financial accounting 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
What is accouting?
process of identifying, measuring and communicating financial information about a business entity
2
New cards
gross profit
sales revenue less purchase costs
3
New cards
net profit
sales revenue less total costs
4
New cards
what does an income statement do
it summaries all income and expenditure over a period of time
5
New cards
separate entity concept
business activities are kept separate from owners
6
New cards
what is a balance sheet
financial statement which shows financial position at a specific point of time
7
New cards
accounting equation
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
8
New cards
what is an asset?
- resources owned/controlled by the business to give future economic benefit
- cash in bank, stock, machinery
- cash in bank, stock, machinery
9
New cards
liability
- what business owes
- bank debt, taxes
- bank debt, taxes
10
New cards
capital
- investment by the owner
- money introduced and retained profit
- money introduced and retained profit
11
New cards
expenditure
- revenue
- capital
- revenue
- capital
is a transaction or event which causes a decrease in ownership interest
- revenue expenditure = expense used in period or matches with revenue for the period
- capital expenditure = expense used on items in this and future periods
- revenue expenditure = expense used in period or matches with revenue for the period
- capital expenditure = expense used on items in this and future periods
12
New cards
nominal ledger
the main place where accounting transactions are recorded.
13
New cards
main principles of bookkeeping
- dual effect
- separate entity concept
- accounting equation
- separate entity concept
- accounting equation
14
New cards
how is accounting equation linked to dual effect
every transaction has two effects on the accounting equation
( if assets increase then liabilities or capital must increase)
( if assets increase then liabilities or capital must increase)
15
New cards
DEAD CLIC
Debit
- Expenses
- Assets
- Drawings
Credit
- Liabilities
- Income
- Capital
- Expenses
- Assets
- Drawings
Credit
- Liabilities
- Income
- Capital
16
New cards
what is balancing figure
- used to make debit and credit total equal
- put at the bottom of the smaller side
- put at the bottom of the smaller side
17
New cards
where does capital, cash, loan, drawings go
balance sheet
18
New cards
where does purchases, sales, expenses go
income statement
19
New cards
why would a suspense account be on a balance sheet
an error has been made
20
New cards
what does the IASB framework set out
concepts which underlie the preparation of financial statements
21
New cards
key accounting assumptions
accruals - expenses should be matched to the period hey relate and to the expenses they generate
going concern - assume entity will continue to trade for the foreseeable future
going concern - assume entity will continue to trade for the foreseeable future
22
New cards
cash flow = ?
cash in - cash out
23
New cards
what is an accrual
expenses incurred but not invoiced yet
24
New cards
what is a prepayment
expenses paid in advance
25
New cards
adjustments are needed to comply with
IASB and UK company law
26
New cards
how is an accrual recognised in BS and IS
recognise the liability in the BS (Cr Accruals), increase the expenses in the IS (Dr Expense)
27
New cards
how is a prepayment recognised in IS and BS
decrease expense in IS (Cr Expense), recognise the asses in the BS (Dr Prepayment)
28
New cards
what is the prudence concept
recognising a profit very slowly but when u anticipate a loss u account for it fast
29
New cards
difference between bad and doubtful debt
bad debt = definitely irrecoverable, not getting the money
Doubtful deft = some chance of recovery but also a risk of non payment
Doubtful deft = some chance of recovery but also a risk of non payment
30
New cards
how do u recognise a bad debt
as an expense in the IS
31
New cards
how do u recognise doubtful debt
Dr bad debt expense
Cr Doubtful Debts Provision.
\
Cr Doubtful Debts Provision.
\
32
New cards
which method should be used for inventory valuation
FIFO or WAC in financial accounting, used every year
33
New cards
what is net realisable value
estimated future selling price less ll additional costs to be incurred before sale
34
New cards
what is deprecation and why do we need it
the systematic allocation of a non-current asset over its useful economic life.
need it to spread the cost of a non current asset gradually over the years of its use and wearing out.
need it to spread the cost of a non current asset gradually over the years of its use and wearing out.
35
New cards
how do u calculate deprecation
1. straight line method
2. reducing balance method
2. reducing balance method
36
New cards
who is VAT administered by
HMRC
37
New cards
what are the types of supple (3)
- standard rate
- zero rated
- exempt
- zero rated
- exempt
38
New cards
what are the two types of discount
trade and early settlement
39
New cards
payables?
debt owed by a business (liabilities)
40
New cards
what is the standard rate of VAT
20%
41
New cards
what is the zero rate of VAT
10%
42
New cards
when do u calculate VAT in respect to discount
after all discounts
43
New cards
what’s a non-current asset
assets and property owned by a business that are not easily converted to cash within a year - long term asset
44
New cards
when can VAT not be recovered?
when a registered VAT business buys a motor car
45
New cards
what’s NBV
net book value - which is the original purchase cost minus the deprecation charged to date on that asset
46
New cards
residual value?
estimated amount that a company can acquire when they dispose of an asset at the end of its useful life
47
New cards
receivables?
amount owed to a business
48
New cards
difference between a profit and loss account and a balance sheet?
