VCE BM Unit 4: AOS1: Reviewing Performance-The Need for Change
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Business Change
•the alteration of behaviours, policies, and practices of a business. Businesses are constantly evolving and adapting to improve their performance in certain areas.
No matter the situation, strong leadership and management skills are required for successful execution
•outcomes can be both positive and negative.
Examples of Business Change
•Flexible/Work from home options
•Netflix banning account sharing
•The move to electric vehicles
•Ringwood SC removing bells
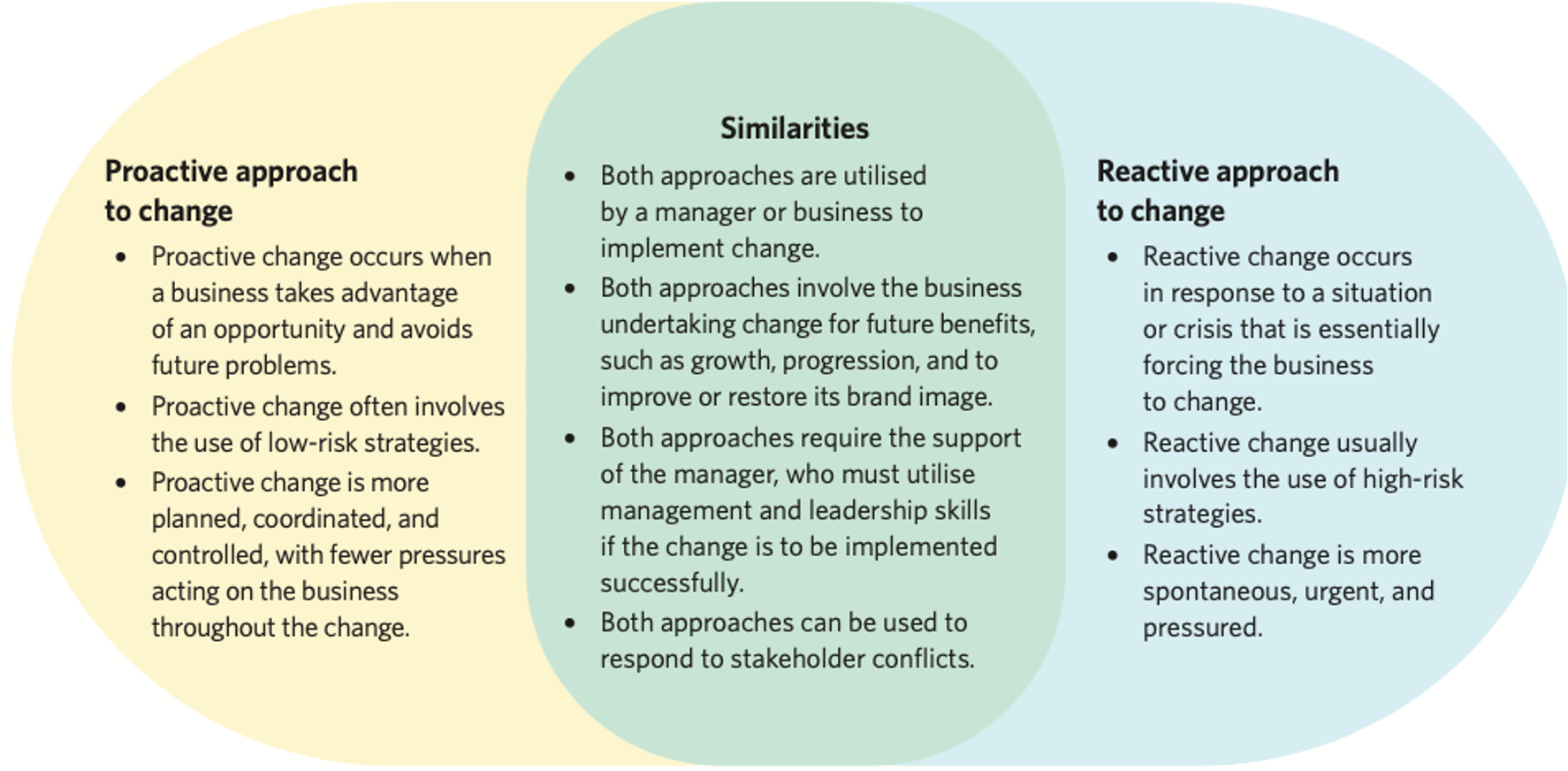
Proactive approach to Business Change
•when a business changes to avoid future problems or take advantage of an opportunity to gain a competitive advantage.
•This could be because of a:
•gap in the market
•change in market trends which poses a new business opportunity
•investment in new technology
Reactive approach to Business Change
•when a business undertakes change in response to a situation or crisis.
•Businesses will usually try to avoid this type of change, however sometimes it is necessary.
Comparison of types of approaches to change
Key Performance Indicators
criteria that measure a business’ efficiency and effectiveness in achieving its different objectives.
can be used to identify specific areas within the business where change is necessary and can be used continuously to determine the success of the implemented change.
For a business to use ____ to its advantage, the ___ must be relevant to the area of the business being analysed, a reliable measure of performance, and be used to compare business performance over time.
Percentage of market share (KPI)
measures the proportion of a business’ total sales, compared to the total sales in the industry, expressed as a percentage figure.
can highlight the proportion of customers that a business and its competitors are able to engage with and therefore shows a business’s impact and success in the market.

