Openstax Psychology Chapter 3
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Glial Cell
cell in the nervous system that: plays a role in formation of myelin and blood brain barrier, responds to injury, removes debris, enhances learning and memory
Neuronal Membrane
covers entire cell and separates the inside from the outside environment
Dendrite
receiving end of the neuron
Cell Body
soma/central area; maintains cell's vital functions
Axon
extends from cell body, sends messages to other neurons (messages go one-way only)
Axon Terminal
end of axon; where neurotransmitter production and release happens
Brain-communication
electro-chemical
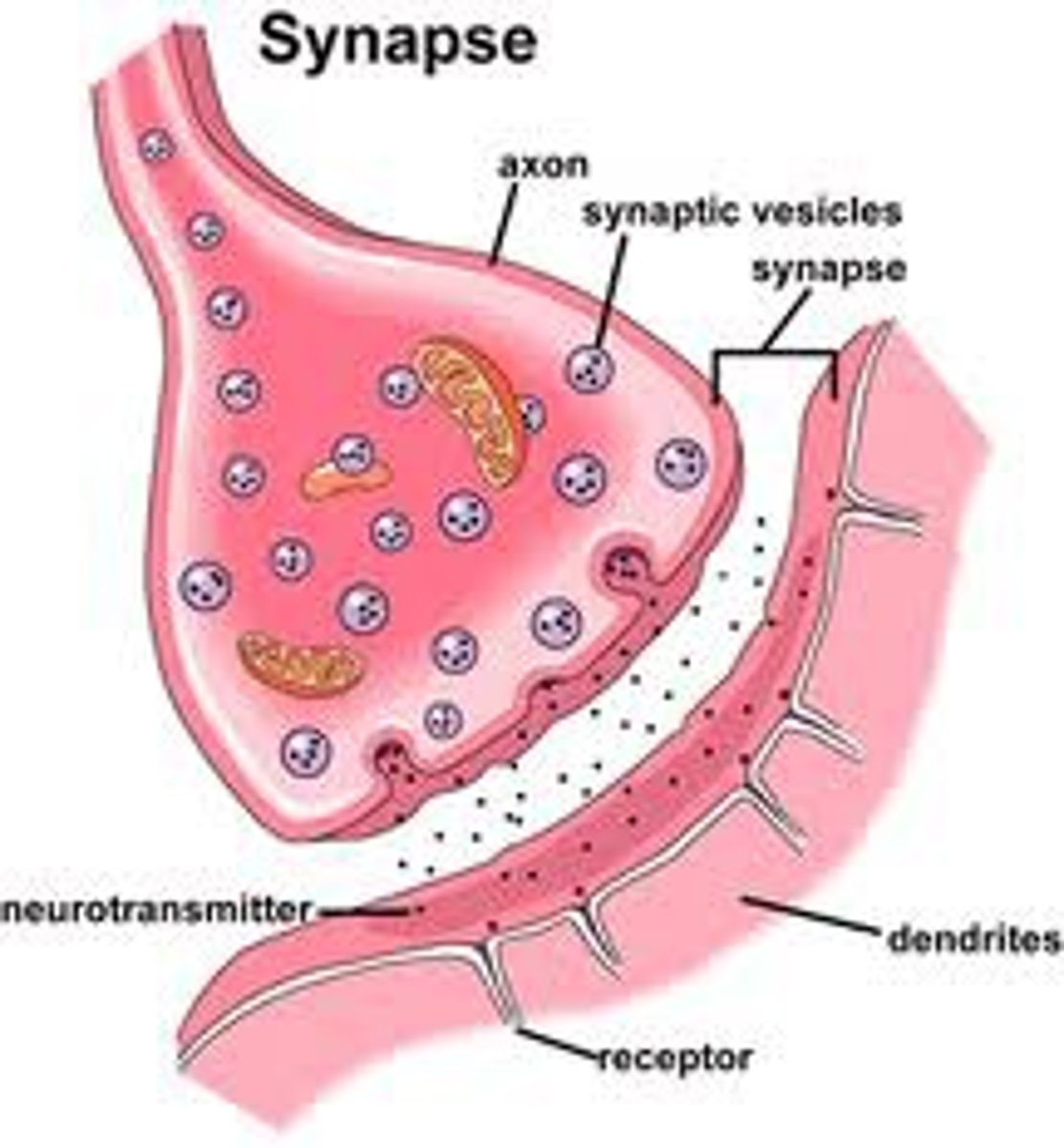
Synaptic Vesicles
small capsules that make neurotransmitter and release into the synaptic cleft
Pre-synaptic Membrane
semi-permeable covering on the end of the axon terminal
Synaptic Cleft
small space between axon and dendrite
Post-synaptic Membrane
semi-permeable covering on the end of the dendrite
Myelin
fat covering on axon
Chemical Messengers
Neurotransmitters
Serotonin
happy mood
Dopamine
motor function and rewarding feeling
