Theatre Appreciation
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Pantomime
story or action performed without words relying on body language
stage business
small actions used to fill time, create character, and sometimes to make the action “more realistic”
Open Up/Cheat Out
Facing as much towards the audience as possible
Diction
The actors ability to be understood by the audience
Volume
The actors ability to be heard by the audience
Cue
The last words or actions indicating the time for another actor to speak or move
aside
Lines said to the audience that other actors onstage are not supposed to be hearing
pick up cues
A direction for the actor to begin responding immediately without allowing any lapse time
Tableau/ Tableau vivant
A living picture. A group of actors/performers arranged to represent a scene
Notes
At the end of each rehearsal, the director will give his/her notes, which are his/her comments on
the performance
Auditions
Readings before a director to determine casting of a play
Call Backs
An additional audition for the final actors being considered. Similar to semifinals in sports
Clear the Stage
A direction given to all actors, musicians, and technicians to leave the stage area prior
to the beginning of a play
Places
The direction for all actors, musicians, and technicians to go to their proper position and be
ready for the beginning of a play or scene
strike
taking down, changing out and putting away costumes, props and sets after a production
run through
An uninterrupted rehearsal of a scene, act, or the entire play
Curtain Call/Bows
The carefully choreographed appearance of actors on stage after the performance to
acknowledge the applause of the audience
blackout
Lighting term: switching all lights out at once, leaving the stage in complete darkness
Blocking
Setting the actors' positions and moves during the rehearsal process
Box Office
the place where the tickets are sold
Properties
Small items which actors carry
onto or around the stage
Rake
Many stage floors, usually in theatres built for dance or variety, are higher at the back than at the
front, to give the audience a better view. These stages are said to be "raked", and the "rake" is the angle of slope from back to front. In most modern theatres it is the audience seating that is raked, not the stage.
revolve
A stage or, more usually, part of a stage, which can revolve 360 degrees
set
The scenery for a particular show or individual scene
Upstage
The area of the stage that is the furthest from the audience
Downstage
The area of the stage that is the closest to the audience
Stage Right
The right side of the stage from the actor’s point of view (facing the audience.)
Stage Left
The left side of the stage from the actor’s point of view (facing the audience.)
Center
Center of the stage.
Full Front
Facing the audience.
Full Back
Facing away from the audience.
Cross
Movement from one area of the stage to another.
Blocking
The set movement of all the actors onstage throughout the play.
actor/audience configuration, critical attitude born (do it right or die!), defined playing space
Primitive Theater Major Contributions
ritual
A ceremony which pays tribute to, or requests something from a deity and implies control over said deity. Also implies a body of believers accept it as effective and important to life.
assured food supply through magic and ritual, provided vicarious experience, calmed certain fears
3 Ways Theatre Answered Basic Societal Needs for the
Primitives
threshing floor
Area where grain is winnowed. Wheat separated from
the chaff. Also became a place for
performative actions or rituals. Since the space was
important for life (food) the space became sacred. That
which separated the sacred from the profane was the threshold.
Qualities of the Threshold by Eliade
1. Threshold is the limit, the boundary, the frontier, that
distinguishes and opposes two worlds. Conflict
2. Paradoxical place where those worlds communicate.
Passage from the profane to the sacred world becomes
possible.
3. Numerous rites accompany passing the threshold—a
bow, prostration, genuflection,...
4. Threshold has guardians
5. Within the sacred precincts the profane world is
transcended.