Net Profit (KPI)
calculated by subtracting total expenses incurred from total business revenue earned, over a specific period of time.
Expenses are the costs that a business incurs from conducting its operations.
Revenue is the sum of all income that a business has generated from business activities, usually from selling goods and services to its customers.

Rate of Productivity growth (KPI)
The change in the total output produced from a given level of inputs over time, expressed as a percentage figure.
Productivity is a measure of performance that indicates how many inputs (resources) it takes to produce an output (goods or services).

Number of sales (KPI)
The total quantity of goods and services sold by a business over a specific period of time.
A business’s financial performance can be measured using this KPI, as it indicates how well goods and services are received by customers.
Number of Customer Complaints (KPI)
The number of customers who notified the business of their dissatisfaction over a specific period of time.
Rate of Staff Absenteeism (KPI)
The average number of days employees are not present when scheduled to be at work, for a specific period of time.
May be due to illness, personal leave, or applying for work elsewhere, which can cost a business in terms of its productivity, time, and finances.
A human resource manager would examine this KPI as an indicator of staff morale.

Staff Morale
The collective attitudes, satisfaction, and overall outlook that employees have of the workplace. Staff morale can influence a business’s productivity, workplace safety, attendance, and staff turnover.
Level of staff turnover (KPI)
The percentage of employees that leave a business over a specific period of time and must be replaced.
Human resource managers can analyse this KPI to examine staff morale, employee satisfaction, and the strength of interpersonal relationships within the business.

Number of workplace accidents (KPI)
The number of injuries and unsafe incidents that occur at a work location over a specific period of time.
High incidents of workplace accidents can negatively affect staff morale, decrease motivation, increase rates of staff absenteeism, and increase the level of staff turnover, as employees feel that their safety is not the business’s priority.
Workplace accidents can occur due to:
•old or faulty equipment
•poorly trained employees
•dangerous nature of work tasks
unsafe working practices
Level of wastage (KPI)
The amount of inputs and outputs that are discarded during the production process.
A business manages resources more efficiently by reducing waste, which can cut production costs.
Number of Website Hits
The amount of customer visits that a business’ online platform receives for a specific period of time.
This is a useful indicator of a business’ customer engagement and customers’ overall interest in the business and its products
This KPI also provides analytical data that can allow businesses to determine what specific products and areas of the business are receiving the most consumer interest.
Lewin’s Force Field Analysis
