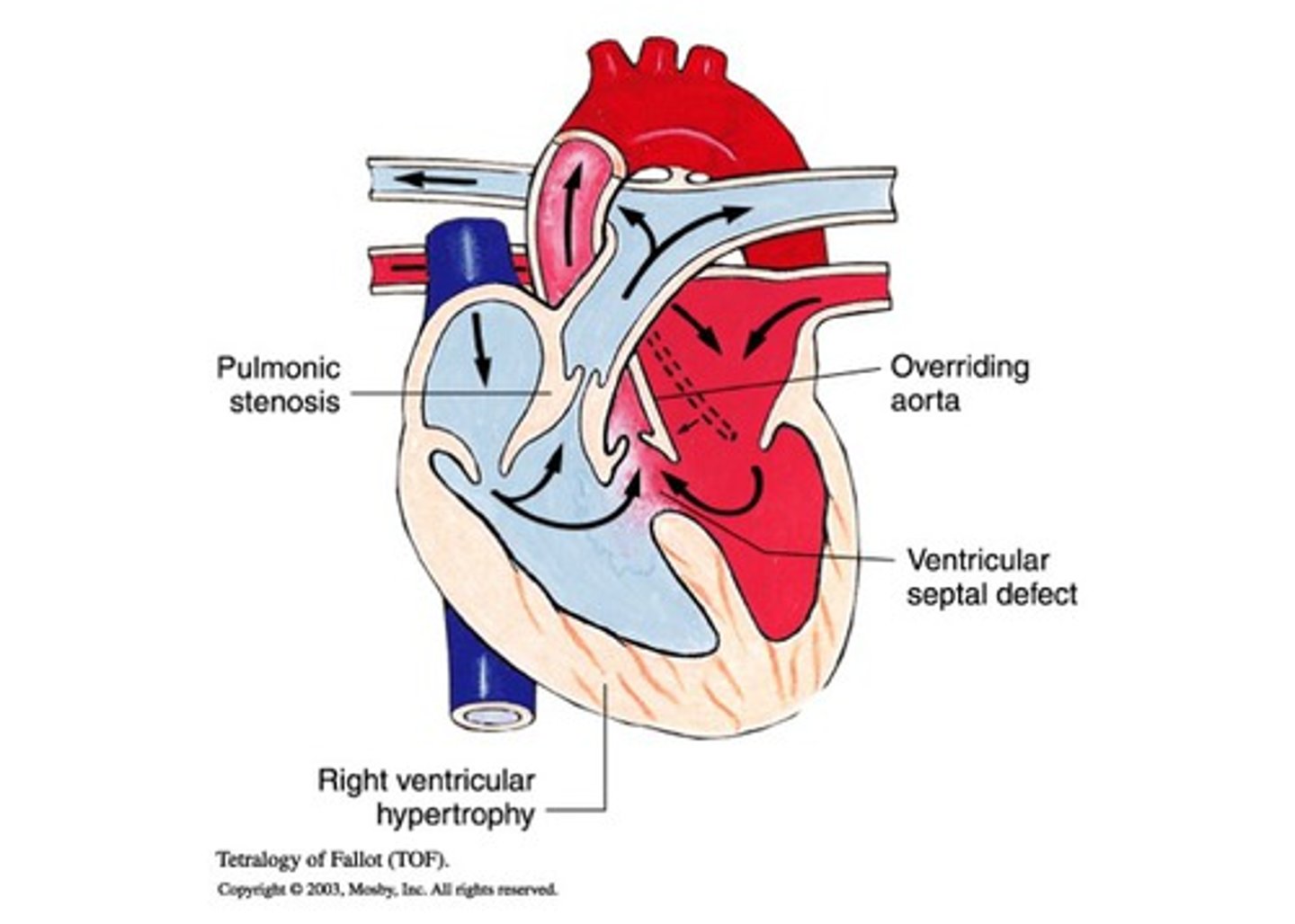
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an overriding aorta.