Acetylcholine
muscle control and cortical (cortex) arousal
Anadamide
pain reduction, increase appetite
Norepinephrine
mood, hunger, sleep, adrenaline
GABA
inhibitory
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
Glutamate
information and learning
Localizatio of Function
researcher's attempts to identify the function of each individual brain area (but areas likely work together to produce our perceptions)
Forebrain (including cerebral cortex)
the site of most of the brain's conscious functions
Corpus Callosum
bundle of nerve fibers connecting the cerebrum's two hemispheres
Thalamus
area that relays nerve signals to the cerebral cortex; sensory gateway
Hypothalamus
control the body's endocrine, or hormone-producing, system (controls emotions)
Cerebellum
regulates balance and body control; balance and coordination
Brain Stem
regulates control of involuntary functions, breathing, heart rate
Frontal Lobe
motorfunction, language, memory, and executive function
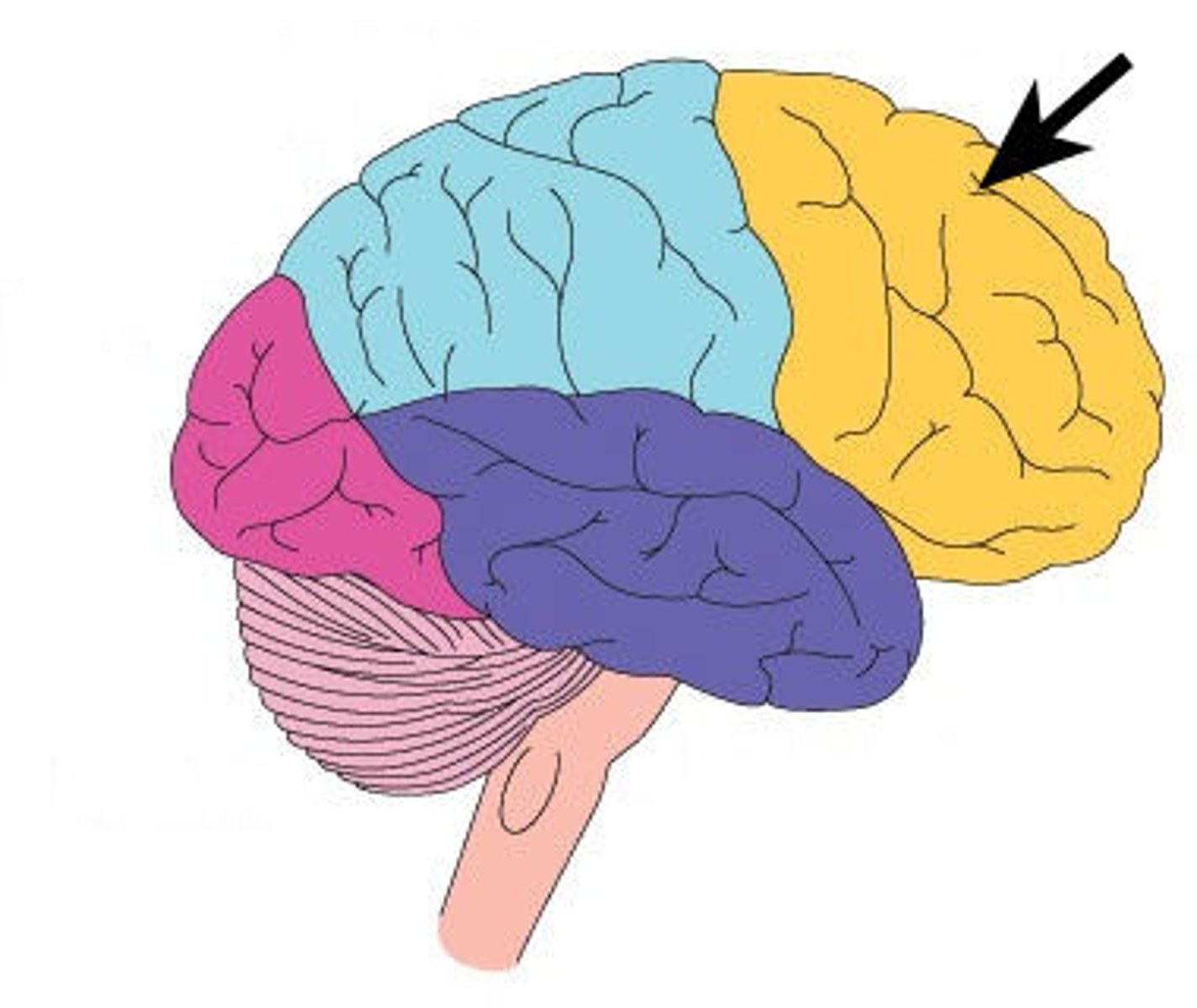
Motor Cortex
voluntary movement
Prefrontal Cortex
thinking, planning, language, etc.