•a theoretical model that determines if businesses should proceed with a proposed change.
Steps of a Force Field Analysis
The principles of Lewin’s Force Field Analysis theory are conducted in a step-by-step process:
Pre-requisites: Identify the change and identify the driving and restraining forces
1.Weighting the driving and restraining forces
2.Ranking the driving and restraining forces
3.Implementing a response (action plan)
4.Evaluating the response
Following these steps helps a business make a clear analysis of the driving and restraining forces of the proposed change, in order to respond to them and ensure the successful implementation of change.
FFA Step 1: Weighting
•the process of scoring and attributing a value to the driving and restraining forces.
•This principle enables the business to assign a ‘weight’ to determine the level of impact each force can potentially have on the change.
•Typically, involves assigning a numerical score between 1 (a low score) to 5 (a high score).
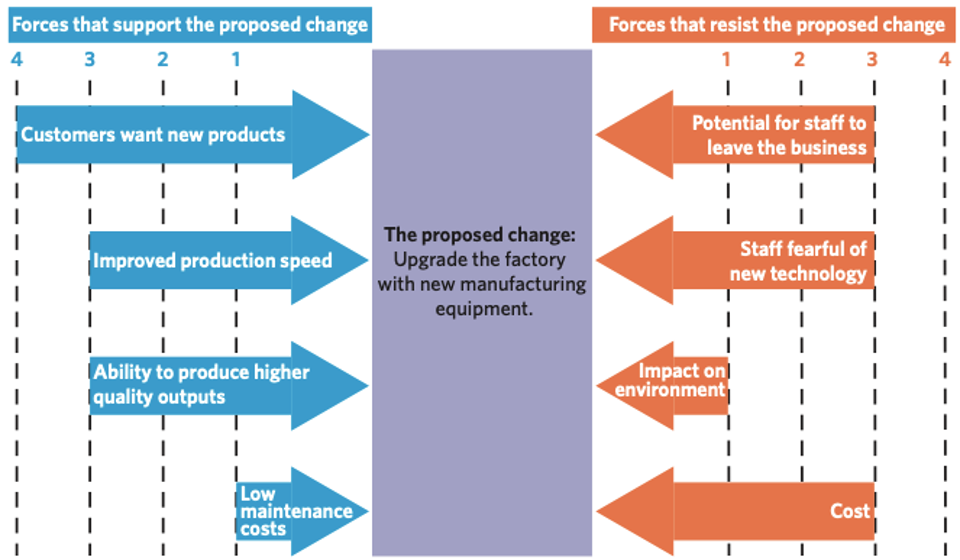
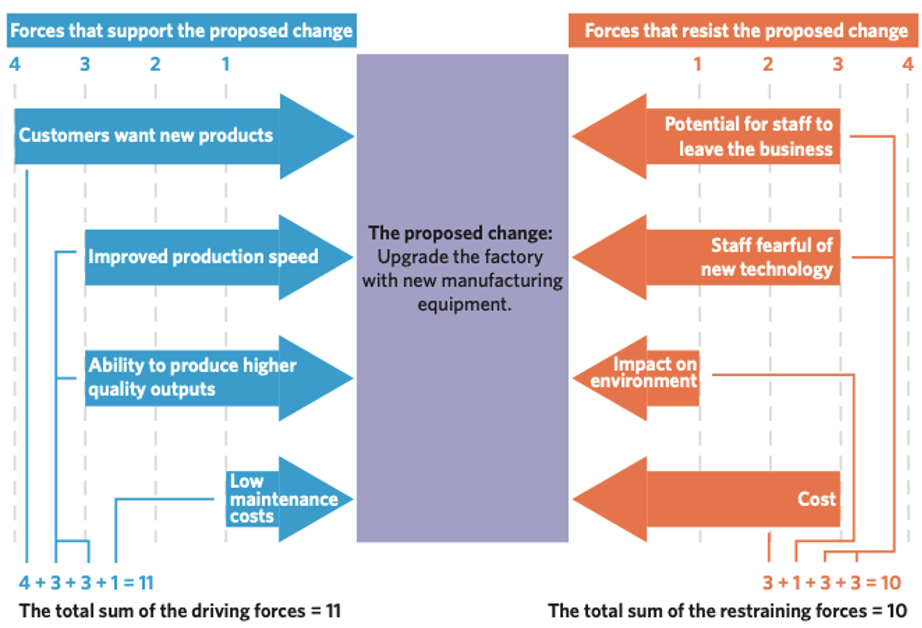
FFA Step 2: Ranking
arranging the forces in order of value and determining the total score of driving and restraining forces.
A business change can only be implemented successfully when driving forces are stronger than restraining forces.
Evaluate the overall balance between driving and restraining forces. Determine whether the driving forces outweigh the restraining forces or vice versa.
This step helps determine which driving forces could most easily be strengthened further, and which restraining forces are most important to be removed or minimised.
FFA Step 3: Implementing a Response
Based on the analysis (ranking), develop strategies to strengthen the driving forces and weaken the restraining forces. This might involve leveraging strengths, addressing weaknesses, mitigating risks, or changing perceptions.
•During the implementation of a response, an action plan that details the following can be created to support the implementation of the response to strengthen or weaken a force:
•what needs to be done
•who is responsible
•resources required
•deadlines for task completion
•how the business will continuously strengthen the driving forces and weaken the restraining forces
FFA Step 4: Evaluating the Response (monitoring)
•Has the response successfully addressed the driving and restraining forces
Implement the strategies developed and monitor their effectiveness over time. Adjust the approach as needed based on ongoing assessments.
•This step refers to comparing the impact of the response to the anticipated change and determining whether further action needs to be taken.
•If KPI targets indicate a negative change, the Force Field Analysis may need to be redone, because restraining and driving forces may have strengthened, weakened, or changed.
Evaluation of Lewin’s Force Field Analysis
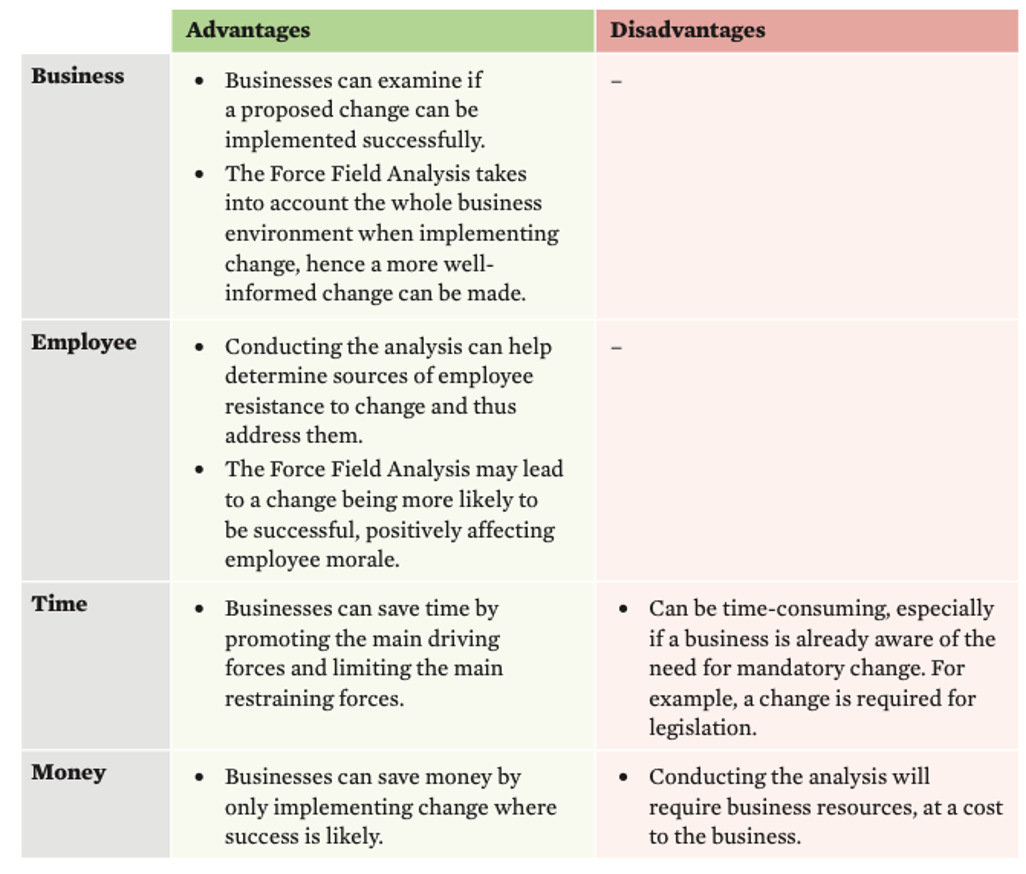
Flow chart of Lewin’s Force Field Analysis

Driving forces
Factors affecting the business environment that promote and support business change.
