Environmental Geoscience Exam 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
When you observe water flowing in a permanent stream, where does the water come from?
D. All of the above
C. Groundwater rising from springs
Surface runoff
B. Water temporarily trapped in soil
D. All of the above
During the process of headward erosion, the distance from the mouth to the source of the stream ...
A. increases.
C. stays the same.
D. No answer text provided.
B. decreases.
A. increases.
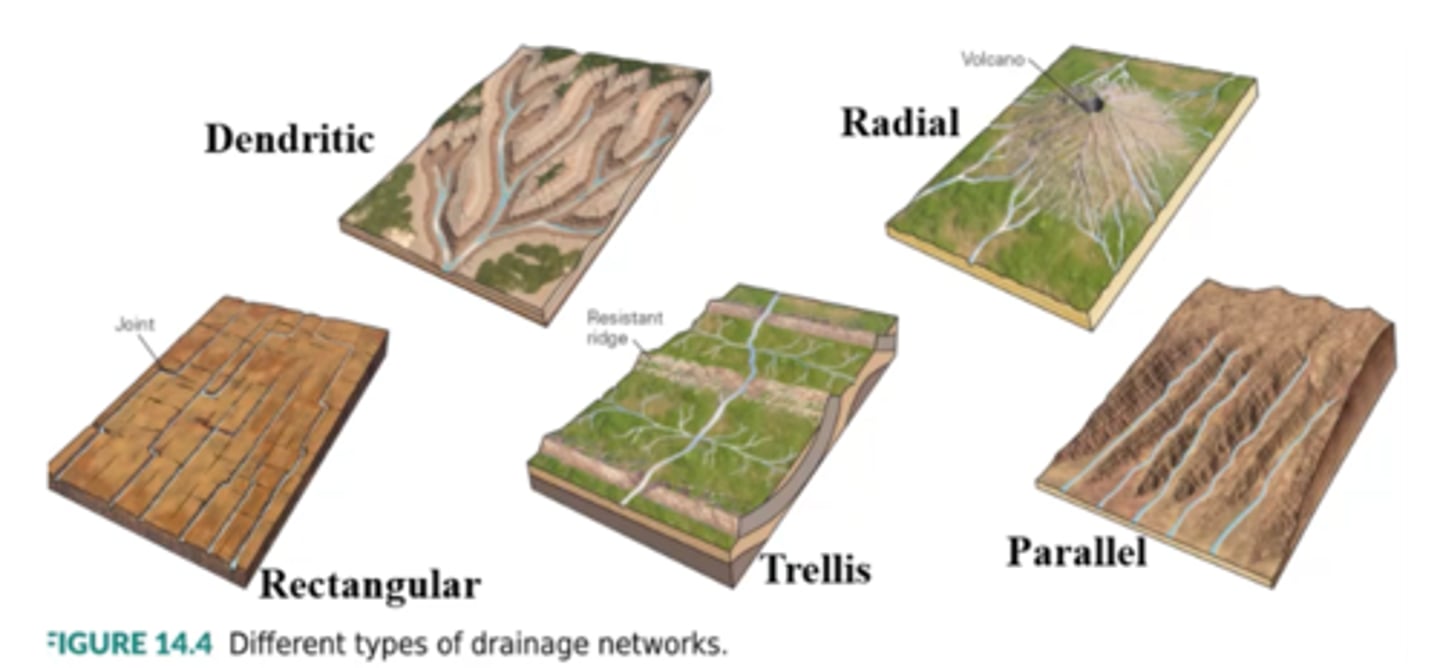
Which of the following map patterns represents a dendritic drainage network?
B (tree-like fan)
The so-called continental divide of North America separates ...
a. rivers that drain into Hudson Bay from those that drain into the Atlantic.
b. rivers that drain into the Great Basin of Utah and Nevada from those that drain into the Pacific.
c. rivers that drain into the Atlantic from the Mississippi drainage network.
d. rivers that drain into the Atlantic from those that drain into the Pacific.
d. rivers that drain into the Atlantic from those that drain into the Pacific.