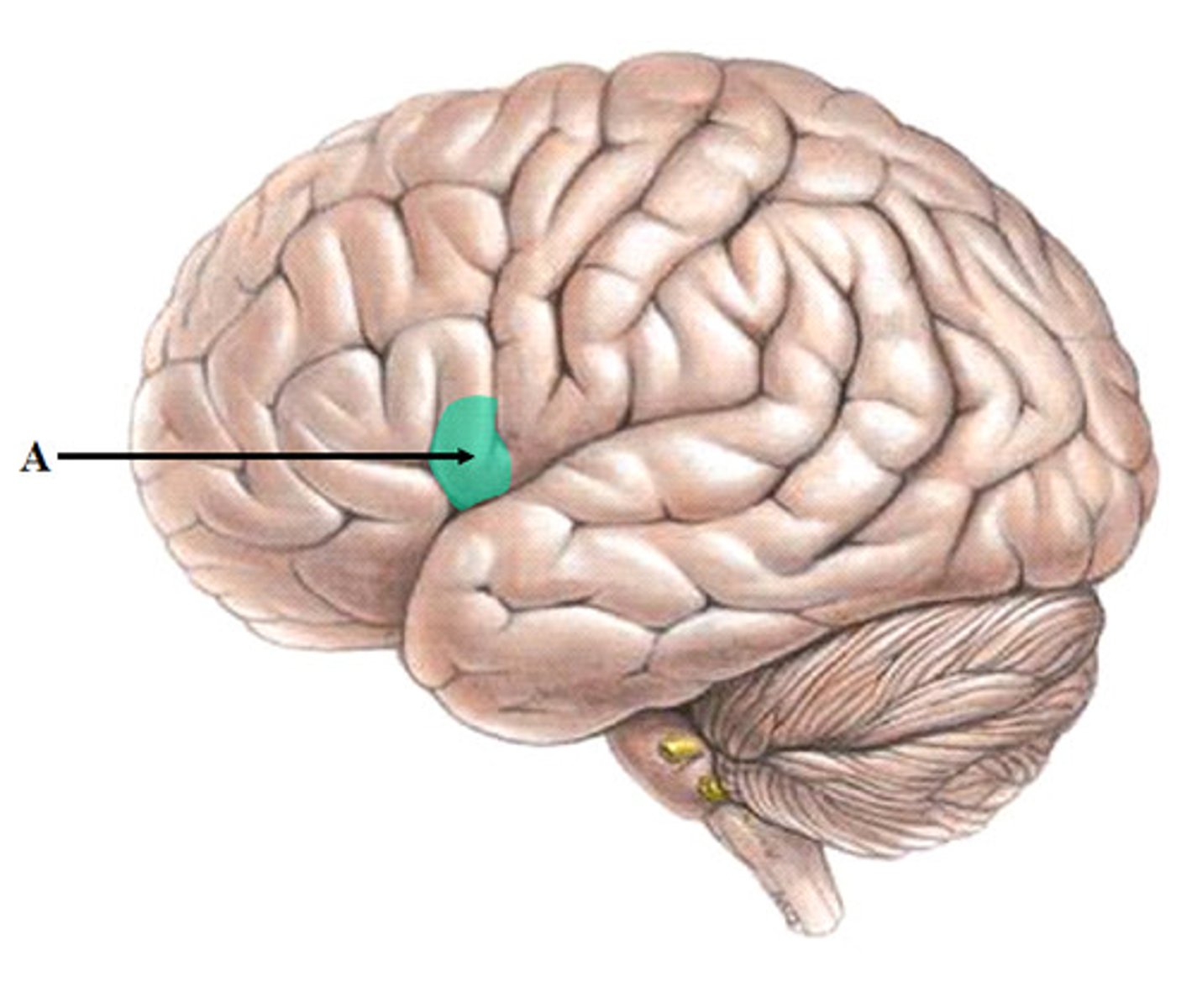
Broca's Area
language production
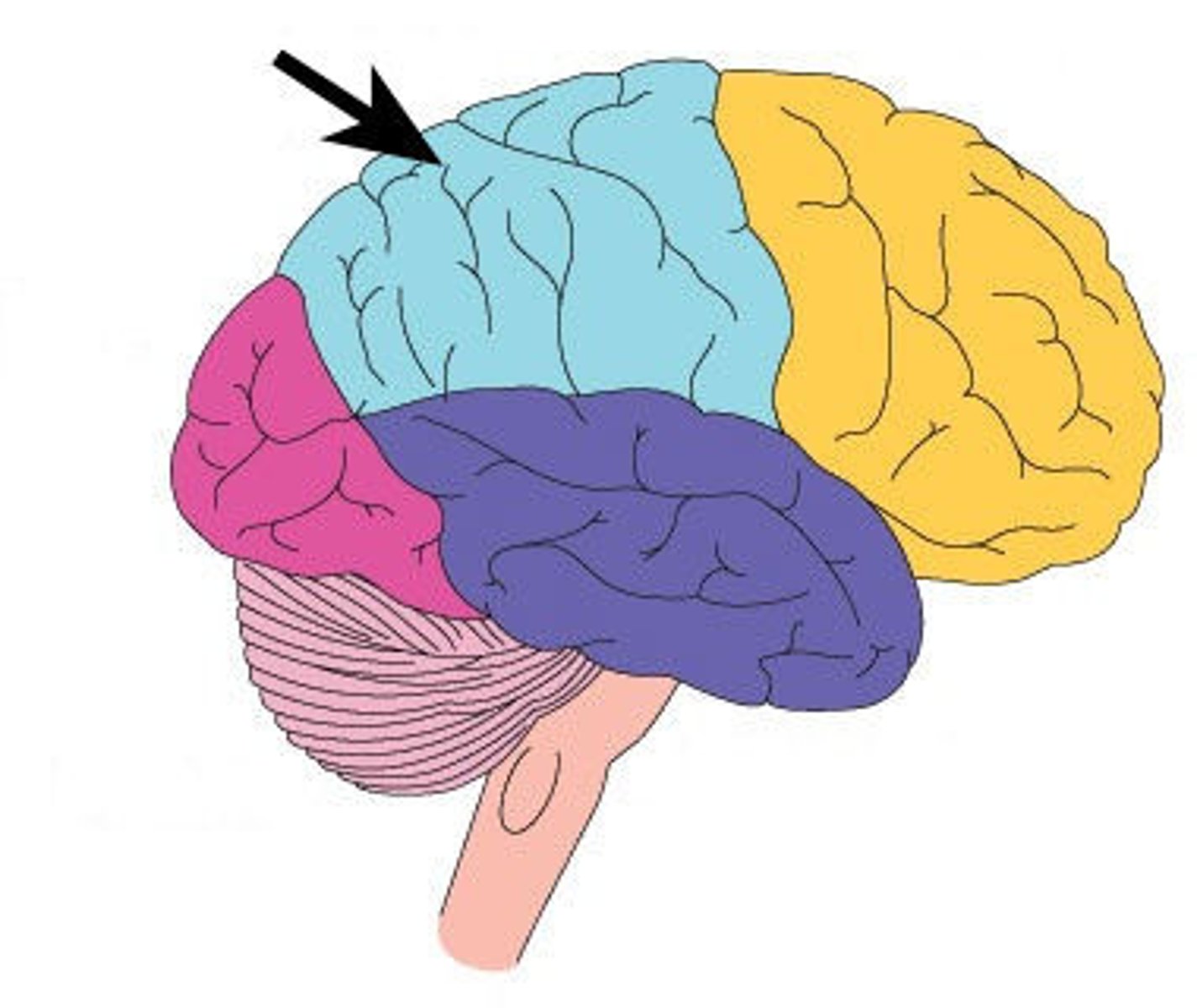
Parietal Lobe
somatosensory cortex: touch, pressure, pain information; spatial perception; object