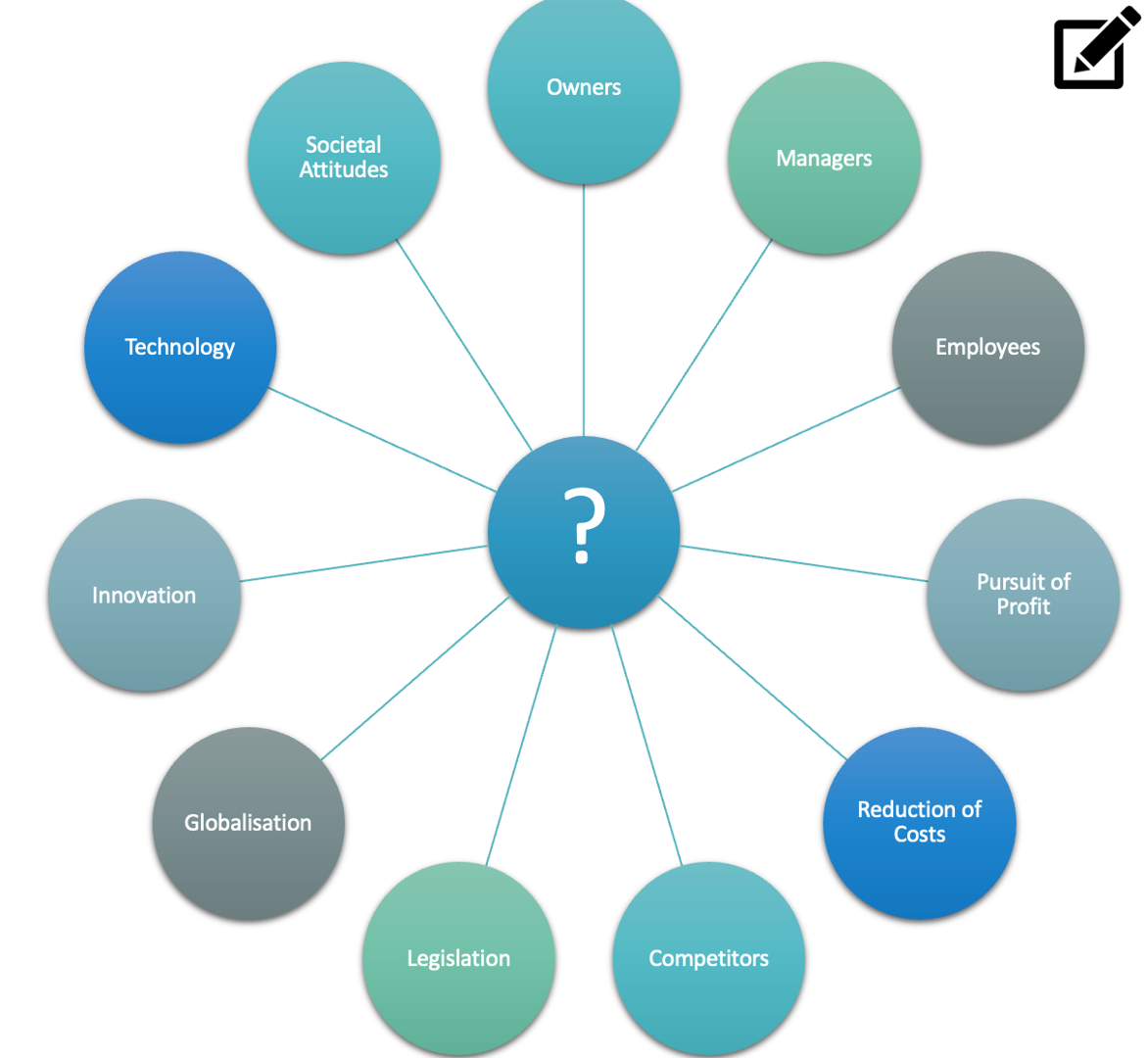
Driving force: Owners
•Owners may actively seek out and support change in order to remain competitive in the business’ rapidly and continuously changing environment.
•They have an interest in the financial performance of the business.
•Due to these interests, owners can act as a driving force for change if they believe change will be beneficial to future business performance.
Driving Force: Managers
•Managers can act as a driving force for change when the proposed change will enhance the business’ ability to meet objectives.
•When a manager wants the change to occur, their management style, attitude, and leadership can encourage successful implementation of the change.
•Managers set an example for other employees to follow.
•Because managers are also employees of a business, they are concerned with their job security and financial incentives, which leads them to seek opportunities for business change.
