Aphasia
5.0(1)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/26
Last updated 3:24 PM on 1/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
asphasia
difficult with language/speech
2
New cards
dysarthria
difficult/unclear articulation of speech (slurred, breathy, hoarse, very loud/quiet speech)
3
New cards
apraxia
neurological disorder inability to perform movements - limb and oral
4
New cards
dysphagia
Swallowing difficulties - includes coughing and choking when eating/drinking
5
New cards
respirating
breathing difficulties affecting volume of voice and sequencing and coordinated breathing
6
New cards
phonation
production of utterances of speech sounds\####
Aphasia
Aphasia
7
New cards
Symptoms of aphasia
Difficulty understanding
Difficulty word finding
Can't read
Cant spell
Grammatical errors in speech
Phonological erros- paraphasia
Semnatic errors cat-dog- paraphasia
Difficulty word finding
Can't read
Cant spell
Grammatical errors in speech
Phonological erros- paraphasia
Semnatic errors cat-dog- paraphasia
8
New cards
Boston classification for aphasia
Believes functions are localised to a specific region
BDAE- Boston diagnostic aphasia examination
BDAE- Boston diagnostic aphasia examination
9
New cards
Broca's aphasia
Non fluent aphasia
Slow, effrtful, agrammatic output
Have comprehension but low expression
Often noun out out and short simple phrases
Poor naming, writing, reading around and repition
Slow, effrtful, agrammatic output
Have comprehension but low expression
Often noun out out and short simple phrases
Poor naming, writing, reading around and repition
10
New cards
Wernickes aphasia
Fluent aphasia
Difficulty with comprehension but have low expression
Excessive expressive output
Paraphasia - semantic and phonemic
Neologisms
Auditory comprehension is worse then written
Impaired naming and repition
Visual processing (hemianopia) can be common
Difficulty with comprehension but have low expression
Excessive expressive output
Paraphasia - semantic and phonemic
Neologisms
Auditory comprehension is worse then written
Impaired naming and repition
Visual processing (hemianopia) can be common
11
New cards
Conduction aphasia
Lesion in temporary- parietal border
Primary impairment- poor repetition
Have phonological errors but fluent speech
Word finding difficulties, naming , repetition, reading aloud and writing
Are aware they make mistakes
Primary impairment- poor repetition
Have phonological errors but fluent speech
Word finding difficulties, naming , repetition, reading aloud and writing
Are aware they make mistakes
12
New cards
Anomic aphasia
Often temporary parietal lesion
Fluent aphasia with word finding difficulties, circumlocutions and pauses
About to recognise and describe objects but often cannot name
Intact - comprehension, reading aloud and repetition
Fluent aphasia with word finding difficulties, circumlocutions and pauses
About to recognise and describe objects but often cannot name
Intact - comprehension, reading aloud and repetition
13
New cards
Global aphasia
Most severe
Lesion is late caused by occlusion of left middle cerebral artery
Severe motor and sensory impairments
Visual fields impaired and oral apraxia
Non fluent aphasia - 1 word utterances
Sometimes able to produce over learned sequences- numbers, dates (repeated a lot in life)
Serverly impaired- comprehension, naming, repetition, reading writing
Lesion is late caused by occlusion of left middle cerebral artery
Severe motor and sensory impairments
Visual fields impaired and oral apraxia
Non fluent aphasia - 1 word utterances
Sometimes able to produce over learned sequences- numbers, dates (repeated a lot in life)
Serverly impaired- comprehension, naming, repetition, reading writing
14
New cards
Transcortical aphasia
3 types- motor, sensory and mixed
Have god comprehension
Caused by infarcts (Lsions) to border of 2 artery zones (a trashed areas)
Result from lesion isolating speech areas from cerebral cortex
Have god comprehension
Caused by infarcts (Lsions) to border of 2 artery zones (a trashed areas)
Result from lesion isolating speech areas from cerebral cortex
15
New cards
Transcortical motor aphasia
Lesion: usually anterior or superior to Broca's area
Non fluent speech, agrammatic and echolocation
Poor initiation, written output, reading around,
Good repition, comprehension, abilities
Non fluent speech, agrammatic and echolocation
Poor initiation, written output, reading around,
Good repition, comprehension, abilities
16
New cards
Transcortical sensory aphasia TSA
Lesion- parietal- occipital region
Has expressive language
Fluent but broken speech - phonological errors and word finding difficulties
Severely impaired comprehension verbal and written , reading aloud, naming and writing
Intact repetition - words and entrances
Has expressive language
Fluent but broken speech - phonological errors and word finding difficulties
Severely impaired comprehension verbal and written , reading aloud, naming and writing
Intact repetition - words and entrances
17
New cards
Oral apraxia
Difficulty in coordinating muscle tissue
18
New cards
Agrammatic output
Missing out words
Not using full sentences
Telegraphic speech\####
Impacts from stroke
Not using full sentences
Telegraphic speech\####
Impacts from stroke
19
New cards
Model of coping- parr et al 2007
Experience of aphasia
Pre aphasia identity (biography, attributes, status, prospects)
Experience of aphasia
Knowledge of aphasia
Personal and family attitudes and beliefs
Account of aphasia (biography,aphasic,identity, prospects)
Pre aphasia identity (biography, attributes, status, prospects)
Experience of aphasia
Knowledge of aphasia
Personal and family attitudes and beliefs
Account of aphasia (biography,aphasic,identity, prospects)
20
New cards
Assessments of functional communication
Communicative Abilities of Daily Living: Holland (1980)
• Edinburgh Functional Communication Profile: Skinner et al (1984)
• Everyday Communicative Needs Assessment (Worrall 1992)
• Edinburgh Functional Communication Profile: Skinner et al (1984)
• Everyday Communicative Needs Assessment (Worrall 1992)
21
New cards
4 types of repair - analysis of frequency
Self-initiated self-repair: Most common in normal
conversation, suggests competence
Self-initiated other-repair: Common in WFD- repair yourself and then other person does it for them
Other-initiated self-repair: Asking for clarity- convo partner
Other-initiated other-repair: Initiating and carrying out repair e.g. 'you're wrong, it's not x, it's y'!- convo partner initiates and repairs convo
conversation, suggests competence
Self-initiated other-repair: Common in WFD- repair yourself and then other person does it for them
Other-initiated self-repair: Asking for clarity- convo partner
Other-initiated other-repair: Initiating and carrying out repair e.g. 'you're wrong, it's not x, it's y'!- convo partner initiates and repairs convo
22
New cards
Aphasia can effect turn taking
Word-finding problems
➢ Silences/pauses
➢ Comprehension
'Minimal turns' common e.g. 'mm hm' •
Short turns e.g. 'yes', 'no', 'maybe'
➢ Silences/pauses
➢ Comprehension
'Minimal turns' common e.g. 'mm hm' •
Short turns e.g. 'yes', 'no', 'maybe'
23
New cards
Assessment of conversation
Capps
Spparc
Ca samples
Spparc
Ca samples
24
New cards
Talking mats
Often used for ald
Explain and talk about the picture
Organise pictures by thumbs up, not sure ad thumbs down
Shows what they want to work on and dint
Explain and talk about the picture
Organise pictures by thumbs up, not sure ad thumbs down
Shows what they want to work on and dint
25
New cards
Total communication
To communicate a complex message
Gesture
• Pictorial materials
• Drawing
• Writing
• Written words
• Environmental props or objects
Gesture
• Pictorial materials
• Drawing
• Writing
• Written words
• Environmental props or objects
26
New cards
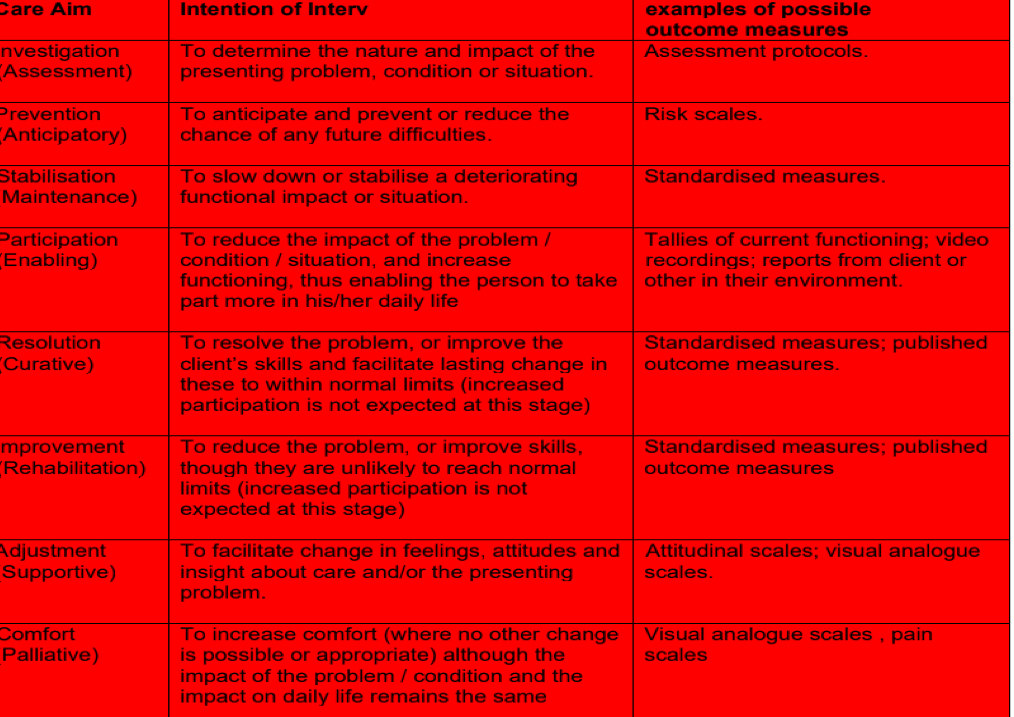
Malcomess care aims
• Investigation (assessment)
• Anticipatory (prevention)
• Stabilisation (maintenance)
• Participation (enabling)
• Resolution (curative)
• Improvement(rehabilitation)
• Adjustment(supportive)
• Comfort(palliative)
• Anticipatory (prevention)
• Stabilisation (maintenance)
• Participation (enabling)
• Resolution (curative)
• Improvement(rehabilitation)
• Adjustment(supportive)
• Comfort(palliative)
27
New cards