shape/orientation; integrates vision and touch input w/ motor output
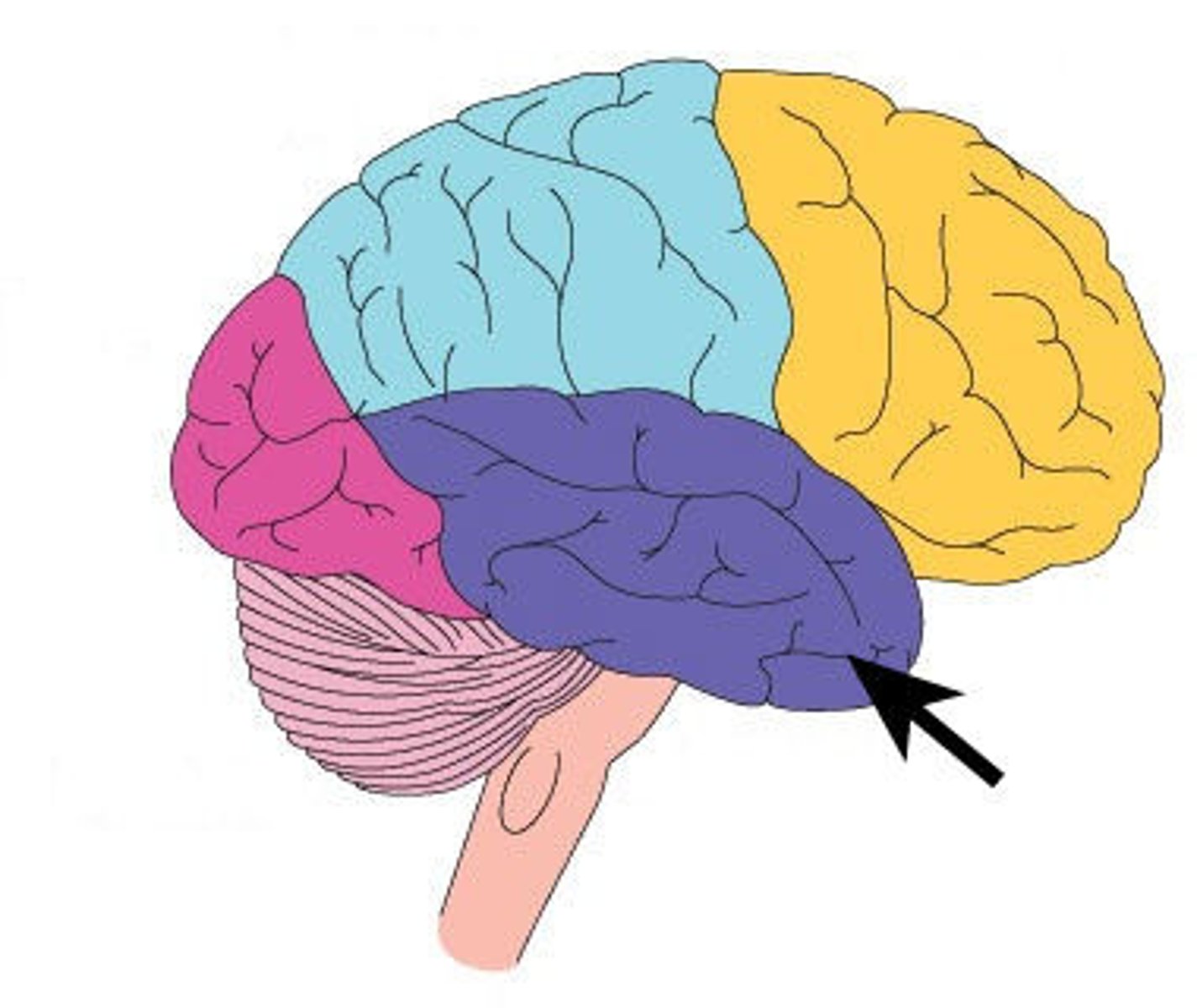
Temporal Lobe
hearing, understanding language, autobiographical memories
Wernicke's Area