Driving Force: Employees
•Employees are responsible for achieving the business’ objectives.
•They have a personal interest in the performance of the business, given it provides them with work and an income.
•Employees may focus their attention on their working conditions, training, wage, and benefits that the business can offer them.
•Employees may act as a driving force for proposed changes that would improve their work environment.
Driving Force: Pursuit of Profit
•Businesses are encouraged to implement changes that improve their financial performance.
Driving Force: Reduction of costs
•Businesses may implement change to improve efficiency and effectiveness and reduce unnecessary costs that may arise in business processes.
•These changes can include:
•reduce wastage
•improve productivity
•source materials from a cheaper supplier
•relocate to benefit from less expensive rent
Driving Force: Competitors
•If a business fails to compete within its respective market, it will struggle to survive.
•Competitors are a driving force for change as a business must always adapt to remain competitive.
Driving Force: Legislation
•All businesses are required to comply with laws and regulations to avoid fines, suspensions, or closure.
•A business may be forced to change if new legislation is introduced.
Driving Force: Globalisation
the process by which governments, businesses, and people across the globe are becoming more interconnected, allowing for increased international trade and cultural exchange.•More businesses are operating on a global scale due to the removal of trade barriers.
•Businesses take advantage of economies of scale by finding more efficient and cheaper ways to produce their products.
•Cultural homogenisation has resulted in customers accepting and demanding goods and services originating from different cultures.
•Globalisation is a driving force for change as it provides opportunities for businesses to expand to new countries, particularly to gain a competitive advantage.
Driving Force: Technology
•Using technology, businesses can increase the efficiency and effectiveness of their operations, cutting costs and improving overall productivity.
Driving Force: Innovation
•With constant pressure from competitors, businesses should always aim to improve existing products and services or introduce new ones.
Driving Force: Societal Attitudes
•As the attitudes and beliefs of society are constantly changing, businesses need to ensure that their operations align with societal attitudes and behaviours.
Restraining Forces
factors that resist a business change or actively try to stop it.
If _________________ exceed driving forces, a business change is unlikely to be successful.
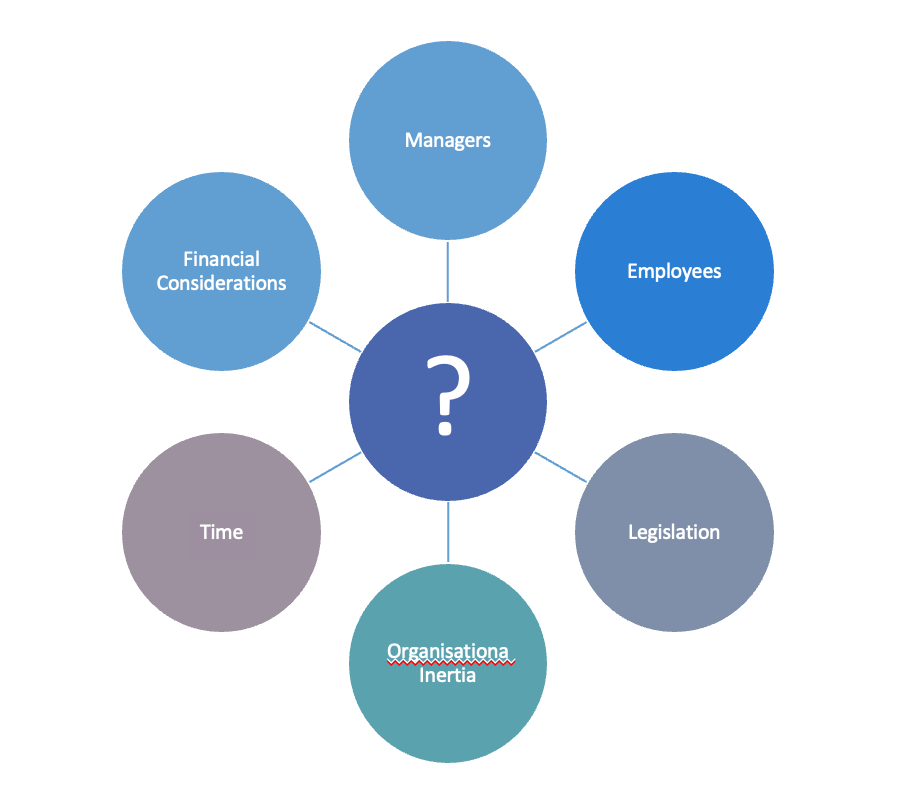
Restraining Force: Managers
•Managers may be unwilling to introduce a business change if they do not support the change.
•Managers may not support a change if they do not believe the change will be beneficial for the business’s performance, or if the proposed change threatens their position.
•To overcome organisational inertia, a business may have to change leadership, restructure the business, or create work environments that promote new directions.
Restraining Force: Employees
•Employees may resist a business change if the outcome is uncertain, they fear they cannot adapt, it affects their job security or work routine, or they don’t to see a reason for the change.
•Employees may even actively oppose these changes by carrying out industrial action.
•To overcome employees as a restraining force, managers usually have to persuade or create incentives for the proposed changes to be adopted, often needing to demonstrate key leadership and management skills.
Restraining Force: Legislation
Legislation can prevent a business from implementing business change and thus act as a restraining force.