1st aortic arch
degenerates but leaves behind, maxillary artery
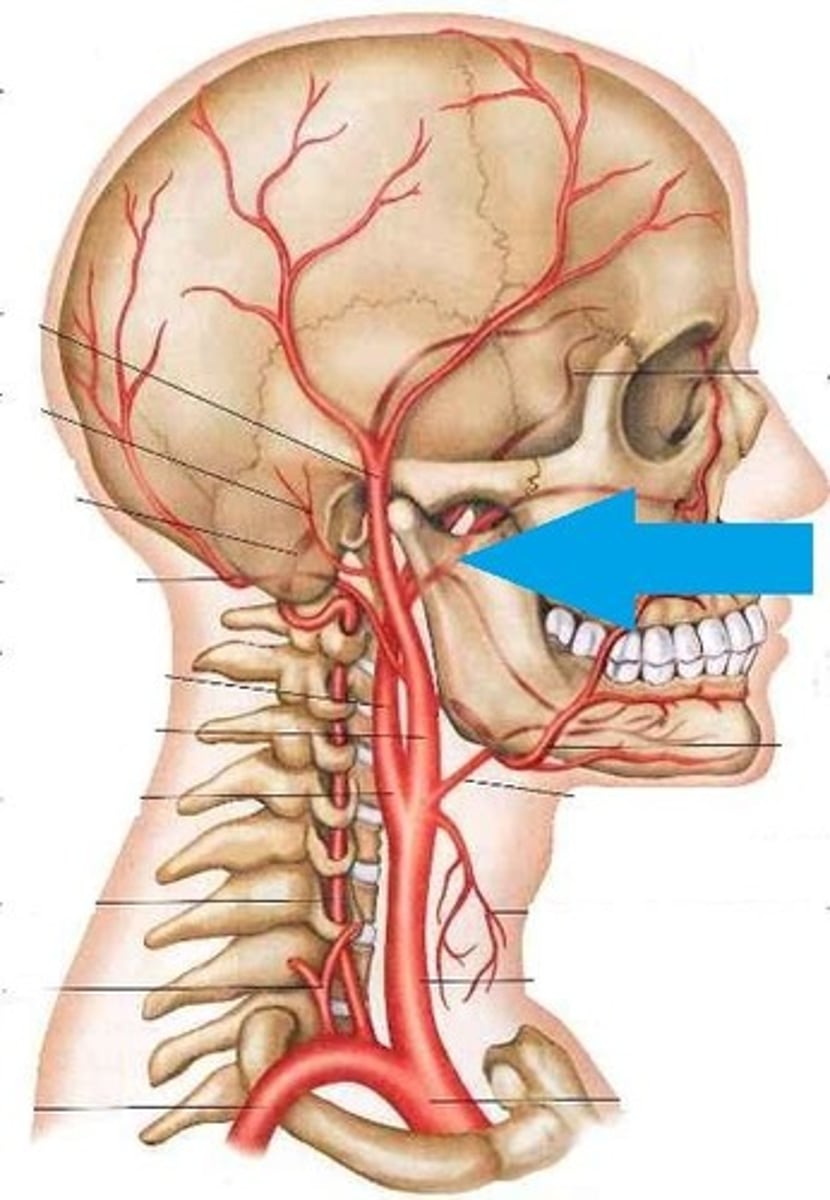
2nd aortic arch
degenerates but leaves behind stapedial artery (tiny blood vessel in ear)
3rd aortic arch (III)
common carotid artery and proximal part of internal carotid artery
4th aortic arch (IV)
- Left --> Aortic arch
- Right --> proximal part of R. sublcavian artery
5th aortic arch
degenerates
6th aortic arch (VI)
- left --> Ductus arteriosus
- right --> pulmonary arteries
cardinal veins form
systemic venous circulation
anterior cardinal veins form
internal jugular veins, superior vena cava
posterior cardinal veins form
inferior vena cava
Vitelline veins form
portal system, hepatic portal veins
Umbilical veins form
ductus venosus - ligamentum venosum
Vitelline veins in the growing liver form the ___________.
the hepatic sinusoids
What vessel develops from the vitelline anastomotic network around the duodenum?
The portal vein.
Which structure connects the left umbilical vein to the right hepatocardiac channel (hepatic portion of IVC)?
Ductus venosus
What happens to the proximal part of the left vitelline vein?
It disappears
Q: What are the three components of the IVC?
Hepatic, subcardinal, sacrocardinal
What does the anastomosis between the anterior cardinal veins form?
The left brachiocephalic vein
What does the terminal portion of the left posterior cardinal vein become?
Left superior intercostal vein
Which veins form the internal jugular veins?
Distal anterior cardinal veins