The Balance Sheet is a statement of assets, liabilities and capital, whereas the Profit and Loss account is a statement of income and expenses.
49
New cards
what are creditors
people that are lending money to the business
50
New cards
when can u claim capital on a car
when its for business use
51
New cards
examples of capital items
equipment, machinery, buildings, facilities, and vehicles
52
New cards
what is the cost of sales lay out
sales = a
\
cost of sales:
opening inventory = b
\+ purchases = c
\- closing stock= d
\
gross profit = a-(b\`+c-d)
\
cost of sales:
opening inventory = b
\+ purchases = c
\- closing stock= d
\
gross profit = a-(b\`+c-d)
53
New cards
what is inventory valued at
the lower out of cost or NRV
54
New cards
how do u calculate NRV
selling price - selling cost
55
New cards
bad debt provisions and movement?
only debit the movement between provisions
56
New cards
is receivables an asset or a liability
asset
57
New cards
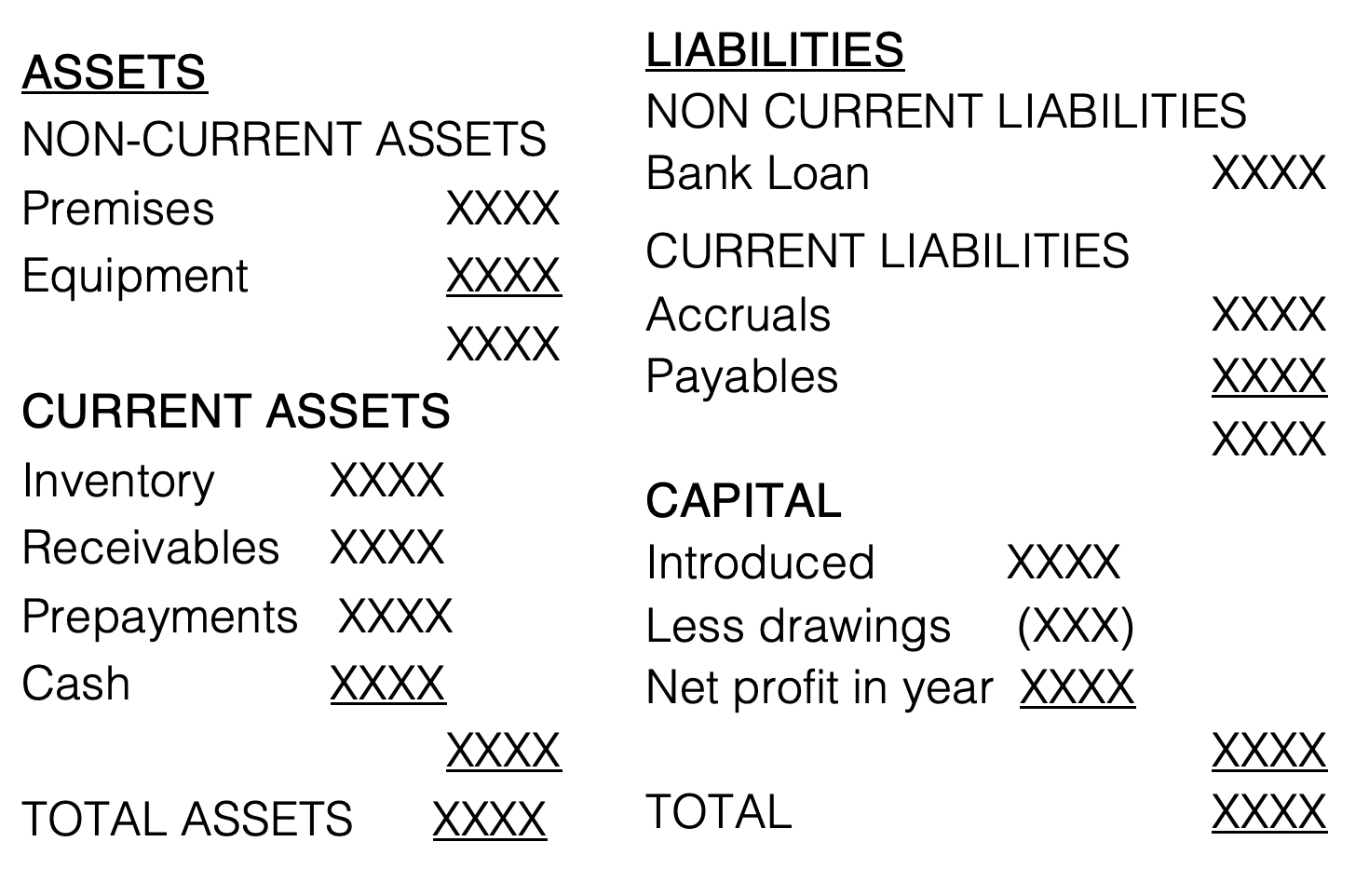
what does the balance sheet look like?