To overcome a legislative restraining force, a business may have to apply for licences, obtain permits, or change contracts and agreements so they comply with the law.
Restraining Force: Organisational Inertia
•Organisational inertia is the tendency for a business to maintain established ways of operating.
•To overcome organisational inertia, a business may have to change leadership, restructure the business, or create work environments that promote new directions.
Restraining Force: Time
Change takes time, and having insufficient time to work through the change can cause resistance.
•Time restrictions may be due to other restraining forces.
•To overcome time as a restraining force, a business may need to implement the change progressively in stages or another business is engaged to assist with implementing the change.
Restraining Force: Financial Considerations
•Most business changes will incur a cost for it to be introduced or implemented such as, equipment, redundancy packages, training, and/or reorganisation of the business.
•If the business cannot finance the change, it will need to explore different ways of obtaining the required funds or alter the change to suit its financial position.
Porter’s Generic Strategies
•In 1985, Michael Porter proposed that businesses can gain a competitive advantage by adopting one of two generic strategies:
•Lower cost
•Differentiation
•Porter emphasised that a business should only implement one generic strategy. The appropriateness of which strategy to implement differs depending on the business’ situation.
Porter’s Lower Cost Strategy
This strategy involves a business offering customers similar or lower-priced products compared to the industry average, while remaining profitable by achieving the lowest cost of operations among competitors.
•Most viable in an industry with a large amount of cost-conscious customers with little brand loyalty.
•Porter states that only one business should aim to use this strategy in any industry.
•When a business can achieve the lowest costs of operations, it gains a competitive advantage using one of three pricing approaches
•Example: ALDI Supermarkets
Pricing approaches of Porter’s lower cost strategy
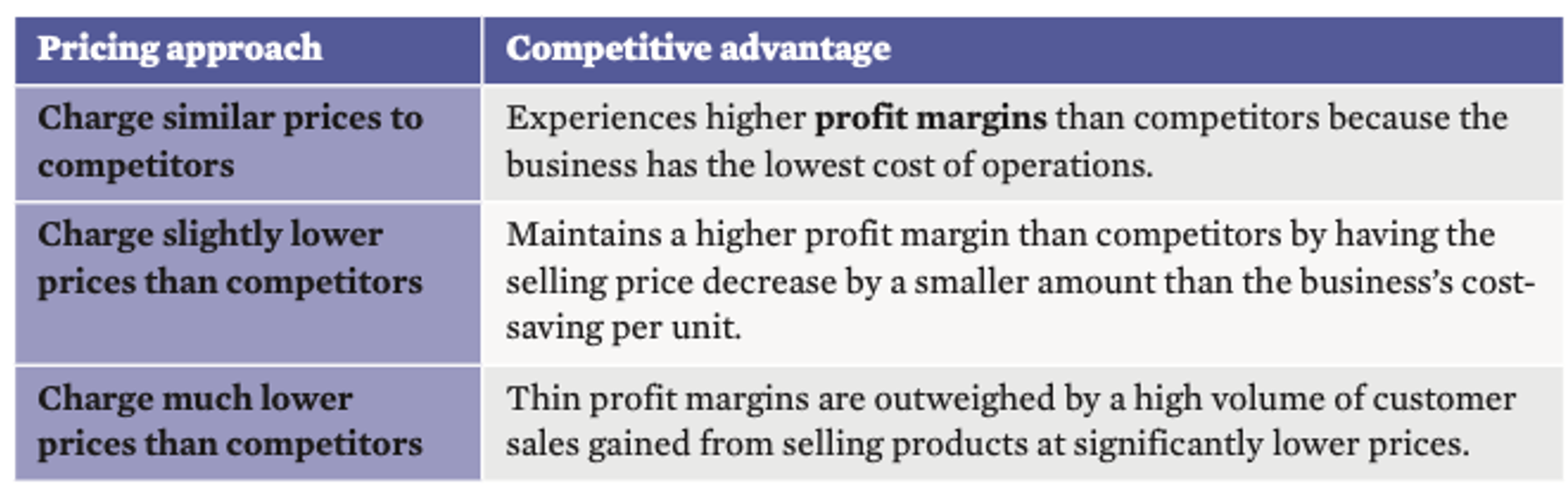
Cost reduction approaches for Porter’s lower cost strategy

Evaluation of Porter’s lower cost strategy
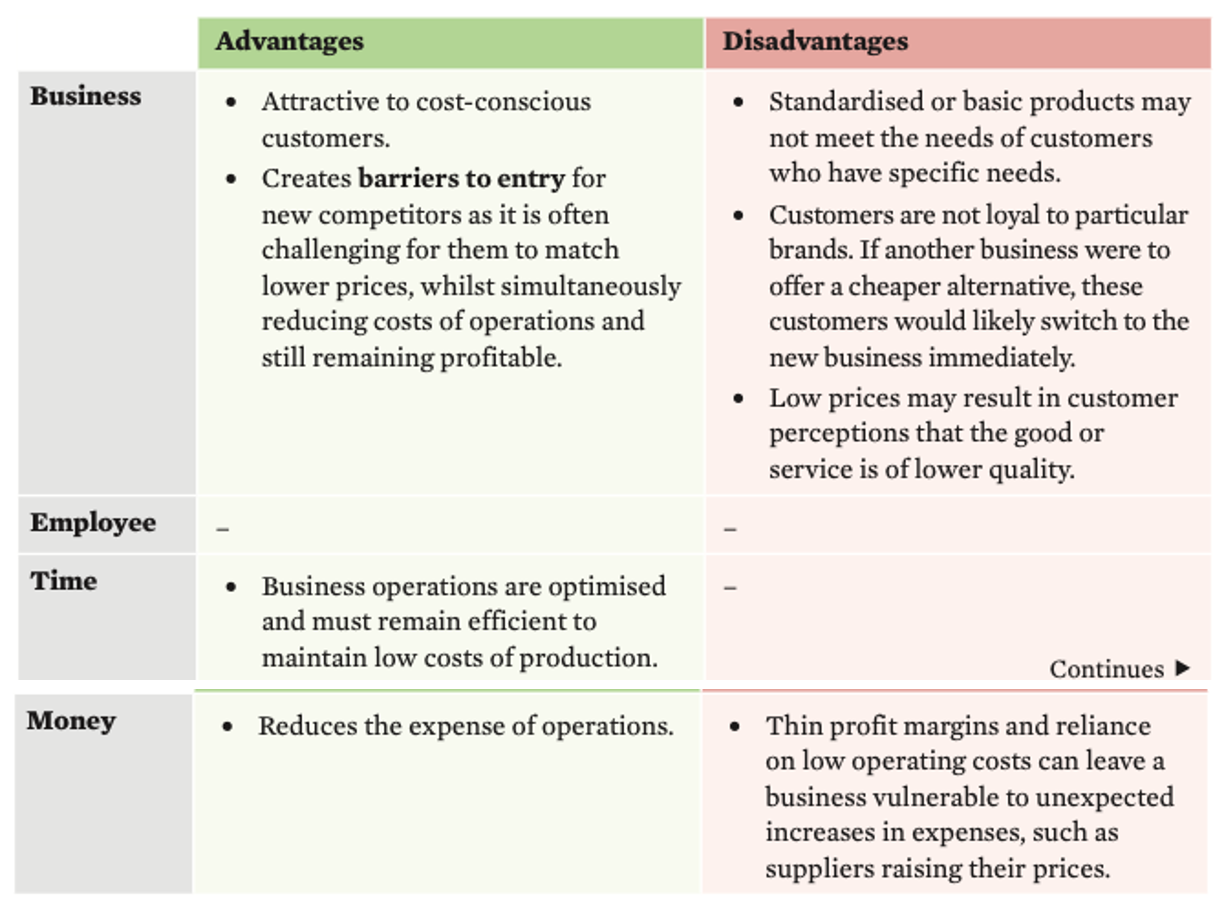
Porter’s Differentiation strategy
•This strategy involves offering customers unique services or product features that are of perceived value to customers, which can then be sold at a higher price than competitors.
•This is suitable for markets where customers are not price sensitive and specific customer needs are currently either unmet or under-served or those markets that are highly competitive.