understanding speech
Occipital Lobe
visual cortex: vision
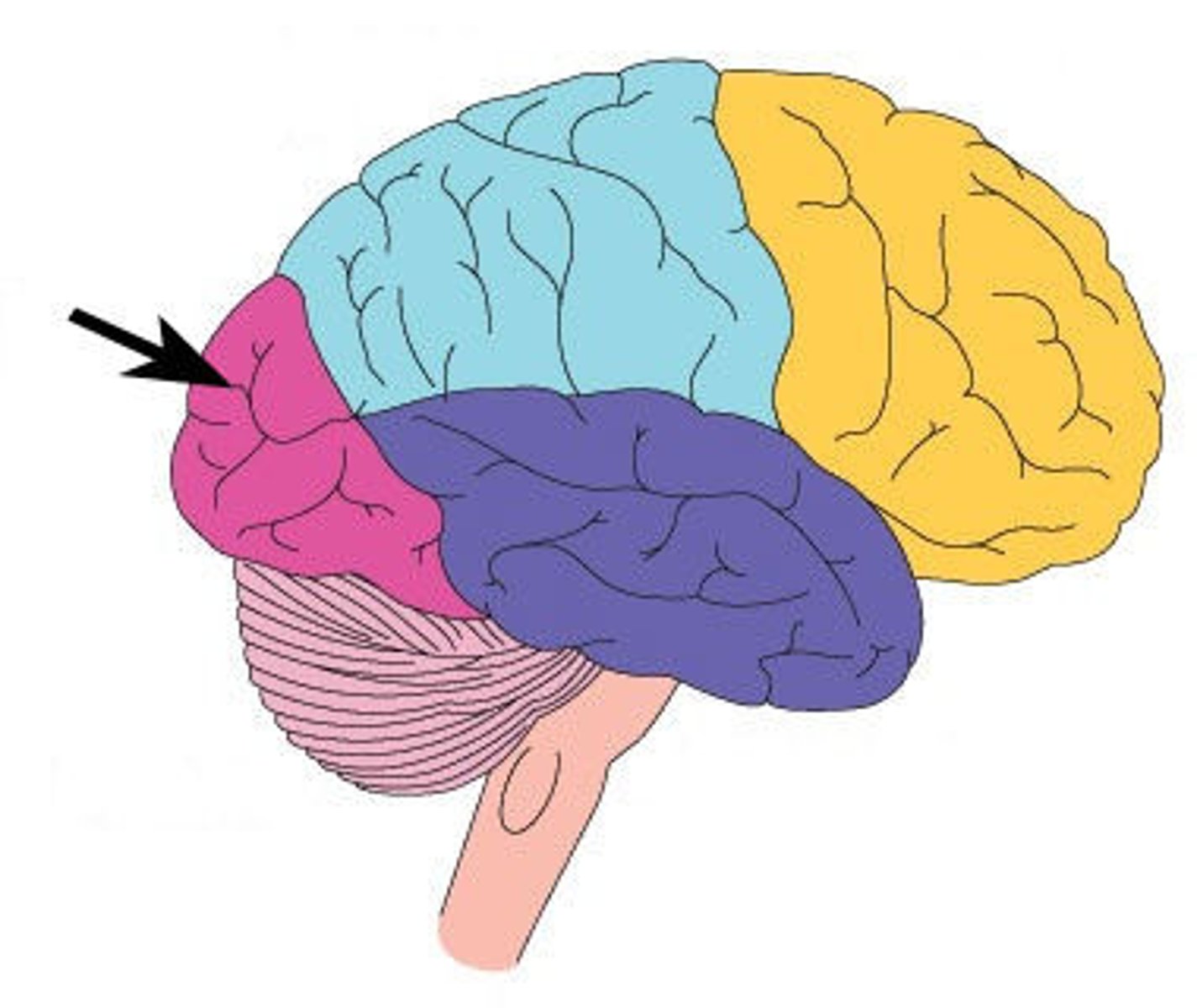
The Limbic System
emotional center
Amygdala
threat sensor (sometimes hippocampus)
Midbrain
contains limbic system
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
regulates cortical arousal
Hindbrain (brainstem)
between the spinal cord and midbrain
Medulla
regulation of critical functions (heart rate, breathing, etc.)