Why do the courses of rivers in some locations cut across resistant rock ridges rather than find a path around them?
a. The stream course was established when the stream flowed over a uniform substrate, and it was superposed on the non-uniform substrate below.
b. Rivers are able to erode resistant (hard) rock layers faster than they can erode soft rock layers.
c. rivers always develop courses that avoid resistant rocks.
d. Some rivers are ephemeral and thus can cut through anything.
a. The stream course was established when the stream flowed over a uniform substrate, and it was superposed on the non-uniform substrate below.
The longitudinal profile of a stream is typically _______ . The lowest elevation below which a stream cannot cut is called its ______ and occurs at the stream's ________ .
Group of answer choices
A. convex-up / water table / source
B. convex-up / base level / mouth
C. concave-up / base level / mouth
D. concave-up / tributary / source
C. concave-up / base level / mouth
The velocity of water flow in a stream ...
a. tends to be fastest at shallow depths near the stream's center.
b. is fastest along the walls of the stream's channel.
c. is fastest along the bed of the stream.
d. is constant everywhere in the stream.
a. tends to be fastest at shallow depths near the stream's center.
The portion of a stream's sediment load that consists of tiny solid grains carried along with the water but not bouncing off the stream bed is a stream's ________ .
C. Bed load
B. Dissolved load
A. Suspended load
D. None of the above
A. Suspended load
Which of the following changes in the landscape is likely if the ultimate base level of a stream drops significantly?
a. Alluvium fills up the stream's valley.
b. The stream downcuts to form a canyon.
c. The stream starts developing meanders.
d. Nothing much, because the longitudinal profile is constant.
b. The stream downcuts to form a canyon.
Alluvial fans form when ...
a. an ephemeral stream emerges from the mouth of a canyon and spreads over a broad plain.
b. a stream undercuts a cliff, which collapses and spreads sediment in a fan-shaped area.the gradient of a stream increases and the water becomes more turbulent.a stream goes over a waterfall.
a. an ephemeral stream emerges from the mouth of a canyon and spreads over a broad plain.
Which of the following statements about ocean currents is correct?
B. Currents affect only surface water; deep water is always stationary.
A. Currents always transport warm water.
C. The flow of surface currents is driven primarily by the wind.
D. The flow in currents is perfectly laminar (i.e., they never produce turbulence).
C. The flow of surface currents is driven primarily by the wind.
Because of the Coriolis Effect, a current in the Northern Hemisphere that flows north will be deflected to the _______ .
B. south
C. west
D. the Coriolis Effect does not influence current flow.
A. east
east
Thermohaline circulation in the oceans is driven by _______ . It is responsible for ________ .
D. momentum of Earth's rotation / the sinking of warm water at equatorial latitudes
B. wind / transporting surface water from polar regions toward the equator
A. density differences caused by contrasts in salinity and temperature / mixing deep and shallow water
C. upwelling and downwelling along coasts / plankton productivity
A. density differences caused by contrasts in salinity and temperature / mixing deep and shallow water
Which of the following statements about the tides is correct?
C. Centrifugal force caused by the spin of the Earth on its axis contributes to the tide-generating force.
A. Tides are entirely a consequence of the gravitational pull of the Moon.
D. Tides are generated partly due to gravitational pull of the Moon and (to a lesser extent) the Sun, and partly due to centrifugal "force" caused by motion of the Earth-Moon system around its center of mass.
B. Tides are entirely a consequence of the combined gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun.
D. Tides are generated partly due to gravitational pull of the Moon and (to a lesser extent) the Sun, and partly due to centrifugal "force" caused by motion of the Earth-Moon system around its center of mass.
Which statement concerning the movement of water in waves of the open ocean is correct?
A. Water particles move with the wave and thus can migrate tens to hundreds of kilometers as the wave moves.
C. Water molecules follow a circular path as the wave passes.
B. Water molecules go up and down, along a vertical straight line, as the wave passes.
D. The motion of water molecules at the ocean's surface is the same as that at the floor of the ocean as a wave passes.
C. Water molecules follow a circular path as the wave passes.
Longshore drift of sand on a beach occurs when . . .