•A business can create a point of differentiation for its product by:
•introducing new technology.
•innovating its original good or service.
•improving durability
•advertising
•niche marketing
Example: Tesla
Perceived value
a customer’s opinion on the benefits they receive when they purchase a good or service.
Point of differentiation
the unique selling features or elements that positively distinguish a business’s good or service from its competitors.
Evaluation of Porter’s differentiation strategy
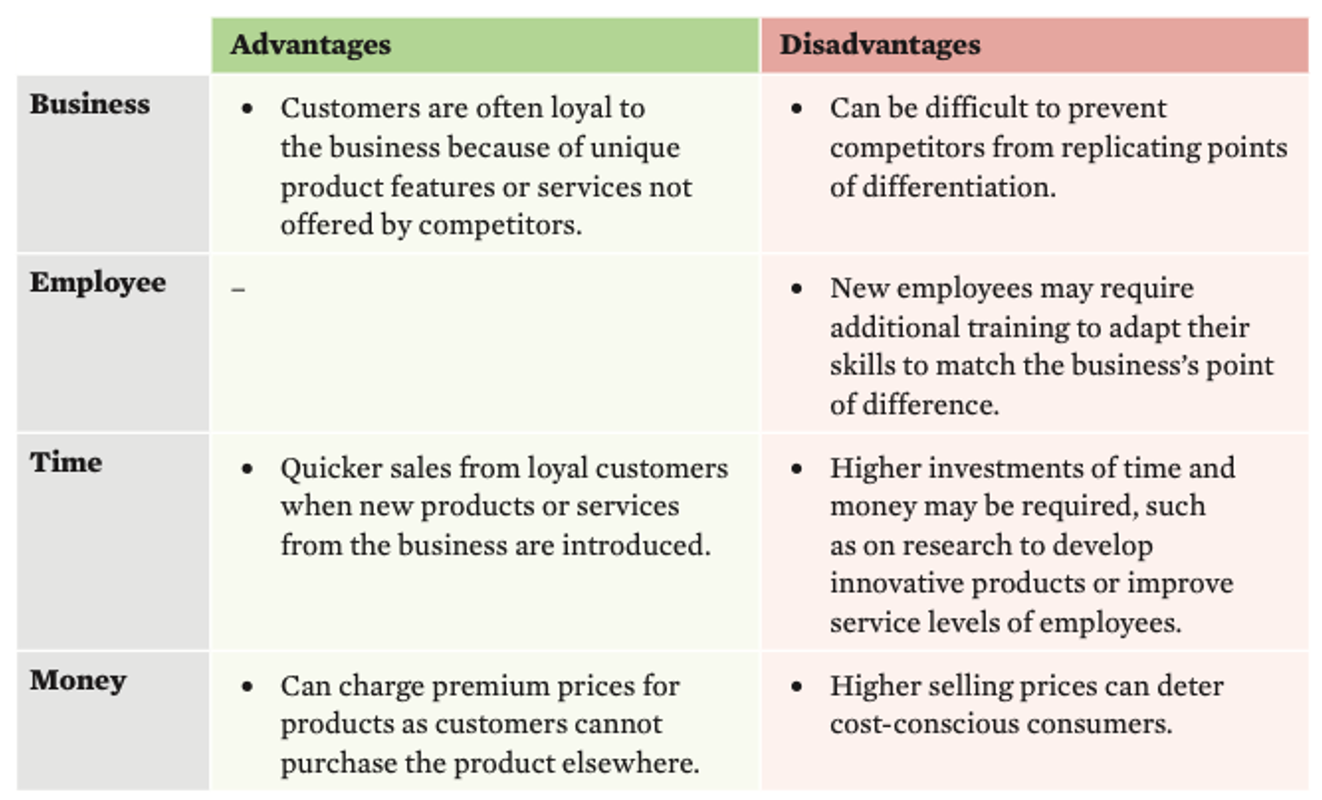
Comparison of the Lower cost and Differentiation strategies

Evaluation of Net Profit
Advantages:
-provides a broad overview of the business’s performance which can be shared to build stakeholder confidence
-can be used for future planning as a benchmark of performance
Disadvantages:
-can be timely to identify and calculate a businesses revenue and expenses
-is not indicative of a businesses corporate culture, staff morale etc
Evaluation of Percentage of Market share
Advantages:
-clearly shows a businesses position relative to competitors
-can be used to assess the effectiveness of marketing strategies
Disadvantages:
-can be timely/costly to calculate
-does not provide a clear insight into intangible elements of a businesses environment such as staff morale and a positive corporate culture.
Evaluation of Number of Sales
Advantages:
-can be used to quickly identify popular goods/services sold by a business (ie used to identify customer trends)
-can be used to save money (ie business can identify where they are making the least amount of sales)
Disadvantages:
-timely/costly to calculate
-does not provide insight into intangible elements of business environment such as employee morale and corporate culture
Evaluation of Rate of Productivity growth
Advantages:
-gives a clear benchmark for a businesses performance
-can indicate levels of staff morale and a positive corporate culture
Disadvantages:
-timely/costly to measure
-does not directly measure financial performance or the behaviour of customers
Evaluation of Number of Workplace accidents
Advantages:
-ensures legal compliance as businesses are meeting their minimum reporting requirements/ prevents action being taken against the business
-can help to indicate staff morale and level of corporate culture
Disadvantages:
-does not give an indication of the businesses financial performance
-may be skewed due to underreporting as employees fear disciplanary action
Evaluation of Level of wastage
Advantages:
-can help a business to identify areas for improvement which can result in cost reduction
-helps a business to address the issue of wastage which can help them to address the environmental component of corporate social responsibility