plot, character, thought, diction, music, spectacle
Aristotle’s 6 elements
plot
the arrangement of incidents; the life and soul of tragedy; usually can be stated in 25 words or less
character
the quality about human beings that we determine by viewing their actions and choices
thought
what the play is about; man vs…
diction
how language is used; how the thought is articulated; can vary from writer to writer
music
used to heighten emotions of the audience
spectacle
the physical environment the play is put in; what you can see
theatron
where audience sat
“seeing place”
on semi-circular terraced rows of benches
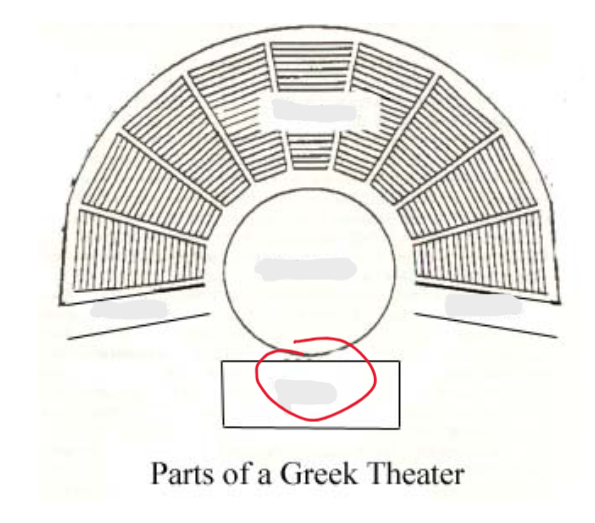
skene
meaning “tent”
on the far side of the orchestra was this stage building
covered structure where actors would store masks/costumes
allowed for quick costume changes beyond sight of the audience
orchestra
the core of any Greek theatre
“dancing space” for the chorus and main performance space
pinakes
painted panels; temporary scenic elements usually placed in the openings of the Greek skene
periaktoi
a revolving triangular prism made of wood, bearing on each of its three sides a different pictured scene
tragedy
shows us pain and gives us pleasure
The tragic hero/heroin disturbs a balance in nature—a balance which sooner or later must right itself
simple, stressed ideal
What kind of plot Aeschylus used?
Prometheus Bound
What play did Aeschylus write?
embodied great passion and principle
What kind of characters did Aeschylus have?
there is ultimate justice, pride must be stripped from the hero, justice falls where it is deserved
What kind of thought did Aeschylus have in his work?
Sophocles
Which playwright wrote Oedipus Rex?
Aeschylus
Which playwright wrote Prometheus Bound?
all is known/covers whole story, consequential issue covered and solved, fate of hero is accomplished
What kind of plot did Sophocles have in his work?
noble and dignified characters, character revealed through choices made
What kind of characters did Sophocles have in his work?
noble character confronts some terrible crisis, suffers beyond fault, yet remains dignity
What kind of thought did Sophocles have in his work?
Euripides
Which playwright wrote Medea?
Human issues, use Gods as justifications for actions
What kind of plot did Euripides use in his work?
women as major characters, not particularly dignified, distraught, men less than ideal
What kind of characters did Euripides use in his work?
morality of the Gods is less than any good man, Gods will never be perfect, therefore humans are doomed
What kind of thought did Euripides use in his work?
Aristophanes
the playwright that is a gossip?
theatron
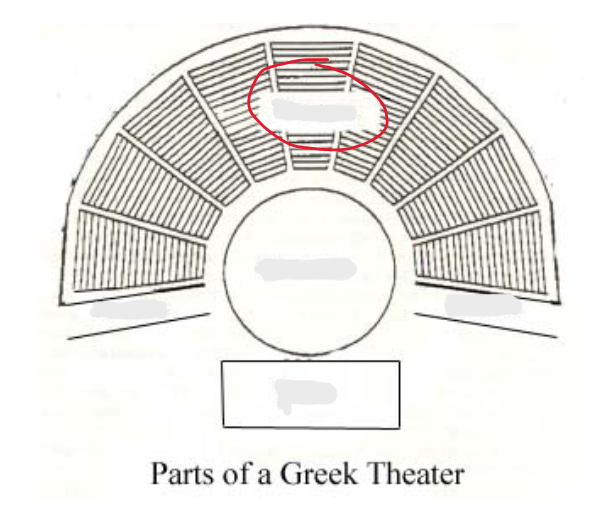
orchestra
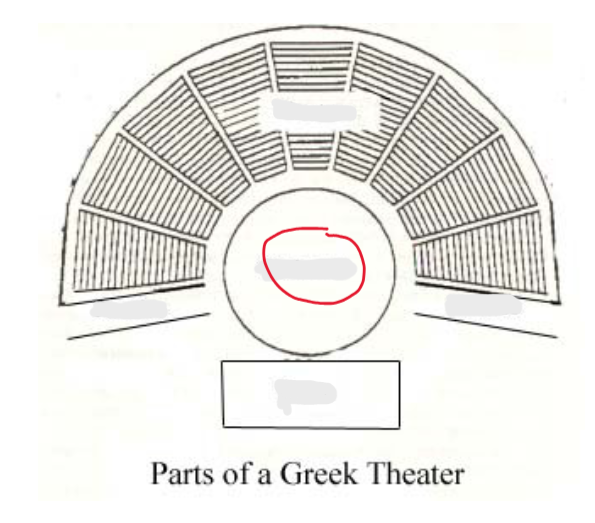
skene
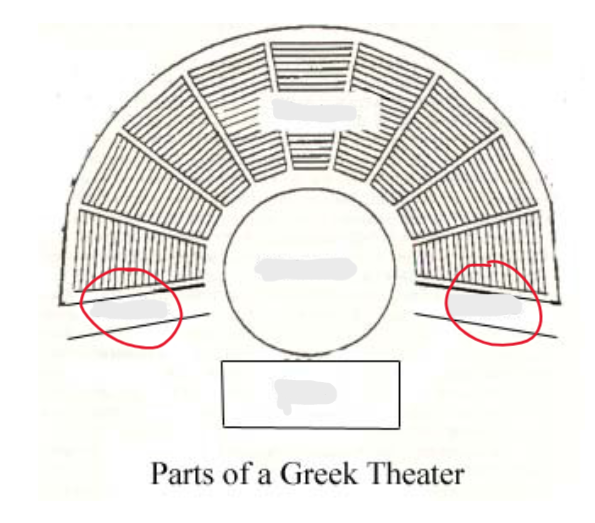
Parodos
tetrology
consists of three tragedies and one satyr play
satyr play
a spoof on a tragedy; satire
comedy genre
Humorous story about a normal person in laughable circumstances
or vice versaunhappiness —> happiness
tragedy genre
Serious story about a good person, usually an important and
powerful oneThey suffer a significant downfall due to his or her own flaws and
misstepsHappiness -> Unhappiness
comedy and tragedy
the two basic theatrical genres
drama, tragicomedy, farce, melodrama, issue play
all the subdramas
drama
Neither a comedy nor a tragedy
Serious story about one or more characters at a time of flux and crisis in
their livesCommon characteristics: intense conflict, strong emotions, & personal
themes
tragicomedy
Combination of sad and funny story elements
May be either a series of tragic events with a happy ending or vice versa
farce
Form of comedy
Designed to evoke laughter but relies more on buffoonery, physical
humor, and ludicrously improbably situations
melodrama
Story about good triumphing over evil
Happiness -> unhappiness -> happiness
Common characteristics: strong plot, archetypal characters, exaggerated
conflict, sensational elements, & a victim of circumstances
issue play
Story organized around a social or political issue and the author’s ideas
about how to address itPurpose: to arouse the audience emotionally, teach them a lesson, and provoke them to take certain new actions in their lives
upper stage right
A
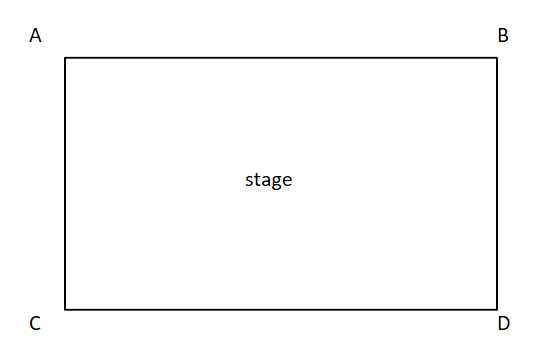
upper stage left
B
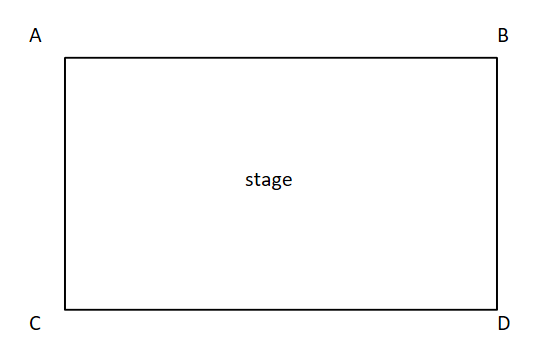
down stage right
C
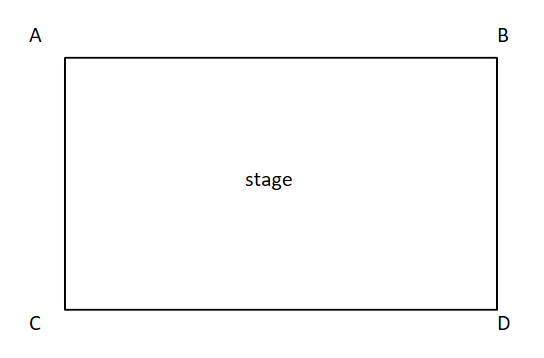
down stage left
D
practical
a property on stage that actually works/functions (running sink)