A. waves approach the shore at an angle.
B. there are particularly large tides.
C. a river enters the sea, and the river water flows along the coast.
D. wave fronts are parallel to the beach.
A. waves approach the shore at an angle.
Along a rocky coast, the sequence of landform development follows which sequence?
←first last→
C. sea stack → rocky headland → sea arch
D. sea stack → sea arch → rocky headland
B. sea arch → rocky headland → sea stack
A. rocky headland → sea arch → sea stack
A. rocky headland → sea arch → sea stack
Which of the following statements about coral reefs is correct?
C. As time passes, seamounts emerge from the sea, and atolls become fringing reefs.
A. More reefs are developing as the oceans get warmer.
B. Large areas of existing reefs have been dying off due to bleaching and various coral diseases.
D. The coral making reefs is a species of algae that secretes a siliceous shell.
B. Large areas of existing reefs have been dying off due to bleaching and various coral diseases.
The deepest places in the ocean are ________, where water depths reach _________ .
C. abyssal plains / 4.5 km
D. trenches / 11 km
B. transform faults / 3.0 km
A. mid-ocean ridges / 2.0 km
D. trenches / 11 km
What does ocean water consist of?
C. a solution containing various ions; mostly Na+ and Cl-, but also SO42-, Mg2+, Ca2+, and K+
D. a mixture of water and suspended crystals of various salts
B. a solution of only halite (NaCl) in water
A. pure H2O
C. a solution containing various ions; mostly Na+ and Cl-, but also SO42-, Mg2+, Ca2+, and K+
1) If we say that a rock has high porosity but low permeability, we mean that . . .
A. the rock contains very little open space (e.g., cracks or pores), but openings are interconnected, so that water can pass through the rock fairly easily.
C. the rock can contain abundant groundwater that can flow quite easily.
B. the rock contains abundant open space (e.g., cracks or pores), but the spaces are isolated from one another so that water cannot pass through the rock easily.
B. the rock contains abundant open space (e.g., cracks or pores), but the spaces are isolated from one another so that water cannot pass through the rock easily.
3) The water table is ________ beneath hills than beneath valleys in humid climate. This is because the water table sinks ______ after it rains.
A. higher / immediately
C. higher / very slowly
B. lower / very slowly
D. lower / immediately
C. higher / very slowly
4) What drives the natural flow of groundwater?
C. gravity alone
B. heat
D. the weight of overlying rock
A. pressure and gravity
A. pressure and gravity
5) Groundwater flow typically occurs at rates on the order of _______. According to Darcy's law, what happens to the rate of groundwater flow if the permeability increases?
D. 5 cm/century / flow rate stays the same
B. 10 km/day / flow rate decreases
C. 5 cm/day / flow rate increases
A. 1 km/day / flow rate increases
C. 5 cm/day / flow rate increases
6) If you pump water out of the ground at a well faster than it can be replenished by groundwater flow or by infiltration, what happens to the water table?
D. The water table sinks in a cone-shaped area around the well.
A. The water table stays horizontal, but rises.
C. Nothing—the water table always stays constant in depth.
B. The water table rises to a peak around the well.
D. The water table sinks in a cone-shaped area around the well.
7) Potential energy driving flow, is due to_______.
Aquifer porosity
Aquifer permeability
Air pressure
Surface topography
Surface topography
8) Which statement is correct, in reference to a flowing artesian well?
A. The water flows out of the well on its own, and the potentiometric surface is below the ground.
D. The potentiometric surface in the region of the well lies below the water table.
B. The water flows up the well but not out to the surface, because the potentiometric surface is below the ground.
C. The potentiometric surface in the region of the well lies above the ground surface
C. The potentiometric surface in the region of the well lies above the ground surface
9) You are driving down the highway in a desert, just after it rained very heavily, and see some ephemeral streams in the low areas bordering the highway. Can you estimate the depth to the water table from this observation?
- Maybe
- yes
- No
no
10) What statement is correct?
- water table forms were the air pressure is in equilibrium with water pressure.
- Above the water table, there is no pores.
- In saturated zone pores are filled with water.
- Below the water table, pores are filled with air.
In saturated zone pores are filled with water.
Which of the following statements about the flow of ice in glaciers is correct?
C. All of the ice in a specific glacier flows at the same rate.
A. Even in the coldest glacier, liquid water occurs between ice grains so the ice grains can slide past each other.
B. Glaciers flow for a variety of reasons: in some cases, ice grains are able to change shape plastically, in some cases glaciers slide on a wet substrate, and in some cases ice grains slip past each other on water films.
B. Glaciers flow for a variety of reasons: in some cases, ice grains are able to change shape plastically, in some cases glaciers slide on a wet substrate, and in some cases ice grains slip past each other on water films.
Large cracks in glaciers are called ________ . They tend to form in the _________ part of a glacier, where the ice is ______ .
B. lobes / upper / plastic
A. surges / lower / plastic
D. crevasses / upper / brittle
C. crevasses / lower / plastic
D. crevasses / upper / brittle
What factor determines the direction in which ice flows?
A. The surface slope of the ice.
B. The slope of the substrate beneath the ice.
C. The Coriolis effect.
D. The direction that water streams beneath the ice flow.
A. The surface slope of the ice.
What processes happen in the zone of ablation?
D. Glacial ice follows a flow trajectory that takes it down to greater depths.
A. Snow accumulates.
C. Ice gradually is lost, due to a combination of melting, sublimation, and calving.
B. The rate of snow accumulation is balanced by the rate of snow sublimation.
C. Ice gradually is lost, due to a combination of melting, sublimation, and calving.
Which of the following processes occurs during glacial retreat?
A. Ice flows back toward the origin of the glacier.
C. The rate of accumulation exceeds the rate of sublimation.
D. The ice stops flowing and simply melts away.
B. The position of the glacier's toe (terminus) moves back toward the origin of the glacier, even though ice continues to flow toward the toe.
B. The position of the glacier's toe (terminus) moves back toward the origin of the glacier, even though ice continues to flow toward the toe.
How can you tell the direction that ice flowed in a region that was covered by ice during the last ice age?
B. Flow direction is perpendicular to the direction of glacial striations.
A. Flow direction is parallel to the direction of glacial striations.
C. Flow direction is always down the slope of the land surface in an area.
D. Once the glacier has melted, it is impossible to tell which way it flowed.
A. Flow direction is parallel to the direction of glacial striations.
Which of the following statements about glacially carved valleys is correct?
D. Glacial valleys tend to have gentle slopes near the top, but have steep slopes near the bottom.
A. They are V-shaped.
C. Side valleys intersect the trunk valley at the same elevation.
B. They are U-shaped.
B. They are U-shaped.
Which of the following is a characteristic of glacial till?
A. layers of well-sorted sediment
D. very poor sorting, with large clasts suspended in a fine-grained matrix
C. very sticky silt
B. the presence of very fine, laminated shale
D. very poor sorting, with large clasts suspended in a fine-grained matrix
A(n) ______ accumulates at the toe of a glacier. The sediment comprising it ___________ .
B. kame / fell from mountain ridges onto the side of the glacier
A. lateral moraine / was deposited in under-ice tunnels
C. lateral moraine / was pushed into place by the bulldozer effect of moving ice
D. end moraine / was carried by the ice in conveyor-belt fashion
D. end moraine / was carried by the ice in conveyor-belt fashion
Knob and kettle topography forms when . . .