Ventricles
extend throughout the brain and spinal cord, carrying cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which provides nutrition and cushion
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Allele
Different forms of a gene
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
dominant gene
A gene that is expressed in the offspring whenever it is present
Recessive
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
Most genetic disorders of humans are caused by
recessive alleles
Polygenic
describes a characteristic that is influenced by many genes (most traits)
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
gene-environment interaction
situation in which the effects of genes depend on the environment in which they are expressed
range of reaction
asserts our genes set the boundaries within which we can operate, and our environment interacts with the genes to determine where in that range we will fall
genetic environmental correlation
view of gene-environment interaction that asserts our genes affect our environment, and our environment influences the expression of our genes
Epigenetics
how the same genotype can be expressed different ways
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system, info processes
Soma
cell body
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
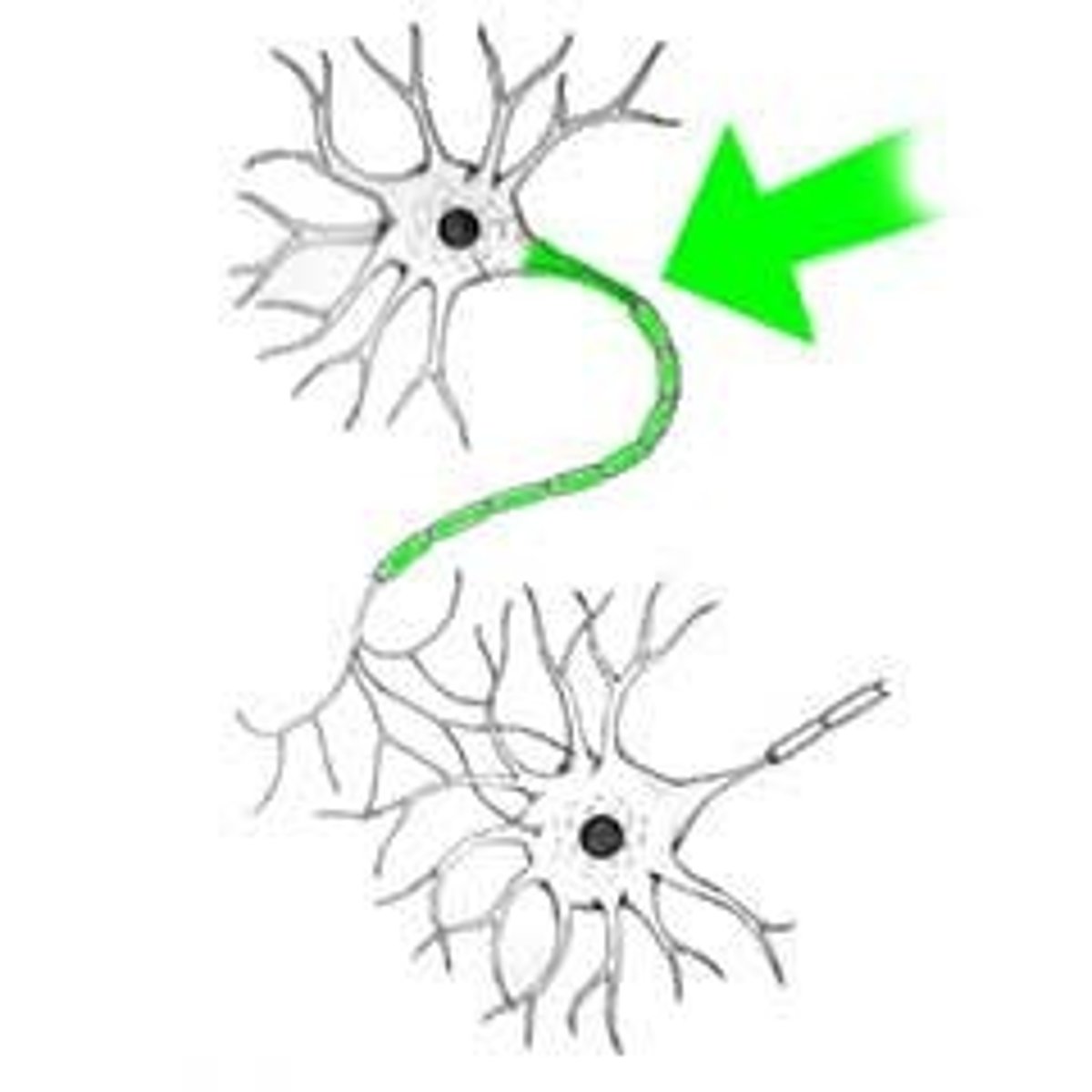
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
what environment does a neuron exist
water
threshold of excitation
the value of the membrane potential that must be reached to produce an action potential
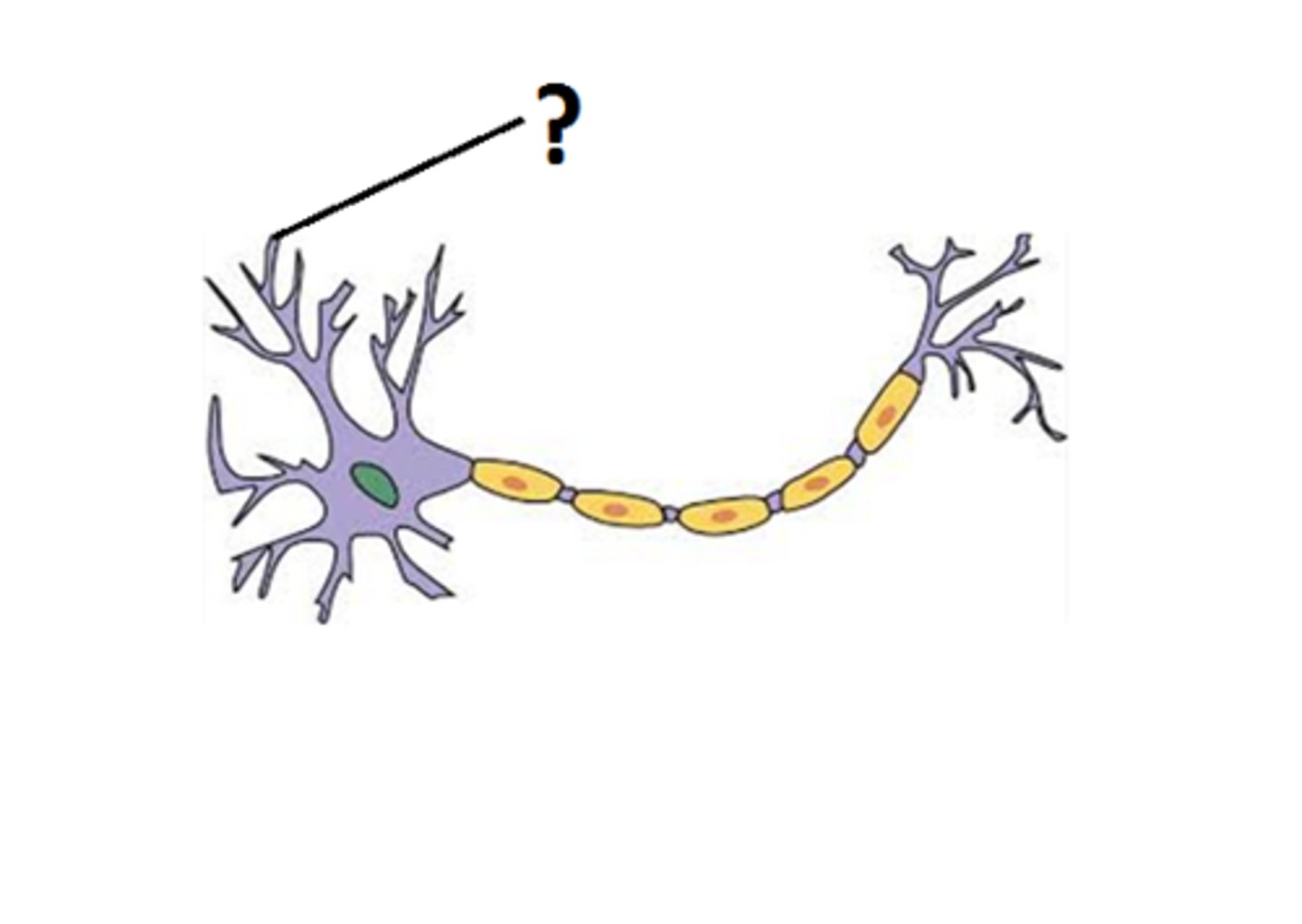
dendrites
a neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
action potentional
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
all or none law
the rule that neurons are either on or off
peak of action potential
sodium channels close
resisting potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane.
positive outside, negative inside
Hyperpolarization
The movement of the membrane potential of a cell away from rest potential in a more negative direction.
Repolarization
Period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Biological Perspective