Disadvantages:
-does not clearly indicate intangible business elements such as staff morale
-can be complex to measure for example differentiating between avoidable and unavoidable waste (trimmings vs defects)
Evaluation of Level of staff turnover
Advantages:
-provides a clear indication of a businesses corporate culture and level of staff morale
-can be used to develop future planning such as the use of a retention development program
Disadvantages:
-focusing in retaining employees at all costs can result in a quantity over quality mindset
-Constantly focusing on turnover rates can create a negative atmosphere among employees, as it may imply a lack of trust or job security.
Evaluation of Rate of Staff Absenteeism
Advantages:
-tracking absenteeism over time can inform future planning ie are there periods of time where a large number of employees take leave
-indicates levels of staff morale and provides an insight into the businesses corporate culture
Disadvantages:
-doesnt account for presenteeism (staff attending work whilst ill/injured) which also has an impact on productivity
-excessive measurement can create a negative corporate culture especially if staff are absent due to illness/injury
Evaluation of number of customer complaints
Advantages
-complaints are a clear indication of customer satisfaction which can directly correlate to business success
-Complaint data provides valuable insights into areas where products or services may not meet customer expectations.
Disadvantages:
-may not be wholly accurate of the business or employees performance as employees may be caught on a bad day and complaints are subject to customer bias
-this KPI is reliant on customers taking initiative to interact with the business to express their dissatisfaction and as a result may not be wholly indicative of total satisfaction/dissatisfaction (eg does not recognise customers who are satisfied or customers who are dissatisfied but have not left a complaint)
Evaluation of Number of Website hits
Advantages:
-Website hits serve as a metric to evaluate the overall performance and popularity of the website. Higher traffic numbers generally indicate a greater level of interest in the organization's offerings or content.
-Tracking website hits allows organizations to benchmark their performance against competitors or industry standards.
Disadvantages:
-high levels of visitation does not necessarily correlate to a high level of engagement/sales, further exacerbated by bots
-Website hits provide numerical data but lack context about visitor intent, preferences, and needs. Understanding user motivations requires additional qualitative research and analysis beyond quantitative metrics.