D. rocks embedded in the base of the glacier gouge deep depressions into bedrock.
C. ice plucks chunks off bedrock and leaves an indentation.
B. the glacier flows over sediment and molds it into streamlined hills.
A. blocks of ice get buried by till and then melt.
A. blocks of ice get buried by till and then melt.
2. What can the study of fossil pollen tell us about global climate change during the past 100,000 years?
B. Not much — pollen is so delicate that it is not well preserved in the geologic record.
C. Not much — pollen grains all look much the same.
A. The latitudes at which temperate forests exists migrate through time, in response to temperature changes.
D. Average surface air temperatures have been constant to within 1°C.
A. The latitudes at which temperate forests exists migrate through time, in response to temperature changes.
3. What do changes in the ratio of 18O to 16O in the shells of plankton, as a function of time, tell us?
A. that the atmosphere has undergone unidirectional change over long periods of time
C. that plankton species have evolved in ways that make them preferentially incorporate one isotope instead of the other
B. that sea water temperature changes with time, because the ratio of isotopes incorporated into shells depends on temperature
D. that plankton shells lose one isotope faster than they lose the other
B. that sea water temperature changes with time, because the ratio of isotopes incorporated into shells depends on temperature
4. How can dendrochronologists determine the record of climate from tree rings for times before the currently oldest tree was alive?
A. correlation of tree-ring patterns in living trees with patterns in wood from trees that were alive at the time of some of these living trees
C. measuring oxygen isotopes in tree rings
B. making uranium-lead dates of long-dead trees
D. use of tree rings for paleoclimate studies applies only to living trees
A. correlation of tree-ring patterns in living trees with patterns in wood from trees that were alive at the time of some of these living trees
5. The record of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere shows clearly that . . .
D. the concentration of this gas was constant until 1960, at which time it started to increase.
B. the concentration of this gas has steadily increased since accurate measurements began.
A. the concentration of this gas does not vary with the seasons.
C. the concentration of this gas has decreased steadily since accurate measurements began.
B. the concentration of this gas has steadily increased since accurate measurements began.
6. Which of the following statements about sea-level measurements during the past century is correct?
B. Sea level goes up and down a bit, but overall has steadily risen by about 10 - 12 cm since 1910.
C. There is no way to accurately measure sea-level change.
A. Sea level goes up and down within a narrow range, but basically has been constant.
B. Sea level goes up and down a bit, but overall has steadily risen by about 12 - 15 cm since 1910.
7. Which of the following processes removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
- Respiration of animals
- Volcanism
- Burning of coal and other fossil fuels
- photosynthesis
- photosynthesis
8. Which of these is the longest-lasting sink for CO2?
- Limestone and oil and gas deposits
- The atmosphere
- Plant tissues and cellulose
- Air bubbles within glacial ice
- Limestone and oil and gas deposits
9. A blogger writes that global warming is a myth, noting that their city had its coldest ever-recorded temperature last winter. Which statement about their statement is not correct?
- Blogger is correct and has proven that global warming is not occurring.
- Blogger is confusing weather with climate.
- Blogger is confusing a single measurement point with an evaluation made from hundreds or thousands or more data points.
- Blogger is correct and has proven that global warming is not occurring.
10. Astronomers suggest that the end of the Earth will occur in about _____ , when the Sun becomes a ___________ .
A. 1 billion years / supernova
C. 5 billion years / red giant
B. 2 billion years / neutron star
D. 30 billion years / dark cinder
C. 5 billion years / red giant
Deltas form because _______. The finest sediment typically accumulates _________ the shore.
A. water slows at the mouth of the stream / closest to
B. water speeds up at the mouth of the stream / farthest from
C. water slows at the mouth of the stream / farthest from
D. water speeds up at the mouth of the stream / closest to
A. water slows at the mouth of the stream / closest to
If geologists calculate that the recurrence interval of a flood of a certain size is 100 years then...
A. such a flood happens every 100 years
B. the probability that such a flood will happen next year is 1%
C. if such a flood happened last year, another is less likely to occur than if it happened 20 years ago
D. it is possible for even larger flood to have a shorter recurrence interval
B. the probability that such a flood will happen next year is 1%
As the velocity of flow decreases______?
A. flow tends to become more laminar
B. the maximum flow velocity decreases
C. suspended sediments starts to be deposited
D. all of the above.
D. all of the above.
Moving down stream, the flow of a stream or river becomes less________.
A. turbulent
B. saline
C. meandering
D. laminar
turbulent
The base level of a tributary would become _________ if a dam and reservoir were constructed if a dam and reservoir were constructed where it flowed into a trunk stream.
A. lower
B. slower
C. faster
D. higher
higher
The inner edge of meander, where sediment is deposited, is a(n)__________.
A. meander neck
B. cut bank
C. point bar
D. abandoned meander
C. point bar
V-shaped stream valley results from the down cutting of stream erosion and ______.
A. mass wasting on the valley side
B. isostatic rebound
C. the "rule of V's"
D. conservation of angular momentum
A. mass wasting on the valley side
At a delta______________.
A. stream gradient decreases
B. a single channel breaks into multiple radiating distributary channels
C. A and B correct
D. none
C. A and B correct
If a 50-year flood occurs on the Mississippi RIver in 2010, what is the probability that a flood of the same magnitude will occur in 2011?
A. 0%
B. 1%
C. 2%
D. 50%
2%
How does oceanic crust differ from continental crust?
a) Ocean crust is composed almost entirely of basalt and gabbro, whereas continental crust includes many kinds of igneous and metamorphic rocks.
b) All of the other answers are correct.
c) Oceanic crust is significantly denser than continental crust.
d) Ocean crust is about 7 - 10 km thick, whereas continental crust is about 35 - 70 km thick.
b) All of the other answers are correct.
How deep are the abyssal plains of the ocean? / How high is the highest mountain on land (i.e., Mt. Everest)?
a) Abyssal plains range from 3 to 5 km deep. / Mt. Everest is 8.8 km high.
b) Abyssal plains range from 8 to 15 km deep. / Mt. Everest is 6.8 km high.
c) Abyssal plains range from 10 to 20 km deep. / Mt. Everest is 5.2 km.
d) Abyssal plains range from 30 to 50 km deep. / Mt. Everest is 4.4 km high.
a) Abyssal plains range from 3 to 5 km deep. / Mt. Everest is 8.8 km high.
What underlies the broad continental shelves that border some shorelines?
a) Continental shelves are underlain by normal continental crust that happens to be pulled below sea level by the weight of the attached oceanic crust.
b) Continental shelves are underlain by very thick continental crust.
c) Continental shelves are underlain by very thick piles of basalt, erupted at a hot spot volcano.
d) Continental shelves are underlain by continental crust that was stretched during rifting, has subsided, and has been buried by sediment.
d) Continental shelves are underlain by continental crust that was stretched during rifting, has subsided, and has been buried by sediment.
The deepest places in the ocean are ________, where water depths reach _________ .
a) trenches / 11 km
b) mid-ocean ridges / 2.0 km
c) abyssal plains / 4.5 km
d) transform faults / 3.0 km
a) trenches / 11 km
Most of the igneous rocks within oceanic abyssal plains are ______________.
A. Exposed at the surface of the sea floor
B. Covered by sand and gravel introduced by rivers at deltas
C. Covered by clay and the skeletal remains of microplankton
D. Covered by limestone made up of the fragments of large invertebreate shells
C. Covered by clay and the skeletal remains of microplankton
The density of seawater increases with _______________.
A. Increasing temperature and increasing salinity
B. Decreasing temperature and increasing salinity
C. Increasing temperature and decreasing salinity
D. Decreasing temperature and decreasing salinity
B. Decreasing temperature and increasing salinity
Upwelling currents exist along the east coast lands at the equator because of ________________.
A. sea-level variation between the worlds ocean
B. the upwelling of denser, more saline cold bottom waters
C. the divergence of surface currents that are part of oppositely spinning gyres in the two hemispheres
D. variation in tidal behavior between the two hemispheres
C. the divergence of surface currents that are part of oppositely spinning gyres in the two hemispheres
Gyres__________.
A. rotate clockwise in northern hemisphere and counterclockwise in the southern hemisphere
B. rotate counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere
C. are caused by coriolis effect
D. both a and c are corect
D. both a and c are corect
An ocean wave that was causes by wind will disturb the water to a depth equal to__________.
A. wavelength
B. surface amplitude
C. bottom of the sea floor
D. one-half of its wavelength
D. one-half of its wavelength
The local magnitude of the tidal effect is controlled by ________ .
A. steepness of intertidal beach
B. position of sun
C. bathymetry of region
D. A and C
D. A and C
A well sorted sediment will have ___________ porosity than a poorly sorted sediment.
A. greater
B. less
C. A and B correct, depending on pressure
D. approx the same
greater
The rate of groundwater flow per unit area through a body of rock or sediment depends ____________.
A. only on the slope of the water table locally
B. only on the porosity of the rock or sediment
C. only on the slope of the water table and permeability of the rock or sediment
D. only on the slope of the water table and porosity of the rock or sediment
on the slope of the water table and the permeability of the rock or sediment
Venice, Italy, has largely subsided beneath sea-level because of ____________.
a.polar ice caps melting due to global warming
b.extensive nearby groundwater mining and sediment compaction
c.tectonic forces related to the gradual, ongoing collision of Africa and Europe
d.None of the above are correct; Venice was built underwater during the Middle Ages.
b.extensive nearby groundwater mining and sediment compaction
You find a huge new cave system and discover it has multiple, extensive levels, each about 500 ft below the one above it. What can you infer about the water table in the region?
a.It used to be higher.
b.It periodically dropped further and further.
c.It lies beneath an aquitard
d.Both a and b are correct.
d.Both a and b are correct.
A bedrock that has no intergranular porosity, but that has extensive interconnected fractures, ____________.
a. is impermeable
c. has secondary porosity
b. is probably permeable
d. Both b and c are correct
D - both a and b are correct
Which list correctly orders the three types of subsurface water from shallowest to deepest?
a.groundwater, soil moisture, vadose zone water
b.soil moisture, groundwater, vadose zone water
c.groundwater, vadose zone water, soil moisture
d.soil moisture, vadose zone water, groundwater
D - soil moisture, vadose zone water, groundwater
You can recognize a karst terrain by_______.
A. abundant sandstone bedrock
B. dendritic river networks
C. convoluted shorelines
D. the presence of sinkholes and disappearing streams
D. the presence of sinkholes and disappearing streams
A plume of contamination will . . .
A. move in the same direction as groundwater flow.
B. move in the opposite direction to groundwater flow.
C. move perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow.
D. gradually rise directly beneath the source.
A. move in the same direction as groundwater flow.
What happens as a consequence of pore collapse due to groundwater depletion?
A. land subsidence
B. saline intrusion
C. contamination
D. flow reversal
A. land subsidence
How can you tell where a perched water table intersects the face of a hill?
A. the land surface is particularly dry.
B. the material making up the ground is not consolidated.
C. a spring flows
C. a spring flows
Unconsolidated gravel, containing abundant pores that are well connected to one another, would make a good _______, because it could hold ________, accessible water.
A. aquitard / abundant
B. aquifer / abundant
C. aquitard / very little
D. aquifer / very little
B. aquifer / abundant
Which of the following is an example of unidirectional change on Earth?
A. carbon cycle
B. rock cycle
C. hydrological cycle
D. evolution of life
D. evolution of life
Geologic dating methods indicate that the oldest rocks on Earth formed about _____ , whereas the earliest life had appeared by at least _____ .
A. 3.9 Ga / 542 Ma
B. 3.5 Ga / 4.0 Ga
C. 4.0 Ga / 3.8 Ga
D. 4.5 Ga / 800 Ma
C. 4.0 Ga / 3.8 Ga
What is the difference between climate change and climate variability, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in simple words?
A. A variable climate means, for example, that colder days may occur duing warm periods. In contrast, climate change could mean that warm periods would lead to an increasing # of cold days.
B. A variable climate means, for example, that cold days may occur only during summer periods. In contrast, climate change means , that warmer periods would lead to an increasing # cold days in the winter.
C. Variable climate means, that cold days may occur during warm periods. In constract climate change could mean that warm periods would lead to an increasing number of warm days.
D. Variable climate means, that warm periods would lead to a higher number of warm days. In contrast, climate change could mean that cold days may occur during warm periods.
C. Variable climate means, that cold days may occur during warm periods. In constract climate change could mean that warm periods would lead to an increasing number of warm days.
Which statement is NOT true, regarding global warming.
A. an increasing CO2 concentration in the atmosphere was observed since the 1950s.
B. CO2 levels derived from ice cores provide time series up to several thousand years into the past.
C. an increasing CO2 concentration causes an expansion of the greenhouse effect, which leads to global warming
D. climate models are able to reproduce observed temperature trends over the past century without including a rise in greenhouse gases.
D. climate models are able to reproduce observed temperature trends over the past century without including a rise in greenhouse gases.
Which statement is a valid scientific expression?
A. A human-cause of climate change is so obvious; we should believe it.
B. An overwhelming amount of scientific evidence points to the fact that current global warming is caused by human
C> climate change is definitely not caused by
B. An overwhelming amount of scientific evidence points to the fact that current global warming is caused by human
A biogeochemical cycle means that _________.
A. movement of biogeochemical minerals over time through the rock cycle
B. exchange of chemicals among magmatic and solid-phase system
C. transitioning and residence and specific chemicals among living and nonliving systems.
D. Both, A and B are correct
C. transitioning and residence of specific chemicals among living and nonliving systems.
Which geologic event is NOT suspected as a soruce of major climate change?
A. massive eruption of flood basalts
B. eruption of supervolcanoes
C. impact of asteroids
D. very large earthquake
D. very large earthquake
An example of worldwide climatological and ecosystem change caused by a geologic event is the ______.
A. permo-triassic impact event
B. impact of meteor at the end of the Cretaceous
C. Increase in atmospheric oxygen content from approx. 1 to 22%, at the end of Cretaceous
D. Cambrian eruption of approximately 3 million cubic km basalt in what is now Siberia
B. impact of meteor at the end of the Cretaceous
Tectonic uplift and resultant chemical weathering ____________ CO2 to/from the atmosphere.
A. remove
B. add
C. have no net effect on
D. nearly triple
A. remove
Which of the following is NOT an example of biogeological changes that are recently occuring and attributing to warming of the northern hemisphere?
A. the elevations at which mosquitoes can survive
B. The average weight of polar bears
C. The southerly limit of reindeer in the Scandinavian countries and Kazakhstan
D. The average spring date at which tree sap begins to flow
C. The southerly limit of reindeer in the Scandinavian countries and Kazakhstan
In the last few decades, global warming has been most strongly affecting the climate and wildlife of _________ regions.
A. equatorial
B. temperature
C. polar
D. Deep-sea
polar
Which of these processes contributes the most to the formation of ice-margin lake?
A) Glacial subsidence
B) Erosion of loess
C) Moraine retreat
D) Glacier Rebound
A) glacial subsidence
Cape Code, Massachuseets and Long Island, New York are both examples of:
A) Dumlines
B) Lateral Moraines
C) Eskers
D) End Moraines
D) End Moraines
Stratified sorted sand and gravel are deposited by:
A) Mountain Glaciers
B) Continental Glaciers
C) Glacial outwash streams
D) Wind
C) Glacial outwash streams
The record of marine sedimentation suggests that there were on the order of ___ glaciations and interglacials during the pleistocene.
A) 4
B) 3
C) 20
D) 600
C) 20
During the last ice age, the climate in the southwest of the United States was ______: as a concequence, ______ formed
A) drier/ large dune fields
B) permafrost / vast areas of patterned ground
C) wetter / pluvial lakes
D) substantially below freezing / continental glaciers
C) wetter / pluvial lakes
Which factor determines the direction in which ice flows?
A) The surface slope of the ice
B) The slope of the substrate beneath the ice
C) The Coriolis effect
D) The direction that water streams beneath ice flow
B) The surface slope of the ice
A well-sorted sediment will have ____ porosity than a poorly sorted sediment.
A) Greater
B) Less
C) A and B can be correct, depending on pressure
D) Approximately the same
A) Greater
Which statement is correct?
A) Above the water table, there are no pores
B) Below the water table, pores are filled with air
C) In saturated zone, pores are filled with water
D) Water table forms where the air pressure is in equilibrium with water pressure
C) In saturated zone, pores are filled with water