the psychological perspective that emphasizes the influence of biology on behavior
Angonist
molecules similar enouch to a neurotransmitter that bind to its receptor and mimic its effects (example: morphine and codeine to endorphins)
SSRIs
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
psychotropic medications
drugs that mainly affect the brain and reduce many symptoms of mental dysfunctioning
CNS (central nervous system)
brain and spinal cord
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
somatic nervous system
Division of the PNS that controls the body's skeletal muscles.
efferent
motor neurons
afferent
sensory neurons
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
sympathetic nervous system
prepares the body for action in threatening situations
parasympathetic nervous system
returns the body to normal after a response to stress
fight or flight response
the initial reaction of the body to stress during the alarm stage part of sympathetic
Where does the spinal cord end?
just below the ribs
How many segments are in the spinal cord?
30
cerebral cortex
uneven surface of the brain, patterns of folds know as gyri and the grooves are sulci
longitudinal fissure
separates brain hemispheres
Lateralization
specialization of function in each hemisphere (left and right)
corpus callosum
a broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain.
Computerized Tomography (CT)
An imaging technology in which computers are used to enhance X-ray images
Position Emisson Tomography (PET)
scans of the living brain
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
technique that uses magnetic fields to indirectly visualize brain structure
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
A noninvasive imaging technique that uses magnetic fields to map brain activity by measuring changes in the brain's blood flow and oxygen levels
electroeencephalography (EEG)
process of recording electrical brain activity
endocrine system
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells.
pituitary gland
the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
thyroid gland
produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth